A to Z Classes
Cbse, ncert and icse solution online, class 8 science case study question, case study question class 8 science (cbse / ncert board).
Class 8 Science Case Study Question and Answer: CBSE / NCERT Board Class 8 Science Case Study Question prepared by expert Science Teacher. Students can learn Case Based Question / Paragraph Type Question for NCERT Class 8 Science.
There are total 18 chapter Crop Production and Management, Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
, Synthetic Fibres and Plastics, Materials: Metals and Non-Metals, Coal and Petroleum, Combustion and Flame, Conservation of Plants and Animals, Cell – Structure and Functions, Reproduction in Animals, Reaching the Age of Adolescence, Force and Pressure, Friction, Sound, Chemical Effects of Electric Current, Some Natural Phenomena, Light, Stars and the Solar System, Pollution of Air and Water
For any problem during learning any Case or any doubts please comment us. We are always ready to help You.

CBSE Class 8 Science Case Study Question
- Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management Case Study Question
- Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe Case Study Question
- Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Case Study Question
- Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals Case Study Question
- Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum Case Study Question
- Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame Case Study Question
- Chapter 7 Conservation of Plants and Animals Case Study Question
- Chapter 8 Cell – Structure and Functions Case Study Question
- Chapter 9 Reproduction in Animals Case Study Question
- Chapter 10 Reaching the Age of Adolescence Case Study Question
- Chapter 11 Force and Pressure Case Study Question
- Chapter 12 Friction Case Study Question
- Chapter 13 Sound Case Study Question
- Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current Case Study Question
- Chapter 15 Some Natural Phenomena Case Study Question
- Chapter 16 Light Case Study Question
- Chapter 17 Stars and the Solar System Case Study Question
- Chapter 18 Pollution of Air and Water Case Study Question
What is Case Study Question?
Ans. At case Study there will one paragraph and on the basis of that concept some question will made. Students have to solve that question.
How many marks will have at case based question?
Most of time 5 questions will made from each case. There will 1 or 2 marks for each question.
Important links:
Copyright © 2024 | WordPress Theme by MH Themes
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
- NCERT Solutions
- Chapter 1 Crop Production And Management

NCERT Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management FREE PDF Download
Vedantu’s Class 8 Science Chapter 1 NCERT Solutions has all the questions and answers in the chapter. This chapter explores "Crop Production and Management," explaining key principles essential for grasping agricultural practices and their importance. By downloading the Crop Production And Management Class 8 PDF, students can thoroughly understand the main concepts presented in the curriculum. Emphasising clarity and depth, these resources are invaluable for students progressing through the first chapter of their Science syllabus.

Download the FREE PDF of class 8 science chapter 1 question answer updated according to the Class 8 Science syllabus . Start with Vedantu to pursue a path of academic excellence!
Quick Insights for Solutions of NCERT Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
NCERT Solutions for Science Class 8 Chapter 1 offers insights into the General Introduction: Importance and Scope of Crop Production and Management.
This section provides concise learnings on various methods of crop production, including soil preparation, sowing, application of manure and fertilisers, irrigation, and weed control. It also covers harvesting, storage, and modern agricultural techniques to enhance crop yield.
Students will gain an understanding of topics like Kharif and Rabi crops, traditional and modern agricultural tools, and the importance of organic farming, which are essential for comprehending basic agricultural practices.
Detailed explanations on crop rotation, mixed cropping, and sustainable agricultural practices are provided to ensure long-term productivity and environmental health.
Utilising these Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Short Question Answers can help students assess their level of preparation and understanding of crop production and management concepts.
The chapter is aligned with the revised syllabus for the academic year 2024-25 and offers resources such as class notes, important concepts, and exemplar solutions.
Access Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management Class 8 PDF
1. Select the correct word from the following list and fill in the blanks.
float, water, crop, nutrients, preparation
(a) The same kind of plants grown and cultivated on a large scale at a place is called _________.
(b) The first step before growing crops is ________ of the soil.
Ans: Preparation
(c) Damaged seeds would _________ on top of water.
(d) For growing a crop, sufficient sunlight, _________ and _________ from the soil are essential.
Ans: Water and nutrients.
2. Match items in column A with those in column B.
A | B |
The table showing the matched answers is as below,
A | B |
e) Paddy and maize d) Wheat, gram, pea b) Urea and super phosphate c) Animal excreta, cow dung, urine and plant waste |
3. Give two examples of each.
Kharif crop
Ans: Examples:
Kharif crops - maize and millets.
Rabi crops - wheat and oats.
4. Write a paragraph in your own words on each of the following.
Preparation of soil
Sowing
a. Preparation of soil:
i. The first method in crop management is soil preparation. This process is done by loosening the soil with the help of a plough which helps in ploughing or tilling it.
ii. Loosening of soil particles adds humus and nutrients and increases the absorption of water and manure in the soil which increases crop yields.
i. After the soil preparation, the best seeds are chosen to sow in the soil for production.
ii. Seeds are sown with the help of a seed drill which is in the funnel shape used in modern-day tractors to sow the seeds at a particular depth in the soil.
c. Weeding:
i. Unwanted plants which grow and interfere along with the other plants to reduce their yield are called weeds. Unwanted plants are removed by the process called weeding
ii. We have to remove weeds as they compete with the plants in light and space and take up the nutrients given to the plant from the soil. Xanthium, Parthenium, etc. are some common weeds that affect the growth of plants.
iv. Weedicides are used to control the weeds which is a chemical that only kills the weeds, not the crops.
d. Threshing:
i. After the crop harvesting, the last step in which the grains are separated from the chaff is called threshing.
ii. “Combine” is a machine that carries out this threshing process. The combine is the combination of harvester and thresher which harvests crops and also separates the grains.
5. Explain how fertilisers are different from manure.
Ans: The table showing the difference between fertilizers and manure is as below,
Sl.No | Properties | Fertiliser | Manure |
1 | Availability | Fertilisers are commercially available plant nutrients. | They are natural substances prepared by the decomposition of animal excreta and plant wastes. |
2 | Types | They tend to be either inorganic or organic in nature. | They can be organic with large quantities and little amounts of plant nutrients. |
3 | Use | They provide nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium for the healthy growth of plants. | They contribute to the organic matter and nutritional enrichment of the soil. |
4 | Guidelines | The addition of fertilisers to the soil requires special guidelines such as dose time and post addition precautions. | The application of manure does not necessitate any particular instructions. |
5 | Humus | A fertiliser seems to provide/add no humus to the soil. | Manure enriches the soil with humus and improves its fertility. |
6 | Causes | Its excessive use causes water pollution. It is unable to restore the soil's organic materials. | It helps to safeguard the environment and recycle farm waste. |
6. What is irrigation? Describe two methods of irrigation that conserve water.
Ans: Irrigation:
Supplying water to the crops in the field at various intervals for the growth of the plants is called irrigation.
Intervals differ from crop to crop, season to season, and are also affected by the type of soil and rainfall.
The irrigation sources may include ponds, lakes, canals rivers, and dams.
Two methods of which conserve water are drip irrigation and sprinkler irrigation:
Drip irrigation: It has an arrangement of pipes or tubes with small holes from which plants are watered drop by drop at the base of the root, so that water cannot be wasted.
Sprinkler irrigation: It has an arrangement of vertical pipes with rotating nozzles on the top for the distribution of water to uneven or sandy lands without wastage of water.
7. If wheat is sown in the Kharif season, what would happen? Discuss.
Kharif season is from June to October. If wheat is planted during this season, it is possible that the entire crop will be damaged due to a variety of issues including a lack of optimal temperature, adaptability, and insect availability.
The rainy season is included in the Kharif season, which is not conducive to wheat crop growth, as wheat grows well in the winter or rabi season. As a result, the wheat crop must not be planted during the Kharif season, but rather during the Rabi season.
8. Explain how soil gets affected by the continuous plantation of crops in a field.
Soil minerals such as potassium, nitrogen, phosphorus, as well as other nutrients are depleted as a result of persistent soil plantation. It takes up all the plant nutrients which take a long time to replenish.
These ions are important for all plants to undergo proper growth. If a continuous plantation is done these minerals won’t get time to replenish and the crop yield decreases immediately.
9. What are weeds? How can we control them?
Ans: Weeds:
Undesirable or unwanted plants that grow along with crop plants that reduce crop productivity are known as weeds. Xanthium, Parthenium, etc. are some common weeds.
Weeds compete for light, nutrients, and space with the crop. As a consequence, crop plants receive less light, nutrients, and space to grow. We have to remove weeds as they compete with the plants in light and space and take up the nutrients given to the plant from the soil.
This, in turn, reduces their productivity. Thus, various weeding methods are employed.
Some important weeding methods to control the growth of weeds are:
Weeds can be controlled using weedicides. It is a chemical, which is sprayed in the fields to kill all available weeds. Weedicides are not harmful to crops.
Weeds are also removed by tilling before sowing crops. Weeds are uprooted by tilling. The optimum time to get rid of weeds would be before they blossom and release seeds.
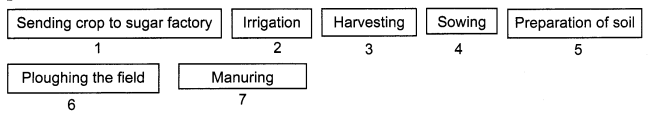
10. Arrange the following boxes in proper order to make a flow chart of sugarcane crop production.

Ans: Sugarcane production involves several processes such as growing the crops by preparing the soil first by ploughing it, then sowing the seeds and using manures. Then water is supplied by the irrigation method. After the crop production, harvesting is done, then the crops can be sent to a factory.

11. Complete the following word puzzle with the help of clues given below.
1. Providing water to the crops.
2. Keeping crop grains for a long time under proper conditions.
5. Certain plants of the same kind grow on a large scale.
Across
3. A machine used for cutting the matured crop.
4. A rabi crop that is also one of the pulses.
6. A process of separating the grain from the chaff.

1. Providing water to the crops - IRRIGATION
2. Keeping crop grains for a long time under proper conditions - STORAGE
5. Certain plants of the same kind grow on a large scale - CROP
3. A machine used for cutting the matured crop - HARVESTER
4. A rabi crop that is also one of the pulses - GRAM
6. A process of separating the grain from chaff - WINNOWING

