- EXPLORE Random Article
- Happiness Hub

How to Write an English Assignment
Last Updated: December 6, 2021
wikiHow is a “wiki,” similar to Wikipedia, which means that many of our articles are co-written by multiple authors. To create this article, 20 people, some anonymous, worked to edit and improve it over time. This article has been viewed 48,983 times.
Writing an English assignment can be troublesome at times. The students lack the proper information which is required to write an assignment. Apart from this there are many more things which are necessary for an assignment writing and such things are highlighted in this article.

- Take second advice from a close friend. Some mistakes you may not see or be used to seeing, and a second opinion can help catch some of the mistakes that you won't see the first time through.

Community Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.openpolytechnic.ac.nz/current-students/study-tips-and-techniques/assignments/step-by-step-guide-to-assignment-writing/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/understanding-assignments/
- ↑ https://www.uq.edu.au/student-services/learning/structuring-your-assignment
- ↑ https://www.uts.edu.au/current-students/support/helps/self-help-resources/academic-writing
About this article
Did this article help you.

- About wikiHow
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info

Understanding Assignments
What this handout is about.
The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms and practices into meaningful clues to the type of writing your instructor expects. See our short video for more tips.
Basic beginnings
Regardless of the assignment, department, or instructor, adopting these two habits will serve you well :
- Read the assignment carefully as soon as you receive it. Do not put this task off—reading the assignment at the beginning will save you time, stress, and problems later. An assignment can look pretty straightforward at first, particularly if the instructor has provided lots of information. That does not mean it will not take time and effort to complete; you may even have to learn a new skill to complete the assignment.
- Ask the instructor about anything you do not understand. Do not hesitate to approach your instructor. Instructors would prefer to set you straight before you hand the paper in. That’s also when you will find their feedback most useful.
Assignment formats
Many assignments follow a basic format. Assignments often begin with an overview of the topic, include a central verb or verbs that describe the task, and offer some additional suggestions, questions, or prompts to get you started.
An Overview of Some Kind
The instructor might set the stage with some general discussion of the subject of the assignment, introduce the topic, or remind you of something pertinent that you have discussed in class. For example:
“Throughout history, gerbils have played a key role in politics,” or “In the last few weeks of class, we have focused on the evening wear of the housefly …”
The Task of the Assignment
Pay attention; this part tells you what to do when you write the paper. Look for the key verb or verbs in the sentence. Words like analyze, summarize, or compare direct you to think about your topic in a certain way. Also pay attention to words such as how, what, when, where, and why; these words guide your attention toward specific information. (See the section in this handout titled “Key Terms” for more information.)
“Analyze the effect that gerbils had on the Russian Revolution”, or “Suggest an interpretation of housefly undergarments that differs from Darwin’s.”
Additional Material to Think about
Here you will find some questions to use as springboards as you begin to think about the topic. Instructors usually include these questions as suggestions rather than requirements. Do not feel compelled to answer every question unless the instructor asks you to do so. Pay attention to the order of the questions. Sometimes they suggest the thinking process your instructor imagines you will need to follow to begin thinking about the topic.
“You may wish to consider the differing views held by Communist gerbils vs. Monarchist gerbils, or Can there be such a thing as ‘the housefly garment industry’ or is it just a home-based craft?”
These are the instructor’s comments about writing expectations:
“Be concise”, “Write effectively”, or “Argue furiously.”
Technical Details
These instructions usually indicate format rules or guidelines.
“Your paper must be typed in Palatino font on gray paper and must not exceed 600 pages. It is due on the anniversary of Mao Tse-tung’s death.”
The assignment’s parts may not appear in exactly this order, and each part may be very long or really short. Nonetheless, being aware of this standard pattern can help you understand what your instructor wants you to do.
Interpreting the assignment
Ask yourself a few basic questions as you read and jot down the answers on the assignment sheet:
Why did your instructor ask you to do this particular task?
Who is your audience.
- What kind of evidence do you need to support your ideas?
What kind of writing style is acceptable?
- What are the absolute rules of the paper?
Try to look at the question from the point of view of the instructor. Recognize that your instructor has a reason for giving you this assignment and for giving it to you at a particular point in the semester. In every assignment, the instructor has a challenge for you. This challenge could be anything from demonstrating an ability to think clearly to demonstrating an ability to use the library. See the assignment not as a vague suggestion of what to do but as an opportunity to show that you can handle the course material as directed. Paper assignments give you more than a topic to discuss—they ask you to do something with the topic. Keep reminding yourself of that. Be careful to avoid the other extreme as well: do not read more into the assignment than what is there.
Of course, your instructor has given you an assignment so that they will be able to assess your understanding of the course material and give you an appropriate grade. But there is more to it than that. Your instructor has tried to design a learning experience of some kind. Your instructor wants you to think about something in a particular way for a particular reason. If you read the course description at the beginning of your syllabus, review the assigned readings, and consider the assignment itself, you may begin to see the plan, purpose, or approach to the subject matter that your instructor has created for you. If you still aren’t sure of the assignment’s goals, try asking the instructor. For help with this, see our handout on getting feedback .
Given your instructor’s efforts, it helps to answer the question: What is my purpose in completing this assignment? Is it to gather research from a variety of outside sources and present a coherent picture? Is it to take material I have been learning in class and apply it to a new situation? Is it to prove a point one way or another? Key words from the assignment can help you figure this out. Look for key terms in the form of active verbs that tell you what to do.
Key Terms: Finding Those Active Verbs
Here are some common key words and definitions to help you think about assignment terms:
Information words Ask you to demonstrate what you know about the subject, such as who, what, when, where, how, and why.
- define —give the subject’s meaning (according to someone or something). Sometimes you have to give more than one view on the subject’s meaning
- describe —provide details about the subject by answering question words (such as who, what, when, where, how, and why); you might also give details related to the five senses (what you see, hear, feel, taste, and smell)
- explain —give reasons why or examples of how something happened
- illustrate —give descriptive examples of the subject and show how each is connected with the subject
- summarize —briefly list the important ideas you learned about the subject
- trace —outline how something has changed or developed from an earlier time to its current form
- research —gather material from outside sources about the subject, often with the implication or requirement that you will analyze what you have found
Relation words Ask you to demonstrate how things are connected.
- compare —show how two or more things are similar (and, sometimes, different)
- contrast —show how two or more things are dissimilar
- apply —use details that you’ve been given to demonstrate how an idea, theory, or concept works in a particular situation
- cause —show how one event or series of events made something else happen
- relate —show or describe the connections between things
Interpretation words Ask you to defend ideas of your own about the subject. Do not see these words as requesting opinion alone (unless the assignment specifically says so), but as requiring opinion that is supported by concrete evidence. Remember examples, principles, definitions, or concepts from class or research and use them in your interpretation.
- assess —summarize your opinion of the subject and measure it against something
- prove, justify —give reasons or examples to demonstrate how or why something is the truth
- evaluate, respond —state your opinion of the subject as good, bad, or some combination of the two, with examples and reasons
- support —give reasons or evidence for something you believe (be sure to state clearly what it is that you believe)
- synthesize —put two or more things together that have not been put together in class or in your readings before; do not just summarize one and then the other and say that they are similar or different—you must provide a reason for putting them together that runs all the way through the paper
- analyze —determine how individual parts create or relate to the whole, figure out how something works, what it might mean, or why it is important
- argue —take a side and defend it with evidence against the other side
More Clues to Your Purpose As you read the assignment, think about what the teacher does in class:
- What kinds of textbooks or coursepack did your instructor choose for the course—ones that provide background information, explain theories or perspectives, or argue a point of view?
- In lecture, does your instructor ask your opinion, try to prove their point of view, or use keywords that show up again in the assignment?
- What kinds of assignments are typical in this discipline? Social science classes often expect more research. Humanities classes thrive on interpretation and analysis.
- How do the assignments, readings, and lectures work together in the course? Instructors spend time designing courses, sometimes even arguing with their peers about the most effective course materials. Figuring out the overall design to the course will help you understand what each assignment is meant to achieve.
Now, what about your reader? Most undergraduates think of their audience as the instructor. True, your instructor is a good person to keep in mind as you write. But for the purposes of a good paper, think of your audience as someone like your roommate: smart enough to understand a clear, logical argument, but not someone who already knows exactly what is going on in your particular paper. Remember, even if the instructor knows everything there is to know about your paper topic, they still have to read your paper and assess your understanding. In other words, teach the material to your reader.
Aiming a paper at your audience happens in two ways: you make decisions about the tone and the level of information you want to convey.
- Tone means the “voice” of your paper. Should you be chatty, formal, or objective? Usually you will find some happy medium—you do not want to alienate your reader by sounding condescending or superior, but you do not want to, um, like, totally wig on the man, you know? Eschew ostentatious erudition: some students think the way to sound academic is to use big words. Be careful—you can sound ridiculous, especially if you use the wrong big words.
- The level of information you use depends on who you think your audience is. If you imagine your audience as your instructor and they already know everything you have to say, you may find yourself leaving out key information that can cause your argument to be unconvincing and illogical. But you do not have to explain every single word or issue. If you are telling your roommate what happened on your favorite science fiction TV show last night, you do not say, “First a dark-haired white man of average height, wearing a suit and carrying a flashlight, walked into the room. Then a purple alien with fifteen arms and at least three eyes turned around. Then the man smiled slightly. In the background, you could hear a clock ticking. The room was fairly dark and had at least two windows that I saw.” You also do not say, “This guy found some aliens. The end.” Find some balance of useful details that support your main point.
You’ll find a much more detailed discussion of these concepts in our handout on audience .
The Grim Truth
With a few exceptions (including some lab and ethnography reports), you are probably being asked to make an argument. You must convince your audience. It is easy to forget this aim when you are researching and writing; as you become involved in your subject matter, you may become enmeshed in the details and focus on learning or simply telling the information you have found. You need to do more than just repeat what you have read. Your writing should have a point, and you should be able to say it in a sentence. Sometimes instructors call this sentence a “thesis” or a “claim.”
So, if your instructor tells you to write about some aspect of oral hygiene, you do not want to just list: “First, you brush your teeth with a soft brush and some peanut butter. Then, you floss with unwaxed, bologna-flavored string. Finally, gargle with bourbon.” Instead, you could say, “Of all the oral cleaning methods, sandblasting removes the most plaque. Therefore it should be recommended by the American Dental Association.” Or, “From an aesthetic perspective, moldy teeth can be quite charming. However, their joys are short-lived.”
Convincing the reader of your argument is the goal of academic writing. It doesn’t have to say “argument” anywhere in the assignment for you to need one. Look at the assignment and think about what kind of argument you could make about it instead of just seeing it as a checklist of information you have to present. For help with understanding the role of argument in academic writing, see our handout on argument .
What kind of evidence do you need?
There are many kinds of evidence, and what type of evidence will work for your assignment can depend on several factors–the discipline, the parameters of the assignment, and your instructor’s preference. Should you use statistics? Historical examples? Do you need to conduct your own experiment? Can you rely on personal experience? See our handout on evidence for suggestions on how to use evidence appropriately.
Make sure you are clear about this part of the assignment, because your use of evidence will be crucial in writing a successful paper. You are not just learning how to argue; you are learning how to argue with specific types of materials and ideas. Ask your instructor what counts as acceptable evidence. You can also ask a librarian for help. No matter what kind of evidence you use, be sure to cite it correctly—see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial .
You cannot always tell from the assignment just what sort of writing style your instructor expects. The instructor may be really laid back in class but still expect you to sound formal in writing. Or the instructor may be fairly formal in class and ask you to write a reflection paper where you need to use “I” and speak from your own experience.
Try to avoid false associations of a particular field with a style (“art historians like wacky creativity,” or “political scientists are boring and just give facts”) and look instead to the types of readings you have been given in class. No one expects you to write like Plato—just use the readings as a guide for what is standard or preferable to your instructor. When in doubt, ask your instructor about the level of formality they expect.
No matter what field you are writing for or what facts you are including, if you do not write so that your reader can understand your main idea, you have wasted your time. So make clarity your main goal. For specific help with style, see our handout on style .
Technical details about the assignment
The technical information you are given in an assignment always seems like the easy part. This section can actually give you lots of little hints about approaching the task. Find out if elements such as page length and citation format (see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial ) are negotiable. Some professors do not have strong preferences as long as you are consistent and fully answer the assignment. Some professors are very specific and will deduct big points for deviations.
Usually, the page length tells you something important: The instructor thinks the size of the paper is appropriate to the assignment’s parameters. In plain English, your instructor is telling you how many pages it should take for you to answer the question as fully as you are expected to. So if an assignment is two pages long, you cannot pad your paper with examples or reword your main idea several times. Hit your one point early, defend it with the clearest example, and finish quickly. If an assignment is ten pages long, you can be more complex in your main points and examples—and if you can only produce five pages for that assignment, you need to see someone for help—as soon as possible.
Tricks that don’t work
Your instructors are not fooled when you:
- spend more time on the cover page than the essay —graphics, cool binders, and cute titles are no replacement for a well-written paper.
- use huge fonts, wide margins, or extra spacing to pad the page length —these tricks are immediately obvious to the eye. Most instructors use the same word processor you do. They know what’s possible. Such tactics are especially damning when the instructor has a stack of 60 papers to grade and yours is the only one that low-flying airplane pilots could read.
- use a paper from another class that covered “sort of similar” material . Again, the instructor has a particular task for you to fulfill in the assignment that usually relates to course material and lectures. Your other paper may not cover this material, and turning in the same paper for more than one course may constitute an Honor Code violation . Ask the instructor—it can’t hurt.
- get all wacky and “creative” before you answer the question . Showing that you are able to think beyond the boundaries of a simple assignment can be good, but you must do what the assignment calls for first. Again, check with your instructor. A humorous tone can be refreshing for someone grading a stack of papers, but it will not get you a good grade if you have not fulfilled the task.
Critical reading of assignments leads to skills in other types of reading and writing. If you get good at figuring out what the real goals of assignments are, you are going to be better at understanding the goals of all of your classes and fields of study.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
- Utility Menu
- Writing Center
- Writing Program
- Designing Essay Assignments
by Gordon Harvey
Students often do their best and hardest thinking, and feel the greatest sense of mastery and growth, in their writing. Courses and assignments should be planned with this in mind. Three principles are paramount:
1. Name what you want and imagine students doing it
However free students are to range and explore in a paper, the general kind of paper you’re inviting has common components, operations, and criteria of success, and you should make these explicit. Having satisfied yourself, as you should, that what you’re asking is doable, with dignity, by writers just learning the material, try to anticipate in your prompt or discussions of the assignment the following queries:
- What is the purpose of this? How am I going beyond what we have done, or applying it in a new area, or practicing a key academic skill or kind of work?
- To what audience should I imagine myself writing?
- What is the main task or tasks, in a nutshell? What does that key word (e.g., analyze, significance of, critique, explore, interesting, support) really mean in this context or this field?
- What will be most challenging in this and what qualities will most distinguish a good paper? Where should I put my energy? (Lists of possible questions for students to answer in a paper are often not sufficiently prioritized to be helpful.)
- What misconceptions might I have about what I’m to do? (How is this like or unlike other papers I may have written?) Are there too-easy approaches I might take or likely pitfalls? An ambitious goal or standard that I might think I’m expected to meet but am not?
- What form will evidence take in my paper (e.g., block quotations? paraphrase? graphs or charts?) How should I cite it? Should I use/cite material from lecture or section?
- Are there some broad options for structure, emphasis, or approach that I’ll likely be choosing among?
- How should I get started on this? What would be a helpful (or unhelpful) way to take notes, gather data, discover a question or idea? Should I do research?
2. Take time in class to prepare students to succeed at the paper
Resist the impulse to think of class meetings as time for “content” and of writing as work done outside class. Your students won’t have mastered the art of paper writing (if such a mastery is possible) and won’t know the particular disciplinary expectations or moves relevant to the material at hand. Take time in class to show them:
- discuss the assignment in class when you give it, so students can see that you take it seriously, so they can ask questions about it, so they can have it in mind during subsequent class discussions;
- introduce the analytic vocabulary of your assignment into class discussions, and take opportunities to note relevant moves made in discussion or good paper topics that arise;
- have students practice key tasks in class discussions, or in informal writing they do in before or after discussions;
- show examples of writing that illustrates components and criteria of the assignment and that inspires (class readings can sometimes serve as illustrations of a writing principle; so can short excerpts of writing—e.g., a sampling of introductions; and so can bad writing—e.g., a list of problematic thesis statements);
- the topics of originality and plagiarism (what the temptations might be, how to avoid risks) should at some point be addressed directly.
3. Build in process
Ideas develop over time, in a process of posing and revising and getting feedback and revising some more. Assignments should allow for this process in the following ways:
- smaller assignments should prepare for larger ones later;
- students should do some thinking and writing before they write a draft and get a response to it (even if only a response to a proposal or thesis statement sent by email, or described in class);
- for larger papers, students should write and get response (using the skills vocabulary of the assignment) to a draft—at least an “oral draft” (condensed for delivery to the class);
- if possible, meet with students individually about their writing: nothing inspires them more than feeling that you care about their work and development;
- let students reflect on their own writing, in brief cover letters attached to drafts and revisions (these may also ask students to perform certain checks on what they have written, before submitting);
- have clear and firm policies about late work that nonetheless allow for exception if students talk to you in advance.
|
A PDF version of the text above. Provides guidance on creating carefully crafted and explicit paper assignments that encourage students to write better papers
|
- Pedagogy Workshops
- Responding to Student Writing
- Commenting Efficiently
- Vocabulary for Discussing Student Writing
- Guides to Teaching Writing
- HarvardWrites Instructor Toolkit
- Additional Resources for Teaching Fellows

