Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey


What is a Theoretical Framework? How to Write It (with Examples)

Theoretical framework 1,2 is the structure that supports and describes a theory. A theory is a set of interrelated concepts and definitions that present a systematic view of phenomena by describing the relationship among the variables for explaining these phenomena. A theory is developed after a long research process and explains the existence of a research problem in a study. A theoretical framework guides the research process like a roadmap for the research study and helps researchers clearly interpret their findings by providing a structure for organizing data and developing conclusions.
A theoretical framework in research is an important part of a manuscript and should be presented in the first section. It shows an understanding of the theories and concepts relevant to the research and helps limit the scope of the research.
Table of Contents
What is a theoretical framework ?
A theoretical framework in research can be defined as a set of concepts, theories, ideas, and assumptions that help you understand a specific phenomenon or problem. It can be considered a blueprint that is borrowed by researchers to develop their own research inquiry. A theoretical framework in research helps researchers design and conduct their research and analyze and interpret their findings. It explains the relationship between variables, identifies gaps in existing knowledge, and guides the development of research questions, hypotheses, and methodologies to address that gap.

Now that you know the answer to ‘ What is a theoretical framework? ’, check the following table that lists the different types of theoretical frameworks in research: 3
| Conceptual | Defines key concepts and relationships |
| Deductive | Starts with a general hypothesis and then uses data to test it; used in quantitative research |
| Inductive | Starts with data and then develops a hypothesis; used in qualitative research |
| Empirical | Focuses on the collection and analysis of empirical data; used in scientific research |
| Normative | Defines a set of norms that guide behavior; used in ethics and social sciences |
| Explanatory | Explains causes of particular behavior; used in psychology and social sciences |
Developing a theoretical framework in research can help in the following situations: 4
- When conducting research on complex phenomena because a theoretical framework helps organize the research questions, hypotheses, and findings
- When the research problem requires a deeper understanding of the underlying concepts
- When conducting research that seeks to address a specific gap in knowledge
- When conducting research that involves the analysis of existing theories
Summarizing existing literature for theoretical frameworks is easy. Get our Research Ideation pack
Importance of a theoretical framework
The purpose of theoretical framework s is to support you in the following ways during the research process: 2
- Provide a structure for the complete research process
- Assist researchers in incorporating formal theories into their study as a guide
- Provide a broad guideline to maintain the research focus
- Guide the selection of research methods, data collection, and data analysis
- Help understand the relationships between different concepts and develop hypotheses and research questions
- Address gaps in existing literature
- Analyze the data collected and draw meaningful conclusions and make the findings more generalizable
Theoretical vs. Conceptual framework
While a theoretical framework covers the theoretical aspect of your study, that is, the various theories that can guide your research, a conceptual framework defines the variables for your study and presents how they relate to each other. The conceptual framework is developed before collecting the data. However, both frameworks help in understanding the research problem and guide the development, collection, and analysis of the research.
The following table lists some differences between conceptual and theoretical frameworks . 5
| Based on existing theories that have been tested and validated by others | Based on concepts that are the main variables in the study |
| Used to create a foundation of the theory on which your study will be developed | Visualizes the relationships between the concepts and variables based on the existing literature |
| Used to test theories, to predict and control the situations within the context of a research inquiry | Helps the development of a theory that would be useful to practitioners |
| Provides a general set of ideas within which a study belongs | Refers to specific ideas that researchers utilize in their study |
| Offers a focal point for approaching unknown research in a specific field of inquiry | Shows logically how the research inquiry should be undertaken |
| Works deductively | Works inductively |
| Used in quantitative studies | Used in qualitative studies |

How to write a theoretical framework
The following general steps can help those wondering how to write a theoretical framework: 2
- Identify and define the key concepts clearly and organize them into a suitable structure.
- Use appropriate terminology and define all key terms to ensure consistency.
- Identify the relationships between concepts and provide a logical and coherent structure.
- Develop hypotheses that can be tested through data collection and analysis.
- Keep it concise and focused with clear and specific aims.
Write a theoretical framework 2x faster. Get our Manuscript Writing pack
Examples of a theoretical framework
Here are two examples of a theoretical framework. 6,7
Example 1 .
An insurance company is facing a challenge cross-selling its products. The sales department indicates that most customers have just one policy, although the company offers over 10 unique policies. The company would want its customers to purchase more than one policy since most customers are purchasing policies from other companies.
Objective : To sell more insurance products to existing customers.
Problem : Many customers are purchasing additional policies from other companies.
Research question : How can customer product awareness be improved to increase cross-selling of insurance products?
Sub-questions: What is the relationship between product awareness and sales? Which factors determine product awareness?
Since “product awareness” is the main focus in this study, the theoretical framework should analyze this concept and study previous literature on this subject and propose theories that discuss the relationship between product awareness and its improvement in sales of other products.
Example 2 .
A company is facing a continued decline in its sales and profitability. The main reason for the decline in the profitability is poor services, which have resulted in a high level of dissatisfaction among customers and consequently a decline in customer loyalty. The management is planning to concentrate on clients’ satisfaction and customer loyalty.
Objective: To provide better service to customers and increase customer loyalty and satisfaction.
Problem: Continued decrease in sales and profitability.
Research question: How can customer satisfaction help in increasing sales and profitability?
Sub-questions: What is the relationship between customer loyalty and sales? Which factors influence the level of satisfaction gained by customers?
Since customer satisfaction, loyalty, profitability, and sales are the important topics in this example, the theoretical framework should focus on these concepts.
Benefits of a theoretical framework
There are several benefits of a theoretical framework in research: 2
- Provides a structured approach allowing researchers to organize their thoughts in a coherent way.
- Helps to identify gaps in knowledge highlighting areas where further research is needed.
- Increases research efficiency by providing a clear direction for research and focusing efforts on relevant data.
- Improves the quality of research by providing a rigorous and systematic approach to research, which can increase the likelihood of producing valid and reliable results.
- Provides a basis for comparison by providing a common language and conceptual framework for researchers to compare their findings with other research in the field, facilitating the exchange of ideas and the development of new knowledge.

Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. How do I develop a theoretical framework ? 7
A1. The following steps can be used for developing a theoretical framework :
- Identify the research problem and research questions by clearly defining the problem that the research aims to address and identifying the specific questions that the research aims to answer.
- Review the existing literature to identify the key concepts that have been studied previously. These concepts should be clearly defined and organized into a structure.
- Develop propositions that describe the relationships between the concepts. These propositions should be based on the existing literature and should be testable.
- Develop hypotheses that can be tested through data collection and analysis.
- Test the theoretical framework through data collection and analysis to determine whether the framework is valid and reliable.
Q2. How do I know if I have developed a good theoretical framework or not? 8
A2. The following checklist could help you answer this question:
- Is my theoretical framework clearly seen as emerging from my literature review?
- Is it the result of my analysis of the main theories previously studied in my same research field?
- Does it represent or is it relevant to the most current state of theoretical knowledge on my topic?
- Does the theoretical framework in research present a logical, coherent, and analytical structure that will support my data analysis?
- Do the different parts of the theory help analyze the relationships among the variables in my research?
- Does the theoretical framework target how I will answer my research questions or test the hypotheses?
- Have I documented every source I have used in developing this theoretical framework ?
- Is my theoretical framework a model, a table, a figure, or a description?
- Have I explained why this is the appropriate theoretical framework for my data analysis?
Q3. Can I use multiple theoretical frameworks in a single study?
A3. Using multiple theoretical frameworks in a single study is acceptable as long as each theory is clearly defined and related to the study. Each theory should also be discussed individually. This approach may, however, be tedious and effort intensive. Therefore, multiple theoretical frameworks should be used only if absolutely necessary for the study.
Q4. Is it necessary to include a theoretical framework in every research study?
A4. The theoretical framework connects researchers to existing knowledge. So, including a theoretical framework would help researchers get a clear idea about the research process and help structure their study effectively by clearly defining an objective, a research problem, and a research question.
Q5. Can a theoretical framework be developed for qualitative research?
A5. Yes, a theoretical framework can be developed for qualitative research. However, qualitative research methods may or may not involve a theory developed beforehand. In these studies, a theoretical framework can guide the study and help develop a theory during the data analysis phase. This resulting framework uses inductive reasoning. The outcome of this inductive approach can be referred to as an emergent theoretical framework . This method helps researchers develop a theory inductively, which explains a phenomenon without a guiding framework at the outset.

Q6. What is the main difference between a literature review and a theoretical framework ?
A6. A literature review explores already existing studies about a specific topic in order to highlight a gap, which becomes the focus of the current research study. A theoretical framework can be considered the next step in the process, in which the researcher plans a specific conceptual and analytical approach to address the identified gap in the research.
Theoretical frameworks are thus important components of the research process and researchers should therefore devote ample amount of time to develop a solid theoretical framework so that it can effectively guide their research in a suitable direction. We hope this article has provided a good insight into the concept of theoretical frameworks in research and their benefits.
References
- Organizing academic research papers: Theoretical framework. Sacred Heart University library. Accessed August 4, 2023. https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803&p=185919#:~:text=The%20theoretical%20framework%20is%20the,research%20problem%20under%20study%20exists .
- Salomao A. Understanding what is theoretical framework. Mind the Graph website. Accessed August 5, 2023. https://mindthegraph.com/blog/what-is-theoretical-framework/
- Theoretical framework—Types, examples, and writing guide. Research Method website. Accessed August 6, 2023. https://researchmethod.net/theoretical-framework/
- Grant C., Osanloo A. Understanding, selecting, and integrating a theoretical framework in dissertation research: Creating the blueprint for your “house.” Administrative Issues Journal : Connecting Education, Practice, and Research; 4(2):12-26. 2014. Accessed August 7, 2023. https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1058505.pdf
- Difference between conceptual framework and theoretical framework. MIM Learnovate website. Accessed August 7, 2023. https://mimlearnovate.com/difference-between-conceptual-framework-and-theoretical-framework/
- Example of a theoretical framework—Thesis & dissertation. BacherlorPrint website. Accessed August 6, 2023. https://www.bachelorprint.com/dissertation/example-of-a-theoretical-framework/
- Sample theoretical framework in dissertation and thesis—Overview and example. Students assignment help website. Accessed August 6, 2023. https://www.studentsassignmenthelp.co.uk/blogs/sample-dissertation-theoretical-framework/#Example_of_the_theoretical_framework
- Kivunja C. Distinguishing between theory, theoretical framework, and conceptual framework: A systematic review of lessons from the field. Accessed August 8, 2023. https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1198682.pdf
Editage All Access is a subscription-based platform that unifies the best AI tools and services designed to speed up, simplify, and streamline every step of a researcher’s journey. The Editage All Access Pack is a one-of-a-kind subscription that unlocks full access to an AI writing assistant, literature recommender, journal finder, scientific illustration tool, and exclusive discounts on professional publication services from Editage.
Based on 22+ years of experience in academia, Editage All Access empowers researchers to put their best research forward and move closer to success. Explore our top AI Tools pack, AI Tools + Publication Services pack, or Build Your Own Plan. Find everything a researcher needs to succeed, all in one place – Get All Access now starting at just $14 a month !
Related Posts

Back to School – Lock-in All Access Pack for a Year at the Best Price

Journal Turnaround Time: Researcher.Life and Scholarly Intelligence Join Hands to Empower Researchers with Publication Time Insights
- Privacy Policy