Important Questions of NCERT Science Class 8 Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
Let’s start with the basics. All the topics are described in the easy question-answer format so that students’ basics get cleared easily and they understand each term deeply.
1. What is a crop? What are its types?
A crop can be defined as plants of the same type that are grown and cultivated as a source of food. This is done in a large cultivable land. There are also different types of crops. These different types of crops are:
Rabi Crops: These crops are grown during the winter season, which is from October to March.
Kharif Crops: These crops are sown during the rainy season, which is from July to October.
2. What are the process and tools required for preparing the soil?
Before any seed can be sown, the soil is prepared for the crop. This is done so that seeds can be properly sewn inside the land. There are several processes and tools that are used for preparing the soil. We have discussed those methods and tools in a list that is mentioned below.
Ploughing or Tilling
Ploughing or tilling is the process through which the soil is loosened and turned. This is done with the help of a plough.
As mentioned above, a plough is a device that is mainly used by farmers for various purposes like loosening the soil and adding fertilizers to the soil. A plough can also be used to remove weeds and scraping of soil. Usually, a plough shaft is the main part of a plough, which is made from a log of wood.
A ploughshare is another part of a plough and it can be explained as a triangular iron strip. The other end of the shaft has a handle. The other end is attached to a beam. This beam is pulled by the bull after it is placed on the neck of the bull. A wooden plough can also be operated by a man. These days many farmers are also switching to iron ploughs.
A hoe is a tool that can be used for digging up the soil. This tool can also be used to remove weeds and loosen up the soil before planting a sapling into the soil.
A cultivator is a tool that is attached to a tractor. It helps in loosening the soil. There are many farmers who prefer to use cultivators instead of ploughs as cultivators are faster.
3. What is sowing? How to sow a seed?
Soil preparation is necessary before sowing seeds. Sowing is the process of planting seeds in the soil.
Steps to sow seed:
Firstly The quality of the seed is crucial for determining crop yield. Selecting good seeds involves placing them in water to check for dead or damaged seeds.
Dead and damaged seeds will float on water, while good seeds will sink.
Traditional tools such as scythes, shovels, ploughs, and pickaxes were used before modern agricultural practices.
Traditional sowing tools resembled funnels with two or three tubes for placing seeds in the soil.
Seed drills are now used with tractors for uniform and efficient sowing.
Seed drills ensure that seeds are sown at a specific depth and covered with soil.
Nurseries are places where young trees and plants are grown for later transplantation.
Nurseries are considered repositories of saplings by experts.
After sowing, seeds undergo germination and the plant starts to emerge.
Adding manure or fertilizers is the next task for the farmer after seed germination.
4. What are manure and fertilizers?
Aspect | Manure | Fertilizers |
Origin | Obtained naturally from the decomposition of organic matter like plant residues, animal waste, and compost. | Manufactured in factories using chemical processes or mined from natural deposits. |
Composition | Contains various nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, but in lower concentrations compared to fertilizers. Additionally, manure is rich in organic matter, which improves soil structure, water holding capacity, and beneficial microbial activity. | Contain high concentrations of specific nutrients, often nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (NPK). They lack the organic matter content of manure. |
Effects | Releases nutrients gradually over time, making it a more sustainable option. It also helps in maintaining soil health in the long term. | Provide a quick boost of nutrients to plants, leading to increased crop yield in the short term. However, excessive or improper use of fertilizers can harm soil health, pollute water bodies, and disrupt the natural ecosystem. |
The choice between manure and fertilisers requires considering these differences. Excessive use of fertilisers can result in pollution and pH changes in the soil. Some farmers choose to leave their land fallow to naturally replenish lost nutrients and minerals. After a period of time, the land can be used again.
5. What is crop rotation?
In crop rotation, the same crop is not grown continuously. This prevents the erosion of the fertility of the soil. Also, another major part of growing crops is protecting the crops from weeds.
6. What are weeds? What is tilling?
Weeds can be defined as undesirable plants that grow naturally along with the main crop. The weeds are harmful because they compete with the crop by absorbing all the nutrients, water, light, and space.
Tilling is a process that can be done after sowing the crops. This process helps in killing and uprooting the weeds. One can also choose to remove weeds by physically uprooting the weeds from the soil or by chopping the weeds to the ground level. This is known as the manual removal method.
Some farmers also use weedicides, which are chemicals that are used for killing weeds. Students should remember that weedicides do not harm the main crop. After that, harvesting is performed.
7. What is harvesting? What are the methods to harvest the crops?
Harvesting can be explained as the process of cutting the crop once it has matured.
There are two main methods through which harvesting can be done. These methods are:
Manual method where a sickle can be used.
The mechanical method in which a harvester, which is a huge machine, can be used.
8. What is threshing and winnowing?
Threshing is also the process that can be used for loosening the grains from the chaff. This process can be performed manually or with the help of machines. Winnowing is also a method for separating grain seeds from the chaff. But this method is done with the help of the wind. Because of the wind, the lighter chaff will fly away and the heavier grains will fall down.
9. How the grains are stored?
Once the grain is separated, then the storage of the grains is left. Ideally, the grains should be stored in silos and granaries after harvesting. One should ensure that grains are stored in a dry place that does not have any fungal infestation or rodent infestation. Fumigation of the storage place should also be done to make sure that the storage place is free from microbes.
For students who do not know what granaries mean, it is the place where the freshly obtained food grains are stored. Also, animal husbandry is defined as the management and care of farm animals. This is done to obtain milk, eggs, or meat.
NCERT Class 8 Science Chapter 1 - Quick Overview of Detailed Structure of Topics
S. No | Topics of Crop Production and Management Class 8 |
1 | Agricultural Practices |
2 | Basic Practices of Crop Production |
3 | Preparation of Soil |
4 | Agricultural Implements |
5 | Sowing |
6 | Adding Manure and Fertilisers |
7 | Irrigation |
8 | Protection from Weeds |
9 | Harvesting |
10 | Storage |
11 | Food from Animals |
Science Class 8 Chapter 1- Important Terms
Crop: When a large number of plants of the same type are grown together in one location, it is referred to as a crop.
Kharif Crops: Crops planted during the rainy season are known as Kharif crops. In India, the rainy season typically spans from June to September. Examples of Kharif crops include paddy, maize, soybean, groundnut, and cotton.
Rabi Crops: Crops cultivated in the winter season, from October to March, are referred to as rabi crops. Some common rabi crops are wheat, gram, pea, mustard, and linseed.
Tilling or ploughing: The action of loosening and overturning the soil.
Crop Rotation: The same crop is not grown continuously in crop rotation. This prevents the erosion of the fertility of the soil. Another major part of growing crops is protecting them from weeds.
Benefits of Referring to Vedantu’s NCERT Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Solutions
Referring to NCERT solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 PDF offers several benefits:
NCERT Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Question Answer provides clear explanations of concepts covered in the chapter, helping students understand the topic thoroughly.
Covers important concepts such as agricultural practices, soil preparation, sowing, and irrigation methods.
Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Short Question Answer assists students in completing their last-minute revision efficiently and effectively.
Ch 1 Class 8 Science solutions follow a structured format, making it easier for students to navigate through different topics and sections of the chapter.
Detailed methodologies for solving numerical problems and understanding agricultural practices.
Crop Production And Management Class 8 solutions include practice questions and exercises that allow students to test their understanding of the concepts discussed in the chapter.
By referring to Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Question Answer, students can prepare effectively for exams as the solutions cover all the topics and questions likely to be asked in the assessments.
Science Class 8 Chapter 1 solutions align with the curriculum prescribed by educational boards, ensuring that students cover the topics and concepts required for their academic year.
Students can use Class 8 Science Chapter 1 PDF solutions to assess their understanding and identify areas where they may need further practice or clarification.
Important Study Materials for Class 8 Science Chapter 1: Crop Production and Management
Students have the opportunity to obtain additional study materials related to Chapter 1- Crop Production and Management Class 8. These additional resources can be downloaded to provide further reference.
S. No | Links for Chapter 1: Crop Production and Management Study Materials |
1 |
|
2 |
|
3 |
|
Conclusion
NCERT Science Class 8 Chapter 1, Crop Production And Management Solutions, provided by Vedantu, offers comprehensive guidance and support to students in understanding the fundamental concepts of agricultural practices. Through clear explanations, practice questions, and additional resources, Vedantu ensures that students can grasp the fundamentals of crop production and management effectively. Ch 1 Class 8 Science Solutions not only helps in academic learning but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the importance of agriculture in our lives. With Vedantu's assistance, students are well-equipped to excel in their studies and develop a strong foundation in agricultural science.
Links for Chapter-wise NCERT Solutions Class 8 Science
NCERT Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter-wise List |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Important Links for Class 8 Science
S. No | Important Resources for Class 8 Science |
1 |
|
2 |
|
3 |
|
4 |
|

FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
1. What topics are covered in NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 - Crop Production and Management?
The NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 - Crop Production and Management cover various topics such as types of crops, agricultural practices, crop production cycle, sowing methods, soil preparation, irrigation, fertilisers, pests and diseases, and harvesting techniques.
2. How can NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 - Crop Production and Management help me understand the concepts better?
The NCERT Solutions provide detailed explanations, diagrams, and examples that break down the concepts of crop production and management into easily understandable parts. By following the solutions, you can gain a clear understanding of the processes involved in crop production, from soil preparation to harvesting, and comprehend the importance of various agricultural practices.
3. Are the NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 - Crop Production and Management easy to follow?
Yes, the NCERT Solutions provided by Vedantu are designed to be student-friendly and easy to follow. The solutions use simple language and step-by-step explanations to ensure that students can grasp the concepts easily. Additionally, the solutions include diagrams and examples to further enhance comprehension.
4. Can the NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 - Crop Production and Management help me with exam preparation?
Absolutely! The NCERT Solutions cover all the important topics and questions from the chapter, which are likely to be asked in exams. By going through the solutions, practising the provided questions, and understanding the concepts thoroughly, you can strengthen your exam preparation and perform well in your science examinations.
5. Are the NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 - Crop Production and Management available online?
Yes, Vedantu provides the NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 - Crop Production and Management online. You can access these solutions on Vedantu's website or through their mobile app. They are readily available for free, allowing you to study and revise the chapter conveniently at any time and from anywhere with an internet connection.
6. What is crop production and management class 8?
Crop production and management in Class 8 is a subject that teaches students about the entire process of growing crops, from planting seeds to harvesting and storing the final product. It covers various aspects, including:
Soil preparation: Making the soil loose and fertile for healthy plant growth.
Sowing: Planting seeds at the right depth and spacing.
Manure and fertilizers: Adding nutrients to the soil for better crop yield.
Irrigation: Providing water to the crops regularly.
Weed control: Removing unwanted plants that compete with crops for resources.
Protection from pests and diseases: Safeguarding crops from harmful insects and illnesses.
Harvesting: Gathering the mature crops.
Storage: Preserve the harvested crops for later use.
By understanding these practices, students gain valuable knowledge about the importance of agriculture and the efforts involved in ensuring a sustainable food supply.
7. What is crop class 8 very short answer?
Crop refers to plants grown for their edible parts, such as grains, fruits, vegetables, and pulses. Studying crops helps students understand their role in agriculture and appreciate the diverse range of plants that provide us with food.
8. What are the important topics in class 8 science chapter 1?
Some of the important topics in Class 8 Science Chapter 1- Crop Production and Management are:
Basic Practices of Crop Production
Agricultural Implements
Food from Animals
Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Question Answer will help students understand the concepts of the following topics and enhance their learning.
9. What are the two broad cropping patterns followed in India?
The two broad cropping patterns followed in India are:
NCERT Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Solutions provides more insights on the topics and helps students to excel in the examinations.
Crop Production and Management Class 8 Science Extra Questions and Answers
Crop Production and Management Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Extra Questions and Answers is provided here. We prepared these extra questions based on the latest NCERT Class 8 Science Book. CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management Extra Questions will help you to properly understand a particular concept of the chapter.
Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management Extra Questions
Very short answer type question.
Question 1: Give few examples of weedicides.
Answer: 2, 4-D
Question 2: Name the bacteria which fix atmospheric nitrogen.
Answer: Rhizobium bacteria
Question 3: What is called weeding?
Answer: The removal of weeds is called weeding.
Question 4: Name the tool used for tilling of soil.
Answer: Tilling of soil is done by using a plough.
Question 5: How are crumbs broken?
Answer: Crumbs are broken with the help of plank.
Question 6: Write 2 natural methods of replenishing the soil with nutrients.
Answer: i. Use of manure ii. Crop rotation
Question 7: How is levelling of soil done?
Answer: The levelling of soil is done with the help of a leveller.
Question 8: What are the two ways of sowing the seeds?
Answer: Seeds can be sown manually or by seed drills.
Question 9: How is ploughing done nowadays?
Answer: Nowadays ploughing is done by tractor driven cultivator.
Question 10: What is sowing?
Answer: Sowing is the process of planting seeds in the soil.
Question 11: Name two categories of crops based on season.
Answer: Two categories of crop based on season are kharif and rabi crops.
Question 12: What is threshing?
Answer: Separation of the grains from the chaff is called threshing.
Question 13: How are grains stored at home?
Answer: Dried neem leaves are used for storing food grains at home.
Question 14: What are called crumbs?
Answer: The ploughed field may have big pieces of soil called crumbs.
Question 15: Why is it important to level the field after ploughing?
Answer: The field is levelled for sowing as well as for irrigation purposes.
Question 16: What are good quality seeds?
Answer: Good quality seeds are clean and healthy seeds of a good variety.
Question 17: Give some examples of Rabi crop?
Answer: Examples of rabi crops are wheat, gram, pea, mustard and linseed.
Question 18: What is harvesting?
Answer: Harvesting is the cutting of the mature crop manually or by machines.
Question 19: Name the two modern methods of irrigation that help us to use water economically.
Answer: Sprinkler System and Drip system
Question 20: Why can paddy not be grown in the winter season?
Answer: Paddy requires a lot of water. Therefore, it is grown only in the rainy season.
Question 21: Why proper storage of crop products is important?
Answer: Proper storage of crop products is important to prevent them from spoilage.
Question 22: Give some examples of Kharif crop.
Ans. Examples of Kharif crops are Paddy, maize, soyabean, groundnut, cotton, etc.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1: What are the benefits of eating fish?
Answer: Fish is good for health. We get cod liver oil from fish which is rich in vitamin D.
Question 2: How do fertilisers help farmers?
Answer: The use of fertilisers has helped farmers to get better yield of crops such as wheat, paddy and maize.
Question 3: How are crops categorised in India?
Answer: In India, crops can be broadly categorised into two types based on seasons – rabi and kharif crops.
Question 4: How is harvesting done in India?
Answer: Harvesting in our country is either done manually by sickle or by a machine called harvester.
Question 5: What is winnowing?
Answer: After threshing, grains are separated from chaff with help of wind. This process is called winnowing.
Question 6: List some festivals that are associated with the harvest season.
Answer: Special festivals associated with the harvest season are Pongal, Baisakhi, Holi, Diwali, Nabanya and Bihu.
Question 7: What is crop rotation?
Answer: Crop rotation is a method of replenishing the soil with nutrients by growing different crops alternately.
Question 8: Why should excessive supply of water to plants be avoided?
Answer: Excessive supply of water to plants should be avoided because roots get damaged and the plants die.
Question 9: Why some seeds float on water?
Answer: Damaged seeds become hollow and are thus lighter. Therefore, they float on water.
Question 10: Why does farmer rotate crops in the field?
Answer: Farmer rotates crops in the field because crop rotation helps in the replenishment of the soil nutrients.
Question 11: What are the different sources of irrigation?
Answer: Sources of irrigation: The sources of irrigation are— wells, tube-wells, ponds, lakes, rivers, dams and canals.
Question 12: What is the right time to spray weedicides?
Answer: The weedicides are sprayed during the vegetative growth of weeds before flowering and seed formation.
Question 13: How is threshing carried out?
Answer: Threshing is carried out with the help of a machine called ‘combine’ which is in fact a combined harvester and thresher.
Question 14: What are the advantages of using manure in crop fields?
Answer: The use of manure improves soil texture as well as its water retaining capacity. It replenishes the soil with all the nutrients.
Question 15: In summer, the frequency of watering is higher. Why is it so?
Answer: In summer, the frequency of watering is higher due to the increased rate of evaporation of water from the soil and the leaves.
Question 16: Why does the loosening of soil allow the roots to breathe easily?
Answer: Loosening of soil allow the roots to breathe easily because air fill up the spaces between the soil particles and provides airy soil to the roots.
Question 17: How are grains stored in godowns?
Answer: For storing large quantities of grains in big godowns, specific chemical treatments are required to protect them from pests and microorganisms.
Question 18: Is it a good practice to burn the stubs left in the field? Give reasons.
Answer: No, it is not a good practice to burn the stubs left in the field because it causes pollution. It may also catch fire and damage the crops lying in the fields.
Question 19: How weeds are removed manually?
Answer: The manual removal includes physical removal of weeds by uprooting or cutting them close to the ground, from time to time. This is done with the help of a khurpi.
Question 20: What are the harmful effects of using fertilisers?
Answer: Harmful effects of using fertilisers
- Excessive use of fertilizers has made the soil less fertile.
- Fertilizers have also become a source of water pollution.
Question 21: What do you understand by agricultural practices?
Answer: Cultivation of crops involves several activities undertaken by farmers over a period of time. These activities or tasks are referred to as agricultural practices.
Question 22: What is animal husbandry?
Answer: Animals reared at home or in farms, have to be provided with proper food, shelter and care. When this is done on a large scale, it is called animal husbandry.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1: What precautions should be taken while spraying weedicides and why?
Answer: Spraying of weedicides may affect the health of farmers. So they should use these chemicals very carefully. They should cover their nose and mouth with a piece of cloth during spraying of these chemicals.
Question 2: Explain in detail the structure and use of hoe.
Answer: It is a simple tool which is used for removing weeds and for loosening the soil. It has a long rod of wood or iron. A strong, broad and bent plate of iron is fixed to one of its ends and works like a blade. It is pulled by animals.
Question 3: What are fertilisers? Give some examples.
Answer: Fertilisers are chemical substances which are rich in a particular nutrient. Some examples of fertilisers are— urea, ammonium sulphate, super phosphate, potash, NPK (Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium).
Question 4: Why appropriate distance between the seeds is important?
Answer: An appropriate distance between the seeds is important to avoid overcrowding of plants. This allows plants to get sufficient sunlight, nutrients and water from the soil.
Question 5: Why earthworms and microbes are called friends of farmer?
Answer: The loosened soil helps in the growth of earthworms and microbes present in the soil. These organisms are friends of the farmer since they further turn and loosen the soil and add humus to it.
Question 6: What are kharif crops?
Answer: The crops which are sown in the rainy season are called kharif crops. The rainy season in India is generally from June to September. Paddy, maize, soyabean, groundnut, cotton, etc., are kharif crops.
Question 7: What are rabi crops?
Answer: The crops grown in the winter season are called rabi crops. Their time period is generally from October to March. Examples of rabi crops are wheat, gram, pea, mustard and linseed.
Question 8: Why do farmers add manure to the soil?
Answer: Continuous growing of crops makes the soil poorer in certain nutrients. Therefore, farmers have to add manure to the fields to replenish the soil with nutrients.
Question 9: What will happen if field is not ploughed before sowing the seeds?
Answer: Disadvantage of not ploughing the field are:
- Seeds cannot be sown at proper depth.
- Water and air holding capacity of soil will be poor.
Question 10: What is called a crop?
Answer: When plants of the same kind are grown and cultivated at one place on a large scale, it is called a crop. For example, crop of wheat means that all the plants grown in a field are that of wheat.
Question 11: What is seed drill?
Answer: This tool sows the seeds uniformly at proper distances and depths. It ensures that seeds get covered by the soil after sowing. This prevents damage caused by birds. Sowing by using a seed drill saves time and labour.
Question 12: Why traditional methods of irrigation are cheaper, but less efficient?
Answer: The water available in wells, lakes and canals is lifted up by different methods in different regions, for taking it to the fields. Cattle or human labour is used in these methods. So, these methods are cheaper, but less efficient.
Question 13: How can we separate good, healthy seeds from the damaged ones?
Answer: Take a beaker and fill half of it with water. Put a handful of wheat seeds and stir well. Wait for some time. Are there seeds which float on water? Seeds that float on water are the damaged ones. Damaged seeds become hollow and are thus lighter. Therefore, they float on water.
Question 14: What are the advantages of drip system of irrigation?
Answer: Advantages of drip system of irrigation are:
- It is the best technique for watering fruit plants, gardens and trees.
- The system provides water to plants drop by drop. Water is not wasted at all.
- It is a boon in regions where availability of water is poor.
Question 15: How is turning and loosening of soil important for cultivation of crops?
Answer: Since only a few centimetres of the top layer of soil supports plant growth, turning and loosening of soil brings the nutrient-rich soil to the top so that plants can use these nutrients. Thus, turning and loosening of soil is very important for cultivation of crops.
Question 16: Explain how soil gets affected by the continuous plantation of crops in a field.
Answer: Continuous plantation of crops in a field makes the soil deficient in certain nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, etc. These nutrients are essential for the growth of plants. As such soil does not get time to replenish the lost nutrients, the crop yield decreases automatically.
Question 17: What are the traditional methods of irrigation?
Answer: The various traditional ways are:
- moat (pulley-system)
- dhekli, and
- rahat (Lever system)
Question 18: Why it is necessary to remove weeds? Or Why is weeding necessary?
Answer: The removal of weeds is called weeding. Weeding is necessary since weeds compete with the crop plants for water, nutrients, space and light. Thus, they affect the growth of the crop. Some weeds interfere even in harvesting and may be poisonous for animals and human beings.
Question 19: What is manure and how is it prepared? Or How is organic manure obtained?
Answer: Manure is an organic substance obtained from the decomposition of plant or animal wastes. Farmers dump plant and animal waste in pits at open places and allow it to decompose. The decomposition is caused by some microorganisms. The decomposed matter is used as organic manure.
Question 20: Why is water essential for plant? Discuss.
Answer: Water is essential because germination of seeds does not take place under dry conditions. Nutrients dissolved in water get transported to each part of the plant. Water also protects the crop from both frost and hot air currents. To maintain the moisture of the soil for healthy crop growth, fields have to be watered regularly.
Question 21: What are the characteristics of good quality seeds?
Answer: Following are the characteristics of a good quality seed:
- It should be clean.
- It should be healthy and of good variety.
- It should have high yield.
- It should be disease resistant.
Question 22: Why is it necessary to dry the harvested food grains before storage?
Answer: The fresh crop has more moisture. If freshly harvested grains (seeds) are stored without drying, they may get spoilt or attacked by organisms, losing their germination capacity. Hence, before storing them, the grains are properly dried in the sun to reduce the moisture in them. This prevents the attack by insect pests, bacteria and fungi.
Question 23: Why drilling is the best method for sowing of seeds? Or Explain the method used these days to sow seeds.
Answer: Nowadays the seed drill is used for sowing with the help of tractors. Seed drill sows the seeds uniformly at proper distances and depths. It ensures that seeds get covered by the soil after sowing. This prevents damage caused by birds. Sowing by using a seed drill saves time and labour. Hence, it is considered as the best method for sowing of seeds.
Question 24: What are the advantages of sprinkler system of irrigation?
Answer: Advantages of sprinkler system of irrigation
- This system is more useful on the uneven land where sufficient water is not available.
- Water gets sprinkled on the crop as if it is raining.
- Sprinkler is very useful for sandy soil.
- Water is also distributed more evenly across crops helping to avoid wastage.
Question 25: What are the steps involved in agricultural practices?
Answer: Steps involved in agricultural practices are:
- Preparation of soil
- Adding manure and fertilisers
- Protecting from weeds
Question 26: Why organic manure is considered better than fertilisers? Or What are the advantages of organic manure?
Answer: The organic manure is considered better than fertilisers. This is because
- It enhances the water holding capacity of the soil.
- It makes the soil porous due to which exchange of gases becomes easy.
- It increases the number of friendly microbes.
- It improves the texture of the soil.
Question 27: If wheat is sown in the kharif season, what would happen? Discuss.
Answer: Wheat is a rabi crop and grown in the winter season. Their time period is generally from October to March. It needs a cool, dry, and clear climate for better growth and yield. Kharif season is generally from June to September. Kharif crops require a huge amount of water and hot weather to grow. If wheat is grown in Kharif season it will be affected adversely as hot and humid climate is not ideal for the cultivation of wheat.
Question 25: Name the three tools used for ploughing. Write function of each.
Answer: Tools used for ploughing are:
Plough: This is being used since ancient times for tilling the soil, adding fertilisers to the crop, removing the weeds, scraping of soil, etc.
Hoe: It is a simple tool that is used for removing weeds and for loosening the soil.
Cultivator: Nowadays ploughing is done by tractor driven cultivator. The use of cultivators saves labour and time.
Question 26: Explain how fertilisers are different from manure.
Answer: Difference between fertilisers and manure
| 1. A fertiliser is an inorganic salt. | 1. Manure is a natural substance obtained by the decomposition of cattle dung, human waste and plant residues. |
| 2. A fertiliser is prepared in factories. | 2. Manure can be prepared in the fields. |
| 3. A fertiliser does not provide any humus to the soil. | 3. Manure provides a lot of humus to the soil. |
| 4. Fertilisers are very rich in plant nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. | 4. Manure is relatively less rich in plant nutrients. |
Question 27: How a plough works?
Answer: Plough is used for tilling the soil, adding fertilisers to the crop, removing the weeds, scraping of soil, etc. This implement is made of wood and is drawn by a pair of bulls or other animals (horses, camels, etc.). It contains a strong triangular iron strip called ploughshare. The main part of the plough is a long log of wood which is called a ploughshaft. There is a handle at one end of the shaft. The other end is attached to a beam which is placed on the bulls’ necks. One pair of bulls and a man can easily operate the plough.
Question 28: What are weeds? How can we control them?
Answer: In a field many other undesirable plants may grow naturally along with the crop. These undesirable plants are called weeds. Weeds can be controlled in the following ways:
- Tilling before sowing of crops helps in uprooting and killing of weeds.
- The manual removal of weeds by uprooting or cutting them close to the ground, from time to time. This is done with the help of a khurpi. A seed drill is also used to uproot weeds.
- Weeds are also controlled by using certain chemicals, called weedicides, like 2,4-D. These are sprayed in the fields to kill the weeds.
Question 28: What is irrigation? Describe two methods of irrigation which conserve water.
Answer: The supply of water to crops at different intervals is called irrigation.
Sprinkler System: This system is more useful on the uneven land where sufficient water is not available. The perpendicular pipes, having rotating nozzles on top, are joined to the main pipeline at regular intervals. When water is allowed to flow through the main pipe under pressure with the help of a pump, it escapes from the rotating nozzles. It gets sprinkled on the crop as if it is raining. Sprinkler is very useful for sandy soil.
Drip system: In this system, the water falls drop by drop just at the position of the roots. So, it is called drip system. It is the best technique for watering fruit plants, gardens and trees. The system provides water to plants drop by drop. Water is not wasted at all.
Question 29: Why is tilling of soil important? Or Why is turning and loosening of soil important? Or Give any three advantages of ploughing.
Answer: Importance of tilling are as follows:
- This allows the roots to penetrate deep into the soil. The loose soil allows the roots to breathe easily even when they go deep into the soil.
- The loosened soil helps in the growth of earthworms and microbes present in the soil. They further turn and loosen the soil and add humus to it.
- This brings the nutrient-rich soil to the top so that plants can use these nutrients.
Question 30: Write a paragraph in your own words on each of the following.
(a) Preparation of soil (b) Sowing (c) Weeding (d) Threshing
Answer: (a) Preparation of soil
- The preparation of soil is the first step before growing a crop.
- One of the most important tasks in agriculture is to turn the soil and loosen it. This allows the roots to penetrate deep into the soil. The process of loosening and turning of the soil is called tilling or ploughing. This is done by using a plough.
- The ploughed field may have big pieces of soil called crumbs. It is necessary to break these crumbs with a plank.
- The field is levelled for sowing as well as for irrigation purposes. The levelling of soil is done with the help of a leveller.
- Sometimes, manure is added to the soil before tilling. This helps in proper mixing of manure with soil. The soil is watered before sowing.
(b) Sowing
- Sowing is the most important part of crop production. Before sowing, good quality seeds are selected.
- The tool used traditionally for sowing seeds is shaped like a funnel. The seeds are filled into the funnel, passed down through two or three pipes having sharp ends. These ends pierce into the soil and place seeds there.
- Nowadays the seed drill is used for sowing with the help of tractors. This tool sows the seeds uniformly at proper distances and depths. It ensures that seeds get covered by the soil after sowing. This prevents damage caused by birds. Sowing by using a seed drill saves time and labour.
(c) Weeding
- The removal of weeds is called weeding. Weeding is necessary since weeds compete with the crop plants for water, nutrients, space and light.
- Farmers adopt many ways to remove weeds and control their growth. Tilling before sowing of crops helps in uprooting and killing of weeds, which may then dry up and get mixed with the soil.
- The best time for the removal of weeds is before they produce flowers and seeds.
- The manual removal includes physical removal of weeds by uprooting or cutting them close to the ground, from time to time. This is done with the help of a khurpi. A seed drill is also used to uproot weeds.
(d) Threshing
In the harvested crop, the grain seeds need to be separated from the chaff. This process is called threshing. This is carried out with the help of a machine called ‘combine’ which is in fact a combined harvester and thresher.
At Study Path, you can also learn more about Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management by accessing the free exhaustive list of study materials and resources related to the chapter such as NCERT Solutions, Notes, Important Questions, and MCQ.
- New QB365-SLMS
- 12th Standard Materials
- 11th Standard Materials
- 10th Standard Materials
- 9th Standard Materials
- 8th Standard Materials
- 7th Standard Materials
- 6th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard CBSE Materials
- 11th Standard CBSE Materials
- 10th Standard CBSE Materials
- 9th Standard CBSE Materials
- 8th Standard CBSE Materials
- 7th Standard CBSE Materials
- 6th Standard CBSE Materials
- Tamilnadu Stateboard
- Scholarship Exams
- Scholarships