- Ask LitCharts AI
- Discussion Question Generator
- Essay Prompt Generator
- Quiz Question Generator

- Literature Guides
- Poetry Guides
- Shakespeare Translations
- Literary Terms
How to Write an Essay
Use the links below to jump directly to any section of this guide:
Essay Writing Fundamentals
How to prepare to write an essay, how to edit an essay, how to share and publish your essays, how to get essay writing help, how to find essay writing inspiration, resources for teaching essay writing.
Essays, short prose compositions on a particular theme or topic, are the bread and butter of academic life. You write them in class, for homework, and on standardized tests to show what you know. Unlike other kinds of academic writing (like the research paper) and creative writing (like short stories and poems), essays allow you to develop your original thoughts on a prompt or question. Essays come in many varieties: they can be expository (fleshing out an idea or claim), descriptive, (explaining a person, place, or thing), narrative (relating a personal experience), or persuasive (attempting to win over a reader). This guide is a collection of dozens of links about academic essay writing that we have researched, categorized, and annotated in order to help you improve your essay writing.
Essays are different from other forms of writing; in turn, there are different kinds of essays. This section contains general resources for getting to know the essay and its variants. These resources introduce and define the essay as a genre, and will teach you what to expect from essay-based assessments.
Purdue OWL Online Writing Lab
One of the most trusted academic writing sites, Purdue OWL provides a concise introduction to the four most common types of academic essays.
"The Essay: History and Definition" (ThoughtCo)
This snappy article from ThoughtCo talks about the origins of the essay and different kinds of essays you might be asked to write.
"What Is An Essay?" Video Lecture (Coursera)
The University of California at Irvine's free video lecture, available on Coursera, tells you everything you need to know about the essay.
Wikipedia Article on the "Essay"
Wikipedia's article on the essay is comprehensive, providing both English-language and global perspectives on the essay form. Learn about the essay's history, forms, and styles.
"Understanding College and Academic Writing" (Aims Online Writing Lab)
This list of common academic writing assignments (including types of essay prompts) will help you know what to expect from essay-based assessments.
Before you start writing your essay, you need to figure out who you're writing for (audience), what you're writing about (topic/theme), and what you're going to say (argument and thesis). This section contains links to handouts, chapters, videos and more to help you prepare to write an essay.
How to Identify Your Audience
"Audience" (Univ. of North Carolina Writing Center)
This handout provides questions you can ask yourself to determine the audience for an academic writing assignment. It also suggests strategies for fitting your paper to your intended audience.
"Purpose, Audience, Tone, and Content" (Univ. of Minnesota Libraries)
This extensive book chapter from Writing for Success , available online through Minnesota Libraries Publishing, is followed by exercises to try out your new pre-writing skills.
"Determining Audience" (Aims Online Writing Lab)
This guide from a community college's writing center shows you how to know your audience, and how to incorporate that knowledge in your thesis statement.
"Know Your Audience" ( Paper Rater Blog)
This short blog post uses examples to show how implied audiences for essays differ. It reminds you to think of your instructor as an observer, who will know only the information you pass along.
How to Choose a Theme or Topic
"Research Tutorial: Developing Your Topic" (YouTube)
Take a look at this short video tutorial from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill to understand the basics of developing a writing topic.
"How to Choose a Paper Topic" (WikiHow)
This simple, step-by-step guide (with pictures!) walks you through choosing a paper topic. It starts with a detailed description of brainstorming and ends with strategies to refine your broad topic.
"How to Read an Assignment: Moving From Assignment to Topic" (Harvard College Writing Center)
Did your teacher give you a prompt or other instructions? This guide helps you understand the relationship between an essay assignment and your essay's topic.
"Guidelines for Choosing a Topic" (CliffsNotes)
This study guide from CliffsNotes both discusses how to choose a topic and makes a useful distinction between "topic" and "thesis."
How to Come Up with an Argument
"Argument" (Univ. of North Carolina Writing Center)
Not sure what "argument" means in the context of academic writing? This page from the University of North Carolina is a good place to start.
"The Essay Guide: Finding an Argument" (Study Hub)
This handout explains why it's important to have an argument when beginning your essay, and provides tools to help you choose a viable argument.
"Writing a Thesis and Making an Argument" (University of Iowa)
This page from the University of Iowa's Writing Center contains exercises through which you can develop and refine your argument and thesis statement.
"Developing a Thesis" (Harvard College Writing Center)
This page from Harvard's Writing Center collates some helpful dos and don'ts of argumentative writing, from steps in constructing a thesis to avoiding vague and confrontational thesis statements.
"Suggestions for Developing Argumentative Essays" (Berkeley Student Learning Center)
This page offers concrete suggestions for each stage of the essay writing process, from topic selection to drafting and editing.
How to Outline your Essay
"Outlines" (Univ. of North Carolina at Chapel Hill via YouTube)
This short video tutorial from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill shows how to group your ideas into paragraphs or sections to begin the outlining process.
"Essay Outline" (Univ. of Washington Tacoma)
This two-page handout by a university professor simply defines the parts of an essay and then organizes them into an example outline.
"Types of Outlines and Samples" (Purdue OWL Online Writing Lab)
Purdue OWL gives examples of diverse outline strategies on this page, including the alphanumeric, full sentence, and decimal styles.
"Outlining" (Harvard College Writing Center)
Once you have an argument, according to this handout, there are only three steps in the outline process: generalizing, ordering, and putting it all together. Then you're ready to write!
"Writing Essays" (Plymouth Univ.)
This packet, part of Plymouth University's Learning Development series, contains descriptions and diagrams relating to the outlining process.
"How to Write A Good Argumentative Essay: Logical Structure" (Criticalthinkingtutorials.com via YouTube)
This longer video tutorial gives an overview of how to structure your essay in order to support your argument or thesis. It is part of a longer course on academic writing hosted on Udemy.
Now that you've chosen and refined your topic and created an outline, use these resources to complete the writing process. Most essays contain introductions (which articulate your thesis statement), body paragraphs, and conclusions. Transitions facilitate the flow from one paragraph to the next so that support for your thesis builds throughout the essay. Sources and citations show where you got the evidence to support your thesis, which ensures that you avoid plagiarism.
How to Write an Introduction
"Introductions" (Univ. of North Carolina Writing Center)
This page identifies the role of the introduction in any successful paper, suggests strategies for writing introductions, and warns against less effective introductions.
"How to Write A Good Introduction" (Michigan State Writing Center)
Beginning with the most common missteps in writing introductions, this guide condenses the essentials of introduction composition into seven points.
"The Introductory Paragraph" (ThoughtCo)
This blog post from academic advisor and college enrollment counselor Grace Fleming focuses on ways to grab your reader's attention at the beginning of your essay.
"Introductions and Conclusions" (Univ. of Toronto)
This guide from the University of Toronto gives advice that applies to writing both introductions and conclusions, including dos and don'ts.
"How to Write Better Essays: No One Does Introductions Properly" ( The Guardian )
This news article interviews UK professors on student essay writing; they point to introductions as the area that needs the most improvement.
How to Write a Thesis Statement
"Writing an Effective Thesis Statement" (YouTube)
This short, simple video tutorial from a college composition instructor at Tulsa Community College explains what a thesis statement is and what it does.
"Thesis Statement: Four Steps to a Great Essay" (YouTube)
This fantastic tutorial walks you through drafting a thesis, using an essay prompt on Nathaniel Hawthorne's The Scarlet Letter as an example.
"How to Write a Thesis Statement" (WikiHow)
This step-by-step guide (with pictures!) walks you through coming up with, writing, and editing a thesis statement. It invites you think of your statement as a "working thesis" that can change.
"How to Write a Thesis Statement" (Univ. of Indiana Bloomington)
Ask yourself the questions on this page, part of Indiana Bloomington's Writing Tutorial Services, when you're writing and refining your thesis statement.
"Writing Tips: Thesis Statements" (Univ. of Illinois Center for Writing Studies)
This page gives plentiful examples of good to great thesis statements, and offers questions to ask yourself when formulating a thesis statement.
How to Write Body Paragraphs
"Body Paragraph" (Brightstorm)
This module of a free online course introduces you to the components of a body paragraph. These include the topic sentence, information, evidence, and analysis.
"Strong Body Paragraphs" (Washington Univ.)
This handout from Washington's Writing and Research Center offers in-depth descriptions of the parts of a successful body paragraph.
"Guide to Paragraph Structure" (Deakin Univ.)
This handout is notable for color-coding example body paragraphs to help you identify the functions various sentences perform.
"Writing Body Paragraphs" (Univ. of Minnesota Libraries)
The exercises in this section of Writing for Success will help you practice writing good body paragraphs. It includes guidance on selecting primary support for your thesis.
"The Writing Process—Body Paragraphs" (Aims Online Writing Lab)
The information and exercises on this page will familiarize you with outlining and writing body paragraphs, and includes links to more information on topic sentences and transitions.
"The Five-Paragraph Essay" (ThoughtCo)
This blog post discusses body paragraphs in the context of one of the most common academic essay types in secondary schools.
How to Use Transitions
"Transitions" (Univ. of North Carolina Writing Center)
This page from the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill explains what a transition is, and how to know if you need to improve your transitions.
"Using Transitions Effectively" (Washington Univ.)
This handout defines transitions, offers tips for using them, and contains a useful list of common transitional words and phrases grouped by function.
"Transitions" (Aims Online Writing Lab)
This page compares paragraphs without transitions to paragraphs with transitions, and in doing so shows how important these connective words and phrases are.
"Transitions in Academic Essays" (Scribbr)
This page lists four techniques that will help you make sure your reader follows your train of thought, including grouping similar information and using transition words.
"Transitions" (El Paso Community College)
This handout shows example transitions within paragraphs for context, and explains how transitions improve your essay's flow and voice.
"Make Your Paragraphs Flow to Improve Writing" (ThoughtCo)
This blog post, another from academic advisor and college enrollment counselor Grace Fleming, talks about transitions and other strategies to improve your essay's overall flow.
"Transition Words" (smartwords.org)
This handy word bank will help you find transition words when you're feeling stuck. It's grouped by the transition's function, whether that is to show agreement, opposition, condition, or consequence.
How to Write a Conclusion
"Parts of An Essay: Conclusions" (Brightstorm)
This module of a free online course explains how to conclude an academic essay. It suggests thinking about the "3Rs": return to hook, restate your thesis, and relate to the reader.
"Essay Conclusions" (Univ. of Maryland University College)
This overview of the academic essay conclusion contains helpful examples and links to further resources for writing good conclusions.
"How to End An Essay" (WikiHow)
This step-by-step guide (with pictures!) by an English Ph.D. walks you through writing a conclusion, from brainstorming to ending with a flourish.
"Ending the Essay: Conclusions" (Harvard College Writing Center)
This page collates useful strategies for writing an effective conclusion, and reminds you to "close the discussion without closing it off" to further conversation.
How to Include Sources and Citations
"Research and Citation Resources" (Purdue OWL Online Writing Lab)
Purdue OWL streamlines information about the three most common referencing styles (MLA, Chicago, and APA) and provides examples of how to cite different resources in each system.
EasyBib: Free Bibliography Generator
This online tool allows you to input information about your source and automatically generate citations in any style. Be sure to select your resource type before clicking the "cite it" button.
CitationMachine
Like EasyBib, this online tool allows you to input information about your source and automatically generate citations in any style.
Modern Language Association Handbook (MLA)
Here, you'll find the definitive and up-to-date record of MLA referencing rules. Order through the link above, or check to see if your library has a copy.
Chicago Manual of Style
Here, you'll find the definitive and up-to-date record of Chicago referencing rules. You can take a look at the table of contents, then choose to subscribe or start a free trial.
How to Avoid Plagiarism
"What is Plagiarism?" (plagiarism.org)
This nonprofit website contains numerous resources for identifying and avoiding plagiarism, and reminds you that even common activities like copying images from another website to your own site may constitute plagiarism.
"Plagiarism" (University of Oxford)
This interactive page from the University of Oxford helps you check for plagiarism in your work, making it clear how to avoid citing another person's work without full acknowledgement.
"Avoiding Plagiarism" (MIT Comparative Media Studies)
This quick guide explains what plagiarism is, what its consequences are, and how to avoid it. It starts by defining three words—quotation, paraphrase, and summary—that all constitute citation.
"Harvard Guide to Using Sources" (Harvard Extension School)
This comprehensive website from Harvard brings together articles, videos, and handouts about referencing, citation, and plagiarism.
Grammarly contains tons of helpful grammar and writing resources, including a free tool to automatically scan your essay to check for close affinities to published work.
Noplag is another popular online tool that automatically scans your essay to check for signs of plagiarism. Simply copy and paste your essay into the box and click "start checking."
Once you've written your essay, you'll want to edit (improve content), proofread (check for spelling and grammar mistakes), and finalize your work until you're ready to hand it in. This section brings together tips and resources for navigating the editing process.
"Writing a First Draft" (Academic Help)
This is an introduction to the drafting process from the site Academic Help, with tips for getting your ideas on paper before editing begins.
"Editing and Proofreading" (Univ. of North Carolina Writing Center)
This page provides general strategies for revising your writing. They've intentionally left seven errors in the handout, to give you practice in spotting them.
"How to Proofread Effectively" (ThoughtCo)
This article from ThoughtCo, along with those linked at the bottom, help describe common mistakes to check for when proofreading.
"7 Simple Edits That Make Your Writing 100% More Powerful" (SmartBlogger)
This blog post emphasizes the importance of powerful, concise language, and reminds you that even your personal writing heroes create clunky first drafts.