Home » Theoretical Framework – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Theoretical Framework – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Theoretical Framework
Definition:
Theoretical framework refers to a set of concepts, theories, ideas , and assumptions that serve as a foundation for understanding a particular phenomenon or problem. It provides a conceptual framework that helps researchers to design and conduct their research, as well as to analyze and interpret their findings.
In research, a theoretical framework explains the relationship between various variables, identifies gaps in existing knowledge, and guides the development of research questions, hypotheses, and methodologies. It also helps to contextualize the research within a broader theoretical perspective, and can be used to guide the interpretation of results and the formulation of recommendations.
Types of Theoretical Framework
Types of Types of Theoretical Framework are as follows:
Conceptual Framework
This type of framework defines the key concepts and relationships between them. It helps to provide a theoretical foundation for a study or research project .
Deductive Framework
This type of framework starts with a general theory or hypothesis and then uses data to test and refine it. It is often used in quantitative research .
Inductive Framework
This type of framework starts with data and then develops a theory or hypothesis based on the patterns and themes that emerge from the data. It is often used in qualitative research .
Empirical Framework
This type of framework focuses on the collection and analysis of empirical data, such as surveys or experiments. It is often used in scientific research .
Normative Framework
This type of framework defines a set of norms or values that guide behavior or decision-making. It is often used in ethics and social sciences.
Explanatory Framework
This type of framework seeks to explain the underlying mechanisms or causes of a particular phenomenon or behavior. It is often used in psychology and social sciences.
Components of Theoretical Framework
The components of a theoretical framework include:
- Concepts : The basic building blocks of a theoretical framework. Concepts are abstract ideas or generalizations that represent objects, events, or phenomena.
- Variables : These are measurable and observable aspects of a concept. In a research context, variables can be manipulated or measured to test hypotheses.
- Assumptions : These are beliefs or statements that are taken for granted and are not tested in a study. They provide a starting point for developing hypotheses.
- Propositions : These are statements that explain the relationships between concepts and variables in a theoretical framework.
- Hypotheses : These are testable predictions that are derived from the theoretical framework. Hypotheses are used to guide data collection and analysis.
- Constructs : These are abstract concepts that cannot be directly measured but are inferred from observable variables. Constructs provide a way to understand complex phenomena.
- Models : These are simplified representations of reality that are used to explain, predict, or control a phenomenon.
How to Write Theoretical Framework
A theoretical framework is an essential part of any research study or paper, as it helps to provide a theoretical basis for the research and guide the analysis and interpretation of the data. Here are some steps to help you write a theoretical framework:
- Identify the key concepts and variables : Start by identifying the main concepts and variables that your research is exploring. These could include things like motivation, behavior, attitudes, or any other relevant concepts.
- Review relevant literature: Conduct a thorough review of the existing literature in your field to identify key theories and ideas that relate to your research. This will help you to understand the existing knowledge and theories that are relevant to your research and provide a basis for your theoretical framework.
- Develop a conceptual framework : Based on your literature review, develop a conceptual framework that outlines the key concepts and their relationships. This framework should provide a clear and concise overview of the theoretical perspective that underpins your research.
- Identify hypotheses and research questions: Based on your conceptual framework, identify the hypotheses and research questions that you want to test or explore in your research.
- Test your theoretical framework: Once you have developed your theoretical framework, test it by applying it to your research data. This will help you to identify any gaps or weaknesses in your framework and refine it as necessary.
- Write up your theoretical framework: Finally, write up your theoretical framework in a clear and concise manner, using appropriate terminology and referencing the relevant literature to support your arguments.
Theoretical Framework Examples
Here are some examples of theoretical frameworks:
- Social Learning Theory : This framework, developed by Albert Bandura, suggests that people learn from their environment, including the behaviors of others, and that behavior is influenced by both external and internal factors.
- Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs : Abraham Maslow proposed that human needs are arranged in a hierarchy, with basic physiological needs at the bottom, followed by safety, love and belonging, esteem, and self-actualization at the top. This framework has been used in various fields, including psychology and education.
- Ecological Systems Theory : This framework, developed by Urie Bronfenbrenner, suggests that a person’s development is influenced by the interaction between the individual and the various environments in which they live, such as family, school, and community.
- Feminist Theory: This framework examines how gender and power intersect to influence social, cultural, and political issues. It emphasizes the importance of understanding and challenging systems of oppression.
- Cognitive Behavioral Theory: This framework suggests that our thoughts, beliefs, and attitudes influence our behavior, and that changing our thought patterns can lead to changes in behavior and emotional responses.
- Attachment Theory: This framework examines the ways in which early relationships with caregivers shape our later relationships and attachment styles.
- Critical Race Theory : This framework examines how race intersects with other forms of social stratification and oppression to perpetuate inequality and discrimination.
When to Have A Theoretical Framework
Following are some situations When to Have A Theoretical Framework:
- A theoretical framework should be developed when conducting research in any discipline, as it provides a foundation for understanding the research problem and guiding the research process.
- A theoretical framework is essential when conducting research on complex phenomena, as it helps to organize and structure the research questions, hypotheses, and findings.
- A theoretical framework should be developed when the research problem requires a deeper understanding of the underlying concepts and principles that govern the phenomenon being studied.
- A theoretical framework is particularly important when conducting research in social sciences, as it helps to explain the relationships between variables and provides a framework for testing hypotheses.
- A theoretical framework should be developed when conducting research in applied fields, such as engineering or medicine, as it helps to provide a theoretical basis for the development of new technologies or treatments.
- A theoretical framework should be developed when conducting research that seeks to address a specific gap in knowledge, as it helps to define the problem and identify potential solutions.
- A theoretical framework is also important when conducting research that involves the analysis of existing theories or concepts, as it helps to provide a framework for comparing and contrasting different theories and concepts.
- A theoretical framework should be developed when conducting research that seeks to make predictions or develop generalizations about a particular phenomenon, as it helps to provide a basis for evaluating the accuracy of these predictions or generalizations.
- Finally, a theoretical framework should be developed when conducting research that seeks to make a contribution to the field, as it helps to situate the research within the broader context of the discipline and identify its significance.
Purpose of Theoretical Framework
The purposes of a theoretical framework include:
- Providing a conceptual framework for the study: A theoretical framework helps researchers to define and clarify the concepts and variables of interest in their research. It enables researchers to develop a clear and concise definition of the problem, which in turn helps to guide the research process.
- Guiding the research design: A theoretical framework can guide the selection of research methods, data collection techniques, and data analysis procedures. By outlining the key concepts and assumptions underlying the research questions, the theoretical framework can help researchers to identify the most appropriate research design for their study.
- Supporting the interpretation of research findings: A theoretical framework provides a framework for interpreting the research findings by helping researchers to make connections between their findings and existing theory. It enables researchers to identify the implications of their findings for theory development and to assess the generalizability of their findings.
- Enhancing the credibility of the research: A well-developed theoretical framework can enhance the credibility of the research by providing a strong theoretical foundation for the study. It demonstrates that the research is based on a solid understanding of the relevant theory and that the research questions are grounded in a clear conceptual framework.
- Facilitating communication and collaboration: A theoretical framework provides a common language and conceptual framework for researchers, enabling them to communicate and collaborate more effectively. It helps to ensure that everyone involved in the research is working towards the same goals and is using the same concepts and definitions.
Characteristics of Theoretical Framework
Some of the characteristics of a theoretical framework include:
- Conceptual clarity: The concepts used in the theoretical framework should be clearly defined and understood by all stakeholders.
- Logical coherence : The framework should be internally consistent, with each concept and assumption logically connected to the others.
- Empirical relevance: The framework should be based on empirical evidence and research findings.
- Parsimony : The framework should be as simple as possible, without sacrificing its ability to explain the phenomenon in question.
- Flexibility : The framework should be adaptable to new findings and insights.
- Testability : The framework should be testable through research, with clear hypotheses that can be falsified or supported by data.
- Applicability : The framework should be useful for practical applications, such as designing interventions or policies.
Advantages of Theoretical Framework
Here are some of the advantages of having a theoretical framework:
- Provides a clear direction : A theoretical framework helps researchers to identify the key concepts and variables they need to study and the relationships between them. This provides a clear direction for the research and helps researchers to focus their efforts and resources.
- Increases the validity of the research: A theoretical framework helps to ensure that the research is based on sound theoretical principles and concepts. This increases the validity of the research by ensuring that it is grounded in established knowledge and is not based on arbitrary assumptions.
- Enables comparisons between studies : A theoretical framework provides a common language and set of concepts that researchers can use to compare and contrast their findings. This helps to build a cumulative body of knowledge and allows researchers to identify patterns and trends across different studies.
- Helps to generate hypotheses: A theoretical framework provides a basis for generating hypotheses about the relationships between different concepts and variables. This can help to guide the research process and identify areas that require further investigation.
- Facilitates communication: A theoretical framework provides a common language and set of concepts that researchers can use to communicate their findings to other researchers and to the wider community. This makes it easier for others to understand the research and its implications.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Thesis Format – Templates and Samples

Research Paper Outline – Types, Example, Template

Dissertation vs Thesis – Key Differences

Research Topics – Ideas and Examples

Data Verification – Process, Types and Examples

Research Contribution – Thesis Guide
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
What is a Theoretical Framework? | A Step-by-Step Guide
Published on 14 February 2020 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 10 October 2022.
A theoretical framework is a foundational review of existing theories that serves as a roadmap for developing the arguments you will use in your own work.
Theories are developed by researchers to explain phenomena, draw connections, and make predictions. In a theoretical framework, you explain the existing theories that support your research, showing that your work is grounded in established ideas.
In other words, your theoretical framework justifies and contextualises your later research, and it’s a crucial first step for your research paper , thesis, or dissertation . A well-rounded theoretical framework sets you up for success later on in your research and writing process.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Why do you need a theoretical framework, how to write a theoretical framework, structuring your theoretical framework, example of a theoretical framework, frequently asked questions about theoretical frameworks.
Before you start your own research, it’s crucial to familiarise yourself with the theories and models that other researchers have already developed. Your theoretical framework is your opportunity to present and explain what you’ve learned, situated within your future research topic.
There’s a good chance that many different theories about your topic already exist, especially if the topic is broad. In your theoretical framework, you will evaluate, compare, and select the most relevant ones.
By “framing” your research within a clearly defined field, you make the reader aware of the assumptions that inform your approach, showing the rationale behind your choices for later sections, like methodology and discussion . This part of your dissertation lays the foundations that will support your analysis, helping you interpret your results and make broader generalisations .
- In literature , a scholar using postmodernist literary theory would analyse The Great Gatsby differently than a scholar using Marxist literary theory.
- In psychology , a behaviourist approach to depression would involve different research methods and assumptions than a psychoanalytic approach.
- In economics , wealth inequality would be explained and interpreted differently based on a classical economics approach than based on a Keynesian economics one.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
To create your own theoretical framework, you can follow these three steps:
- Identifying your key concepts
- Evaluating and explaining relevant theories
- Showing how your research fits into existing research
1. Identify your key concepts
The first step is to pick out the key terms from your problem statement and research questions . Concepts often have multiple definitions, so your theoretical framework should also clearly define what you mean by each term.
To investigate this problem, you have identified and plan to focus on the following problem statement, objective, and research questions:
Problem : Many online customers do not return to make subsequent purchases.
Objective : To increase the quantity of return customers.
Research question : How can the satisfaction of company X’s online customers be improved in order to increase the quantity of return customers?
2. Evaluate and explain relevant theories
By conducting a thorough literature review , you can determine how other researchers have defined these key concepts and drawn connections between them. As you write your theoretical framework, your aim is to compare and critically evaluate the approaches that different authors have taken.
After discussing different models and theories, you can establish the definitions that best fit your research and justify why. You can even combine theories from different fields to build your own unique framework if this better suits your topic.
Make sure to at least briefly mention each of the most important theories related to your key concepts. If there is a well-established theory that you don’t want to apply to your own research, explain why it isn’t suitable for your purposes.
3. Show how your research fits into existing research
Apart from summarising and discussing existing theories, your theoretical framework should show how your project will make use of these ideas and take them a step further.
You might aim to do one or more of the following:
- Test whether a theory holds in a specific, previously unexamined context
- Use an existing theory as a basis for interpreting your results
- Critique or challenge a theory
- Combine different theories in a new or unique way
A theoretical framework can sometimes be integrated into a literature review chapter , but it can also be included as its own chapter or section in your dissertation. As a rule of thumb, if your research involves dealing with a lot of complex theories, it’s a good idea to include a separate theoretical framework chapter.
There are no fixed rules for structuring your theoretical framework, but it’s best to double-check with your department or institution to make sure they don’t have any formatting guidelines. The most important thing is to create a clear, logical structure. There are a few ways to do this:
- Draw on your research questions, structuring each section around a question or key concept
- Organise by theory cluster
- Organise by date
As in all other parts of your research paper , thesis, or dissertation , make sure to properly cite your sources to avoid plagiarism .
To get a sense of what this part of your thesis or dissertation might look like, take a look at our full example .
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
While a theoretical framework describes the theoretical underpinnings of your work based on existing research, a conceptual framework allows you to draw your own conclusions, mapping out the variables you may use in your study and the interplay between them.
A literature review and a theoretical framework are not the same thing and cannot be used interchangeably. While a theoretical framework describes the theoretical underpinnings of your work, a literature review critically evaluates existing research relating to your topic. You’ll likely need both in your dissertation .
A theoretical framework can sometimes be integrated into a literature review chapter , but it can also be included as its own chapter or section in your dissertation . As a rule of thumb, if your research involves dealing with a lot of complex theories, it’s a good idea to include a separate theoretical framework chapter.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a dissertation , thesis, research paper , or proposal .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, October 10). What is a Theoretical Framework? | A Step-by-Step Guide. Scribbr. Retrieved 3 September 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/the-theoretical-framework/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples, how to write a results section | tips & examples, how to write a discussion section | tips & examples.