CBSE 8th Standard CBSE all question papers, important notes , study materials , Previuous Year questions, Syllabus and exam patterns. Free 8th Standard CBSE all books and syllabus online. Practice Online test for free in QB365 Study Material. Important keywords, Case Study Questions and Solutions. Updates about latest education news and Scholorships in one place.
8th Standard CBSE Subjects
8th standard cbse study materials.

Study Materials for Other CBSE Board Standards

Class VI to XII
Tn state board / cbse, 3000+ q&a's per subject, score high marks.

Latest CBSE 8th Standard CBSE Study Material Updates
- CBSE Notes For Class 8
- Class 8 Science Notes
- Chapter 1: Crop Production And Management
Crop Production And Management Class 8 Notes
Plants of the same kind that are grown and cultivated as a source of food in a large cultivable land is called a crop.
To know more about Crops, visit here .
Types of Crops
Crops, which are grown in the winter season (from October to March) are called Rabi crops. The crops, which are sown in the rainy season (from July to October) are called Kharif crops.
For more information on Food Production and Management, watch the below video

Preparation of Soil
- Preparation of soil is the first step in cultivating crops for food production.
- The soil is prepared for sowing the seeds of the crop.
- This is carried out using various processes and tools.
To know more about Agriculture Soil Formation and Preparation, visit here .
For more information on Farming, watch the below video
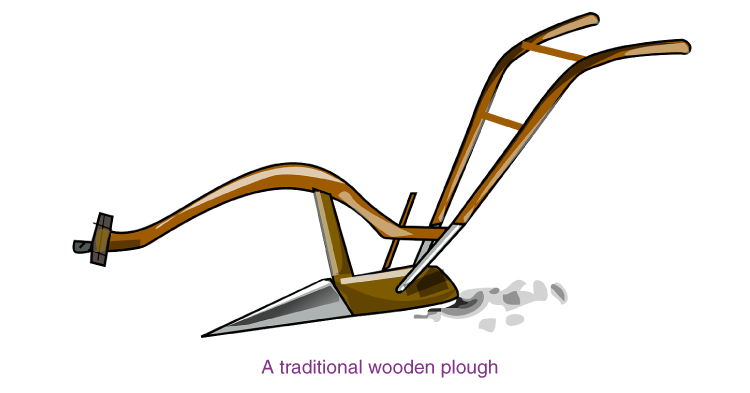
Tilling or Ploughing
The process of loosening and turning of the soil is called tilling or ploughing and is done by using a plough.
- A plough is a device that is used by farmers for different purposes, such as adding fertilizers, tilling and loosening the soil.
- It is also used for adding fertilizers to the soil, removing weeds, scraping of soil, etc.
- The ploughshare is the triangular iron strip.
- A ploughshaft is the main part of the plough, which is made using a log of wood.
- The other end of the shaft has a handle.
- The other end is attached to a beam which is placed on the bull’s neck.
- A wooden, traditional plough can be operated by a pair of ox and a man.
- Nowadays, these wooden ploughs are being replaced by iron ploughs.
- A cultivator is attached to the tractor and helps in loosening soil.
- Cultivators are used instead of ploughs since they are faster.

For more information on Irrigation, watch the below video

- Sowing is the process of planting seeds in the soil.
- The seeds are sowed in the soil that is loosened by a cultivator or plough.
To know more about Sowing, visit here .
Quality of the Seeds
- The quality of the seed is an important factor that determines the crop yield.
- The selection of good seeds is done by putting the seeds in water.
- The dead and damaged seeds become hollow and float on water, whereas the good seeds sink.
To know more about Selection and Sowing of Seeds, visit here .
Traditional Tools
- Before the advent of modern agricultural machinery, traditional tools were used by farmers.
- These include ploughs, shovels, scythes and pickaxes.
- The traditional tool used to sow the seeds was like a funnel.
- Once seeds were put into this funnel, they would go into 2-3 tubes having sharp ends.
- The ends will pierce into the soil and place the seeds there.
- Seed drills are used for sowing with the help of tractors.
- It ensures that seeds are sown uniformly, at a particular depth and are covered by soil after sowing.
- A nursery is a place where young plants and trees are grown for planting elsewhere.
- Nursery acts as a repository of saplings.
Germination of Seeds
- Germination of the seed happens when the seed is sown in the land and watered.
- A plant starts to emerge from the seed and starts to grow.
Adding Manure and Fertilisers
Manure/fertilizers.
- Manures and fertilizers are substances that are added to the soil to increase its fertility.
- Manures are made by decomposition of organic substances, and fertilizers are made of inorganic chemicals.
Differences between Manure and Fertilizers
| Fertilizer is an inorganic salt | Manure is prepared from organic matter such as human waste, cow dung and farm waste, etc |
| Fertilizers are manufactured in factories | Manures can be prepared on farms |
| Fertilizers are added in comparatively smaller quantities | Manures need to be added in large quantities as the nutrient content is less |
| Fertilizers do not provide any humus to the soil | Manures provide a lot of humus to the soil |
To know more about Manure and Fertilizer, visit here .
Disadvantages of Using Fertilizers
- Excessive use of fertiliser can cause pollution.
- It can also change the pH of the soil in certain rare cases.
Leaving the Land Fallow
- When land is left fallow for a certain period of time, the land replenishes its nutrients by itself.
- This land can be used for agriculture again.

Crop Rotation
- Crop rotation ensures that the same crop will not grow continuously and lead to the erosion of soil fertility.
- By growing crops that require different sets of nutrients, we can ensure that soil fertility is restored.
Protecting from Weeds
Weeds are undesirable plants that may grow naturally along with the crop.
- Weeds compete with the crops by absorbing all the water, nutrients, space and light.
To know more about Weeds, visit here .
- Tilling is a process done before sowing of crops that helps in uprooting and killing weeds.
Manual Removal
- Manual removal includes physical removal of weeds by uprooting them from the soil or chopping them off to ground level periodically.
- Chemicals used to kill the weeds are known as weedicides.
- They usually don’t damage the crop.
- Harvesting is the process of cutting the crop after it is mature.
Methods of Harvesting
- Harvesting is done by two methods.
- First is the manual method, where a sickle is used.
- Second is the mechanical method, where a huge machine called a harvester is used.
- Threshing is the process of loosening the grains from the chaff.
- While it can be done manually, a machine is used that separates all the grain seeds these days.