"Editing Tips for Effective Writing" (Univ. of Pennsylvania)
On this page from Penn's International Relations department, you'll find tips for effective prose, errors to watch out for, and reminders about formatting.
"Editing the Essay" (Harvard College Writing Center)
This article, the first of two parts, gives you applicable strategies for the editing process. It suggests reading your essay aloud, removing any jargon, and being unafraid to remove even "dazzling" sentences that don't belong.
"Guide to Editing and Proofreading" (Oxford Learning Institute)
This handout from Oxford covers the basics of editing and proofreading, and reminds you that neither task should be rushed.
In addition to plagiarism-checkers, Grammarly has a plug-in for your web browser that checks your writing for common mistakes.
After you've prepared, written, and edited your essay, you might want to share it outside the classroom. This section alerts you to print and web opportunities to share your essays with the wider world, from online writing communities and blogs to published journals geared toward young writers.
Sharing Your Essays Online
Go Teen Writers
Go Teen Writers is an online community for writers aged 13 - 19. It was founded by Stephanie Morrill, an author of contemporary young adult novels.
Tumblr is a blogging website where you can share your writing and interact with other writers online. It's easy to add photos, links, audio, and video components.
Writersky provides an online platform for publishing and reading other youth writers' work. Its current content is mostly devoted to fiction.
Publishing Your Essays Online
This teen literary journal publishes in print, on the web, and (more frequently), on a blog. It is committed to ensuring that "teens see their authentic experience reflected on its pages."
The Matador Review
This youth writing platform celebrates "alternative," unconventional writing. The link above will take you directly to the site's "submissions" page.
Teen Ink has a website, monthly newsprint magazine, and quarterly poetry magazine promoting the work of young writers.
The largest online reading platform, Wattpad enables you to publish your work and read others' work. Its inline commenting feature allows you to share thoughts as you read along.
Publishing Your Essays in Print
Canvas Teen Literary Journal
This quarterly literary magazine is published for young writers by young writers. They accept many kinds of writing, including essays.
The Claremont Review
This biannual international magazine, first published in 1992, publishes poetry, essays, and short stories from writers aged 13 - 19.
Skipping Stones
This young writers magazine, founded in 1988, celebrates themes relating to ecological and cultural diversity. It publishes poems, photos, articles, and stories.
The Telling Room
This nonprofit writing center based in Maine publishes children's work on their website and in book form. The link above directs you to the site's submissions page.
Essay Contests
Scholastic Arts and Writing Awards
This prestigious international writing contest for students in grades 7 - 12 has been committed to "supporting the future of creativity since 1923."
Society of Professional Journalists High School Essay Contest
An annual essay contest on the theme of journalism and media, the Society of Professional Journalists High School Essay Contest awards scholarships up to $1,000.
National YoungArts Foundation
Here, you'll find information on a government-sponsored writing competition for writers aged 15 - 18. The foundation welcomes submissions of creative nonfiction, novels, scripts, poetry, short story and spoken word.
Signet Classics Student Scholarship Essay Contest
With prompts on a different literary work each year, this competition from Signet Classics awards college scholarships up to $1,000.
"The Ultimate Guide to High School Essay Contests" (CollegeVine)
See this handy guide from CollegeVine for a list of more competitions you can enter with your academic essay, from the National Council of Teachers of English Achievement Awards to the National High School Essay Contest by the U.S. Institute of Peace.
Whether you're struggling to write academic essays or you think you're a pro, there are workshops and online tools that can help you become an even better writer. Even the most seasoned writers encounter writer's block, so be proactive and look through our curated list of resources to combat this common frustration.
Online Essay-writing Classes and Workshops
"Getting Started with Essay Writing" (Coursera)
Coursera offers lots of free, high-quality online classes taught by college professors. Here's one example, taught by instructors from the University of California Irvine.
"Writing and English" (Brightstorm)
Brightstorm's free video lectures are easy to navigate by topic. This unit on the parts of an essay features content on the essay hook, thesis, supporting evidence, and more.
"How to Write an Essay" (EdX)
EdX is another open online university course website with several two- to five-week courses on the essay. This one is geared toward English language learners.
Writer's Digest University
This renowned writers' website offers online workshops and interactive tutorials. The courses offered cover everything from how to get started through how to get published.
Writing.com
Signing up for this online writer's community gives you access to helpful resources as well as an international community of writers.
How to Overcome Writer's Block
"Symptoms and Cures for Writer's Block" (Purdue OWL)
Purdue OWL offers a list of signs you might have writer's block, along with ways to overcome it. Consider trying out some "invention strategies" or ways to curb writing anxiety.
"Overcoming Writer's Block: Three Tips" ( The Guardian )
These tips, geared toward academic writing specifically, are practical and effective. The authors advocate setting realistic goals, creating dedicated writing time, and participating in social writing.
"Writing Tips: Strategies for Overcoming Writer's Block" (Univ. of Illinois)
This page from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign's Center for Writing Studies acquaints you with strategies that do and do not work to overcome writer's block.
"Writer's Block" (Univ. of Toronto)
Ask yourself the questions on this page; if the answer is "yes," try out some of the article's strategies. Each question is accompanied by at least two possible solutions.
If you have essays to write but are short on ideas, this section's links to prompts, example student essays, and celebrated essays by professional writers might help. You'll find writing prompts from a variety of sources, student essays to inspire you, and a number of essay writing collections.
Essay Writing Prompts
"50 Argumentative Essay Topics" (ThoughtCo)
Take a look at this list and the others ThoughtCo has curated for different kinds of essays. As the author notes, "a number of these topics are controversial and that's the point."
"401 Prompts for Argumentative Writing" ( New York Times )
This list (and the linked lists to persuasive and narrative writing prompts), besides being impressive in length, is put together by actual high school English teachers.
"SAT Sample Essay Prompts" (College Board)
If you're a student in the U.S., your classroom essay prompts are likely modeled on the prompts in U.S. college entrance exams. Take a look at these official examples from the SAT.
"Popular College Application Essay Topics" (Princeton Review)
This page from the Princeton Review dissects recent Common Application essay topics and discusses strategies for answering them.
Example Student Essays
"501 Writing Prompts" (DePaul Univ.)
This nearly 200-page packet, compiled by the LearningExpress Skill Builder in Focus Writing Team, is stuffed with writing prompts, example essays, and commentary.
"Topics in English" (Kibin)
Kibin is a for-pay essay help website, but its example essays (organized by topic) are available for free. You'll find essays on everything from A Christmas Carol to perseverance.
"Student Writing Models" (Thoughtful Learning)
Thoughtful Learning, a website that offers a variety of teaching materials, provides sample student essays on various topics and organizes them by grade level.
"Five-Paragraph Essay" (ThoughtCo)
In this blog post by a former professor of English and rhetoric, ThoughtCo brings together examples of five-paragraph essays and commentary on the form.
The Best Essay Writing Collections
The Best American Essays of the Century by Joyce Carol Oates (Amazon)
This collection of American essays spanning the twentieth century was compiled by award winning author and Princeton professor Joyce Carol Oates.
The Best American Essays 2017 by Leslie Jamison (Amazon)
Leslie Jamison, the celebrated author of essay collection The Empathy Exams , collects recent, high-profile essays into a single volume.
The Art of the Personal Essay by Phillip Lopate (Amazon)
Documentary writer Phillip Lopate curates this historical overview of the personal essay's development, from the classical era to the present.
The White Album by Joan Didion (Amazon)
This seminal essay collection was authored by one of the most acclaimed personal essayists of all time, American journalist Joan Didion.
Consider the Lobster by David Foster Wallace (Amazon)
Read this famous essay collection by David Foster Wallace, who is known for his experimentation with the essay form. He pushed the boundaries of personal essay, reportage, and political polemic.
"50 Successful Harvard Application Essays" (Staff of the The Harvard Crimson )
If you're looking for examples of exceptional college application essays, this volume from Harvard's daily student newspaper is one of the best collections on the market.
Are you an instructor looking for the best resources for teaching essay writing? This section contains resources for developing in-class activities and student homework assignments. You'll find content from both well-known university writing centers and online writing labs.
Essay Writing Classroom Activities for Students
"In-class Writing Exercises" (Univ. of North Carolina Writing Center)
This page lists exercises related to brainstorming, organizing, drafting, and revising. It also contains suggestions for how to implement the suggested exercises.
"Teaching with Writing" (Univ. of Minnesota Center for Writing)
Instructions and encouragement for using "freewriting," one-minute papers, logbooks, and other write-to-learn activities in the classroom can be found here.
"Writing Worksheets" (Berkeley Student Learning Center)
Berkeley offers this bank of writing worksheets to use in class. They are nested under headings for "Prewriting," "Revision," "Research Papers" and more.
"Using Sources and Avoiding Plagiarism" (DePaul University)
Use these activities and worksheets from DePaul's Teaching Commons when instructing students on proper academic citation practices.
Essay Writing Homework Activities for Students
"Grammar and Punctuation Exercises" (Aims Online Writing Lab)
These five interactive online activities allow students to practice editing and proofreading. They'll hone their skills in correcting comma splices and run-ons, identifying fragments, using correct pronoun agreement, and comma usage.
"Student Interactives" (Read Write Think)
Read Write Think hosts interactive tools, games, and videos for developing writing skills. They can practice organizing and summarizing, writing poetry, and developing lines of inquiry and analysis.
This free website offers writing and grammar activities for all grade levels. The lessons are designed to be used both for large classes and smaller groups.
"Writing Activities and Lessons for Every Grade" (Education World)
Education World's page on writing activities and lessons links you to more free, online resources for learning how to "W.R.I.T.E.": write, revise, inform, think, and edit.
- PDFs for all 136 Lit Terms we cover
- Downloads of 1992 LitCharts Lit Guides
- Teacher Editions for every Lit Guide
- Explanations and citation info for 42,068 quotes across 1992 books
- Downloadable (PDF) line-by-line translations of every Shakespeare play
Need something? Request a new guide .
How can we improve? Share feedback .
LitCharts is hiring!

- Quizzes, saving guides, requests, plus so much more.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write an Essay
Last Updated: July 22, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Christopher Taylor, PhD and by wikiHow staff writer, Megaera Lorenz, PhD . Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014. There are 18 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 7,982,016 times.
An essay is a common type of academic writing that you'll likely be asked to do in multiple classes. Before you start writing your essay, make sure you understand the details of the assignment so that you know how to approach the essay and what your focus should be. Once you've chosen a topic, do some research and narrow down the main argument(s) you'd like to make. From there, you'll need to write an outline and flesh out your essay, which should consist of an introduction, body, and conclusion. After your essay is drafted, spend some time revising it to ensure your writing is as strong as possible.
Understanding Your Assignment

- The compare/contrast essay , which focuses on analyzing the similarities and differences between 2 things, such as ideas, people, events, places, or works of art.
- The narrative essay , which tells a story.
- The argumentative essay , in which the writer uses evidence and examples to convince the reader of their point of view.
- The critical or analytical essay, which examines something (such as a text or work of art) in detail. This type of essay may attempt to answer specific questions about the subject or focus more generally on its meaning.
- The informative essay , that educates the reader about a topic.

- How long your essay should be
- Which citation style to use
- Formatting requirements, such as margin size , line spacing, and font size and type
Christopher Taylor, PhD
Christopher Taylor, Professor of English, tells us: "Most essays will contain an introduction, a body or discussion portion, and a conclusion. When assigned a college essay, make sure to check the specific structural conventions related to your essay genre , your field of study, and your professor's expectations."

- If you're doing a research-based essay , you might find some inspiration from reading through some of the major sources on the subject.
- For a critical essay, you might choose to focus on a particular theme in the work you're discussing, or analyze the meaning of a specific passage.

- If you're having trouble narrowing down your topic, your instructor might be able to provide guidance or inspiration.
Planning and Organizing Your Essay

- Academic books and journals tend to be good sources of information. In addition to print sources, you may be able to find reliable information in scholarly databases such as JSTOR and Google Scholar.
- You can also look for primary source documents, such as letters, eyewitness accounts, and photographs.
- Always evaluate your sources critically. Even research papers by reputable academics can contain hidden biases, outdated information, and simple errors or faulty logic.
Tip: In general, Wikipedia articles are not considered appropriate sources for academic writing. However, you may be able to find useful sources in the “References” section at the end of the article.

- You might find it helpful to write your notes down on individual note cards or enter them into a text document on your computer so you can easily copy, paste , and rearrange them however you like.
- Try organizing your notes into different categories so you can identify specific ideas you'd like to focus on. For example, if you're analyzing a short story , you might put all your notes on a particular theme or character together.

- For example, if your essay is about the factors that led to the end of the Bronze Age in the ancient Middle East, you might focus on the question, “What role did natural disasters play in the collapse of Late Bronze Age society?”

- One easy way to come up with a thesis statement is to briefly answer the main question you would like to address.
- For example, if the question is “What role did natural disasters play in the collapse of Late Bronze Age society?” then your thesis might be, “Natural disasters during the Late Bronze Age destabilized local economies across the region. This set in motion a series of mass migrations of different peoples, creating widespread conflict that contributed to the collapse of several major Bronze Age political centers.”