Theoretical vs Conceptual Framework
What they are & how they’re different (with examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) | March 2023
If you’re new to academic research, sooner or later you’re bound to run into the terms theoretical framework and conceptual framework . These are closely related but distinctly different things (despite some people using them interchangeably) and it’s important to understand what each means. In this post, we’ll unpack both theoretical and conceptual frameworks in plain language along with practical examples , so that you can approach your research with confidence.
Overview: Theoretical vs Conceptual
What is a theoretical framework, example of a theoretical framework, what is a conceptual framework, example of a conceptual framework.
- Theoretical vs conceptual: which one should I use?
A theoretical framework (also sometimes referred to as a foundation of theory) is essentially a set of concepts, definitions, and propositions that together form a structured, comprehensive view of a specific phenomenon.
In other words, a theoretical framework is a collection of existing theories, models and frameworks that provides a foundation of core knowledge – a “lay of the land”, so to speak, from which you can build a research study. For this reason, it’s usually presented fairly early within the literature review section of a dissertation, thesis or research paper .

Let’s look at an example to make the theoretical framework a little more tangible.
If your research aims involve understanding what factors contributed toward people trusting investment brokers, you’d need to first lay down some theory so that it’s crystal clear what exactly you mean by this. For example, you would need to define what you mean by “trust”, as there are many potential definitions of this concept. The same would be true for any other constructs or variables of interest.
You’d also need to identify what existing theories have to say in relation to your research aim. In this case, you could discuss some of the key literature in relation to organisational trust. A quick search on Google Scholar using some well-considered keywords generally provides a good starting point.
Typically, you’ll present your theoretical framework in written form , although sometimes it will make sense to utilise some visuals to show how different theories relate to each other. Your theoretical framework may revolve around just one major theory , or it could comprise a collection of different interrelated theories and models. In some cases, there will be a lot to cover and in some cases, not. Regardless of size, the theoretical framework is a critical ingredient in any study.
Simply put, the theoretical framework is the core foundation of theory that you’ll build your research upon. As we’ve mentioned many times on the blog, good research is developed by standing on the shoulders of giants . It’s extremely unlikely that your research topic will be completely novel and that there’ll be absolutely no existing theory that relates to it. If that’s the case, the most likely explanation is that you just haven’t reviewed enough literature yet! So, make sure that you take the time to review and digest the seminal sources.
Need a helping hand?
A conceptual framework is typically a visual representation (although it can also be written out) of the expected relationships and connections between various concepts, constructs or variables. In other words, a conceptual framework visualises how the researcher views and organises the various concepts and variables within their study. This is typically based on aspects drawn from the theoretical framework, so there is a relationship between the two.
Quite commonly, conceptual frameworks are used to visualise the potential causal relationships and pathways that the researcher expects to find, based on their understanding of both the theoretical literature and the existing empirical research . Therefore, the conceptual framework is often used to develop research questions and hypotheses .
Let’s look at an example of a conceptual framework to make it a little more tangible. You’ll notice that in this specific conceptual framework, the hypotheses are integrated into the visual, helping to connect the rest of the document to the framework.
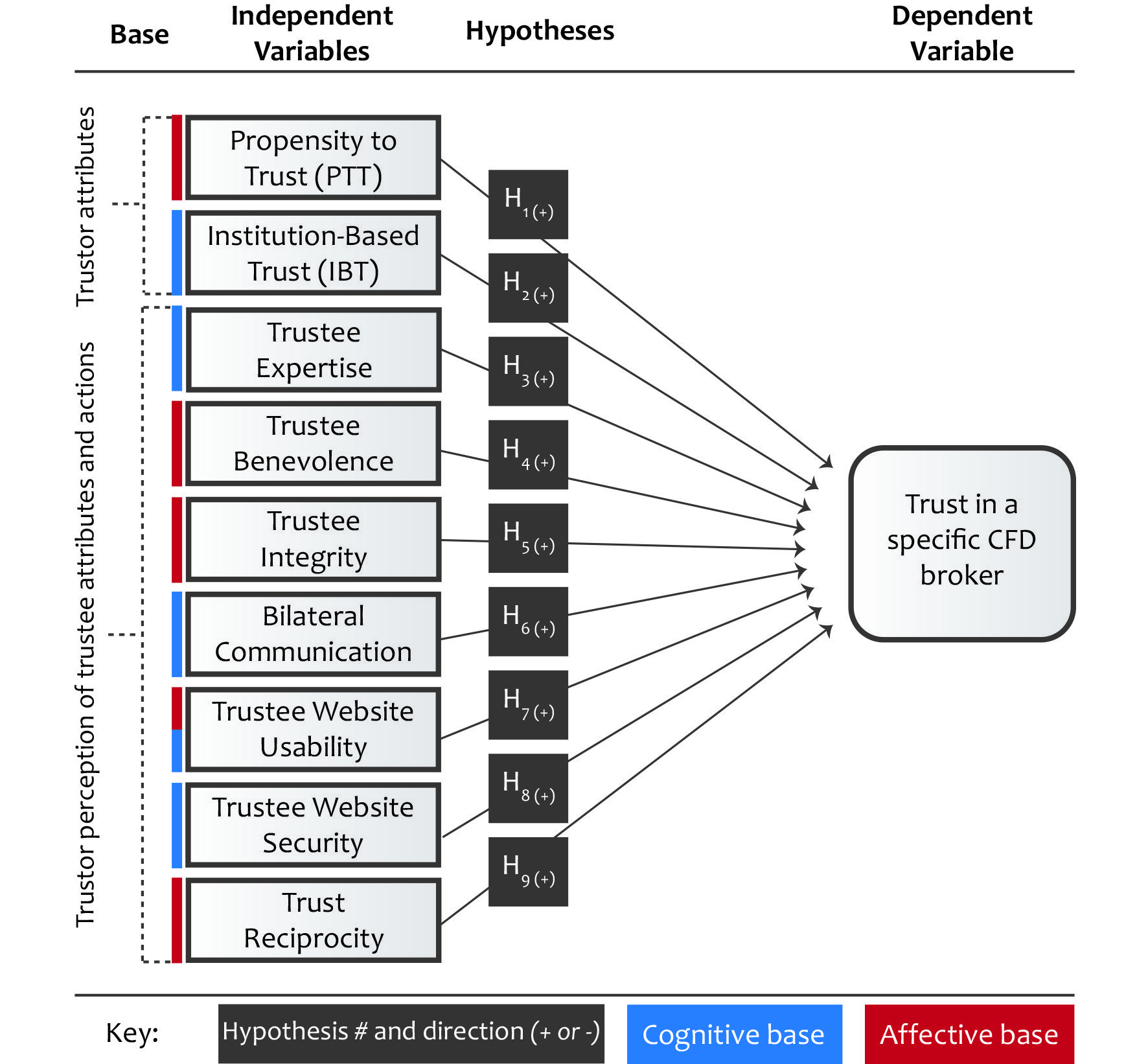
As you can see, conceptual frameworks often make use of different shapes , lines and arrows to visualise the connections and relationships between different components and/or variables. Ultimately, the conceptual framework provides an opportunity for you to make explicit your understanding of how everything is connected . So, be sure to make use of all the visual aids you can – clean design, well-considered colours and concise text are your friends.
Theoretical framework vs conceptual framework
As you can see, the theoretical framework and the conceptual framework are closely related concepts, but they differ in terms of focus and purpose. The theoretical framework is used to lay down a foundation of theory on which your study will be built, whereas the conceptual framework visualises what you anticipate the relationships between concepts, constructs and variables may be, based on your understanding of the existing literature and the specific context and focus of your research. In other words, they’re different tools for different jobs , but they’re neighbours in the toolbox.
Naturally, the theoretical framework and the conceptual framework are not mutually exclusive . In fact, it’s quite likely that you’ll include both in your dissertation or thesis, especially if your research aims involve investigating relationships between variables. Of course, every research project is different and universities differ in terms of their expectations for dissertations and theses, so it’s always a good idea to have a look at past projects to get a feel for what the norms and expectations are at your specific institution.
Want to learn more about research terminology, methods and techniques? Be sure to check out the rest of the Grad Coach blog . Alternatively, if you’re looking for hands-on help, have a look at our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through the research process, step by step.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
23 Comments
Thank you for giving a valuable lesson
good thanks!
VERY INSIGHTFUL
thanks for given very interested understand about both theoritical and conceptual framework
I am researching teacher beliefs about inclusive education but not using a theoretical framework just conceptual frame using teacher beliefs, inclusive education and inclusive practices as my concepts
good, fantastic
great! thanks for the clarification. I am planning to use both for my implementation evaluation of EmONC service at primary health care facility level. its theoretical foundation rooted from the principles of implementation science.
This is a good one…now have a better understanding of Theoretical and Conceptual frameworks. Highly grateful
Very educating and fantastic,good to be part of you guys,I appreciate your enlightened concern.
Thanks for shedding light on these two t opics. Much clearer in my head now.
Simple and clear!
The differences between the two topics was well explained, thank you very much!
Thank you great insight
Superb. Thank you so much.
Hello Gradcoach! I’m excited with your fantastic educational videos which mainly focused on all over research process. I’m a student, I kindly ask and need your support. So, if it’s possible please send me the PDF format of all topic provided here, I put my email below, thank you!
I am really grateful I found this website. This is very helpful for an MPA student like myself.
I’m clear with these two terminologies now. Useful information. I appreciate it. Thank you
I’m well inform about these two concepts in research. Thanks
I found this really helpful. It is well explained. Thank you.
very clear and useful. information important at start of research!!
Wow, great information, clear and concise review of the differences between theoretical and conceptual frameworks. Thank you! keep up the good work.
thank you so much. Educative and realistic.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