To know more about Threshing, visit here .
- Winnowing is the process that separates grain seeds from the chaff using the help of the wind.
- Due to the wind, the lighter chaff flies away, and the heavier grains fall down.
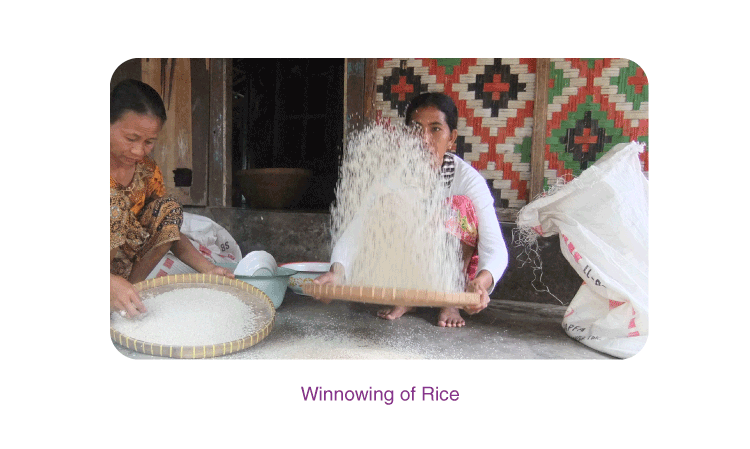

To know more about Winnowing, visit here .
- Storage of the grains is an important step in agriculture.
- After harvesting steps, the ready grains are stored in granaries or silos.
- The grains have to be stored in a dry place that does not have a rodent or fungal infestation.
- Fumigation of storage places is carried out to make it free from microbes.
- Granaries are the place where freshly obtained food grains are stored.
To know more about Storage of Grains, visit here .
Animal Husbandry
- Animal husbandry is the management and care of farm animals for milk, egg or meat.
To know more about Animal Husbandry, visit here .
At BYJU’S, learn more about crop production and management and other related topics, including class 8 Science notes .
Also Read:-
Frequently Asked Questions on CBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
What are the different types of irrigation methods.
The four main types of irrigation are Surface, Sprinkler, Drip and Subsurface.
What are biofertilizers?
Biofertilizers are living microbes that enhance plant nutrition by either mobilizing or increasing nutrient availability in soils. Various microbial taxa, including beneficial bacteria and fungi are currently used as biofertilizers, as they successfully colonize the rhizosphere, rhizoplane or root interior.
What is animal husbandry?
Animal husbandry is the branch of agriculture concerned with animals that are raised for meat, fibre, milk or other dairy products.
| CBSE Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Helped me a lot
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
October 4, 2019 by Veerendra
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management PDF will assist you in scoring more marks. This includes 1 mark Questions, 2 Mark Questions, 3 Mark Numericals Questions, 5 Marks Numerical Questions, Multiple Choice Questions, and previous year questions from Crop Production and Management Chapter. Topics and Sub Topics in Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management:
| 1 | Crop Production and Management |
| 1.1 | Agricultural Practices |
| 1.2 | Basic Practices of Crop Production |
| 1.3 | Preparation of Soil |
| 1.4 | Sowing |
| 1.5 | Adding Manure and Fertilisers |
| 1.6 | Irrigation |
| 1.7 | Protection from Weeds |
| 1.8 | Harvesting |
| 1.9 | Storage |
| 1.10 | Food from Animals |
Crop Production and Management Class 8 Science NCERT Textbook Questions
Question 1. Select the correct word from the following list and fill in the blanks. float, water, crop, nutrients, preparation (a) The same kind of plants grown and cultivated on a large scale at a place is called _____ (b) The first step before growing crops is _______ of the soil. (c) Damaged seeds would ______ on top of the water. (d) For growing a crop, sufficient sunlight and ______ and ______ from the soil are essential. Answer: (a) crop (b) preparation (c) float (d) water, nutrients
Question 2. Match items in column A with those in column B.
| A | B |
| (i) Kharif crops | (a) Food for cattle |
| (ii) Rabi crops | (b) Urea and superphosphate |
| (iii) Chemical fertilisers | (c) Animal excreta, cow dung, urine and plant waste |
| (iv) Organic manure | (d) Wheat, gram, pea |
| (e) Paddy and maize |
Answer: (i) (e) (ii) (d) (iii) (b) (iv) (c)
Question 3. Give two examples of each. (a) Kharif crop (b) Rabi crop Answer: (a) Kharif crop: Paddy and maize (b) Rabi crop: Wheat and gram
Question 4. Write a paragraph in your own words on each of the following. (a) Preparation of soil (b) Sowing (c) Weeding (d) Threshing Answer: (a) Preparation of soil: Soil preparation is necessary before growing a crop. It involves tilling and loosening the soil. This allows the roots to penetrate deep in the soil and to breath easily even when they are deep.
(b) Sowing: The process of putting seeds into the soil is called sowing. The tool used traditionally for sowing seeds is funnel-shaped. Nowadays a seed drill is used for sowing with the help of tractors. This tool sows the seed uniformly at a proper distance and depth.
(c) Weeding: Some undesirable plants grow along with crop and these unwanted plants are called weeds. The process of removing these unwanted plants is called weeding.
(d) Threshing: The process of separating the grain seeds from the chaff is called threshing.
Question 5. Explain how fertilisers are different from manure. Answer:
| Fertilisers | Manures |
| (i) A fertiliser is an inorganic salt. | (i) Manure is a natural substance obtained by the decomposition of cattle dung, human waste and plant residues. |
| (ii) A fertiliser is prepared in factories. | (ii) Manure can be prepared in the fields. |
| (iii) A fertiliser does not provide any humus to the soil. | (iii) Manure provides a lot of humus to the soil. |
| (iv) Fertilisers are very rich in plant nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. | (iv) Manure is relatively less rich in plant nutrients. |
Question 6. What is irrigation? Describe two methods of irrigation which conserve water. Answer: The artificial method of watering the plants for assisting in their growth is called irrigation. Main sources of irrigation are wells, tube-wells, ponds, lakes, rivers. Two methods which help us to conserve water are: (i) Sprinkler irrigation system: This irrigation system has an arrangement of vertical pipes with rotating nozzles on the top. It is more useful in the uneven and sandy land where sufficient water is not available.
(ii) Drip irrigation system: This irrigation system has an arrangement of pipes or tubes with very small holes in them to water plants drop by drop just at the base of the root. It is very efficient as water is not wasted at all.
Question 7. If wheat is sown in the kharif season, what would happen? Discuss. Answer: Wheat crop is sown from November/December to March/April. It is grown in winter and requires less water. If wheat is sown in Kharif season, its production will be decreased considerably.
Question 8. Explain how soil gets affected by the continuous plantation of crops in a field. Answer: Continuous plantation of crops makes the soil poorer in certain nutrients as the crops take up nutrients from the soil. The soil becomes infertile. It does not get enough time to replenish the nutrients.
Question 9. What are the weeds? How can we control them? Answer: The undesirable and unwanted plants which grow naturally along with the crop are called weeds. The growth of weeds can be controlled by adopting many ways. Tilling before sowing of crops helps in the uprooting and killing of weeds, which may then dry up and get mixed with the soil. Weeds are also controlled by using certain chemicals, called weedicides. Weedicides are sprayed in the fields to kill the weeds.
Crop Production and Management Class 8 Science NCERT Intext Activities Solved
Activity 1 (NCERT Textbook, Page 4) Take a beaker and fill half of it with water. Put a handful of wheat seeds and stir well. Wait for some time. Solution: We observe that most of the seeds sink while some float on water. Damaged seeds become hollow and lighter so they float. In this way, we can separate damage seeds from the healthier ones.