- When you write the outline, think about how you would like to organize your essay. For example, you might start with your strongest arguments and then move to the weakest ones. Or, you could begin with a general overview of the source you're analyzing and then move on to addressing the major themes, tone, and style of the work.
- Introduction
- Point 1, with supporting examples
- Point 2, with supporting examples
- Point 3, with supporting examples
- Major counter-argument(s) to your thesis
- Your rebuttals to the counter-argument(s)
Drafting the Essay

- For example, if you're writing a critical essay about a work of art, your introduction might start with some basic information about the work, such as who created it, when and where it was created, and a brief description of the work itself. From there, introduce the question(s) about the work you'd like to address and present your thesis.
- A strong introduction should also contain a brief transitional sentence that creates a link to the first point or argument you would like to make. For example, if you're discussing the use of color in a work of art, lead-in by saying you'd like to start with an overview of symbolic color use in contemporary works by other artists.
Tip: Some writers find it helpful to write the introduction after they've written the rest of the essay. Once you've written out your main points, it's easier to summarize the gist of your essay in a few introductory sentences.

- For example, your topic sentence might be something like, “Arthur Conan Doyle's Sherlock Holmes stories are among the many literary influences apparent in P. G. Wodehouse's Jeeves novels.” You could then back this up by quoting a passage that contains a reference to Sherlock Holmes.
- Try to show how the arguments in each paragraph link back to the main thesis of your essay.

- When creating transitions, transitional phrases can be helpful. For example, use words and phrases such as “In addition,” “Therefore,” “Similarly,” “Subsequently,” or “As a result.”
- For example, if you've just discussed the use of color to create contrast in a work of art, you might start the next paragraph with, “In addition to color, the artist also uses different line weights to distinguish between the more static and dynamic figures in the scene.”

- For example, if you're arguing that a particular kind of shrimp decorates its shell with red algae to attract a mate, you'll need to address the counterargument that the shell decoration is a warning to predators. You might do this by presenting evidence that the red shrimp are, in fact, more likely to get eaten than shrimp with undecorated shells.

- The way you cite your sources will vary depending on the citation style you're using. Typically, you'll need to include the name of the author, the title and publication date of the source, and location information such as the page number on which the information appears.
- In general, you don't need to cite common knowledge. For example, if you say, “A zebra is a type of mammal,” you probably won't need to cite a source.
- If you've cited any sources in the essay, you'll need to include a list of works cited (or a bibliography ) at the end.

- Keep your conclusion brief. While the appropriate length will vary based on the length of the essay, it should typically be no longer than 1-2 paragraphs.
- For example, if you're writing a 1,000-word essay, your conclusion should be about 4-5 sentences long. [16] X Research source
Revising the Essay

- If you don't have time to spend a couple of days away from your essay, at least take a few hours to relax or work on something else.

- Excessive wordiness
- Points that aren't explained enough
- Tangents or unnecessary information
- Unclear transitions or illogical organization
- Spelling , grammar , style, and formatting problems
- Inappropriate language or tone (e.g., slang or informal language in an academic essay)

- You might have to cut material from your essay in some places and add new material to others.
- You might also end up reordering some of the content of the essay if you think that helps it flow better.

- Read over each line slowly and carefully. It may be helpful to read each sentence out loud to yourself.
Tip: If possible, have someone else check your work. When you've been looking at your writing for too long, your brain begins to fill in what it expects to see rather than what's there, making it harder for you to spot mistakes.

Expert Q&A

Reader Videos
Share a quick video tip and help bring articles to life with your friendly advice. Your insights could make a real difference and help millions of people!
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.yourdictionary.com/articles/essay-types
- ↑ https://students.unimelb.edu.au/academic-skills/resources/essay-writing/six-top-tips-for-writing-a-great-essay
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/common_writing_assignments/research_papers/choosing_a_topic.html
- ↑ https://writingcenter.fas.harvard.edu/tips-reading-assignment-prompt
- ↑ https://library.unr.edu/help/quick-how-tos/writing/integrating-sources-into-your-paper
- ↑ https://advice.writing.utoronto.ca/researching/notes-from-research/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.fas.harvard.edu/pages/developing-thesis
- ↑ https://writingcenter.fas.harvard.edu/pages/outlining
- ↑ https://lsa.umich.edu/sweetland/undergraduates/writing-guides/how-do-i-write-an-intro--conclusion----body-paragraph.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/academic_writing/essay_writing/argumentative_essays.html
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/transitions/
- ↑ https://lsa.umich.edu/sweetland/undergraduates/writing-guides/how-do-i-incorporate-a-counter-argument.html
- ↑ https://www.plagiarism.org/article/how-do-i-cite-sources
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/conclusions/
- ↑ https://www.utsc.utoronto.ca/twc/sites/utsc.utoronto.ca.twc/files/resource-files/Intros-Conclusions.pdf
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/proofreading/steps_for_revising.html
- ↑ https://open.lib.umn.edu/writingforsuccess/chapter/8-4-revising-and-editing/
- ↑ https://writing.ku.edu/writing-process
About This Article

If you need to write an essay, start by gathering information from reputable sources, like books from the library or scholarly journals online. Take detailed notes and keep track of which facts come from which sources. As you're taking notes, look for a central theme that you're interested in writing about to create your thesis statement. Then, organize your notes into an outline that supports and explains your thesis statement. Working from your outline, write an introduction and subsequent paragraphs to address each major point. Start every paragraph with a topic sentence that briefly explains the main point of that paragraph. Finally, finish your paper with a strong conclusion that sums up the most important points. For tips from our English Professor co-author on helpful revision techniques, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Muhammad Talha Javaid
Feb 7, 2019
Did this article help you?
Gabrielle Mattijetz
May 8, 2017
Shahzad Saleem
Jun 20, 2018
Barbara Gonzalez
Aug 6, 2016
Kniziel Sanders
Oct 17, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life
- Tips for Reading an Assignment Prompt
- Asking Analytical Questions
- Introductions
- What Do Introductions Across the Disciplines Have in Common?
- Anatomy of a Body Paragraph
- Transitions
- Tips for Organizing Your Essay
- Counterargument
- Conclusions
- Strategies for Essay Writing: Downloadable PDFs
- Brief Guides to Writing in the Disciplines
How to Write a Perfect Assignment: Step-By-Step Guide
Table of contents
- 1 How to Structure an Assignment?
- 2.1 The research part
- 2.2 Planning your text
- 2.3 Writing major parts
- 3 Expert Tips for your Writing Assignment
- 4 Will I succeed with my assignments?
- 5 Conclusion
How to Structure an Assignment?
To cope with assignments, you should familiarize yourself with the tips on formatting and presenting assignments or any written paper, which are given below. It is worth paying attention to the content of the paper, making it structured and understandable so that ideas are not lost and thoughts do not refute each other.
If the topic is free or you can choose from the given list — be sure to choose the one you understand best. Especially if that could affect your semester score or scholarship. It is important to select an engaging title that is contextualized within your topic. A topic that should captivate you or at least give you a general sense of what is needed there. It’s easier to dwell upon what interests you, so the process goes faster.
To construct an assignment structure, use outlines. These are pieces of text that relate to your topic. It can be ideas, quotes, all your thoughts, or disparate arguments. Type in everything that you think about. Separate thoughts scattered across the sheets of Word will help in the next step.
Then it is time to form the text. At this stage, you have to form a coherent story from separate pieces, where each new thought reinforces the previous one, and one idea smoothly flows into another.
Main Steps of Assignment Writing
These are steps to take to get a worthy paper. If you complete these step-by-step, your text will be among the most exemplary ones.
The research part
If the topic is unique and no one has written about it yet, look at materials close to this topic to gain thoughts about it. You should feel that you are ready to express your thoughts. Also, while reading, get acquainted with the format of the articles, study the details, collect material for your thoughts, and accumulate different points of view for your article. Be careful at this stage, as the process can help you develop your ideas. If you are already struggling here, pay for assignment to be done , and it will be processed in a split second via special services. These services are especially helpful when the deadline is near as they guarantee fast delivery of high-quality papers on any subject.
If you use Google to search for material for your assignment, you will, of course, find a lot of information very quickly. Still, the databases available on your library’s website will give you the clearest and most reliable facts that satisfy your teacher or professor. Be sure you copy the addresses of all the web pages you will use when composing your paper, so you don’t lose them. You can use them later in your bibliography if you add a bit of description! Select resources and extract quotes from them that you can use while working. At this stage, you may also create a request for late assignment if you realize the paper requires a lot of effort and is time-consuming. This way, you’ll have a backup plan if something goes wrong.
Planning your text
Assemble a layout. It may be appropriate to use the structure of the paper of some outstanding scientists in your field and argue it in one of the parts. As the planning progresses, you can add suggestions that come to mind. If you use citations that require footnotes, and if you use single spacing throughout the paper and double spacing at the end, it will take you a very long time to make sure that all the citations are on the exact pages you specified! Add a reference list or bibliography. If you haven’t already done so, don’t put off writing an essay until the last day. It will be more difficult to do later as you will be stressed out because of time pressure.
Writing major parts
It happens that there is simply no mood or strength to get started and zero thoughts. In that case, postpone this process for 2-3 hours, and, perhaps, soon, you will be able to start with renewed vigor. Writing essays is a great (albeit controversial) way to improve your skills. This experience will not be forgotten. It will certainly come in handy and bring many benefits in the future. Do your best here because asking for an extension is not always possible, so you probably won’t have time to redo it later. And the quality of this part defines the success of the whole paper.
Writing the major part does not mean the matter is finished. To review the text, make sure that the ideas of the introduction and conclusion coincide because such a discrepancy is the first thing that will catch the reader’s eye and can spoil the impression. Add or remove anything from your intro to edit it to fit the entire paper. Also, check your spelling and grammar to ensure there are no typos or draft comments. Check the sources of your quotes so that your it is honest and does not violate any rules. And do not forget the formatting rules.
with the right tips and guidance, it can be easier than it looks. To make the process even more straightforward, students can also use an assignment service to get the job done. This way they can get professional assistance and make sure that their assignments are up to the mark. At PapersOwl, we provide a professional writing service where students can order custom-made assignments that meet their exact requirements.
Expert Tips for your Writing Assignment
Want to write like a pro? Here’s what you should consider:
- Save the document! Send the finished document by email to yourself so you have a backup copy in case your computer crashes.
- Don’t wait until the last minute to complete a list of citations or a bibliography after the paper is finished. It will be much longer and more difficult, so add to them as you go.
- If you find a lot of information on the topic of your search, then arrange it in a separate paragraph.
- If possible, choose a topic that you know and are interested in.
- Believe in yourself! If you set yourself up well and use your limited time wisely, you will be able to deliver the paper on time.
- Do not copy information directly from the Internet without citing them.
Writing assignments is a tedious and time-consuming process. It requires a lot of research and hard work to produce a quality paper. However, if you are feeling overwhelmed or having difficulty understanding the concept, you may want to consider getting accounting homework help online . Professional experts can assist you in understanding how to complete your assignment effectively. PapersOwl.com offers expert help from highly qualified and experienced writers who can provide you with the homework help you need.
Will I succeed with my assignments?
Anyone can learn how to be good at writing: follow simple rules of creating the structure and be creative where it is appropriate. At one moment, you will need some additional study tools, study support, or solid study tips. And you can easily get help in writing assignments or any other work. This is especially useful since the strategy of learning how to write an assignment can take more time than a student has.
Therefore all students are happy that there is an option to order your paper at a professional service to pass all the courses perfectly and sleep still at night. You can also find the sample of the assignment there to check if you are on the same page and if not — focus on your papers more diligently.
So, in the times of studies online, the desire and skill to research and write may be lost. Planning your assignment carefully and presenting arguments step-by-step is necessary to succeed with your homework. When going through your references, note the questions that appear and answer them, building your text. Create a cover page, proofread the whole text, and take care of formatting. Feel free to use these rules for passing your next assignments.
When it comes to writing an assignment, it can be overwhelming and stressful, but Papersowl is here to make it easier for you. With a range of helpful resources available, Papersowl can assist you in creating high-quality written work, regardless of whether you’re starting from scratch or refining an existing draft. From conducting research to creating an outline, and from proofreading to formatting, the team at Papersowl has the expertise to guide you through the entire writing process and ensure that your assignment meets all the necessary requirements.
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.

4 Key Points for Effective Assignment Writing

Methodology
By Christina Desouza
Writing an effective assignment is more of an art than a science. It demands critical thinking, thorough research, organized planning, and polished execution. As a professional academic writer with over four years of experience, I've honed these skills and discovered proven strategies for creating standout assignments.
In this article, I will delve into the four key steps of assignment writing, offering detailed advice and actionable tips to help students master this craft.
1. Start With Research
In-depth research is the cornerstone of any high-quality assignment. It allows you to gain a profound understanding of your topic and equip yourself with relevant data, compelling arguments, and unique insights.
Here's how to do it right:
● Diversify Your Sources
Don't limit yourself to the first page of Google results. Make use of academic databases like JSTOR , Google Scholar , PubMed , or your school's online library. These resources house a plethora of scholarly articles, research papers, and academic books that can provide you with valuable information.
● Verify Information
Remember, not all information is created equal. Cross-check facts and data from multiple reliable sources to ensure accuracy. Look for consensus among experts on contentious issues.
● Stay Organized
Keep track of your resources as you go. Tools like Zotero or Mendeley can help you organize your references and generate citations in various formats. This will save you from scrambling to find sources when you're wrapping up your assignment.
1. Prepare Assignment Structure

Creating a well-planned structure for your assignment is akin to drawing a roadmap. It helps you stay on track and ensures that your ideas flow logically. Here's what to consider:
● Develop an Outline
The basic structure of an assignment includes an introduction, body, and conclusion. The introduction should present the topic and establish the purpose of your assignment. The body should delve into the topic in detail, backed by your research. The conclusion should summarize your findings or arguments without introducing new ideas.
● Use Subheadings
Subheadings make your assignment easier to read and follow. They allow you to break down complex ideas into manageable sections. As a rule of thumb, each paragraph should cover one idea or argument.
● Allocate Word Count
Assignments often come with word limits. Allocate word count for each section of your assignment based on its importance to avoid overwriting or underwriting any part.
1. Start Assignment Writing
Writing your assignment is where your research and planning come to fruition. You now have a robust foundation to build upon, and it's time to craft a compelling narrative.
Here's how to accomplish this:
● Write a Gripping Introduction
Your introduction is the gateway to your assignment. Make it captivating. Start with a hook—a surprising fact, an interesting quote, or a thought-provoking question—to grab your readers' attention. Provide an overview of what your assignment is about and the purpose it serves. A well-crafted introduction sets the tone for the rest of the assignment and motivates your readers to delve deeper into your work.