Eureka! When I learnt how to write a theoretical framework
Feb 6, 2019

Have you checked out the rest of The PhD Knowledge Base ? It’s home to hundreds more free resources and guides, written especially for PhD students.
Have you ever had a eureka moment? A moment where something that you’ve misunderstood for ages becomes crystal clear?
I did, about half way through my PhD.
Did I come up with a ground breaking discovery that would revolutionise my field? Did I develop a new theory that would change the way we think about the world?
I finally understood how to write a theoretical framework.
Sound silly? It isn’t.
During the one-on-one PhD coaching sessions I run, the issue of how to write a theory framework comes up more frequently than any other. The theoretical framework is important, but many people find it difficult. I know I struggled with it.
Then someone explained the theory framework to me in such a simple way. Here’s the eureka moment: The theoretical framework is like a toolbox.
Simple, right?
Let me explain. In the literature review you highlighted the problem that needs ‘fixing’. The theoretical framework – the ’toolbox’ – details the theories, propositions, hypotheses (if you’re using them) and concepts – the ’tools’ – that you will use to address or make sense of this problem.
So, your job in a theoretical framework chapter is to discuss in detail what the tools look like, how they behave, how they have been used before, how they relate to one another, how they are relevant to your aims and objectives and what the drawbacks are from using them. The methods chapter then discusses how you will use (operationalise) those tools.
Hello, Doctor…
Sounds good, doesn’t it? Be able to call yourself Doctor sooner with our five-star rated How to Write A PhD email-course. Learn everything your supervisor should have taught you about planning and completing a PhD.
Now half price. Join hundreds of other students and become a better thesis writer, or your money back.
What is a theoretical framework?
In the literature review you highlighted the problem that needs ‘fixing’. The theoretical framework – the ’toolbox’ – details the theories, propositions, hypotheses (if you’re using them) and concepts – the ’tools’ – that you will use to address or make sense of this problem.
The list of potential explanations for why responses differ is enormous.
You could approach this question with a focus on, say, psychology, power, gender, economics, and so on. The best we can typically hope for – and this is particularly true in much of the social sciences – is an interpretation of the truth.
So – and this is important – we use theory to focus our attention on a small sub-set of all potential explanations, on one particular viewpoint.
Now I know I’m getting into messy epistemological and ontological waters here. I am an interpretivist, so I see theory as a ‘lens’ that you apply to make sense of the world. That’s the shape of my toolbox.
But, even if you’re a positivist you still pick and choose theoretical concepts and hypotheses from a range of available options; you just use them in a different way (rather than a lens, they become testable propositions, or measurement tools).
Without a theoretical framework we are left with a potentially endless choice of potential viewpoints, which would make our data collection and analysis and our discussion hugely chaotic.

Master your lit review & theory framework.
Learn what goes where (and why), and how it all fit together with this free, interactive guide to the PhD literature review and theory framework.
In other words, if we don’t know how to focus our attention, how we can present a coherent explanation?
The theoretical framework is a natural extension of the literature review. The purpose of the literature review, amongst other things, is to highlight gaps and shortcomings with the existing work in your field.
The theoretical framework details the perspective you will take to address that gap and shortcoming.
For example, in my doctoral research, my literature review focused on government responses to climate change and pointed out that there hadn’t been much discussion on local government.
The theoretical framework then made an informed decision to come at it from a particular theoretical perspective (institutional theory, if you’re interested) and then discussed what that theory looks like, highlighting the key concepts and ideas.
In your own research you will also need to make an informed decision about the particular theory you will employ to guide you through the rest of the research.
The theoretical framework is a natural extension of the literature review. The purpose of the literature review, amongst other things, is to highlight gaps and shortcomings with the existing work in your field. The theoretical framework details the perspective you will take to address that gap and shortcoming.
So, the job of the theoretical framework isn’t to repeat the literature review . Instead, think of it as a separate, mini literature review , this time focusing on the theory you will employ. You don’t have to discuss every particular use and discussion of the theoretical position you employ. If you did, you’d quickly run out of space and time.
Remember, your examiners are likely to already be familiar with the theory, meaning that rather than discuss every possible thing that there is to discuss about it, you instead need to discuss how and why the theory has been adapted and adopted to the context of your research.
How to structure a theoretical framework
- You need to have a solid grasp of your aims and objectives. These define the space in which your research will sit and your goals when conducting it. You will need to briefly recap these when you start writing your theoretical framework, both to remind the reader and so that you can relate your theory to these overarching aims.
- What theory/theories are you using? Here you need to define and explain each theory you draw upon and, in doing so, discuss the leading proponents and applications. This shows that you understand the theory you are going to adopt.
- You then need to spend time critically arguing why you are adopting this particular theory. There are a lot of potential theories you could use. Why this one? Importantly, you should relate your choice to the discussions in the literature review and your aims and objectives.
- Can the theory/theories be broken down into different schools? Which one are you siding with and why?
- A theory contains a number of concepts. Which will you be drawing upon? Why these ones? Have you defined them properly? The way you approach this section will be influenced by your epistemological and ontological perspective and, thus, whether you use hypotheses or not. If you are using hypotheses, you need to state them as such.
- How do the concepts relate to your aims and objectives?
- Have you clearly stated your ontological and epistemological perspective?
- Are you the first to use this particular theory in this particular way? What benefits or drawbacks does that bring?
- Can you spot any drawbacks with applying this theory? Does it fail to account for a particular dimension of a phenomenon? Is it difficult to operationalize?
- How are your concepts related? Are you using them as hypotheses? Or as a model to make sense of the data? Somewhere in between? Be explicit about how they are all related and what you plan on doing with them.