Activity 3 (NCERT Textbook, Page 12) Make the following Table in your notebook and complete it.
| S. No. | Food | Sources |
| 1. | Milk | Cow, Buffalo, She-goat, She-camel |
| 2. | Meat | Goat, Hen, Pig, Duck, Sheep |
| 3. | Egg | Hen, Duck, Goose |
| 4. | Honey | Honey bee |
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 – 1 Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1. Select the correct word from the following list and fill in the blanks : [NCERT] float, water, crop, nutrients, preparation (a) The same kind of plants grown on a large scale at a place is called ………….. (b) The first step before growing crops is …………. of the soil. (c) Damaged seeds would …………. on top of water. (d) For growing a crop sufficient sunlight, …………….. and …….. the soil are essential. Solution: (a) crop (b) preparation (c) float (d) nutrients, water
Question 2. Match items in column ‘A’ with those in column ‘B’ [NCERT]
| (A) | (B) |
| 1. Kharif crops 2. Rabi crops 3.Chemicalfertilisers 4. Organic manure | (a) Food for cattle (b) Urea and super phosphate (c) Animal excreta,cowdung, urine and plant waste. (d) Wheat, gram, pea. (e) Paddy and maize |
| (A) | (B) |
| 1. Kharif crops 2. Rabi crops 3. Chemical fertilisers 4. Organic manure | (e) Paddy and maize (d) Wheat, gram, pea (b) Urea and super phosphate (c) Animal excreta, cow dung, urine and plant waste. |
Question 3. What are crops? Solution: Crops are plants of the same kind grown in large quantities for food.
Question 4. What is the basis of classification of crops in our country? Solution: In our country, crops are classified on the basis of the season in which they grow.
Question 5. What are kharif crops? Solution: The crops which are sown in the rainy season and harvested in September/October are called kharif crops.
Question 6. What are summer crops? Solution: The crops which are grown in the summer season and harvested before rainy season are called summer crops or zayed crops.
Question 7. Name two summer season crops. Solution: Moong and muskmelon are summer season crops.
Question 8. What are rabi crops? Solution: The crops which are grown in the winter season and harvested in March/April are called rabi crops.
Question 9. Why paddy cannot be grown in the summer season? Solution: Paddy requires a lot of water, so it can only be grown during rainy season.
Question 10. What is meant by agricultural practices? Solution: The activities undertaken by farmers over a period of time for cultivation of crops are known as agricultural practices.
Question 11. Write a paragraph in your own words on preparation of soil. Solution: Soil is prepared by tilling i.e., loosening and turning of soil.
Question 12. Name the tool used for tilling of soil. Solution: A plough is used for tilling of soil.
Question 13. What are crumbs? Solution: A ploughed field may have big pieces of soil called crumbs.
Question 14. How are crumbs broken? Solution: The crumbs are broken with the help of a plank.
Question 15. Why should loose soil be levelled? Solution: Loose soil be levelled for sowing and irrigation.
Question 16. How is levelling of soil done? Solution: Levelling of soil is done with the help of a leveller.
Question 17. How is ploughing done these days? Solution: Now a days ploughing is done by tractor having a multipronged plough.
Question 18. What is meant by sowing? Solution: Sowing is the process of putting seeds in the soil.
Question 19. What is meant by good quality seeds? Solution: The good quality seeds means clean and healthy seeds of a good variety free from diseases.
Question 20. What is the advantage of sowing seeds with a seed drill? Solution: The advantage of sowing seeds with a seed drill is that the seeds are sown at a proper depth under the soil and the distance between them is uniform.
Question 21. What are manure and fertilisers? Solution: The substances which are added to the soil in the form of nutrients for the healthy growth of plants are called manure and fertilisers.
Question 22. What is organic manure? Solution: Manure obtained from animal or plant waste such as cattle dung, droppings is called organic manure.
Question 23. What is meant by crop rotation? Solution: Growing crops alternatively to prevent depletion of any one nutrient from soil is called crop rotation.
Question 24. What is meant by irrigation? Solution: The supply of water to crops in the fields at different intervals is called irrigation.
Question 25. What is the drip system of irrigation? Solution: Falling of water drop by drop at the roots of the plant is called drip irrigation.
Question 26. Why should weeds be removed? Solution: Weeds compete with the crop plants for water, nutrients, space and light and thus affect the growth of the crop. So, they should be removed.
Question 27. Name the process of removal of weeds. Solution: Weeding is the process of removal of weeds.
Question 28. How is harvesting done in our country? Solution: Harvesting in our country is done either manually by sickle or by a machine called harvester.
Question 29. Name the farm machine used for harvesting and threshing both. Solution: Combine.
Question 30. What is meant by winnowing? Solution: After threshing, the grain is separated from the chaff, with the help of wind. This is known as winnowing.
Question 31. How are food grains stored? Solution: Food grains are dried in the sun to remove the excess moisture and then stored.
Question 32. Why should grains be dried before storage? Solution: Grains should be dried before storage to remove the excess moisture in them, so that microbes are not able to attack the grains.
Question 33. What is meant by animal husbandry? Solution: The study of the care of animals is known as animal husbandry.
Question 34. Name some animals from whom milk can be obtained. Solution: Milk can be obtained from cow, buffalo, she goat and she camel.
Question 35. How is fish useful for us? Solution: Fish is highly nutritious and easily digestible food. Cod liver oil from fish is also a rich source of vitamin D.
Question 36. Name some animals which are reared for their meat. Solution: Sheep, goat, pigs, chicken and fish are reared for their meat.
Question 37. Why is honey so useful? Solution: Honey is an antiseptic and its enzymes help in digestion. It is also used for making several ayurvedic medicines.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 – 2 Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1. If wheat is sown in the kharif season, what would happen? Discuss. [NCERT] Solution: The farmer will not get a good crop because wheat should be sown in winter season.
Question 2. Explain how soil gets affected by the continuous plantation of crops in a field. [NCERT] Solution: When the crops are planted continuously in a field, the soil becomes deficient in nutrients.
Question 3. What are weeds? How can we control them? [NCERT] Solution: Weeds are unwanted plants in the fields. It can be controlled by
- During tilling they are removed.
- By removing them manually.
- By using weedicides.
Question 4.
(a) Give two examples of each : [NCT 2011, NCERT] (i) Kharif crop (ii) Rahi crop (b) Can you explain why most crops have a particular season in which they grow? Solution: (a) (i) Groundnut and cotton. (ii) Pea and mustard. (b) Most crops have a particular season in which they grow because different crops need different temperature, humidity and rainfall.
Question 5. What is a seed drill? Solution: A seed drill is used for sowing seeds. It has a funnel shaped opening leading to long tubes attached to a plough. Seeds are put into the funnel. As the plough makes furrows in the soil, the seeds are deposited in the soil by the drill.
Question 6. Give two reasons why seeds should be sown at correct distance. Solution: Seeds should be sown at a correct distance. The reasons are:
- If the seeds are too close, they will not get enough water, sunlight and nutrients.
- If the seeds are too far apart, there is wastage of field space.
Question 7. Give two methods by which threshing can be done. Solution: Threshing can be done manually by making oxen or buffaloes trample over the cut crop or by a machine called thresher.
Question 8. A farmer grow moong during the rainy season. Will he get a good crop? Solution: The farmer will not get a good crop of moong because moong should be grown during summer season.
Question 9. Why does loosening of soil allow roots to breathe easily? Solution: When soil is loosened, the roots can breathe easily because there is more air present in the soil.
Question 10. A farmer never leaves his field fallow. Will he get a good crop? Solution: If the field is never left fallow, the soil will become deficient in certain nutrients and the farmer will not get a good crop.
Question 11. What are fertilisers? Name two important fertilisers. Solution: Fertilisers are chemical substances which are rich in a particular nutrient. Urea and ammonium sulphate are two fertilisers.
Question 12. Give two disadvantages of using fertilisers excessively. Solution: Disadvantages of using excessive fertilisers :
- Soil fertility is reduced.
- It becomes a source of water pollution.
Question 13. What is the advantage of using manure? Solution: Manure improves soil texture as well as its water retaining capacity.
Question 14. Why should watering be increased during summer? Solution: The frequency of watering is higher in summer due to the increased rate of evaporation of water from the soil and the leaves.
Question 15. Name the two main methods of irrigation used in India nowadays. Solution: Two main methods of irrigation used in India’s nowadays are :
- Sprinkler system
- Drip system.
Question 16. When should the weedicides be sprayed? Solution: The weedicides are sprayed during the vegetative growth of weed before flowering and seed formation.
Question 17. How are grains stored in homes? Solution: At home grains are stored by putting dried neem leaves.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 – 3 Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1. Define lodging. How does it happen? [MSE (Chandigarh) 2008, 2006] Solution: Lodging is the falling of crop plants at the grain maturation stage. It happens due to untimely rains and strong winds.
Question 2.
- What is harvesting?
- Mention two important uses of tilling the soil. [MSE (Chandigarh) 2008]
- Cutting and gathering of crops after maturation is known as harvesting.
- It improves air circulation.
- Roots can penetrate deeper into the soil.
Question 3.
- Define crop.
- Name two categories of crops based on season. [KVS 2005]
- What are pesticides? [KVS 2005]
- The plants of same kind grown at a place is referred to as crop.
- Two categories of crop based on season are kharif and rabi crops.
- Pesticides are chemicals used to protect crops from harmful organisms called pests.
- Earthworms are nature’s ploughmen. How?
- How is soil a resource for all living organisms? Give any two points. [DAV2006]
- It is habitat for many living organisms.
- Plants grow in soil which provide food, shelter, material for clothes.
- Plants grows in soil and provide O2.
- Decomposition occurs in soil.
Question 5. What is irrigation? Describe two methods of irrigation which conserve water. [NCERT] Solution: Supply of water to crops at appropriate intervals is called Irrigation. Two methods of irrigation are :
- Sprinkler system – Where water is sprinkled on the crops as if it is raining.
- Drip system – In this system, the water falls drop by drop just at the position of the roots.
Question 6. Name three natural methods of replenishing the nutrients of the soil. Are these natural methods sufficient to maintain the fertility of the soil? Solution: Field fallow, crop rotation and mixed cropping are three natural methods of replenishing the nutrients of the soil. These natural methods are not enough and farmers have to resort to manures and fertilisers.
Question 7. Give three reasons, why soil should be turned and loosened? Solution:
- It allows the roots to penetrate deep in the soil.
- It helps the growth of earthworms and microbes in the soil.
- Various nutrients held in the dead organisms are released back in the soil.
Question 8. What are the three steps involved in the preparation of soil? Solution:
- Ploughing the soil to loosen it.
- Levelling the soil to ensure uniform distribution of water and nutrients.
- Manuring to provide nutrients to the soil.
Question 9. Name the three tools used for ploughing and give the function of each. Solution:
- Plough – It is used for tilling of soil, adding fertilisers to the crop, removing the weeds, scrapingof soil.
- Hoe – It is used for removing weeds and for loosening the soil.
- Cultivator – Used for ploughing.
Question 10. How is organic manure obtained? Solution: Farmers dump plant and animal waste in pits at open places and allow it to be decomposed by microorganisms. This decomposed material is converted into organic manure.
Question 11. Give three reasons. Why water is important for plants? Solution: Water is important for plants because:
- Nutrients dissolved in water are absorbed by roots of plants.
- Germination of seeds takes place because of water.
- It protects the plant from frost and hot air currents.
Question 12. What are the advantages of sprinkler system of irrigation? Solution: Advantages of using sprinkler system of irrigation are :
- The sprinkler system of irrigation is useful on the uneven lands where water is available in smaller quantities.
- It conserves water.
- It is useful for the sandy soil.
Question 13. Give the advantages of using the drip system of irrigation. Solution: Advangates of using drip system of irrigation are :
- It provides water to plants drop by drop.
- Water is not wasted at all.
- It can be used where availability of water is less.
Question 14. Explain the manual method of removing weeds. Solution: The manual’removal of weeds includes physical removal of weeds by cutting them close to the ground from time to time. This is done with the help of khurpi or a harrow.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 – 5 Mark Questions and Answers
Question 1.
- What are the two ways of sowing the seeds? [DAV2007]
- Give any three advantages of ploughing.
- Seeds can be sown manually or by seed drills.
- Loose soil has lot of air trapped which allows roots to breathe.
- Loose soil allows the roots to penetrate deeper.
- Loose soil helps the growth of microbes and other organisms.
- What will happen if field is not ploughed before sowing the seeds? Give any two disadvantages. [DAV2006]
- How are perishable food items stored on a commercial scale?
- Why should excessive supply of water be avoided?
- What are weeds?
- Seeds cannot be sown at proper depth.
- Water and air holding capacity of soil will be poor.
- Perishable food items can be stored in deep freezers and cold storages.
- Roots get damaged and the plants die because of excessive supply of water.
- They are unwanted plants which grow along with the cultivated plants.
Question 3. (a) Why does farmer rotate crops in the field? (b) Differentiate between manure and fertiliser. [DAV2005] Solution: (a) To replenish the nutrients of the soil. (b)
| Manure | Fertiliser |
| (i) It is natural. (ii) It is organic. (iii) It adds humus to the soil. (iv) It is not nutrient specific. (v) It is cheap. (vi) It is prepared in the fields. | (i) It is man-made. (ii) It is inorganic. (iii) It does not add humus. (iv) It is nutrient specific. (v) It is costly. (vi) It is prepared in factories. |
or (a) (i) While spraying pesticides, nose and mouth should be closed. (ii) Position of the farmer should be such that the wind blows away from his face. (iii) Immediately after spraying is done, hands should be washed, face and mouth should be cleaned with water.
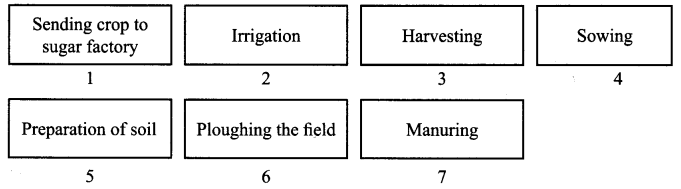
Question 6. Explain the method used these days to sow seeds. Solution: These days the seed drill is used for sowing seeds with the help of a tractor. This sows the seed uniformly at a proper distance and depth. Seeds get covered by soil during sowing with a drill. This prevents damage caused by birds. Sowing by using seed drill saves time and labour.
Question 7. What are the advantages of organic manure? Solution: The advantages of organic manure are :
- It enhances the water holding capacity of the soil.
- It makes the soil porous due to which exchange of gases takes place.
- The number of friendly microbes is increased.
- The organic manure improves the texture of the soil.
Question 8. How does a plough work? Solution: A plough is an agricultural implement used for tilling and loosening of soil. It has a triangular iron strip called plough share. Plough shaft is the main part made of a long wooden log. The other end is hung on the bull’s necks. The plough can be with two bulls and one person.
Question 9. Write a paragraph in your own words on each of the following : [NCERT]
- Preparation of soil
- Preparation of soil : Preparation of the soil involves loosening and turning the soil. This process, known as ploughing, is done by using a wooden or iron plough which is pulled either by an animal or by tractors. Loose soil is then levelled by using a wooden or iron leveller.