● Develop a Comprehensive Body
The body of your assignment is where you delve into the details. Develop your arguments, present your data, and discuss your findings. Use clear and concise language. Avoid jargon unless necessary. Each paragraph should cover one idea or argument to maintain readability.
● Craft a Convincing Conclusion
Your conclusion is your final chance to leave an impression on your reader. Summarize your key findings or arguments without introducing new ideas. Reinforce the purpose of your assignment and provide a clear answer to the question or problem you addressed in the introduction. A strong conclusion leaves your readers with a sense of closure and a full understanding of your topic.
● Write Clearly
Use straightforward sentences and avoid jargon. Your goal is to communicate, not to confuse. Tools like Hemingway Editor can help ensure your writing is clear and concise.
● Use Paraphrasingtool.ai
Paraphrasingtool.ai is an AI-powered tool that can enhance your assignment writing. It reformulates your sentences while preserving their meaning. It not only helps you avoid plagiarism but also enhances the readability of your work.
● Cite Your Sources
Citations are a critical part of assignment writing. They acknowledge the work of others you've built upon and demonstrate the depth of your research. Always include in-text citations and a bibliography at the end. This not only maintains academic integrity but also gives your readers resources to delve deeper into the topic if they wish.
1. Review and Proofread The Assignment
Reviewing and proofreading are the final but critical steps in assignment writing. They ensure your assignment is free from errors and that your ideas are coherently presented. Here's how to do it effectively:
● Take a Break
After you finish writing, take a break before you start proofreading. Fresh eyes are more likely to spot mistakes and inconsistencies.
● Read Aloud
Reading your work aloud can help you identify awkward phrasing, run-on sentences, and typos. You're more likely to catch errors when you hear them, as it requires a different type of processing than reading silently.
● Use Proofreading Tools
Digital tools like Grammarly can be your second pair of eyes, helping you spot grammatical errors, typos, and even issues with sentence structure. However, don't rely solely on these tools—make sure to manually review your work as well.
Effective assignment writing is a skill that takes practice to master. It requires meticulous research, organized planning, clear writing, and careful proofreading. The steps and tips outlined in this article are by no means exhaustive, but they provide a solid framework to start from.
Remember, there is always room for improvement. Don't be disheartened by initial challenges. Each assignment is an opportunity to learn, grow, and sharpen your writing skills. So, be persistent, stay curious, and keep refining your craft. With time and practice, you will find yourself writing assignments that are not just excellent, but truly outstanding.

Module 4: Writing in College
Writing assignments, learning objectives.
- Describe common types and expectations of writing tasks given in a college class

Figure 1 . All college classes require some form of writing. Investing some time in refining your writing skills so that you are a more confident, skilled, and efficient writer will pay dividends in the long run.
What to Do With Writing Assignments
Writing assignments can be as varied as the instructors who assign them. Some assignments are explicit about what exactly you’ll need to do, in what order, and how it will be graded. Others are more open-ended, leaving you to determine the best path toward completing the project. Most fall somewhere in the middle, containing details about some aspects but leaving other assumptions unstated. It’s important to remember that your first resource for getting clarification about an assignment is your instructor—they will be very willing to talk out ideas with you, to be sure you’re prepared at each step to do well with the writing.
Writing in college is usually a response to class materials—an assigned reading, a discussion in class, an experiment in a lab. Generally speaking, these writing tasks can be divided into three broad categories: summary assignments, defined-topic assignments, and undefined-topic assignments.
Link to Learning
Empire State College offers an Assignment Calculator to help you plan ahead for your writing assignment. Just plug in the date you plan to get started and the date it is due, and the calculator will help break it down into manageable chunks.
Summary Assignments
Being asked to summarize a source is a common task in many types of writing. It can also seem like a straightforward task: simply restate, in shorter form, what the source says. A lot of advanced skills are hidden in this seemingly simple assignment, however.
An effective summary does the following:
- reflects your accurate understanding of a source’s thesis or purpose
- differentiates between major and minor ideas in a source
- demonstrates your ability to identify key phrases to quote
- shows your ability to effectively paraphrase most of the source’s ideas
- captures the tone, style, and distinguishing features of a source
- does not reflect your personal opinion about the source
That last point is often the most challenging: we are opinionated creatures, by nature, and it can be very difficult to keep our opinions from creeping into a summary. A summary is meant to be completely neutral.
In college-level writing, assignments that are only summary are rare. That said, many types of writing tasks contain at least some element of summary, from a biology report that explains what happened during a chemical process, to an analysis essay that requires you to explain what several prominent positions about gun control are, as a component of comparing them against one another.
Writing Effective Summaries
Start with a clear identification of the work.
This automatically lets your readers know your intentions and that you’re covering the work of another author.
- In the featured article “Five Kinds of Learning,” the author, Holland Oates, justifies his opinion on the hot topic of learning styles — and adds a few himself.
Summarize the Piece as a Whole
Omit nothing important and strive for overall coherence through appropriate transitions. Write using “summarizing language.” Your reader needs to be reminded that this is not your own work. Use phrases like the article claims, the author suggests, etc.
- Present the material in a neutral fashion. Your opinions, ideas, and interpretations should be left in your brain — don’t put them into your summary. Be conscious of choosing your words. Only include what was in the original work.
- Be concise. This is a summary — it should be much shorter than the original piece. If you’re working on an article, give yourself a target length of 1/4 the original article.
Conclude with a Final Statement
This is not a statement of your own point of view, however; it should reflect the significance of the book or article from the author’s standpoint.
- Without rewriting the article, summarize what the author wanted to get across. Be careful not to evaluate in the conclusion or insert any of your own assumptions or opinions.
Understanding the Assignment and Getting Started

Figure 2 . Many writing assignments will have a specific prompt that sends you first to your textbook, and then to outside resources to gather information.
Often, the handout or other written text explaining the assignment—what professors call the assignment prompt —will explain the purpose of the assignment and the required parameters (length, number and type of sources, referencing style, etc.).
Also, don’t forget to check the rubric, if there is one, to understand how your writing will be assessed. After analyzing the prompt and the rubric, you should have a better sense of what kind of writing you are expected to produce.
Sometimes, though—especially when you are new to a field—you will encounter the baffling situation in which you comprehend every single sentence in the prompt but still have absolutely no idea how to approach the assignment! In a situation like that, consider the following tips:
- Focus on the verbs . Look for verbs like compare, explain, justify, reflect , or the all-purpose analyze . You’re not just producing a paper as an artifact; you’re conveying, in written communication, some intellectual work you have done. So the question is, what kind of thinking are you supposed to do to deepen your learning?
- Put the assignment in context . Many professors think in terms of assignment sequences. For example, a social science professor may ask you to write about a controversial issue three times: first, arguing for one side of the debate; second, arguing for another; and finally, from a more comprehensive and nuanced perspective, incorporating text produced in the first two assignments. A sequence like that is designed to help you think through a complex issue. If the assignment isn’t part of a sequence, think about where it falls in the span of the course (early, midterm, or toward the end), and how it relates to readings and other assignments. For example, if you see that a paper comes at the end of a three-week unit on the role of the Internet in organizational behavior, then your professor likely wants you to synthesize that material.
- Try a free-write . A free-write is when you just write, without stopping, for a set period of time. That doesn’t sound very “free”; it actually sounds kind of coerced, right? The “free” part is what you write—it can be whatever comes to mind. Professional writers use free-writing to get started on a challenging (or distasteful) writing task or to overcome writer’s block or a powerful urge to procrastinate. The idea is that if you just make yourself write, you can’t help but produce some kind of useful nugget. Thus, even if the first eight sentences of your free write are all variations on “I don’t understand this” or “I’d really rather be doing something else,” eventually you’ll write something like “I guess the main point of this is…,” and—booyah!—you’re off and running.
- Ask for clarification . Even the most carefully crafted assignments may need some verbal clarification, especially if you’re new to a course or field. Professors generally love questions, so don’t be afraid to ask. Try to convey to your instructor that you want to learn and you’re ready to work, and not just looking for advice on how to get an A.
Defined-Topic Assignments
Many writing tasks will ask you to address a particular topic or a narrow set of topic options. Defined-topic writing assignments are used primarily to identify your familiarity with the subject matter. (Discuss the use of dialect in Their Eyes Were Watching God , for example.)
Remember, even when you’re asked to “show how” or “illustrate,” you’re still being asked to make an argument. You must shape and focus your discussion or analysis so that it supports a claim that you discovered and formulated and that all of your discussion and explanation develops and supports.
Undefined-Topic Assignments
Another writing assignment you’ll potentially encounter is one in which the topic may be only broadly identified (“water conservation” in an ecology course, for instance, or “the Dust Bowl” in a U.S. History course), or even completely open (“compose an argumentative research essay on a subject of your choice”).

Figure 3 . For open-ended assignments, it’s best to pick something that interests you personally.
Where defined-topic essays demonstrate your knowledge of the content , undefined-topic assignments are used to demonstrate your skills— your ability to perform academic research, to synthesize ideas, and to apply the various stages of the writing process.
The first hurdle with this type of task is to find a focus that interests you. Don’t just pick something you feel will be “easy to write about” or that you think you already know a lot about —those almost always turn out to be false assumptions. Instead, you’ll get the most value out of, and find it easier to work on, a topic that intrigues you personally or a topic about which you have a genuine curiosity.
The same getting-started ideas described for defined-topic assignments will help with these kinds of projects, too. You can also try talking with your instructor or a writing tutor (at your college’s writing center) to help brainstorm ideas and make sure you’re on track.
Getting Started in the Writing Process
Writing is not a linear process, so writing your essay, researching, rewriting, and adjusting are all part of the process. Below are some tips to keep in mind as you approach and manage your assignment.
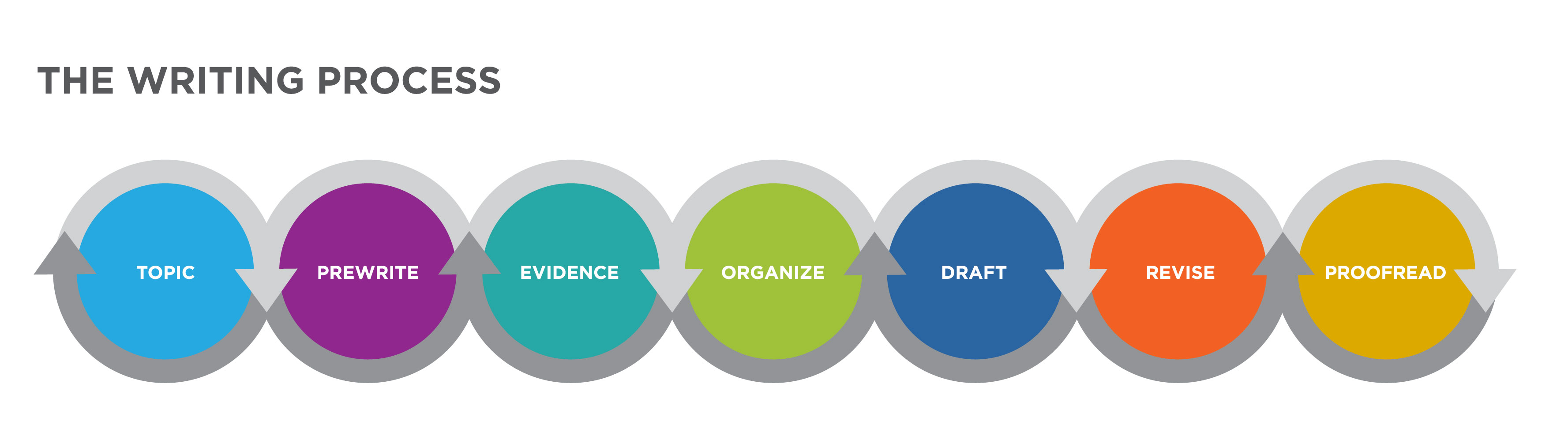
Figure 4 . Writing is a recursive process that begins with examining the topic and prewriting.
Write down topic ideas. If you have been assigned a particular topic or focus, it still might be possible to narrow it down or personalize it to your own interests.
If you have been given an open-ended essay assignment, the topic should be something that allows you to enjoy working with the writing process. Select a topic that you’ll want to think about, read about, and write about for several weeks, without getting bored.

Figure 5 . Just getting started is sometimes the most difficult part of writing. Freewriting and planning to write multiple drafts can help you dive in.
If you’re writing about a subject you’re not an expert on and want to make sure you are presenting the topic or information realistically, look up the information or seek out an expert to ask questions.
- Note: Be cautious about information you retrieve online, especially if you are writing a research paper or an article that relies on factual information. A quick Google search may turn up unreliable, misleading sources. Be sure you consider the credibility of the sources you consult (we’ll talk more about that later in the course). And keep in mind that published books and works found in scholarly journals have to undergo a thorough vetting process before they reach publication and are therefore safer to use as sources.
- Check out a library. Yes, believe it or not, there is still information to be found in a library that hasn’t made its way to the Web. For an even greater breadth of resources, try a college or university library. Even better, research librarians can often be consulted in person, by phone, or even by email. And they love helping students. Don’t be afraid to reach out with questions!
Write a Rough Draft
It doesn’t matter how many spelling errors or weak adjectives you have in it. Your draft can be very rough! Jot down those random uncategorized thoughts. Write down anything you think of that you want included in your writing and worry about organizing and polishing everything later.
If You’re Having Trouble, Try F reewriting
Set a timer and write continuously until that time is up. Don’t worry about what you write, just keeping moving your pencil on the page or typing something (anything!) into the computer.
- Outcome: Writing in College. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Writing in College: From Competence to Excellence. Authored by : Amy Guptill. Provided by : SUNY Open Textbooks. Located at : http://textbooks.opensuny.org/writing-in-college-from-competence-to-excellence/ . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Image of man writing. Authored by : Matt Zhang. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/pAg6t9 . License : CC BY-NC-ND: Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives
- Writing Strategies. Provided by : Lumen Learning. Located at : https://courses.lumenlearning.com/lumencollegesuccess/chapter/writing-strategies/ . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Image of woman reading. Authored by : Aaron Osborne. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/dPLmVV . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Image of sketches of magnifying glass. Authored by : Matt Cornock. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/eBSLmg . License : CC BY-NC: Attribution-NonCommercial
- How to Write a Summary. Authored by : WikiHow. Located at : http://www.wikihow.com/Write-a-Summary . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- How to Write. Provided by : WikiHow. License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
- Image of typing. Authored by : Kiran Foster. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/9M2WW4 . License : CC BY: Attribution

Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Understanding Writing Assignments