The goal of writing up a theoretical framework is to tell the reader why you have chosen particular theories, how they relate to the gap in the literature, and how they relate to your aims and objectives.
A short (but necessary) note on ontology and epistemology
How do i choose theories and create my framework.
Unless you are using an inductive methodological approach (where you generate theory from the data), you will likely approach your fieldwork with a theoretical framework in mind. Which theory or theories you choose is, in part, down to your aims and objectives and whether there is a relevant theory available ‘off-the-shelf’ that is appropriate for your needs.
There are generally three strategies that researchers use to develop their theoretical frameworks:
- There may be theories in your field that have arisen on the basis of repeated observation and testing and which are widely accepted.
- Or, you might find that you need to select concepts from multiple theories and create a novel framework that is unique to your particular context.
- A growing and important trend in social research is to adopt an interdisciplinary perspective when trying to understand the social world. This can be achieved by looking beyond the dominant, well-established theories and thinking about how other theories, particularly those from other disciplines or sub-disciplines, can be used.
In any case, you must consider the following when selecting a theory:
- Identify your ontological and epistemological beliefs.
- List several theories that align with your epistemological position and which can aid your understanding of the phenomenon under investigation.
- Engage in literature review around those theories, both to familiarise yourself with them but also to understand their relevance to your study.
- Ask yourself how each theory connects to your problem, aims & objectives.
- Select the theory or theories that provide more relevant tools for your thesis.
I have more than one theory. What do I do?
Often, you need to combine concepts, hypotheses or ideas from more than one theoretical school. Employing more than one theory is entirely legitimate. I did so in my PhD.
However, you need to consider a few key questions :
Are the theories you are bringing together epistemologically compatible?
Have you discussed each theory in the same level of detail to adequately explain the theory, your justification for its inclusion, its relation to the literature and its potential drawbacks?
What benefits does focusing on more than one theory bring? Perhaps one theory has shortcomings that the other addresses?
What downsides are there to employing more than one theory?
Has anyone else used this combination of theories before you?
The theoretical framework is a tricky section to write, largely because the choice available to you is huge.
But keep that toolbox metaphor in mind.
Each theory contains a number of tools. Your job in the theory framework is to take the tools you need for your project from the most relevant theory/theories and package them up into your own toolbox.
When you’re done, you should see that the theory framework offers:
- Structure, by detailing the key concepts, tools and, where relevant, hypotheses
- A way to connect to other research
- A coherent, joined up set of ideas that structure the writing and help to create an argumentative streak that can run throughout your thesis
- An approach that can be reused in additional contexts once you’re done
Along the way, you need to convince the reader that you’ve picked and applied the most appropriate tools possible, given your aims and objectives.
The theoretical framework frames the research. If you build that frame right, your research will shine. If you don’t then you’ll struggle.
If you need expert guidance to structure, plan or write your theory framework you can get in touch for a one-on-one coaching session . It’s like having a personal trainer, but for your PhD.
Share this:
67 comments.
A great read. Quite some insight into my Phd journey. The conceptual framework?
Glad you found it useful. You having trouble with your conceptual framework?
This is enlightening. I was struggling with my Theoretical framework. I will apply the guidelines here and await feedback from my supervisor. Thanks
I’m glad you found the post useful. Thanks for your kind words.
I came across your posts while helping my wife with her work (I finished my PhD two years ago), and I keep thinking…hmmm the pain I went through to learn this… thank you for making it so easy for others…
Thanks for the kind words. I remember how difficult I found my own PhD, so my motivation is to make life easier for as many other PhD students as possible.
i need some more clear version to develop a theoretical framework. kindly contact me through email. thank you
Great insights. I have read through your thesis. You did a lot of quality work. I see the EM, Environmental Policy Capacity and the institutions theory all discussed. Really detailed and linked. Let me see how mine goes
I’ve sent you an email. I’d be glad to help.
This is very helpful because am really struggling to write my theoretical section. I have a question, I selected a framework but realised it has shortcomings, so I decided to include a model, but also I have another theory. All the three are confusing me how to structure them please I need your help. Thanks
Hi Carolyne,
Thanks for your email. Do you want to have a one-on-one coaching session with me? We’ll be able to get to the bottom of your confusion and clear up your theory problems once and for all. Click here for more details and to book yourself in.
Do you have a structured outline, similar to the overall diss outline, for the theoretical framework?
I sure do. You can find it here: https://www.thephdproofreaders.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/Theoretical-Framework-Template_AW_20190208.pdf
What are the advantages of having a chapter on theoretical framework independent of the Literature Review chapter. Please assist.
Thanks for your comment. Whether or not you need a separate literature review and theory framework chapter depends on how distinct they are from one another and on how complex each chapter is. It may be the case that you need two chapters because to discuss both in one would make the chapter very large, complex and hard to follow. Also, it is often the case that the theory framework builds on and addresses gaps you’ve highlighted in your literature review, so for that reason it makes sense to keep them as two separate chapters.
But which one comes first? I thought theoretical framework comes earlier than literature review or is it in a proposal where it is structured that way?
Typically the lit review comes first, then the theory. The lit review makes the case for the research and the theory framework shows the approach you will take to conduct the research.
Thanks for the kind words :)
Dear Max, I am using multiple related concepts to frame my research. I am confused whether to dedicate a complete chapter to explain only these five concepts, or just operationalise them in one of the chapters. Again, is introducing these concepts early in my introductory chapter a good idea as it forms one of my research questions. This means I have answered the question in the introductory chapter
Thanks for your comment. Whether or not such concepts end up in your introduction/context discussion will depend in part on whether they are framing your research (as in, providing the background or context) or whether you’re using them to answer your research questions (in which case they’ll form part of your theory framework and will therefore come at a later stage).
Dear Max, I was searching how to structure Theoretical framework and came across your writing. Thank you for this, it is really helpful. I’m one of those phd students who struggles with Theoretical framework :/ I would appreciate your help if possible. Could you please outline, how can I reach you?
Thanks for your kind words. I’m glad you’re finding the phD Knowledge Base useful. You can reach me at max[at]thephdproofreaders.com
Speaks soon!
I’m so confused about my theoretical framework. Could you possibly help please?
Sure. Have you checked out the one-on-one PhD coaching service we offer? It sounds just that’s just what you need.
I couldn’t express how grateful I am. MAY YOU BE SHOWERED WITH BLESSINGS
Thanks! I’m glad you found the advice useful.
wow!!! thank you very much , I have been struggling to write my theoretical framework . thank you.
You’re welcome!
Dr. Max I am expecting to learn more on how to pick the right literatures, related to my theme. all of them seem very nice and informative. I am having hard time to select them. and also I have difficulties in starting the sentence of my Introduction. I am researching on “the impact of Prosperity gospel in Tanzanian mainline churches”. my topic is very popular and many has been said … I feel like I am saying what has been said .
Thanks for your comment. I wish you the best of luck.
Hi Max, Great read. Doing my MA Thesis after years away from academia has been a challenge to say the least. Your article provided clarity that I have been asking for/seeking elsewhere (supervision/consultant) for months. Wish I had of found it earlier but glad I came across it.
Thank you and all the best in these uncertain times.
Great! Glad you’re finding the resources useful. Good luck with the rest of the thesis.
Dear Max, thank you very much, many things got clear after reading this. I have a question, I am using political capability approach as my theoretical foundation which is part of RBW theory. So technically it is not a theory but just an approach, so does this indirectly mean that I am USING RBW Theory? Many Thanks
Hi – glad you found it useful. Without knowing more about your project I’m afraid I can’t advise about your choice of theory framework. Have you approached your supervisor with this question?
This is a very helpful article.
Glad you enjoyed it!
This has been one of the best articles that has clearly outlined the Theoretical framework. Kindly do a Youtibe video for auditory learners with real examples. It will greatly assist me especiall. I am glad I found this article.
Thanks for the kind words and for your feedback. I’ll take it on board for future guides.
Thanks so much for this which has helped me with a sticky bit as I move forward to discover new theoretical concepts from slightly outside my field that fit better than those I started out with. A part-time PhD has such a long life that it leaves too much room for changes and adaptations! A big thank you to Rebecca Baker on a Shut Up and Write Session who referred me to this!
I’m glad you found the guide useful. Thanks to you and to Rebecca Baker!
I found this post very helpful, thanks for sharing
Thanks for reading!
Thank you for this crisp advice on Theoretical framework. personally i have been experiencing difficulties selecting appropriate theory related to the study. However your advice was really beneficial. God bless you for your kindness towards us researchers.
Thanks for the kind words Roshni.
Thank you so much for sharing this information regarding the theoretical framework. I revisited my chapter and strengthened it based on the pointers you outlined here. This is a must read before drafting the chapter. Very helpful ?
Thanks for the kind words. I’m glad you found it useful.
This came just in time! I’m taking a research philosophy course and this week’s discussion is “Theory and Theoretical Frameworks”. I found this very helpful.
Great. I hope it helped deepen your understanding.
Thank you Dr Lempriere for this insightful article. I have just started my PhD journey and I found this article to be very useful and eye-opening.
Interesting and excellent read.
Thank you so very much for sharing your intellectual insights on this.
Hi this is really useful thank you. I have a question regarding one of my tools. I realise (quite late) that I am using one tool in a *generalised* way. I could put this another way – the context in which I found this tool constituted a more particular use of this more general tool, and I am seeking to retrieve it for a more general use. This opens the question – on what grounds am I employing a generalised form of this tool? What constraints govern this process of generalisation? Etc. I wish I’d dealt with this earlier… Do you have any thoughts on how I navigate this?
Hi – I’d love to give you advice, but without knowing more about your research and thesis any advice I would give wouldn’t be qualified. Sorry I can’t be of more help.
I loved your explanation, but what if you ARE doing an inductive project?
I found your article very useful, thank you! I am currently building a Foucauldian theoretical framework through which to discuss a phenomena (“Karens”).
Do you any academic articles which I can use to justify using the interpretavist approach (using theory as a lens)? I cant find anything through my searches.
Hi – sorry, we don’t I’m afraid.
Surely, this is a great lesson offered. How I pray I had your email, I would love to learn more from you. Thank you
Been struggling with my Phd and literature review . This has been very helpful. Is it possible for you to share your email so i can engage more with you and get some insights and help
Really really helpful guide, I am so grateful to you for providing this! It is helping me immensely in developing my own framework, a task which previously seemed scary, confusing and impossible!
Thanks for this. It is very useful. So should I first write my Lit review and then only the theoretical framework? TIA
Thanks! It’s hard to say without knowing more about your project, I’m afraid!
Thank you for the wonderful work. I want to know if theoretical frame work can presented in a diagram form
You’re welcome! Yes, your theory framework can be presented visually. It’s a great way of showing the framework in a clean, simplified way. It also serves as a useful reference guide for people to easily refer back to if they want to remind themselves of what your theory framework looks like.
I found your article highly informative. I recently enrolled for my PhD and my supervisor asked me to submit my Research outline. Does the outline have to have that detailed Theoretical framework. Again how best can I choose the theoretical framework suitable for my topic. If I may have a list of Theoretical frameworks I will be happy. I will also be grateful to have a direct contact with you.
A great insight into how to write a theoretical framework, simple and jargon free, the article makes the purpose and the method of writing the chapter explicit. Thank you.
That’s so kind of you Sethu. I’m glad you found it useful.
i WOULD LIKE TO KNOW WHAT IS THE IDEAL PLACE TO SITUATE THE THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK AND CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK WITHIN THE LITERATURE REVIEW? Peter Nemaenzhe
The theory/conceptual framework is often its own chapter between the lit review and methods. Sometimes though you can include it in the literature review, but I would suggest including it towards the end. I.e. do the lit review first, then introduce the theory framework.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Search The PhD Knowledge Base
Most popular articles from the phd knowlege base.
The PhD Knowledge Base Categories
- Your PhD and Covid
- Mastering your theory and literature review chapters
- How to structure and write every chapter of the PhD
- How to stay motivated and productive
- Techniques to improve your writing and fluency
- Advice on maintaining good mental health
- Resources designed for non-native English speakers
- PhD Writing Template
- Explore our back-catalogue of motivational advice
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- Theoretical Framework
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
Theories are formulated to explain, predict, and understand phenomena and, in many cases, to challenge and extend existing knowledge within the limits of critical bounded assumptions or predictions of behavior. The theoretical framework is the structure that can hold or support a theory of a research study. The theoretical framework encompasses not just the theory, but the narrative explanation about how the researcher engages in using the theory and its underlying assumptions to investigate the research problem. It is the structure of your paper that summarizes concepts, ideas, and theories derived from prior research studies and which was synthesized in order to form a conceptual basis for your analysis and interpretation of meaning found within your research.
Abend, Gabriel. "The Meaning of Theory." Sociological Theory 26 (June 2008): 173–199; Kivunja, Charles. "Distinguishing between Theory, Theoretical Framework, and Conceptual Framework: A Systematic Review of Lessons from the Field." International Journal of Higher Education 7 (December 2018): 44-53; Swanson, Richard A. Theory Building in Applied Disciplines . San Francisco, CA: Berrett-Koehler Publishers 2013; Varpio, Lara, Elise Paradis, Sebastian Uijtdehaage, and Meredith Young. "The Distinctions between Theory, Theoretical Framework, and Conceptual Framework." Academic Medicine 95 (July 2020): 989-994.
Importance of Theory and a Theoretical Framework
Theories can be unfamiliar to the beginning researcher because they are rarely applied in high school social studies curriculum and, as a result, can come across as unfamiliar and imprecise when first introduced as part of a writing assignment. However, in their most simplified form, a theory is simply a set of assumptions or predictions about something you think will happen based on existing evidence and that can be tested to see if those outcomes turn out to be true. Of course, it is slightly more deliberate than that, therefore, summarized from Kivunja (2018, p. 46), here are the essential characteristics of a theory.
- It is logical and coherent
- It has clear definitions of terms or variables, and has boundary conditions [i.e., it is not an open-ended statement]
- It has a domain where it applies
- It has clearly described relationships among variables
- It describes, explains, and makes specific predictions
- It comprises of concepts, themes, principles, and constructs
- It must have been based on empirical data [i.e., it is not a guess]
- It must have made claims that are subject to testing, been tested and verified
- It must be clear and concise
- Its assertions or predictions must be different and better than those in existing theories
- Its predictions must be general enough to be applicable to and understood within multiple contexts
- Its assertions or predictions are relevant, and if applied as predicted, will result in the predicted outcome
- The assertions and predictions are not immutable, but subject to revision and improvement as researchers use the theory to make sense of phenomena
- Its concepts and principles explain what is going on and why
- Its concepts and principles are substantive enough to enable us to predict a future
Given these characteristics, a theory can best be understood as the foundation from which you investigate assumptions or predictions derived from previous studies about the research problem, but in a way that leads to new knowledge and understanding as well as, in some cases, discovering how to improve the relevance of the theory itself or to argue that the theory is outdated and a new theory needs to be formulated based on new evidence.
A theoretical framework consists of concepts and, together with their definitions and reference to relevant scholarly literature, existing theory that is used for your particular study. The theoretical framework must demonstrate an understanding of theories and concepts that are relevant to the topic of your research paper and that relate to the broader areas of knowledge being considered.
The theoretical framework is most often not something readily found within the literature . You must review course readings and pertinent research studies for theories and analytic models that are relevant to the research problem you are investigating. The selection of a theory should depend on its appropriateness, ease of application, and explanatory power.