- Sowing : Seeds are sown after preparation of the soil. Seeds can be sown manually or by seed drills by the process called broadcasting. Seeds should be sown at the correct depth and at correct distance.
- Weeding : The process of removing weeds from a field is called weeding. Weeding can be done manually by pulling the weeds out by hand or by using a harrow to uproot them. Weeding can also be done by spraying special chemicals called weedicides.
- Threshing: Threshing is the process of separating the grain from the cut crop. Threshing can be done manually by making oxen or buffaloes trample over the cut crop or by using a machine called thresher.
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 – Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Paddy can be grown in (a) summer season (b) autumn (c) rainy season (d) winter Solution: (c)
Question 2. Wheat can be grown in (a) winter (b) rainy season (c) spring (d) summer Solution: (a)
Question 3. Which of the following is a rabi crop? (a) Paddy (b) Maize (c) Mustard (d) Soyabean Solution: (c)
Question 4. Loosening and turning of the soil is known as (a) tilling (b) broadcasting (c) transplantation (d) manuring Solution: (a)
Question 5. Sowing the seeds manually is known as (a) ploughing (b) broadcasting (c) tilling (d) transplantation Solution: (b)
Question 6. The method of transferring seedlings from nursery to field is known as (a) broadcasting (b) transplantation (c) crop rotation (d) harvesting Solution: (b)
Question 7. Leaving the agricultural land uncultivated for one or more seasons is known as (a) field fallow (b) crop rotation (c) manuring (d) threshing Solution: (a)
Question 8. Chemical substances rich in specific nutrients are called (a) manures (b) fertilisers (c) pesticides (d) weedicides Solution: (b)
Question 9. Chemicals which kill weeds are known as (a) fertilizers (b) pesticides (c) weedicides (d) none of these Solution: (c)
Question 10. Cutting and gathering of crops after maturation is known as (a) harvesting (b) threshing (c) broadcasting (d) tilling Solution: (a)
More CBSE Class 8 Study Material
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 English
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 English Honeydew
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 English It So Happened
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Sanskrit
NCERT Solutions
Free resources.
Quick Resources
Case Study Questions Class 8 Civics The Indian Constitution
Case study questions class 8 civics chapter 1 the indian constitution, cbse case study questions class 8 civics the indian constitution.
By the beginning of the twentieth century, the Indian national movement had been active in the struggle for independence from British rule for several decades. During the freedom struggle the nationalists had devoted a great deal of time to imagining and planning what a free India would be like. Under the British, they had been forced to obey rules that they had had very little role in making. The long experience of authoritarian rule under the colonial state convinced Indians that free India should be a democracy in which everyone should be treated equally and be allowed to participate in government. What remained to be done then was to work out the ways in which a democratic government would be set up in India and the rules that would determine its functioning. This was done not by one person but by a group of around 300 people who became members of the Constituent Assembly in 1946 and who met periodically for the next three years to write India’s Constitution. These members of the Constituent Assembly had a huge task before them. The country was made up of several different communities who spoke different languages, belonged to different religions, and had distinct cultures. Also, when the Constitution was being written, India was going through considerable turmoil. The partition of the country into India and Pakistan was imminent, some of the Princely States remained undecided about their future, and the socio-economic condition of the vast mass of people appeared dismal. All of these issues played on the minds of the members of the Constituent Assembly as they drafted the Constitution. They rose to the occasion and gave this country a visionary document that reflects a respect for maintaining diversity while preserving national unity. The final document also reflects their concern for eradicating poverty through socio-economic reforms as well as emphasising the crucial role the people can play in choosing their representatives.
Answer: By establishing a framework that upheld individual rights, encouraged democratic governance, and aimed to help the socioeconomically disadvantaged, the Constituent Assembly’s crafting of India’s Constitution displayed its steadfast commitment to forging a progressive and inclusive nation. The Constituent Assembly rose to the occasion and gave India a visionary Constitution that provided the groundwork for a democratic and multiethnic country, despite the difficulties faced by partition and societal inequalities.
Federalism refers to the existence of more than one level of government in the country. In India, we have governments at the state level and at the centre. Panchayati Raj is the third tier of government. The vast number of communities in India meant that a system of government needed to be devised that did not involve only persons sitting in the capital city of New Delhi and making decisions for everyone. Instead, it was important to have another level of government in the states so that decisions could be made for that particular area. While each state in India enjoys autonomy in exercising powers on certain issues, subjects of national concern require that all of these states follow the laws of the central government. The Constitution contains lists that detail the issues that each tier of government can make laws on. In addition, the Constitution also specifies where each tier of government can get the money from for the work that it does. Under federalism, the states are not merely agents of the federal government but draw their authority from the Constitution as well. All persons in India are governed by laws and policies made by each of these levels of government.
Answer:The public’s right to hold elected authorities accountable is emphasised strongly in the Constitution. By making sure that representatives answer for their deeds and decisions, it maintains democratic values like accountability, responsiveness, and public service. As a result, a strong and accountable democratic system is fostered, with elected officials prioritising the welfare of their constituents.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
We have a strong team of experienced teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts, dav class 5 math solution chapter 8 simplification of numerical expressions, sikkim scert class 4 english chapter 6d i can read solution, kerala scert class 8 english the sower question answer, up scert solutions class 6 english chapter 10 – the story of a bicycle.
Scholarships
Test Series NEW
- 1.0 CBSE Class 8 Science
Physics, Chemistry, and Biology are three cornerstone subjects in CBSE's 8th-class science curriculum that are very important for the scientific learning process. The curriculum for the 8th class is aimed at sharpening students' understanding of fundamental concepts in science and/or igniting in students the insatiable thirst for curiosity about their environment.
The course contains elements related to physics, chemistry, and biology. Foundational concepts are taught in each of these areas that will be quite useful for future science classes.
This blog will cover topics related to CBSE Class 8 Science, such as the class syllabus, important books, and more, which students must know to score well in Class 8 Science.
- 2.0 CBSE Class 8 Science Syllabus
The CBSE Class 8 syllabus aims to provide students with a profound understanding of mathematical concepts and instil critical thinking skills in them. Instead of focusing on students mastering pre-existing algorithms, the syllabus tries to teach them to understand the basic principles of mathematics. The aim is to make them enjoy the subject and to get them to develop their strategies for solving and posing problems. Mastering the Class 8 Maths syllabus is not solely about being ready for exams. Instead, it is a foundation for excelling in board examinations and developing a solid mathematical mindset. Here's a detailed overview of the CBSE Class 8 Maths syllabus:
The CBSE Class 8 Science syllabus is designed to provide a comprehensive understanding of fundamental scientific concepts across Physics, Chemistry, and Biology. Here is a breakdown of the syllabus:
Chapter 1: Crop Production and Management | 1.1 Agricultural Practices 1.2: Basic Practices of Crop Production 1.3: Preparation of Soil 1.4: Sowing 1.5 Adding Manure and Fertilizers 1.6: Irrigation 1.7: Protection from Weeds 1.8: Harvesting 1.9: Storage 1.10: Food from Animals |
Chapter 2: Microorganisms: Friend and Foe | 2.1 Microorganisms 2.2: Where do Microorganisms Live? 2.3: Microorganisms and Us 2.4: Harmful Microorganisms 2.5: Food Preservation 2.6: Nitrogen Fixation 2.7: Nitrogen cycle |
Chapter 3: Coal and Petroleum | 5.1 Coal 5.2: Petroleum 5.3: Natural Gas 5.4: Some Natural Resources are Limited |
Chapter 4: Combustion and Flame | 6.1 What is Combustion? 6.2: How Do We Control Fire? 6.3Types of Combustion 6.4: Flame 6.5: Structure of a Flame 6.6: What is a Fuel? 6.7: Fuel Efficiency |
Chapter 5: Conservation of Plants and Animals | 7.1 Deforestation and Its Causes 7.2: Consequences of Deforestation 7.3: Conservation of Forest and Wildlife 7.4: Biosphere Reserve 7.5: Flora and Fauna 7.6: Endemic Species 7.7: Wildlife Sanctuary 7.8: National Park 7.9: Red Data Book 7.10: Migration 7.11: Recycling of Paper 7.12: Reforestation |
Chapter 6: Reproduction in Animals | 9.1 Modes of Reproduction 9.2: Sexual Reproduction 9.3: Asexual Reproduction |
Chapter 7: Reaching the Age of Adolescence | 10.1 Adolescence and Pubert 10.2 Changes at Pybert Increases Height 10.3 Secondary Sexual Characters 10.4 Roles of Hormones in Initiating Reproductive Function 10.5 Reproductive Phase of Life in Humans 10.6 How is the Sex Of The Baby Determined? 10.7 Jormones Other than Sex Hormones 10.8 Role of Hormones in Completing The Life History of Insects and Frogs 10.9 Reproductive Health |
Chapter 8: Force and Pressure | 11.1 Force - A Push or a Pull 11.2 Forces Are Due To An Interaction 11.3 Exploring Forces 11.4 A Force Can Change the State of Motion 11.5 Force Can Change the Shape of an Object 11.6 Contact Forces Muscular Force 11.7 Non-contact forces, Magnetic Forces 11.8 Pressure 11.9 Pressure Exerted by Liquids and Gases 11.10 Atmospheric Pressure |
Chapter 9: Friction | 12.1 Force of Friction 12.2 Factors Affecting Friction 12.3 Friction: A Necessary Evil 12.4 Increasing and Reducing Friction 12.5 Wheels Reduce Friction 12.6 Fluid Friction |
Chapter 10: Sound | 13.1 Sound Is Produced by a Vibrating Body 13.2 The Sound Produced by Humans 13.3 Sound Needs a Medium for Propagation 13.4 We Hear Sound Through Our Ears 13.5 Amplitude, Perios and Frequency of a Vibration 13.6 Audible and Inaudible Sounds 13.7 Noise and Music 13.8 Noise Pollution |
Chapter 11: Chemical Effects of Electric Current | 14.1 Do Liquids Conduct Electricity? 14.2 Chemical Effects of Electric Current 14.3 Electroplating |
Chapter 12: Some Natural Phenomena | 15.1 Lightning 15.2 Charging by Rubbing 15.3 Types of Charge and Their Interaction 15.4 Transfer of Charge 15.5 The Story of Lightning 15.6 Lightning Safety 15.7 Earthquakes |
Chapter 13: Light | 16.1 What Makes Things Visible 16.2 Laws of Reflection 16.3 Regular and Diffused Reflection 16.4 Reflected Light Can Be Reflected Again 16.5 Multiple Images 16.6 Sunlight - White or Coloured? 16.7 What Is Inside Our Eyes 16.8 Care of the Eyes 16.9 Visually Impaired Persons Can Read and Write 16.10 What is the Braille System? |
- 3.0 CBSE Class 8 Science Books
The CBSE Class 8 Science books are carefully designed based on the syllabus and help students understand science thoroughly. Moreover, these books include all the essential chapters of Physics, Chemistry, and Biology, with lucid and comprehensive explanations that facilitate students' understanding of key ideas. Focusing on these core subjects aims to develop students' critical thinking abilities, analytical skills, and a strong base in the concepts of science to help them learn in subsequent levels.
1. NCERT Textbook for Class 8 Science
CBSE Class 8 Science books in the curriculum have been specially prepared to support students in developing a good understanding of science. It covers all the important topics of Physics, Chemistry, and Biology while providing clear explanations and interesting content that support students in understanding the core concepts of each discipline. By focusing on the disciplines of these subjects, the books aim to enhance the students' ability to think critically, and analytically, and to help them build a solid foundation in science to prepare them for the sciences in upper grades.
2. Additional Reference Books
These books enhance the academic experience for students, by giving a range of questions, particularly advanced-level questions, that encourage students to utilize concepts and deepen their understanding of the course materials. Here are some additional reference resources students can practice with:
- Lakhmir Singh
- 4.0 CBSE Class 8 Science Mock Tests
CBSE Class 8 Science mock tests are customized to fit each student's strengths and weaknesses and are the most effective way to measure exam preparedness in the subjects. After each mock test, students can learn from their mistakes, work on them, and avoid repeating the same mistakes in the final exam.
Mock tests that are followed by the practice encouraged students to develop time management skills which were applied during the real exam. By getting mock tests regularly, you will be able to follow up on your improvement and keep improving at all times. Improve your performance with ALLEN’s Mock Test designed by by some of India's top expert faculties.
- 5.0 CBSE Class 8 Science Preparation Tips
1. Understanding the Syllabus: Before diving into your studies, it is critical to gain full knowledge of the entire curriculum to avoid overlooking any topics. When you have understood what is required, the best plan is to divide the syllabus into smaller manageable parts. In this way, on the one hand, you can pay attention to the section at a time; on the other hand, you can organize better your study sessions, set realistic goals, and be sure that all topics are covered.
2. Regular revision: To keep information in your mind and make it solid, you need to revise it periodically. Another way is to test yourself on a topic without using the book or notes. Memory is enhanced through this active recall exercise, and areas that require more attention are identified. On top of that, flashcards can be used for reviewing the main ideas, definitions and terms in the course work. By constantly going through these flashcards, one might be able to easily remember what was contained in them keeping the information fresh in one’s mind hence making it easier to retrieve during exams.
3. Practice Regularly: If you want to excel in your examinations, regular practice is very essential. One of the strategies is executing mock tests, this can be an evaluation of personal preparation; hence, one can see where some improvements may be needed. When practising, focus on finishing the questions within the time frame to improve your speed and accuracy.
4. Ask for Doubts: If you are having any doubts or questions while studying, never hesitate to ask for help. Ask your teacher or classmates who can help you understand the problem topics. Learning among one another's classmates helps because the discussion of the concepts confers understanding over and over again, with new insights.
5. Stay Healthy and Focused: Among the most important prerequisites for studying well are health and focus. Therefore, one should get adequate sleep at night to help the mind remain alert and the focus sharp. Wholesome nutrition will help retain one's energy levels throughout the day so that one may focus easily while studying. Breaking up your study sessions by taking small breaks is equally important.
Table of Contents
The CBSE Class 8 Science Examination comprises multiple-choice questions, short-answer questions, and long-answer questions. The paper assesses the students' conceptual knowledge and parameters like knowledge application and problem-solving.
Practical work in science forms an intrinsic part, this enables students to put theoretical knowledge into practice, develop scientific inquiry skills, and gain hands-on experience with experiments. Practical activities deepen understanding and enhance problem-solving ability.
In solving numerical problems in Class 8 Science, you should start by carefully reading the problem and identifying the key information given in the problem. Note down the relevant formulae and solve the problem in a stepwise manner, showing all your steps.
- Linear Equations in One Variable Class 8 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 2