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
How to Decipher the Paper Assignment
Many instructors write their assignment prompts differently. By following a few steps, you can better understand the requirements for the assignment. The best way, as always, is to ask the instructor about anything confusing.
- Read the prompt the entire way through once. This gives you an overall view of what is going on.
- Underline or circle the portions that you absolutely must know. This information may include due date, research (source) requirements, page length, and format (MLA, APA, CMS).
- Underline or circle important phrases. You should know your instructor at least a little by now - what phrases do they use in class? Does he repeatedly say a specific word? If these are in the prompt, you know the instructor wants you to use them in the assignment.
- Think about how you will address the prompt. The prompt contains clues on how to write the assignment. Your instructor will often describe the ideas they want discussed either in questions, in bullet points, or in the text of the prompt. Think about each of these sentences and number them so that you can write a paragraph or section of your essay on that portion if necessary.
- Rank ideas in descending order, from most important to least important. Instructors may include more questions or talking points than you can cover in your assignment, so rank them in the order you think is more important. One area of the prompt may be more interesting to you than another.
- Ask your instructor questions if you have any.
After you are finished with these steps, ask yourself the following:
- What is the purpose of this assignment? Is my purpose to provide information without forming an argument, to construct an argument based on research, or analyze a poem and discuss its imagery?
- Who is my audience? Is my instructor my only audience? Who else might read this? Will it be posted online? What are my readers' needs and expectations?
- What resources do I need to begin work? Do I need to conduct literature (hermeneutic or historical) research, or do I need to review important literature on the topic and then conduct empirical research, such as a survey or an observation? How many sources are required?
- Who - beyond my instructor - can I contact to help me if I have questions? Do you have a writing lab or student service center that offers tutorials in writing?
(Notes on prompts made in blue )
Poster or Song Analysis: Poster or Song? Poster!
Goals : To systematically consider the rhetorical choices made in either a poster or a song. She says that all the time.
Things to Consider: ah- talking points
- how the poster addresses its audience and is affected by context I'll do this first - 1.
- general layout, use of color, contours of light and shade, etc.
- use of contrast, alignment, repetition, and proximity C.A.R.P. They say that, too. I'll do this third - 3.
- the point of view the viewer is invited to take, poses of figures in the poster, etc. any text that may be present
- possible cultural ramifications or social issues that have bearing I'll cover this second - 2.
- ethical implications
- how the poster affects us emotionally, or what mood it evokes
- the poster's implicit argument and its effectiveness said that was important in class, so I'll discuss this last - 4.
- how the song addresses its audience
- lyrics: how they rhyme, repeat, what they say
- use of music, tempo, different instruments
- possible cultural ramifications or social issues that have bearing
- emotional effects
- the implicit argument and its effectiveness
These thinking points are not a step-by-step guideline on how to write your paper; instead, they are various means through which you can approach the subject. I do expect to see at least a few of them addressed, and there are other aspects that may be pertinent to your choice that have not been included in these lists. You will want to find a central idea and base your argument around that. Additionally, you must include a copy of the poster or song that you are working with. Really important!
I will be your audience. This is a formal paper, and you should use academic conventions throughout.
Length: 4 pages Format: Typed, double-spaced, 10-12 point Times New Roman, 1 inch margins I need to remember the format stuff. I messed this up last time =(
Academic Argument Essay
5-7 pages, Times New Roman 12 pt. font, 1 inch margins.
Minimum of five cited sources: 3 must be from academic journals or books
- Design Plan due: Thurs. 10/19
- Rough Draft due: Monday 10/30
- Final Draft due: Thurs. 11/9
Remember this! I missed the deadline last time
The design plan is simply a statement of purpose, as described on pages 40-41 of the book, and an outline. The outline may be formal, as we discussed in class, or a printout of an Open Mind project. It must be a minimum of 1 page typed information, plus 1 page outline.
This project is an expansion of your opinion editorial. While you should avoid repeating any of your exact phrases from Project 2, you may reuse some of the same ideas. Your topic should be similar. You must use research to support your position, and you must also demonstrate a fairly thorough knowledge of any opposing position(s). 2 things to do - my position and the opposite.
Your essay should begin with an introduction that encapsulates your topic and indicates 1 the general trajectory of your argument. You need to have a discernable thesis that appears early in your paper. Your conclusion should restate the thesis in different words, 2 and then draw some additional meaningful analysis out of the developments of your argument. Think of this as a "so what" factor. What are some implications for the future, relating to your topic? What does all this (what you have argued) mean for society, or for the section of it to which your argument pertains? A good conclusion moves outside the topic in the paper and deals with a larger issue.
You should spend at least one paragraph acknowledging and describing the opposing position in a manner that is respectful and honestly representative of the opposition’s 3 views. The counterargument does not need to occur in a certain area, but generally begins or ends your argument. Asserting and attempting to prove each aspect of your argument’s structure should comprise the majority of your paper. Ask yourself what your argument assumes and what must be proven in order to validate your claims. Then go step-by-step, paragraph-by-paragraph, addressing each facet of your position. Most important part!
Finally, pay attention to readability . Just because this is a research paper does not mean that it has to be boring. Use examples and allow your opinion to show through word choice and tone. Proofread before you turn in the paper. Your audience is generally the academic community and specifically me, as a representative of that community. Ok, They want this to be easy to read, to contain examples I find, and they want it to be grammatically correct. I can visit the tutoring center if I get stuck, or I can email the OWL Email Tutors short questions if I have any more problems.
100 Writing Practice Lessons & Exercises
by Joe Bunting | 50 comments
Want to become a better writer? How much time do you spend on your writing practice? Perhaps you want to write novels, or maybe you just want to get better grades in your essay writing assignments , or maybe you'd like to start a popular blog .
If you want to write better, you need practice. But what does a writing practice actually look like? In this post, I'm going to give you everything you need to kick off your writing practice and become a better writer faster.

What Is Writing Practice?
Writing practice is a method of becoming a better writer that usually involves reading lessons about the writing process, using writing prompts, doing creative writing exercises , or finishing writing pieces, like essays, short stories , novels , or books . The best writing practice is deliberate, timed, and involves feedback.
How Do You Practice Writing?
This was the question I had when I first started The Write Practice in 2011. I knew how to practice a sport and how to practice playing an instrument. But for some reason, even after studying it in college, I wasn't sure how to practice writing.
I set out to create the best writing practice I could. The Write Practice is the result.
I found that the best writing practice has three aspects:
Deliberate . Writing whatever you feel like may be cathartic, but it's not an effective way to become a better writer or build your writing skills. You'll get better faster by practicing a specific technique or aspect of the writing process each time you sit down to write.
This is why we have a new lesson about the writing process each day on The Write Practice, followed by a practice prompt at the end so you can put what you learned to use immediately.
Timed . It's no secret writers struggle with focus. There are just too many interesting distractions—Facebook, email, Kim Kardashian's Instagram feed (just kidding about that last one, sort of)—and writing is just too hard sometimes.
Setting a timer, even for just fifteen minutes, is an easy and effective way to stay focused on what's important.
This is why in our writing practice prompt at the end of each post we have a time limit, usually with a link to an online tool egg timer , so you can focus on deliberate practice without getting distracted.
Feedback . Getting feedback is one of the requirements to deliberately practice writing or any other craft. Feedback can look like listening to the reactions of your readers or asking for constructive criticism from editors and other writers.
This is why we ask you to post your writing practice after each lesson, so that you can get feedback from other writers in The Write Practice community. It's also why we set up The Write Practice Pro community , to provide critique groups for writers to get feedback on each finished piece of writing.

Our 100+ Best Creative Writing Practice Exercises and Lessons
Now that you know how we practice writing at The Write Practice, here are our best writing practice lessons to jumpstart your writing skills with some daily writing exercises, for beginner writers to even the most expert writers:
All-Time, Top 10 Writing Lessons and Exercises
These ten posts are our most viewed articles to boost your writing practice:
1. What is Plot? The 6 Elements of Plot and How to Use Them . Great stories use similar elements in wildly different ways to build page-turning stories. Click here to read what they are and learn how to start using them !
2. Top 100 Short Story Ideas . Here are over a hundred writing prompts in a variety of genres. If you need ideas for your next story, check this out!
3. How To Use Neither, Nor, Or, and Nor Correctly . Even good writers struggle figuring out when to use neither/nor and either/or. In this post, our copy-queen Liz Bureman settles the confusion once and for all. Click to continue to the writing exercise
4. Ten Secrets To Write Better Stories . How does Pixar manage to create such great stories, year after year? And how do you write a good story? In this post, I distill everything I've learned about how to write a good story into ten tips. Click to continue to the writing exercise
5. 35 Questions To Ask Your Characters From Marcel Proust . To get to know my characters better, I use a list of questions known as the Proust Questionnaire, made famous by French author, Marcel Proust. Click to continue to the writing exercise
6. How a Scene List Can Change Your Novel-Writing Life . Creating a scene list changed my novel-writing life, and doing the same will change yours too. Includes examples of the scene lists from famous authors. Click to continue to the writing exercise
7. Why You Need to be Using the Oxford Comma . Most people I've met have no idea what the Oxford comma is, but it's probably something that you have used frequently in your writing. Click to continue to the writing exercise
8. Six Surprising Ways to Write Better Interview Questions. The interview is the most-used tool in a journalist's bag. But that doesn't mean novelists, bloggers, and even students can't and don't interview people. Here's how to conduct a great interview. Click to continue to the writing exercise
9. Why You Should Try Writing in Second Person . You've probably used first person and third person point-of-view already. But what about second person? This post explains three reasons why you should try writing from this point-of-view. Click to continue to the writing exercise
10. The Secret to Show, Don't Tell . You've heard the classic writing rule, “Show. Don't Tell.” Every writing blog ever has talked about it, and for good reason. Showing, for some reason, is really difficult. Click to continue to the writing exercise.

12 Exercises and Lessons To Become a Better Writer
How do you become a better writer? These posts share our best advice:
- Want to Be a Better Writer? Cut These 7 Words
- What I Mean When I Say I Am A Writer
- How to Become a Writer: 3 Simple Steps
- 72% of Writers Struggle With THIS
- 7 Lies About Becoming a Writer That You Probably Believe
- 10 Questions to Find Your Unique Writing Voice
- The Best Writing Book I’ve Ever Read
- The Best Way to Become a Better Writer
- The Creative Writer’s Toolkit: 6 Tools You Can’t Write Without
- Should You Write More or Write Better: Quantity vs Quality
- How to Become a Better Writer in One, Simple Step
- 11 Writing Tips That Will Change Your Life
6 Lessons and Exercises from Great Writers
If you want to be a writer, learn from the great writers who have gone before you:
- 23 Essential Quotes from Ernest Hemingway About Writing
- 29 Quotes that Explain How to Become a Better Writer
- 10 Lessons Dr. Seuss Can Teach Writers
- 10 Writing Tips from Ursula Le Guin
- Once Upon a Time: Pixar Prompt
- All the Pretty Words: Writing In the Style of Cormac McCarthy
12 Genre and Format Specific Writing Lessons and Exercises
Here are our best writing lessons for specific types of writing, including essays, screenplays, memoir, short stories, children's books, and humor writing:
- Writing an Essay? Here Are 10 Effective Tips
- How To Write a Screenplay: The 5 Step Process
- How to Write a Great Memoir: a Complete Guide
- How to Write a Short Story from Start to Finish
- How to Write a Thriller Novel
- How to Write a Children's Book
- How to Write a Love Story
- How to Write a Coming of Age Story or Book
- How to Write an Adventure Book
- 5 Key Elements for Successful Short Stories
- 4 Tips to Write a Novel That Will Be Adapted Into a Movie
- Humor Writing for People Who Aren’t Funny
14 Characterization Lessons and Exercises
Good characters are the foundation of good fiction. Here are our best lessons to create better characters:
- Character Development: How to Create Characters Audiences Will Love
- Writing Villains: 9 Evil Examples of the Villain Archetype
- How NOT to Introduce a New Character
- The Strongest Form of Characterization
- The Most Important Character Archetype
- How Do You Build A Strong Character In Your Writing?
- 75+ Antihero Examples and How to Use Them
- How to Explore Your Characters’ Motivations
- 8 Tips for Naming Characters
- The Protagonist: How to Center Your Story
- Heroes vs. Anti-Heroes: Which Is Right For Your Story?
- The Weakest Form of Characterization
- How to Write With an Accent
- How To Create a Character Sketch Using Scrivener
15 Grammar Lessons and Exercises
I talk to so many writers, some of whom are published authors, who struggle with grammar. Here are our best writing lessons on grammar:
- Is It Okay To End A Sentence With A Preposition?
- Contractions List: When To Use and When To Avoid
- Good vs. Well
- Connotation vs. Denotation
- Per Se vs. Per Say
- When You SHOULD Use Passive Voice
- When Do You Use “Quotation Marks”
- Polysyndeton and Asyndeton: Definition and Examples
- The Case Against Twilight
- Affect Versus Effect
- Stop Saying “Literally”
- What Is a Comma Splice? And Why Do Editors Hate Them?
- Intra vs. Inter: Why No One Plays Intermural Sports
- Alright and Alot: Words That Are Not Words
- The Poor, Misunderstood Semicolon
5 Journalism Lessons and Exercises
Want to be a journalist? Or even use techniques from journalism to improve your novel, essay, or screenplay? Here are our best writing lessons on journalism:
- Six Ways to Ask Better Questions In Interviews
- How to Conduct an Author Interview
- Interview In Person or Via Email?
- What If They Don’t Want to Talk to You?
- Eleven Habits of a Highly Effective Interviewers
16 Plot and Structure Lessons and Exercises
Want to write a good story? Our top plot and structure lessons will help:
- The Nine Types of Story and How to Master Them
- Points of a Story: 6 Plot Points Every Story Needs
- How to Shape a Story: The 6 Arcs
- 7 Keys To Write the Perfect First Line of a Novel
- The Secret to Creating Conflict
- 4 Tips to Avoid Having Your Short Story Rejected by a Literary Magazine
- 7 Steps to Creating Suspense
- 5 Elements of Storytelling
- 3 Important Rules for Writing Endings
- A Writer’s Cheatsheet to Plot and Structure
- Overcoming the Monster
- How to Satisfy Your Reader With a Great Ending
- Pow! Boom! Ka-Pow! 5 Tips to Write Fight Scenes
- The Dramatic Question and Suspense in Fiction
- How to Write a Memorable Beginning and Ending
- How to Write the Perfect First Page
6 Lessons and Exercises to Beat Writer's Block
Writer's block is real, and it can completely derail your writing. Here are six lessons to get writing again:
- How To Write Whether You Feel Like it Or Not
- This Fun Creative Writing Exercise Will Change Your Life
- When You Should Be Writing But Can't…
- What to do When Your Word Count is Too Low
- 7 Tricks to Write More with Less Willpower
- When You Don’t Know What to Write, Write About Your Insecurities
7 Literary Technique Lessons and Exercises
These writing and storytelling techniques will teach you a few tricks of the trade you may not have discovered before:
- 3 Tips to “Show, Don’t Tell” Emotions and Moods
- 3 Reasons to Write Stream of Consciousness Narrative
- 16 Observations About Real Dialogue
- Intertextuality As A Literary Device
- Why You Should Use Symbolism In Your Writing
- 6 Ways to Evoke Emotion in Poetry and Prose
- 3 Tips To Write Modern Allegorical Novels
- Symbol vs. Motif: What’s the Difference
3 Inspirational Writing Lessons and Exercises
Need some inspiration? Here are three of our most inspiring posts:
- Why We Write: Four Reasons
- You Must Remember Every Scar
- 17 Reasons to Write Something NOW
3 Publishing Blogging Lessons and Exercises
If you want to get published, these three lessons will help:
- The Secret to Writing On Your Blog Every Day
- How to Publish Your Book and Sell Your First 1,000 Copies
- How to Submit a Short Story for Publication
11 Writing Prompts
Need inspiration or just a kick in the pants to write. Try one of our top writing prompts :
- Grandfathers [writing prompt]
- Out of Place [writing prompt]
- Sleepless [writing prompt]
- Longing [writing prompt]
- Write About Yourself [writing prompt]
- 3 Reasons You Should Write Ghost Stories
- Road Trip [writing prompt]
- Morning [writing prompt]
- The Beach [writing prompt]
- Fall Writing Prompts
- How to Use Six-Word Stories As Writing Prompts
Is It Time To Begin Your Writing Practice?
It's clear that if you want to become a writer, you need to practice writing. We've created a proven process to practice your writing at The Write Practice, but even if you don't join our community, I hope you'll start practicing in some way today.
Personally, I waited far too long to start practicing and it set my writing back years.
How about you? Do you think practicing writing is important? Let me know in the comments section .
Choose one of the writing practice posts above. Then, read the lesson and participate in the writing exercise, posting your work in the Pro Practice Workshop . And if you post, please give feedback to your fellow writers who also posted their practices.
Have fun and happy practicing!
Joe Bunting
Joe Bunting is an author and the leader of The Write Practice community. He is also the author of the new book Crowdsourcing Paris , a real life adventure story set in France. It was a #1 New Release on Amazon. Follow him on Instagram (@jhbunting).
Want best-seller coaching? Book Joe here.