The theoretical framework strengthens the study in the following ways :
- An explicit statement of theoretical assumptions permits the reader to evaluate them critically.
- The theoretical framework connects the researcher to existing knowledge. Guided by a relevant theory, you are given a basis for your hypotheses and choice of research methods.
- Articulating the theoretical assumptions of a research study forces you to address questions of why and how. It permits you to intellectually transition from simply describing a phenomenon you have observed to generalizing about various aspects of that phenomenon.
- Having a theory helps you identify the limits to those generalizations. A theoretical framework specifies which key variables influence a phenomenon of interest and highlights the need to examine how those key variables might differ and under what circumstances.
- The theoretical framework adds context around the theory itself based on how scholars had previously tested the theory in relation their overall research design [i.e., purpose of the study, methods of collecting data or information, methods of analysis, the time frame in which information is collected, study setting, and the methodological strategy used to conduct the research].
By virtue of its applicative nature, good theory in the social sciences is of value precisely because it fulfills one primary purpose: to explain the meaning, nature, and challenges associated with a phenomenon, often experienced but unexplained in the world in which we live, so that we may use that knowledge and understanding to act in more informed and effective ways.
The Conceptual Framework. College of Education. Alabama State University; Corvellec, Hervé, ed. What is Theory?: Answers from the Social and Cultural Sciences . Stockholm: Copenhagen Business School Press, 2013; Asher, Herbert B. Theory-Building and Data Analysis in the Social Sciences . Knoxville, TN: University of Tennessee Press, 1984; Drafting an Argument. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Kivunja, Charles. "Distinguishing between Theory, Theoretical Framework, and Conceptual Framework: A Systematic Review of Lessons from the Field." International Journal of Higher Education 7 (2018): 44-53; Omodan, Bunmi Isaiah. "A Model for Selecting Theoretical Framework through Epistemology of Research Paradigms." African Journal of Inter/Multidisciplinary Studies 4 (2022): 275-285; Ravitch, Sharon M. and Matthew Riggan. Reason and Rigor: How Conceptual Frameworks Guide Research . Second edition. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2017; Trochim, William M.K. Philosophy of Research. Research Methods Knowledge Base. 2006; Jarvis, Peter. The Practitioner-Researcher. Developing Theory from Practice . San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass, 1999.
Strategies for Developing the Theoretical Framework
I. Developing the Framework
Here are some strategies to develop of an effective theoretical framework:
- Examine your thesis title and research problem . The research problem anchors your entire study and forms the basis from which you construct your theoretical framework.
- Brainstorm about what you consider to be the key variables in your research . Answer the question, "What factors contribute to the presumed effect?"
- Review related literature to find how scholars have addressed your research problem. Identify the assumptions from which the author(s) addressed the problem.
- List the constructs and variables that might be relevant to your study. Group these variables into independent and dependent categories.
- Review key social science theories that are introduced to you in your course readings and choose the theory that can best explain the relationships between the key variables in your study [note the Writing Tip on this page].
- Discuss the assumptions or propositions of this theory and point out their relevance to your research.
A theoretical framework is used to limit the scope of the relevant data by focusing on specific variables and defining the specific viewpoint [framework] that the researcher will take in analyzing and interpreting the data to be gathered. It also facilitates the understanding of concepts and variables according to given definitions and builds new knowledge by validating or challenging theoretical assumptions.
II. Purpose
Think of theories as the conceptual basis for understanding, analyzing, and designing ways to investigate relationships within social systems. To that end, the following roles served by a theory can help guide the development of your framework.
- Means by which new research data can be interpreted and coded for future use,
- Response to new problems that have no previously identified solutions strategy,
- Means for identifying and defining research problems,
- Means for prescribing or evaluating solutions to research problems,
- Ways of discerning certain facts among the accumulated knowledge that are important and which facts are not,
- Means of giving old data new interpretations and new meaning,
- Means by which to identify important new issues and prescribe the most critical research questions that need to be answered to maximize understanding of the issue,
- Means of providing members of a professional discipline with a common language and a frame of reference for defining the boundaries of their profession, and
- Means to guide and inform research so that it can, in turn, guide research efforts and improve professional practice.
Adapted from: Torraco, R. J. “Theory-Building Research Methods.” In Swanson R. A. and E. F. Holton III , editors. Human Resource Development Handbook: Linking Research and Practice . (San Francisco, CA: Berrett-Koehler, 1997): pp. 114-137; Jacard, James and Jacob Jacoby. Theory Construction and Model-Building Skills: A Practical Guide for Social Scientists . New York: Guilford, 2010; Ravitch, Sharon M. and Matthew Riggan. Reason and Rigor: How Conceptual Frameworks Guide Research . Second edition. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2017; Sutton, Robert I. and Barry M. Staw. “What Theory is Not.” Administrative Science Quarterly 40 (September 1995): 371-384.
Structure and Writing Style
The theoretical framework may be rooted in a specific theory , in which case, your work is expected to test the validity of that existing theory in relation to specific events, issues, or phenomena. Many social science research papers fit into this rubric. For example, Peripheral Realism Theory, which categorizes perceived differences among nation-states as those that give orders, those that obey, and those that rebel, could be used as a means for understanding conflicted relationships among countries in Africa. A test of this theory could be the following: Does Peripheral Realism Theory help explain intra-state actions, such as, the disputed split between southern and northern Sudan that led to the creation of two nations?
However, you may not always be asked by your professor to test a specific theory in your paper, but to develop your own framework from which your analysis of the research problem is derived . Based upon the above example, it is perhaps easiest to understand the nature and function of a theoretical framework if it is viewed as an answer to two basic questions:
- What is the research problem/question? [e.g., "How should the individual and the state relate during periods of conflict?"]
- Why is your approach a feasible solution? [i.e., justify the application of your choice of a particular theory and explain why alternative constructs were rejected. I could choose instead to test Instrumentalist or Circumstantialists models developed among ethnic conflict theorists that rely upon socio-economic-political factors to explain individual-state relations and to apply this theoretical model to periods of war between nations].
The answers to these questions come from a thorough review of the literature and your course readings [summarized and analyzed in the next section of your paper] and the gaps in the research that emerge from the review process. With this in mind, a complete theoretical framework will likely not emerge until after you have completed a thorough review of the literature .
Just as a research problem in your paper requires contextualization and background information, a theory requires a framework for understanding its application to the topic being investigated. When writing and revising this part of your research paper, keep in mind the following:
- Clearly describe the framework, concepts, models, or specific theories that underpin your study . This includes noting who the key theorists are in the field who have conducted research on the problem you are investigating and, when necessary, the historical context that supports the formulation of that theory. This latter element is particularly important if the theory is relatively unknown or it is borrowed from another discipline.
- Position your theoretical framework within a broader context of related frameworks, concepts, models, or theories . As noted in the example above, there will likely be several concepts, theories, or models that can be used to help develop a framework for understanding the research problem. Therefore, note why the theory you've chosen is the appropriate one.
- The present tense is used when writing about theory. Although the past tense can be used to describe the history of a theory or the role of key theorists, the construction of your theoretical framework is happening now.
- You should make your theoretical assumptions as explicit as possible . Later, your discussion of methodology should be linked back to this theoretical framework.
- Don’t just take what the theory says as a given! Reality is never accurately represented in such a simplistic way; if you imply that it can be, you fundamentally distort a reader's ability to understand the findings that emerge. Given this, always note the limitations of the theoretical framework you've chosen [i.e., what parts of the research problem require further investigation because the theory inadequately explains a certain phenomena].
The Conceptual Framework. College of Education. Alabama State University; Conceptual Framework: What Do You Think is Going On? College of Engineering. University of Michigan; Drafting an Argument. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Lynham, Susan A. “The General Method of Theory-Building Research in Applied Disciplines.” Advances in Developing Human Resources 4 (August 2002): 221-241; Tavallaei, Mehdi and Mansor Abu Talib. "A General Perspective on the Role of Theory in Qualitative Research." Journal of International Social Research 3 (Spring 2010); Ravitch, Sharon M. and Matthew Riggan. Reason and Rigor: How Conceptual Frameworks Guide Research . Second edition. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2017; Reyes, Victoria. Demystifying the Journal Article. Inside Higher Education; Trochim, William M.K. Philosophy of Research. Research Methods Knowledge Base. 2006; Weick, Karl E. “The Work of Theorizing.” In Theorizing in Social Science: The Context of Discovery . Richard Swedberg, editor. (Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press, 2014), pp. 177-194.
Writing Tip
Borrowing Theoretical Constructs from Other Disciplines
An increasingly important trend in the social and behavioral sciences is to think about and attempt to understand research problems from an interdisciplinary perspective. One way to do this is to not rely exclusively on the theories developed within your particular discipline, but to think about how an issue might be informed by theories developed in other disciplines. For example, if you are a political science student studying the rhetorical strategies used by female incumbents in state legislature campaigns, theories about the use of language could be derived, not only from political science, but linguistics, communication studies, philosophy, psychology, and, in this particular case, feminist studies. Building theoretical frameworks based on the postulates and hypotheses developed in other disciplinary contexts can be both enlightening and an effective way to be more engaged in the research topic.
CohenMiller, A. S. and P. Elizabeth Pate. "A Model for Developing Interdisciplinary Research Theoretical Frameworks." The Qualitative Researcher 24 (2019): 1211-1226; Frodeman, Robert. The Oxford Handbook of Interdisciplinarity . New York: Oxford University Press, 2010.
Another Writing Tip
Don't Undertheorize!
Do not leave the theory hanging out there in the introduction never to be mentioned again. Undertheorizing weakens your paper. The theoretical framework you describe should guide your study throughout the paper. Be sure to always connect theory to the review of pertinent literature and to explain in the discussion part of your paper how the theoretical framework you chose supports analysis of the research problem or, if appropriate, how the theoretical framework was found to be inadequate in explaining the phenomenon you were investigating. In that case, don't be afraid to propose your own theory based on your findings.
Yet Another Writing Tip
What's a Theory? What's a Hypothesis?
The terms theory and hypothesis are often used interchangeably in newspapers and popular magazines and in non-academic settings. However, the difference between theory and hypothesis in scholarly research is important, particularly when using an experimental design. A theory is a well-established principle that has been developed to explain some aspect of the natural world. Theories arise from repeated observation and testing and incorporates facts, laws, predictions, and tested assumptions that are widely accepted [e.g., rational choice theory; grounded theory; critical race theory].
A hypothesis is a specific, testable prediction about what you expect to happen in your study. For example, an experiment designed to look at the relationship between study habits and test anxiety might have a hypothesis that states, "We predict that students with better study habits will suffer less test anxiety." Unless your study is exploratory in nature, your hypothesis should always explain what you expect to happen during the course of your research.
The key distinctions are:
- A theory predicts events in a broad, general context; a hypothesis makes a specific prediction about a specified set of circumstances.
- A theory has been extensively tested and is generally accepted among a set of scholars; a hypothesis is a speculative guess that has yet to be tested.
Cherry, Kendra. Introduction to Research Methods: Theory and Hypothesis. About.com Psychology; Gezae, Michael et al. Welcome Presentation on Hypothesis. Slideshare presentation.
Still Yet Another Writing Tip
Be Prepared to Challenge the Validity of an Existing Theory
Theories are meant to be tested and their underlying assumptions challenged; they are not rigid or intransigent, but are meant to set forth general principles for explaining phenomena or predicting outcomes. Given this, testing theoretical assumptions is an important way that knowledge in any discipline develops and grows. If you're asked to apply an existing theory to a research problem, the analysis will likely include the expectation by your professor that you should offer modifications to the theory based on your research findings.
Indications that theoretical assumptions may need to be modified can include the following:
- Your findings suggest that the theory does not explain or account for current conditions or circumstances or the passage of time,
- The study reveals a finding that is incompatible with what the theory attempts to explain or predict, or
- Your analysis reveals that the theory overly generalizes behaviors or actions without taking into consideration specific factors revealed from your analysis [e.g., factors related to culture, nationality, history, gender, ethnicity, age, geographic location, legal norms or customs , religion, social class, socioeconomic status, etc.].
Philipsen, Kristian. "Theory Building: Using Abductive Search Strategies." In Collaborative Research Design: Working with Business for Meaningful Findings . Per Vagn Freytag and Louise Young, editors. (Singapore: Springer Nature, 2018), pp. 45-71; Shepherd, Dean A. and Roy Suddaby. "Theory Building: A Review and Integration." Journal of Management 43 (2017): 59-86.
- << Previous: The Research Problem/Question
- Next: 5. The Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: Sep 4, 2024 9:40 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
Service update: Some parts of the Library’s website will be down for maintenance on August 11.
Secondary menu
- Log in to your Library account
- Hours and Maps
- Connect from Off Campus
- UC Berkeley Home
Search form
Isf 189 & 190: thesis: theoretical frameworks.
- Getting Help
- How to Research
- Research Methods This link opens in a new window
- Theoretical frameworks
- Literature Reviews This link opens in a new window
- Encyclopedias
- Bibliographies
- How to Read Citations
- Locating Journals
- Keywords and Descriptors
- Building searches
- Locating Books
- Find Articles
- Google Scholar & BASE
- Citation Tracing
- Dissertations
- Using AI tools
- Library Prize
- Off-Campus Access
Theoretical/conceptual Frameworks
"Theoretical frameworks provide a particular perspective, or lens, through which to examine a topic. There are many different lenses, such as psychological theories, social theories, organizational theories and economic theories, which may be used to define concepts and explain phenomena. Sometimes these frameworks may come from an area outside of your immediate academic discipline . Using a theoretical framework for your dissertation can help you to better analyze past events by providing a particular set of questions to ask, and a particular perspective to use when examining your topic." 1
Articles and books that incorporate theoretical or conceptual frameworks aren't consistently tagged with terminology that allows them to be easily fournd in literature searches. Searching for these terms in the full text of the articles may surface some. Superior indexing in some databases may include subject headings or descriptors that tag a work with its theoretical framework, but that is not very common. As there is no simple way to identify frameworks you might use for your own research project, persistent and creative searching in the literature, as well as extensive reading, may be your best option.
1 Bezet, Amanda. “Researching Theoretical Frameworks.” Accessed January 24, 2023. https://resources.nu.edu/researchprocess/theoreticalframeworks .
Additional Resources:
The Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper guide at USC is an excellent resource for understanding and applying theoretical frameworks.
Anfara, Vincent, and Norma Mertz. Theoretical Frameworks in Qualitative Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, Inc., 2006. https://doi.org/10.4135/9781412986335 .
The Theoretical Frameworks research guide at National University Library includes an online tutorial on researching theoretical and conceptual frameworks.
Grant, Cynthia, and Azadeh Osanloo. “ Understanding, Selecting, and Integrating a Theoretical Framework in Dissertation Research: Creating the Blueprint for Your ‘House .’” Administrative Issues Journal Education Practice and Research 4, no. 2 (2014): 12–26.
- << Previous: Research Methods
- Next: Literature Reviews >>
- Last Updated: Aug 15, 2024 9:43 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.berkeley.edu/ISF189-190
- Staff Directory
- Library Policies
- Hege Research Award
- Quaker Archives
- Art Gallery
- Student Support
- Teaching & Learning
- Reserving spaces
- Technology Lending
- Interlibrary Loan
- Course Reserves
- Copyright & Fair Use
- Poster Printing
- Virtual Reference
- Research Guides
- Off-campus access
- Digital Scholarship
- Guilford Sources
- Open Educational Resources
- Quaker Collections
- Digital Collections
- College Archives
- Underground Railroad
- Universities Studying Slavery
- Images & Exhibitions
Service Alert