Last Updated on August 25, 2024 by XAM CONTENT
Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 8 maths. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class 8 maths. In this article, you will find case study questions for CBSE Class 8 Maths Chapter 2 Linear Equations in One Variable. It is a part of Case Study Questions for CBSE Class 8 Maths Series.
| Linear Equations in One Variable | |
| Case Study Questions | |
| Competency Based Questions | |
| CBSE | |
| 8 | |
| Maths | |
| Class 8 Studying Students | |
| Yes | |
| Mentioned | |

Table of Contents
Case Study Questions on Linear Equations in One Variable
Passage 1: It is common that government revises fares from time to time based on various factors such as taxes, economy and inflation, for various vehicles like auto-rickshaw, taxis and radio cab etc. The auto and Taxi charge in a city comprise of fixed charge and the charge for the distance covered. Few situations are given below in the form questions. Find the correct option.
Difficulty Level: Medium
Q. 1. If the fixed charge in a city is ₹ x and charge per km is ₹5 and total fare is ₹60 then find the linear equation for the journey of 10 km. (a) x + 50 = 60 (b) x – 50 = 60 (c) x + 50 = 50 (d) None of these
Q. 2. In the above question, what is the value of fixed charge? (a) ₹20 (b) ₹5 (c) ₹10 (d) ₹15
Also read: Linear Equations in One Variable Assertion Reason Questions for Class 8
Q. 3. If in a city a person has to pay ₹110 for a journey of 15 km and fixed charge is ₹20 then what is the charge per km is? (a) ₹12 (b) ₹6 (c) ₹8 (d) no fixed charge
Q. 4. If in a city fixed charge is double of the charge per km and a person paid ₹75 for a journey of 1 km, then the linear equation for the following situation is?
Q. 5. According to the given equation: 2x + 17 = 85, if ₹17 is the fixed charge and the total fare is ₹85 for a journey of 2km then what is the charge per kilometre?
- Algebraic Expressions and Identities Class 8 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 8
- Comparing Quantities Class 8 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 7
- Cube and Cube Roots Class 8 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 6
- Square and Square Roots Class 8 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 5
- Data Handling Class 8 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 4
Understanding Quadrilaterals Class 8 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 3
Rational numbers class 8 case study questions maths chapter 1, download ebooks for cbse class 8 maths.
- Rational Numbers Topicwise Worksheet for CBSE Class 8 Maths
- Linear Equations in One Variable Worksheet for CBSE Class 8 Maths
- Understanding Quadrilaterals Worksheet for CBSE Class 8 Maths
- Data Handling Worksheet for CBSE Class 8 Maths
- Squares and Square Roots Worksheet for CBSE Class 8 Maths
- Cube and Cube Roots Worksheet for CBSE Class 8 Maths
- Comparing Quantities Worksheet for CBSE Class 8 Maths
- Algebraic Expressions and Identities Worksheet for CBSE Class 8 Maths
Topics from which case study questions may be asked
- Linear Equation in One Variable
- Solving an Equation
- Solving Equation having variable on both sides
- Reducing Equation to Simpler Form
Case study questions from the above given topic may be asked.
Download Customised White Label Study Materials in MS Word Format
We are providing teaching resources to teachers and coaching institute looking for customised study materials in MS word format. Our High-quality editable study material which is prepared by the expert faculties are Highly useful for Teachers, Mentors, Tutors, Faculties, Coaching Institutes, Coaching Experts, Tuition Centers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Linear Equations in One Variable Case Study
Q1: what is an algebraic expression.
A1: A combination of constants and variables connected by some or all of the four fundamental operators such as +, –, × and ÷ is called algebraic expression.
Q2: What is an equation?
A2: An equation is like a scale, while manipulating equations we have to keep the scale balanced by doing the same thing to both sides.
Q3: What is linear equation in one variable?
A3: An equation is called linear equation if it has only one degree i.e., the highest power of the variable appearing in equation is 1. e.g., ax + b = 0
Q4: What is solution of an equation?
A4: A number which satisfies an equation is called the solution of the equation.
Q5: How do you solve a linear equation in one variable?
A5: To solve a linear equation in one variable, isolate the variable on one side of the equation by performing inverse operations (such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division) on both sides until the variable is alone.
Q6: What is the solution of a linear equation?
A6: The solution of a linear equation is the value of the variable that satisfies the equation. It is the value that, when substituted into the equation, makes the equation true.
Q7: What does the term ‘one variable’ mean in linear equations?
A7: ‘One variable’ means that the equation contains only a single unknown quantity, typically represented by the letter ‘x’. Other terms or constants may be present, but there is only one variable.
Q8: Can linear equations be represented graphically?
A8: Yes, linear equations can be represented graphically as straight lines on the coordinate plane. The slope-intercept form (y = mx + b) is particularly useful for graphing linear equations.
Q9: Are there any online resources or tools available for practicing linear equations in one variable case study questions?
A9: We provide case study questions for CBSE Class 8 Maths on our website . Students can visit the website and practice sufficient case study questions and prepare for their exams. If you need more case study questions, then you can visit Physics Gurukul website. they are having a large collection of case study questions for all classes.

Related Posts


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Case Study Questions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management. Here we are providing case study questions for CBSE Class 8 science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management. Case Study Questions. Question 1: A boy named Yash from Gwalior who studies in 8th standard is very fond of plants. He has a small garden in the backyard.
Case Study Questions on Crop Production and Management. Questions. Question 1: A boy named Yash from Gwalior who studies in 8th standard is very fond of plants. He has a small garden in the backyard. Where he's planted many small plants and takes good care of them.
Case Study Questions on Rational Numbers. Questions. Passage 1: Aditya who is working in a multinational company earns ₹150000 per month. Out of his earnings he spend 1/10th on food items, 1/4th on shopping with family, 1/5th of remaining on education of his two kids and rest of his money he puts in his savings.
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks. CBSE Case Study Questions Class 8 Science Crop Production and Management Case study 1
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 5 marks, 5 marks. Case Study 1. In 1817, James Mill, a Scottish economist and political philosopher, published a massive three-volume work, A ...
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks. CBSE Case Study Questions Class 8 Geography Resources Case Study 1. Mona and Raju were helping Amma to clean their house.
CBSE Class 8 Science Case Study Question. Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management Case Study Question. Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe Case Study Question. Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics Case Study Question. Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals Case Study Question.
CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter-1 Important Questions - Free PDF Download. Class 8 is very important as the preparation of the board examination starts here. The concepts that you are going to learn in class 8 is going to help you to perform well in class 9 and also in the board examination. Understanding the concepts is important.
NCERT Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management FREE PDF Download. Vedantu's Class 8 Science Chapter 1 NCERT Solutions has all the questions and answers in the chapter. This chapter explores "Crop Production and Management," explaining key principles essential for grasping agricultural practices and their importance.
NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 8 Science Chapter 1 - Free PDF Download. NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management are the most important study materials for CBSE Class 8 Science. In order to get complete knowledge of the chapter Crop Production and Management, learners should solve and practise the answers provided in this NCERT Exemplar.
Answer: Sowing is the process of planting seeds in the soil. Question 11: Name two categories of crops based on season. Answer: Two categories of crop based on season are kharif and rabi crops. Question 12: What is threshing? Answer: Separation of the grains from the chaff is called threshing.
The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class 8 social science. In this article, you will find case study for CBSE Class 8 Social Science Civics Chapter 1 The Indian Constitution. It is a part of Case Study Questions for CBSE Class 8 Social Science Series.
Here we are providing Case Study questions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 1 Rational Numbers. Maths Class 8 Chapter 1. Rational Numbers. Maths. CBSE Class 8. Chapter Covered. Class 8 Maths Chapter 1. Topics. Difference between Fraction and Rational Number.
CBSE 8th Standard CBSE all question papers, important notes , study materials , Previuous Year questions, Syllabus and exam patterns. Free 8th Standard CBSE all books and syllabus online. Practice Online test for free in QB365 Study Material. Important keywords, Case Study Questions and Solutions. Updates about latest education news and ...
Various agricultural practices required for the crop production are listed in the concise crop production and management class 8 notes. The cropping pattern followed in India and a few extra questions are also discussed in the Class 8 science chapter 1 notes.
Social Science Class 8 Chapter List. Old Chapter List. Class 8 Social Science History: Our Pasts - III. Chapter 1 How, When and Where Chapter 2 From Trade to Territory Chapter 3 Ruling the Countryside Chapter 4 Tribals, Dikus and the Vision of a Golden Age Chapter 5 When People Rebel Chapter 6 Colonialism and the City
Crop Production and Management Class 8 Science NCERT Textbook Questions. Question 1. Select the correct word from the following list and fill in the blanks. float, water, crop, nutrients, preparation. (a) The same kind of plants grown and cultivated on a large scale at a place is called _____. (b) The first step before growing crops is ...
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 8 Civics The Indian Constitution. Case Study 1. While all democratic countries are likely to have a Constitution, it is not necessary that all countries that have a Constitution are democratic. The Constitution serves several purposes. First, it lays out certain ideals that form the basis of the kind of country ...
The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class 8 social science. In this article, you will find case study for CBSE Class 8 Social Science History Chapter 1 How, When and Where. It is a part of Case Study Questions for CBSE Class 8 Social Science Series.
Tips for Answering Case Study Questions for Class 8 Maths in Exam. 1. Comprehensive Reading for Context: Prioritize a thorough understanding of the provided case study. Absorb the contextual details and data meticulously to establish a strong foundation for your solution. 2.
Check CBSE Class 8 Science syllabus, chapter weightage, study material and tips to prepare for class 8 science. Exams. Programs. Scholarships. Test Series. NEW. Talk to us. Login. Talk to us CBSE Class 10. CBSE Class 10 Sample Papers ... 1.0 CBSE Class 8 Science. Physics, Chemistry, and Biology are three cornerstone subjects in CBSE's 8th-class ...
Social Science Class 8 Chapter List. Old Chapter List. Class 8 Social Science History: Our Pasts - III. Chapter 1 How, When and Where Chapter 2 From Trade to Territory Chapter 3 Ruling the Countryside Chapter 4 Tribals, Dikus and the Vision of a Golden Age Chapter 5 When People Rebel Chapter 6 Colonialism and the City
Case Study Questions on Linear Equations in One Variable. Questions. Passage 1: It is common that government revises fares from time to time based on various factors such as taxes, economy and inflation, for various vehicles like auto-rickshaw, taxis and radio cab etc. The auto and Taxi charge in a city comprise of fixed charge and the charge for the distance covered.
Case Study Questions for Class 8 Social Science History Chapter 1 How When and Where . Here we are providing case study questions for class 8 social science History Chapter 1 How When and Where. Letters and memos that moved from one branch of the administration to another in the early years of the nineteenth century can still be read in the ...