Work with Joe Bunting?
WSJ Bestselling author, founder of The Write Practice, and book coach with 14+ years experience. Joe Bunting specializes in working with Action, Adventure, Fantasy, Historical Fiction, How To, Literary Fiction, Memoir, Mystery, Nonfiction, Science Fiction, and Self Help books. Sound like a good fit for you?
50 Comments
You have THE BEST content for writing on this blog!!
Thank you, Kristen. This made my morning. 🙂
Thanks Mitch. 🙂
I can’t remember when I started following this website. I have to look in my notebooks because that’s where I did these practices. I didn’t have access to a computer when I did them, so I wrote them out, setting the time limit. But even when I do get to a computer, I have my reservations about putting my practices on the page. even though it’s practice, I want them to be the best, almost perfect. But I know it won’t be. I’ve gotten feedback before that says so. It still gets to me that I didn’t put something together that not everyone liked. I need to get over it. After all, that is what these practices are about: to learn and improve on our craft.
I don’t know either, George, but it’s been several years. Perfectionism is something so many of us face, and it’s made worse when you don’t have a critique community as warm and encouraging as ours is. I hope you and everyone here are always willing to try something new, even if it comes out a little messed up, because you know we’ll support you and try to make you better.
What a great share! Thanks so much!
You’re so welcome, Elizabeth. Thank you for commenting.
when I ran writing classes I wrote. when I am “a member of writing classes” the teacher/leader/facilitator is NOT MY AUDIENCE and so I don’t write as well/as much. I don’t get the feedback I need from fellow students because most of them have never run their own writing projects/workshops. So many people expect you to write their story for them. I’ve actually got quite a few stories of me own. I have finally decided I like owning them. 😉
It sounds like you need a new critique group, Patience! Hope you can find a place where you get the feedback you need.
Wow! Terrific round-up of resources. 🙂
Thanks Stephanie. 🙂
Practice is necessary, period. It doesn’t matter what you want to learn. If you want to improve, practice is vital.
It’s odd. I’ve known and applied that principle for years on a variety of things. Painting. Drawing. Blogging. Gardening. Laundry.
But never writing.
Like you, I had the notion that just writing every day was all it took to improve. Why not the same level of dedication to writing?
Perhaps it’s time to change that!
I can relate, Carrie. It’s easy to confuse the craft of writing with journaling, thinking that you can just write whatever you feel like and you’ll get better, write something worth reading. The truth is that writing interesting things to read is a skill, but the good news is that you can get better at it with practice. Thanks for practicing with us! 🙂
I love these suggestions , and have set Writing Practice as my homepage so the first 15 minutes of my day is spent writing, whether its a practice or exercise here or another that is sprinkled through out this site, Thank you for all you do everyone here at The Write Practice
This is great Debra. I want to write the first 15 minutes of my day too!
I agree with Joe, Do it. Could be your to do list… ( that could lead to something else story wse later)
I love that, Debra. Such a good way to start your day.
Thanks Joe!
The best! Thank you so much for this.
You’re very welcome!
I simply LOVE all the tips and suggestions given on this blog. They are super helpful!
THANK you. We love sharing them with you. 🙂
Hi! You forgot the link to How to Write a Story a Week: A Day-by-Day Guide.
Thanks a lot for your work! This post is amazing.
It’s a great post Thiago. Definitely one of our most shared. Thanks for mentioning it! BTW here’s the link:
https://thewritepractice.com/a-story-a-week/
Wow!! There are so many exercises…. I just love it..! I am gonna really enjoy it..!
Awesome! Thank you for reading and practicing with us. 🙂
I only read halfway , My tootie is jumping all over me, and typing this is a struggle when a 3yr old wants his Toy Story movie on Youtube in this computer. Thank you for this article, will come back later to finish reading.
I know the feeling! Good luck!
Can’t wait to get stuck in with this! 🙂
Very helpful! Thank you!
I’ve just bookmarked this page. Thanks for this wonderful list.
This is awesome! So many helpful tips. I will be coming back to this often. Thanks for posting this!
Wow, so many goodies! Thank you for always providing such amazing content!!
I have enjoyed all these articles. Thank you for the help an inspiration to get my writing on its way. My creativity is boosting with confidence. Tootle loo.
Amazing contents for beginners like me Joe. I am highly inspired by your commitment. Thank you.
Hey, thanks!
Although I have only read half of thisc article, the practice exercises are excellent. Some of them are exactly what a beginning writer like myself needs. I am committing to at least try ALL of them. Thanks Joe!!
very helpful! thank you..
Amazing articles! Thanks so much for sharing!
My god this article made me love this site . You know it’s kinda hard for a beginner writer, who don’t know where to start and fixing goals, even samll ones give us a direction . A place to go , an aim for our creativity so thanks you , this community and this site. Love you all . At your pens ! 😉
Wow. This is great. I find all your posts informative, but this one is the best for me to use as a guide to get my self starting to write….Thank you.
I’m an old lady who wants to publish one more book before I die — have published several, all non-fiction, and done two under contract to a major publisher (reference books). So help me, the BIGGEST problem I have all along, is keeping track of the damned paper work and research that goes into a book!!! Yet I never ever see articles on something as simple as “How to file” — Oh I know, there’s wonderful software these days so probably I will never find a way to get paper organized — everybody will use software and do it on the computer. I’m too old for that — just one look at the learning curve for software, even putting the damned stuff into computer files is even MORE frustrating than paper!! Oh well, somehow I managed in the past to get books published, I may be able to do it one more time.
you enjoy writing more than anything else and you do indeed care to help others write. I love writing but translation from Arabic into English and English into Arabic is taking all of my time from the early hours of the morning till the evening. I will soon get all of your books in order to read them as soon as possible. One thing I am sure of. You know what you are doing very well. Hamzah
Excellent! Many useful tips. Many thanks!
Liz and Joe, I have only looked at a few exercises. Already, I am convinced that your site is one of the best sites out there. Thank your for sharing your wisdom.
Wow, these are the best lessons and exercises for writing. Actually i’m participating in a compitition this wendsday. so, i’m quite nervous and exited. this helped me a lot
Magnificent post ever I have read. This article will help me a lot to write a right way. Thank you.
i need your help to improve to become a better writer please. i think i usually commit moist of these errors and i don;t pay attention to many advices too.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Submit Comment
Join over 450,000 readers who are saying YES to practice. You’ll also get a free copy of our eBook 14 Prompts :
Popular Resources
Best Resources for Writers Book Writing Tips & Guides Creativity & Inspiration Tips Writing Prompts Grammar & Vocab Resources Best Book Writing Software ProWritingAid Review Writing Teacher Resources Publisher Rocket Review Scrivener Review Gifts for Writers
Books By Our Writers

You've got it! Just us where to send your guide.
Enter your email to get our free 10-step guide to becoming a writer.
You've got it! Just us where to send your book.
Enter your first name and email to get our free book, 14 Prompts.
Welcome to the new OASIS website! We have academic skills, library skills, math and statistics support, and writing resources all together in one new home.

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Common Assignments: Journal Entries
Basics of journal entries, related webinar.
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Writing a Successful Response to Another's Post
- Next Page: Read the Prompt Carefully
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Cost of Attendance
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.


- Subject Guides
Academic writing: a practical guide
- Structure & cohesion
- Academic writing
- The writing process
- Academic writing style
- Criticality in academic writing
- Working with evidence
- Referencing
- Assessment & feedback
- Dissertations
- Reflective writing
- Examination writing
- Academic posters
- Feedback on Structure and Organisation
- Feedback on Argument, Analysis, and Critical Thinking
- Feedback on Writing Style and Clarity
- Feedback on Referencing and Research
- Feedback on Presentation and Proofreading
Structure & cohesion
General advice for structuring all types of academic writing.
For advice on structuring specific types of writing, visit the relevant page under 'Types of academic writing'.
Structure in academic writing
Academic writing has a clear, logical structure to communicate your points and show the connections between them; a well-structured assignment is easy for the reader to follow and understand.
These general principles apply to structuring most types of academic writing:
- Use a linear structure where points build on each other - don't jump backward and forwards.
- Start with more general and then move to the more specific ideas and points.
- Put more relevant/important information first.
- Everything is relevant to the main argument or point of the paragraph.
- Use cohesion to join ideas and points clearly - don't make the reader do the work.
- Follow any structural requirements for your assignment or type of writing.
It has a beginning, a middle and an end: a guide to structuring academic writing [Google Slides]

Planning structure
The best way to write a well-structured assignment is to have a good plan before you start writing. What's your argument? What are the main points you want to include? What's a logical way to order these points? Don't just launch into writing with no idea of where you're going!
To make a general plan:
- Make a list of the information and points to include.
- Organise similar points into groups.
- Put the groups in a logical order.
- Within each group, organise the points logically.
- Check the plan to make sure it meets task requirements.
Here's a step-by-step demonstration of planning assignment structure:
Planning: general structure [YouTube] | Planning: general structure [Google Doc]
Paragraph structure
A well-structured paragraph contains one main point or idea - all the information included is relevant to this point. If it's not related to the main point, it probably shouldn't be there!
There are many ways to structure a paragraph, but they generally all include:
- a topic sentence showing the main point
- development of the point: more detail, examples etc.
- evidence to support the point
- critical analysis showing how evidence relates to the main point
- a final wrap-up linking to the overall argument or next paragraph
However, this is only a guide - there are many ways to structure a paragraph. Reading sources from your field will help you to get a feel of ways to organise paragraphs.
Paragraph structure [Google Slides]
If the structure is the order of your points, cohesion is what ties them together and guides the reader through your argument.
Create cohesion using words and phrases that show the relationships between points. For example:
- basic connectives: and, or, but, so
- giving more detail: for example, to illustrate, an example of this is
- showing contrast: however, although, while, conversely, alternatively
- showing similarity: another, also, similarly, collectively, taken together
- cause/effect: leading to, the effect of this is, therefore, this may stem from
- referencing words: this/that, who, which/that, the groups, these findings
- showing implications: this suggests that, these findings may mean that, based on this
Cohesive words and phrases are shown in bold in this example paragraph about how language background affects maths skills development :
The time taken to pronounce number words is another linguistic factor that could affect children’s arithmetical development. If number words take longer to pronounce, fewer items can be held in working memory, which could affect the strategies used to solve arithmetic problems (Geary et al., 1993; Geary et al., 1996). In East Asian languages, number words are generally short, one-syllable words, while in English and other languages they can be much longer. The effect of this on working memory is seen in Chinese children’s longer digit span memory compared to their American peers (Geary et al., 1993). It also seems to influence the choice of strategies used by the two groups to solve arithmetic problems, with Chinese children using faster processes than American children (Geary et al., 1996). This limitation of working memory may mean speakers of less transparent languages rely more on slow procedural strategies than speakers of a transparent language, extending even to adulthood (Campbell & Xue, 2001).
More detailed advice and examples:
- << Previous: Academic writing style
- Next: Criticality in academic writing >>
- Last Updated: Aug 7, 2024 2:21 PM
- URL: https://subjectguides.york.ac.uk/academic-writing

- General & Introductory Education
- Curriculum Tools- General

The English Teacher's Survival Guide: Ready-To-Use Techniques and Materials for Grades 7-12, 2nd Edition
ISBN: 978-0-470-52513-5
Jossey-Bass
Digital Evaluation Copy