Hege Library & Learning Technologies
Guide for Thesis Research
- Introduction to the Thesis Process
- Project Planning
- Literature Review
- Theoretical Frameworks
- Research Methodology
- GC Honors Program Theses
- Thesis Submission Instructions This link opens in a new window
- Accessing Guilford Theses from 1898 to 2020 This link opens in a new window
Some Articles About Theory
The following are articles that may help you understand the importance of theory as a fundamental aspect of academic research.
- It's Just a Theory
- Literature Reviews, Conceptual Frameworks, and Theoretical Frameworks: Terms, Functions, and Distinctions
- Use of Theoretical Frameworks in Research
Why is theory important?

Theories reflect previous study and analysis that has been conducted in your field. They propose explanations for phenomena that occur in an area of study. Over time, theories are reexamined, refined, and sometimes discarded in favor of new ones, always with the purpose of providing ever more accurate explanations for the dynamics that operate in our world.
The following quote, taken from John Kuada's book Research Methodology: A Project Guide for University Students , helps to explain the importance of theory when developing a research project:
“Theory provides the language, the concepts, and assumptions that help researchers to make sense of the phenomenon that they seek to investigate. It enables researchers to connect the issues they are investigating to the existing body of knowledge in the area” (Kuada, 2012, p. 64).
A theory can help researchers make predictions about the phenomena they are setting out to study. They can be informative in terms of determining what variables should be observed, as well as how data should be collected, analyzed, and interpreted on the way to presenting and justifying conclusions.
As a researcher working on a project, it is essential that you be aware of theories that have gained prominence in your field. Think of scholarship as an ongoing conversation. As people publish ideas and develop theories, they help shape that conversation. When you do research and present your findings and ideas, you are joining in on those discussions. You become a contributor. Therefore, it is good to have a sense of what has been said before.
Identify major theories in your field. Be conscious of the fundamental concepts that have guided scholars in your area, and be aware of emerging perspectives and trends. Try to identify a theoretical base from which you can develop your arguments. This will greatly strengthen your positions when the time comes to present your thesis.
Resources About Theory and Theoretical Frameworks

- << Previous: Literature Review
- Next: Research Methodology >>
- Last Updated: Jul 22, 2024 10:48 AM
- URL: https://library.guilford.edu/thesis-guide
- How It Works
- PhD thesis writing
- Master thesis writing
- Bachelor thesis writing
- Dissertation writing service
- Dissertation abstract writing
- Thesis proposal writing
- Thesis editing service
- Thesis proofreading service
- Thesis formatting service
- Coursework writing service
- Research paper writing service
- Architecture thesis writing
- Computer science thesis writing
- Engineering thesis writing
- History thesis writing
- MBA thesis writing
- Nursing dissertation writing
- Psychology dissertation writing
- Sociology thesis writing
- Statistics dissertation writing
- Buy dissertation online
- Write my dissertation
- Cheap thesis
- Cheap dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help
- Pay for thesis
- Pay for dissertation
- Senior thesis
- Write my thesis
Theoretical Framework: Research Writing Guide
In a thesis or dissertation, a theoretical framework is a section where the writer evaluates or discusses the most relevant theories to their study.
The purpose of this section is to:
- Define the key concepts
- Combine and evaluate relevant models and theories
- Explain expectations and assumptions that guide the project
The proper presentation of this information frames the research while justifying the approach taken by the writer. This section does this by showing the established ideas on which you ground your work.
Essentially, this section of a dissertation a foundation that supports the analysis that follows. It also allows the author to convincingly interpret their results and state or explain their relevance in a larger context.
When properly written, this section works like the software or buildings that provide critical support to the other aspects of the study. Writing a strong framework with a strong theoretical basis enhances investigations that lead to the achievement of specific study goals.
A well-written framework reduces a dreadful research topic into two basic concepts. These are:
- The study problem
- The rationale behind its investigation
When writing the framework section, focus on creating a piece that connects you with the existing knowledge via the guidance of relevant theories. Also, provide the basis of your hypothesis and your chosen research methods. A professional dissertation writer will help, if you’re in trouble.
What Is a Theoretical Framework?
- The Length of a Theoretical Framework
Theoretical or Conceptual Framework?
Types of theoretical framework, how to write a theoretical framework.
- Summary of a Theoretical Framework Sample
Just like the name suggests, this part of a dissertation or thesis is about theories. Researchers develop theories to draw connections, explain phenomena, and make predictions.
The simplest theoretical framework definition describes it as a collection of theories or interrelated concepts. It comprises concepts and their definitions, as well as, a reference to existing theory and scholarly literature that will be used in a particular study. Your content in this section of a thesis or dissertation must show your understanding of concepts and theories relevant to your research topic. It must also relate them to the considered broader field of knowledge.
- Some students confuse conceptual vs. theoretical framework. In some cases, learners use these terms interchangeably. But though these terms help readers understand the research problem while guiding the collection, as well as, analysis of information, they are different.
- According to the above definition of theoretical framework, it comprises concepts or theories relevant to a study. It highlights how the author will understand and investigate the research problem.
- On the other hand, a conceptual framework can include several formal theories partly or entirely, and other empirical findings and concepts from the field’s literature. The main difference between theoretical and conceptual framework is that the latter demonstrates the relationships among ideas and their relationship with the study.
- A conceptual framework is commonly used in qualitative research. Although some researchers use a theoretical framework in qualitative research, it is common in quantitative research. A conceptual framework is commonly used in qualitative research, especially in behavioral and social science studies.
The Length of a Theoretical Framework
The complexity and length of this section depend on the topic and study field. Some fields and topics have an obvious and well-established theoretical basis. Others need a more detailed justification and explanation.
Maybe you already know that you will apply a specific theory or several theories to your specific context. For instance, you may intend to use the social impact theory when conducting your market research. In that case, the main task is to discuss the main aspects of this theory and then convince the readers that it offers a solid basis that will enable you to answer the research question. It’s also crucial that you evaluate more theories, as long as, they are relevant to your study. Also, tell your readers why you’ve chosen that specific approach.
In some cases, authors draw on different theories and then combine ideas. This approach can lead to strong research. However, it may require more work because you have to implement the theories in your work.
Most theoretical framework examples range between three and five pages. However, no rules govern the length of this section of a dissertation. Nevertheless, try to keep yours within the range of 3-5 pages. This length is adequate for providing all the relevant information your reader wants to know about your chosen theories and assumptions.
Perhaps, you are torn between a theoretical and conceptual framework. Well, the best approach for deciding what to use in your paper is determining the kind of study you want to conduct. If you must use a theoretical framework in qualitative research, determine the theories you intend to use.
That’s because most types of theoretical framework in qualitative research are found in studies based on existing theories. For instance, you can use this framework when your study is based on motivation theory.
On the other hand, a conceptual framework is ideal for something you will develop based on a theory. Thus, you can use some or all concepts of this theory. Thus, you develop a conceptual framework to solve a problem for which you’re doing the study to find a solution.
At this point, you’re no longer asking, ‘what is theoretical framework?’ But, you most likely want to know the types of frameworks that you can consider for your research. Well, this framework provides a lens or a perspective via which you will examine your topic. And this perspective can be from any study field depending on your academic paper.
For instance, a nursing student can use a theoretical framework in nursing research as long as it defines the concepts while explaining the phenomena in question. However, learners can consider other categories and types of theoretical framework in research.
They include:
- Dynamic and sustainability framework
- Implementation results framework
- Theoretical domains validation framework
- Consolidated implementation research and theoretical domains framework
- Active research implementation framework
- Evaluation framework
The internet has many resources with examples of theoretical framework in qualitative research and quantitative research. Check them out before you use any framework in your research to know what it entails.
This article has already answered the question, ‘what is theoretical framework in research?’ It has also highlighted the types of this framework. But, how do you complete your theoretical framework research work?
Here is a guide for creating this framework for your research:
- Identify the main concepts : Start by picking the main terms of your research problem or research questions. Some concepts can have several definitions. Your framework should define what each concept means clearly. For instance, if concepts like “customer satisfaction” and “customer loyalty” are central to your study, define them and discuss theories that explain their relationship.
- Explain and evaluate relevant theories : Engage in an extensive literature review to find out the definition of the connections between theories and concepts by other researchers. As you compose your framework, focus on critically evaluating different approaches and comparing them. Establish the most appropriate definitions for your research after discussing different theories and models. Mention all important concepts that are connected to the theories that you discuss in your framework. Explain why you choose a well-established theory for your study and what makes it the most suitable for that purpose. If unsure about the best way to do this, check a theoretical framework example online first.
- Demonstrate how your study fits in : In addition to discussing theories by other people, your framework should demonstrate how your project will implement these ideas. That means you have to test whether your chosen theory holds in your specific context. Also, use this theory to interpret the findings of your study. It’s also crucial to challenge or critique the theory. What’s more, combine various theories in a unique or new way. If possible and relevant, use your framework to come up with your research hypothesis.
- Structure your framework : When writing a dissertation or a thesis paper, you can integrate your framework in the literature review chapter. However, you can have it as a separate section or chapter of your paper. If you will be dealing with several complex theories in your paper, have a separate chapter or section for the framework. Nevertheless, you don’t have to follow specific, fixed rules when it comes to structuring the research theoretical framework section. But, your framework should have a logical, clear structure. For instance, you can draw on your study problems or questions and then structure every section around a major concept or question.
These tips should guide you in writing a framework with the theories or concepts you intend to use in your thesis or dissertation. However, you can apply them differently depending on the nature of your study. For instance, a business paper framework may not be the same as a nursing theoretical framework because these are different study fields. However, the concept of creating this framework is the same.
Summary of a Theoretical Framework Sample
For some researchers, an ideal approach is to define theoretical framework. However, some researchers assume the reader already knows what this framework is all about. As such, they go straight to the details. Below is a summary of a theoretical framework in research example.
Company Y wants to resolve the problem of having many customers buy its products online without returning for subsequent purchases. As such, the company management is looking for ways to enhance customer loyalty, hoping that better customer satisfaction will lead to the achievement of this goal.
In your research, you have developed a problem statement, research question, and research question as follows:
- Research problem : Most online buyers do not come back for subsequent purchases.
- Objective : To boost customer loyalty hoping to increase revenue through online sales
- Research questions : How can company Y improve the satisfaction of online customers to enhance customer loyalty?
Your framework should focus on answering these questions:
- Is there a relationship between customer satisfaction and customer loyalty?
- How loyal and satisfied are the online customers of company Y currently?
- What are some of the factors affecting the loyalty and satisfaction of the online customers of company Y?
Customer satisfaction and customer loyalty are major concepts that play a role in such a research paper. Therefore, they should be investigated and measured using theories or concepts that should be featured in the framework.
The information contained in this framework could be different from that of a theoretical framework nursing educators expect. That’s because this framework is meant for a business-oriented research paper. Nevertheless, the approach for writing both frameworks is the same.
The framework section of a thesis or dissertation paper clarifies implicit theories or concepts in a clearly defined manner. It also shows how they connect to the current research and why they are suitable for it. Your academic supervisor will most likely check this section first. Therefore, understanding its purpose and how to write it properly is very important.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Comment * Error message
Name * Error message
Email * Error message
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
As Putin continues killing civilians, bombing kindergartens, and threatening WWIII, Ukraine fights for the world's peaceful future.
Ukraine Live Updates
31 Theoretical Framework Examples