Mary Lou Brandvik , Katherine S. McKnight
This unique time-saving book is packed with tested techniques and materials to assist new and experienced English teachers with virtually every phase of their job from lesson planning to effective discipline techniques. The book includes 175 easy-to-understand strategies, lessons, checklists, and forms for effective classroom management and over 50 reproducible samples teachers can adopt immediately for planning, evaluation, or assignments. It is filled with creative and functional ideas for reading response activities, writing assignments, group and individual projects, and speeches.
- Offers instructions for creating and implementing an effective classroom-wide behavior management program
- Shows how to practice the art of teaching English effectively and reduce time on labor intensive tasks
- Reveals how to work effectively with parents, colleagues, substitute teachers, administrators, and community resources
The second edition includes coverage of technology in the classroom, advice for working with reluctant readers, a wealth of sample teaching units and more.
Katherine S. McKnight , Ph.D. has been a literacy educator for over 20 years. A former high school English teacher, she is currently associate professor of secondary education at National-Louis University and a national consultant for National Council of Teachers of English. She is the author of The Teacher's Big Book of Graphic Organizers , also from Jossey-Bass.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research paper
How to Write a Research Paper | A Beginner's Guide
A research paper is a piece of academic writing that provides analysis, interpretation, and argument based on in-depth independent research.
Research papers are similar to academic essays , but they are usually longer and more detailed assignments, designed to assess not only your writing skills but also your skills in scholarly research. Writing a research paper requires you to demonstrate a strong knowledge of your topic, engage with a variety of sources, and make an original contribution to the debate.
This step-by-step guide takes you through the entire writing process, from understanding your assignment to proofreading your final draft.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Understand the assignment, choose a research paper topic, conduct preliminary research, develop a thesis statement, create a research paper outline, write a first draft of the research paper, write the introduction, write a compelling body of text, write the conclusion, the second draft, the revision process, research paper checklist, free lecture slides.
Completing a research paper successfully means accomplishing the specific tasks set out for you. Before you start, make sure you thoroughly understanding the assignment task sheet:
- Read it carefully, looking for anything confusing you might need to clarify with your professor.
- Identify the assignment goal, deadline, length specifications, formatting, and submission method.
- Make a bulleted list of the key points, then go back and cross completed items off as you’re writing.
Carefully consider your timeframe and word limit: be realistic, and plan enough time to research, write, and edit.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
There are many ways to generate an idea for a research paper, from brainstorming with pen and paper to talking it through with a fellow student or professor.
You can try free writing, which involves taking a broad topic and writing continuously for two or three minutes to identify absolutely anything relevant that could be interesting.
You can also gain inspiration from other research. The discussion or recommendations sections of research papers often include ideas for other specific topics that require further examination.
Once you have a broad subject area, narrow it down to choose a topic that interests you, m eets the criteria of your assignment, and i s possible to research. Aim for ideas that are both original and specific:
- A paper following the chronology of World War II would not be original or specific enough.
- A paper on the experience of Danish citizens living close to the German border during World War II would be specific and could be original enough.
Note any discussions that seem important to the topic, and try to find an issue that you can focus your paper around. Use a variety of sources , including journals, books, and reliable websites, to ensure you do not miss anything glaring.
Do not only verify the ideas you have in mind, but look for sources that contradict your point of view.
- Is there anything people seem to overlook in the sources you research?
- Are there any heated debates you can address?
- Do you have a unique take on your topic?
- Have there been some recent developments that build on the extant research?
In this stage, you might find it helpful to formulate some research questions to help guide you. To write research questions, try to finish the following sentence: “I want to know how/what/why…”
A thesis statement is a statement of your central argument — it establishes the purpose and position of your paper. If you started with a research question, the thesis statement should answer it. It should also show what evidence and reasoning you’ll use to support that answer.
The thesis statement should be concise, contentious, and coherent. That means it should briefly summarize your argument in a sentence or two, make a claim that requires further evidence or analysis, and make a coherent point that relates to every part of the paper.
You will probably revise and refine the thesis statement as you do more research, but it can serve as a guide throughout the writing process. Every paragraph should aim to support and develop this central claim.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

A research paper outline is essentially a list of the key topics, arguments, and evidence you want to include, divided into sections with headings so that you know roughly what the paper will look like before you start writing.
A structure outline can help make the writing process much more efficient, so it’s worth dedicating some time to create one.
Your first draft won’t be perfect — you can polish later on. Your priorities at this stage are as follows:
- Maintaining forward momentum — write now, perfect later.
- Paying attention to clear organization and logical ordering of paragraphs and sentences, which will help when you come to the second draft.
- Expressing your ideas as clearly as possible, so you know what you were trying to say when you come back to the text.
You do not need to start by writing the introduction. Begin where it feels most natural for you — some prefer to finish the most difficult sections first, while others choose to start with the easiest part. If you created an outline, use it as a map while you work.
Do not delete large sections of text. If you begin to dislike something you have written or find it doesn’t quite fit, move it to a different document, but don’t lose it completely — you never know if it might come in useful later.
Paragraph structure
Paragraphs are the basic building blocks of research papers. Each one should focus on a single claim or idea that helps to establish the overall argument or purpose of the paper.
Example paragraph
George Orwell’s 1946 essay “Politics and the English Language” has had an enduring impact on thought about the relationship between politics and language. This impact is particularly obvious in light of the various critical review articles that have recently referenced the essay. For example, consider Mark Falcoff’s 2009 article in The National Review Online, “The Perversion of Language; or, Orwell Revisited,” in which he analyzes several common words (“activist,” “civil-rights leader,” “diversity,” and more). Falcoff’s close analysis of the ambiguity built into political language intentionally mirrors Orwell’s own point-by-point analysis of the political language of his day. Even 63 years after its publication, Orwell’s essay is emulated by contemporary thinkers.
Citing sources
It’s also important to keep track of citations at this stage to avoid accidental plagiarism . Each time you use a source, make sure to take note of where the information came from.
You can use our free citation generators to automatically create citations and save your reference list as you go.
APA Citation Generator MLA Citation Generator
The research paper introduction should address three questions: What, why, and how? After finishing the introduction, the reader should know what the paper is about, why it is worth reading, and how you’ll build your arguments.
What? Be specific about the topic of the paper, introduce the background, and define key terms or concepts.
Why? This is the most important, but also the most difficult, part of the introduction. Try to provide brief answers to the following questions: What new material or insight are you offering? What important issues does your essay help define or answer?
How? To let the reader know what to expect from the rest of the paper, the introduction should include a “map” of what will be discussed, briefly presenting the key elements of the paper in chronological order.
The major struggle faced by most writers is how to organize the information presented in the paper, which is one reason an outline is so useful. However, remember that the outline is only a guide and, when writing, you can be flexible with the order in which the information and arguments are presented.
One way to stay on track is to use your thesis statement and topic sentences . Check:
- topic sentences against the thesis statement;
- topic sentences against each other, for similarities and logical ordering;
- and each sentence against the topic sentence of that paragraph.
Be aware of paragraphs that seem to cover the same things. If two paragraphs discuss something similar, they must approach that topic in different ways. Aim to create smooth transitions between sentences, paragraphs, and sections.
The research paper conclusion is designed to help your reader out of the paper’s argument, giving them a sense of finality.
Trace the course of the paper, emphasizing how it all comes together to prove your thesis statement. Give the paper a sense of finality by making sure the reader understands how you’ve settled the issues raised in the introduction.
You might also discuss the more general consequences of the argument, outline what the paper offers to future students of the topic, and suggest any questions the paper’s argument raises but cannot or does not try to answer.
You should not :
- Offer new arguments or essential information
- Take up any more space than necessary
- Begin with stock phrases that signal you are ending the paper (e.g. “In conclusion”)
There are four main considerations when it comes to the second draft.
- Check how your vision of the paper lines up with the first draft and, more importantly, that your paper still answers the assignment.
- Identify any assumptions that might require (more substantial) justification, keeping your reader’s perspective foremost in mind. Remove these points if you cannot substantiate them further.
- Be open to rearranging your ideas. Check whether any sections feel out of place and whether your ideas could be better organized.
- If you find that old ideas do not fit as well as you anticipated, you should cut them out or condense them. You might also find that new and well-suited ideas occurred to you during the writing of the first draft — now is the time to make them part of the paper.
The goal during the revision and proofreading process is to ensure you have completed all the necessary tasks and that the paper is as well-articulated as possible. You can speed up the proofreading process by using the AI proofreader .
Global concerns
- Confirm that your paper completes every task specified in your assignment sheet.
- Check for logical organization and flow of paragraphs.
- Check paragraphs against the introduction and thesis statement.
Fine-grained details
Check the content of each paragraph, making sure that:
- each sentence helps support the topic sentence.
- no unnecessary or irrelevant information is present.
- all technical terms your audience might not know are identified.
Next, think about sentence structure , grammatical errors, and formatting . Check that you have correctly used transition words and phrases to show the connections between your ideas. Look for typos, cut unnecessary words, and check for consistency in aspects such as heading formatting and spellings .
Finally, you need to make sure your paper is correctly formatted according to the rules of the citation style you are using. For example, you might need to include an MLA heading or create an APA title page .
Scribbr’s professional editors can help with the revision process with our award-winning proofreading services.
Discover our paper editing service
Checklist: Research paper
I have followed all instructions in the assignment sheet.
My introduction presents my topic in an engaging way and provides necessary background information.
My introduction presents a clear, focused research problem and/or thesis statement .
My paper is logically organized using paragraphs and (if relevant) section headings .
Each paragraph is clearly focused on one central idea, expressed in a clear topic sentence .
Each paragraph is relevant to my research problem or thesis statement.
I have used appropriate transitions to clarify the connections between sections, paragraphs, and sentences.
My conclusion provides a concise answer to the research question or emphasizes how the thesis has been supported.
My conclusion shows how my research has contributed to knowledge or understanding of my topic.
My conclusion does not present any new points or information essential to my argument.
I have provided an in-text citation every time I refer to ideas or information from a source.
I have included a reference list at the end of my paper, consistently formatted according to a specific citation style .
I have thoroughly revised my paper and addressed any feedback from my professor or supervisor.
I have followed all formatting guidelines (page numbers, headers, spacing, etc.).
You've written a great paper. Make sure it's perfect with the help of a Scribbr editor!
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- Writing a Research Paper Introduction | Step-by-Step Guide
- Writing a Research Paper Conclusion | Step-by-Step Guide
- Research Paper Format | APA, MLA, & Chicago Templates
More interesting articles
- Academic Paragraph Structure | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
- Checklist: Writing a Great Research Paper
- How to Create a Structured Research Paper Outline | Example
- How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples
- How to Write Recommendations in Research | Examples & Tips
- How to Write Topic Sentences | 4 Steps, Examples & Purpose
- Research Paper Appendix | Example & Templates
- Research Paper Damage Control | Managing a Broken Argument
- What Is a Theoretical Framework? | Guide to Organizing
What is your plagiarism score?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learn the essay writing process, from preparation to revision, with this beginner's guide. Find out how to choose a topic, do research, create an outline, write an introduction, body, and conclusion, and check your essay for errors.
Learn the steps to write an English assignment, from choosing a topic to proofreading and submitting. Find tips on research, structure, language, and expert help.
Learn how to plan, draft, revise, and edit your academic texts with this step-by-step guide. Find examples, tips, and tools for different types of texts, such as essays and research papers.
Learn how to read an assignment prompt, ask analytical questions, develop a thesis, and organize your essay. This guide offers tips and examples for different types of essays, such as research papers, comparative essays, and argumentative essays.
Learn how to read and interpret college writing assignments by identifying the task, audience, evidence, style, and format. This handout provides tips, examples, and key terms to help you unravel your assignment and craft an effective response.
Learn how to write an essay with a clear thesis, logical structure, and persuasive evidence. Follow the five-step process of brainstorming, preparing, drafting, revising, and proofreading, and get tips on different types of essays and common mistakes.
Learn how to create clear and effective essay assignments that help students develop their writing skills and master the material. Find tips on naming the purpose, audience, and criteria of the paper, preparing students in class, and building in process.
Learn how to write a good introduction paragraph for your academic essay with this guide. It covers the main goals, steps and tips for hooking your reader, giving background information, presenting your thesis statement and mapping your essay structure.
This web page offers a comprehensive guide to academic essay writing, with links to resources on topics, arguments, outlines, and more. It does not provide any essay writing service or help, but only advice and information for students who want to improve their own skills.
5. Write an outline to help organize your main points. After you've created a clear thesis, briefly list the major points you will be making in your essay. You don't need to include a lot of detail—just write 1-2 sentences, or even a few words, outlining what each point or argument will be.
Learn how to read an assignment prompt, ask analytical questions, write a thesis, organize your essay, and more. Download PDFs and access email writing center for tips and guidance on writing in different disciplines.
Learn how to structure, plan, and write an assignment using Word with this comprehensive guide. Find tips on research, formatting, citation, and expert help from PapersOwl.
Learn how to write different types of academic papers, such as essays, book reports, research papers, and annotated bibliographies. Find guidelines, examples, and tips for each assignment type.
Learn how to write an effective assignment with four key steps: research, structure, writing, and proofreading. Find out how to start with research, prepare assignment structure, write a gripping introduction and conclusion, and use paraphrasing and citation tools.
Learn 15 foolproof tips for writing a great assignment, from planning your time and structure to citing your sources and checking your spelling. This blog post is aimed at students who want to improve their academic writing skills and avoid common pitfalls.
Learn how to identify and complete different types of writing tasks in college, such as summary, defined-topic, and undefined-topic assignments. Find tips on how to understand the assignment prompt, use effective summarizing language, and get started with a free-write.
Learn how to decipher the paper assignment by reading the prompt carefully, underlining important phrases, and thinking about the purpose, audience, and resources. The web page does not explain the verbs used to explain a writing assignment, but it provides examples of different types of assignments and their requirements.
Learn how to write better with 100+ writing practice lessons and exercises on The Write Practice. Whether you want to write novels, essays, stories, or blogs, you can find tips, prompts, and feedback to improve your skills.
Learn how to write a report for academic, business, or scientific purposes with this comprehensive guide. Find out the types, structure, and requirements of different report formats, and follow the 7 steps to write a report effectively.
At the Walden Library you can email a Librarian through our Ask a Librarian email service. This service is open seven days a week, and is available to all students, as well as faculty and staff. You can email about finding articles or locating online journals, or anything Library related. You can expect a response from the Library within 24 hours.
Learn how to write academic papers in a formal and unbiased style, with clear and precise language, focused and well structured arguments, and well sourced evidence. Find out the types of academic writing, the conventions of different fields, and the useful tools for editing and citing.
Follow any structural requirements for your assignment or type of writing. It has a beginning, a middle and an end: a guide to structuring academic writing [Google Slides] ... 1996). In East Asian languages, number words are generally short, one-syllable words, while in English and other languages they can be much longer. The effect of this on ...
It is filled with creative and functional ideas for reading response activities, writing assignments, group and individual projects, and speeches. Offers instructions for creating and implementing an effective classroom-wide behavior management program Shows how to practice the art of teaching English effectively and reduce time on labor ...
This guide will help you find sources for your Comp I/ENGL 1301 Fifth Writing Assignment, Comparison Essay. Use the tabs above to find sources for your paper, and to find examples of in-text and Works Cited citations in MLA style.
Learn how to choose a research paper topic, conduct preliminary research, develop a thesis statement, create an outline, and write a first draft. This guide covers the basics of academic writing, from understanding the assignment to proofreading your final draft.
Get your creativity flowing with generated writing prompts. Build an outline or structure from the key points you want to include. Generate a first paragraph to build upon. You can go back and revise or delete it later. Find that word that's on the tip of your tongue. 3. Strengthen an existing piece of writing.