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process
A theoretical framework is a theory that can be applied to interpret and understand data in your research study.
A useful working definition comes from Connaway and Radford (2021):
“…a theoretical framework utilizes theory/theories and their constituent elements as the presumed ‘working model’ that drives the investigation and analysis of a social phenomenon.” (Connaway & Radford, 2021)
There are a range of theories that each look at the world through different lenses. Each will shape how we look at and interpret our data.
For example:
- Feminists look at the world through the lens of power and oppression of women.
- Functionalists look at the world and see how the concepts and ideas in our societies have a role in maintaining social order.
- Behaviorists look at the world and see how incentives – rewards and punishments – shape human behavior .
- Postmodernists look at the world and see how language and discourse shape belief systems .
When selecting a theoretical framework, we’re making a conscious decision about our approach and focus. For example, ‘feminism’ and ‘ critical theory ’ are theoretical frameworks that will focus on how power functions in society. This might be useful in a sociological or cultural studies analysis. But they won’t be so useful in a study of classroom learning, which might best be served by ‘behaviorism’ or ‘constructivism’ as your theoretical frames.
Theoretical Framework Examples
1. constructivism.
Scholarly Fields: Psychology, Education
Constructivism is a theory in educational psychology about how people think and learn.
It states that people construct their own understanding and knowledge of the world through experiencing things and reflecting on those experiences.
When new information challenges past beliefs, cognitive dissonance occurs, which is overcome through processes of assimilation and accommodation until we develop a new understanding of what we observe, which is ideally a closer approximation of the truth.
It challenges the previously dominant concept in psychology, behaviorism , that states we learn best through rewards, punishments, and forming associations between concepts.
Example of Constructivism in the Classroom
A researcher examines how students learn about the concept of gravity in a physics classroom. The study would observe the process as the students first encounter basic information, then explore related concepts through hands-on experiments and classroom discussions. The focus of the study would be on how students construct their understanding utilizing prior knowledge and evolving their understanding through experience and reflection.
2. Behaviorism
Behaviorism is a learning theory in behavioral psychology that holds that behaviors are learned through association, trial and error.
This theory takes a principled stance that learning needs to be measurable . Inner cognitive states are not taken into account because thoughts are, to behaviorists, not possible to be measured. Therefore, the theory suggests that behavior must be studied in a systematic and observable manner with no consideration of internal mental states.
A famous behaviorist study is Pavlov’s study of how his dog learned to salivate when he heard a bell ringing, because the dog associated the bell with food. This is now known as a Pavlovian response .
Similarly, B.F. Skinner found that rewarding and punishing rats can lead them into learning how to navigate mazes at faster and faster speeds, demonstrating the observable effects of rewards and punishments in learning.
If you were to use Behaviorism as your theoretical framework, it would likely inform both your research question – where you may want to focus on a situation where you will measure changes in behaviors through rewards and punishments – as well as your research methods, where you’ll likely employ a quantitative research method that measures changes in behaviors, such as application of pre-tests and post-tests in an educational environment.
Example of a Study Using a Behaviorist Theoretical Framework
In a study using a behaviorist framework, a psychologist might investigate the effects of positive reinforcement on the classroom behavior of elementary school children. The experiment could involve implementing a rewards system for a selected behavior, such as raising a hand before speaking, and observing any changes in the frequency of this behavior. The behaviorist theoretical framework would guide the researcher’s expectation that the reinforcement (reward) would increase the occurrence of the desired behavior.
3. Psychoanalytic Theory
Scholarly Fields: Psychology, Social Work
Psychoanalytic and psychodynamic theories , originally proposed by Sigmund Freud, posit that human behavior is the result of the interactions among three component parts of the mind: the id, ego, and superego .
This theory might be used by a psychology student in their research project where they test patients’ behaviors, comparing them to Freud’s (or, for that matter, Carl Jung’s) theoretical ideas about stages of development, interaction between id, ego, and superego, or the power of the subconscious to affect thoughts and behavior.
This theoretical frame is rarely used today, although it acts as a foundation to subsequent theories that are held in higher esteem, such as psychosocial theory, explained next.
Example of a Study Using a Psychoanalytic Theoretical Framework
A researcher using a psychoanalytic framework might study the influence of early childhood experiences on adult relationship patterns. Through in-depth interviews, the study would examine participants’ recollections of their early relationships with their parents and the unconscious conflicts and defenses that may have arisen from these experiences. The study would then look for patterns in the participants’ current relationships that might reflect these early experiences and defense mechanisms.
4. Psychosocial Theory
Psychosocial theory builds upon (and, in some ways, rejects) Freud’s psychoanalytic theory. This theory maintains that subconscious thoughts affect behavior, but focuses on how early social interactions affect outcomes later in life.
Erik Erikson, a central figure in the history of psychosocial theory, theorized that humans go through roughly set-in-stone stages of life, where in each stage, we must overcome challenges like industry vs inferiority (where we need to learn to embrace an industrious and creative personality or else risk having an inferiority complex later in life).
Psychosocial theory can be applied in the study of how people develop psychological complexes in their lives and helps them overcome them by exploring the origins of these complexes.
Example of a Study Using a Psychosocial Theoretical Framework
A study based on a psychosocial framework could explore individual patients’ core challenges and relate them to Erikson’s psychosocial states. The psychosocial theory would guide the interpretation of the results, suggesting that past events, such as being berated by parents, can lead to increased psychological stress.
5. Feminist Theory
Scholarly Fields: Sociology, Cultural Studies, and more
Feminism is a social and political framework that analyzes the status of women and men in society with the purpose of using that knowledge to promote women’s rights and interests.
Generally, a person applying a feminist framework would have at the core of their research question an interest in how women are positioned in society in relation to men, and how their lives and personal agency is shaped and structured by a manufactured gender hirearchy.
Of course, within Feminism, there are a range of conflicting views and perspectives. The intersectional feminists are highly concerned with how black, working-class, and other marginalized women face compounding disadvantages; whereas other feminists might focus exclusively on gender in the workforce, or even how women’s rights intersect with, and are possibly impacted by, trans* rights.
Example of a Study Using a Feminist Theoretical Framework
A researcher could use a feminist theoretical framework to investigate gender bias in workplace promotions within a large corporation. The study might involve collecting and analyzing qualitative data and quantitative data on promotion rates, gender ratios in upper management, and employee experiences related to promotion opportunities. From a feminist perspective, the study would aim to identify any potential systemic inequalities and their impact on women’s career trajectories.
7. Conflict Theory
Scholarly Fields: Sociology, Cultural Studies
Conflict theory is a framework derived from Marxism’s teachings about the operation of power through economic and cultural apparatuses in a society.
It generally works to highlight the role of coercion and power, particularly as it relates to social class and possession of economic capital .
Generally, this approach will involve an examination of the ways the economy, policy documents, media, and so forth, distribute power in a capitalist context . Other conflict theorists might examine non-capitalist contexts, such as workers’ cooperatives with the intention of exploring possibilities for economic and cultural life in a post-capitalist society.
Example of a Study Using a Conflict Theory Framework
A sociologist might utilize conflict theory to study wealth and income disparities within a specific urban community. This study might involve the analysis of economic data, alongside a consideration of social and political structures in the community. The conflict theory would guide an understanding of how wealth and power disparities contribute to social tensions and conflict.
8. Functionalism
Scholarly Fields: Sociology (see the separate concept: Functionalism in Psychology )
Functionalism , based on the works of Durkheim. Merton and their contemporaries, is an approach to sociology that assumes each aspect of society is interdependent and contributes to society’s functioning as a whole.
Functionalism often leans on the analogy of the human body to describe society. Just as the human body has organs which each have a purpose (i.e. a function), each social institution also serves a function to support the whole.
So, a functionalist theoretical framework aims to examine social institutions and social structures (e.g. economic conditions, family relationships, religious practices, media outlets, etc.) to explore how they do or do not fulfill their purposes.
Building on Merton’s work in functionalism, many functionalist studies in sociology also explore how institutions have both manifest functions (intended purposes and consequences) and latent functions (unintended purposes and functions).
Key social institutions explored in functionalism in sociology include: the education system, hospitals, workplaces, factories, religion, and families.
Example of a Study Using a Functionalist Theoretical Framework
A key question in functionalism is: “What is the role of this institution in upholding society, the status quo, and social hierarchies?” Following this approach, an educational researcher using a functionalist framework might study the role of schools in preparing students for various roles in society. They might collect data on curriculum, teaching methods, student performance, and post-graduation outcomes. Using a functionalist lens, the researcher would be interested in how each aspect of the education system contributes to the socialization process and preparation of individuals for adulthood and societal roles.
9. Symbolic Interactionism
Scholarly Fields: Sociology (see: symbolic interactionism in sociology )
The symbolic interaction theory states that the meaning we ascribe to objects, processes, ideas, concepts, and systems are subjective. They are constructed through language, words, and communication, and differ from context to context and culture to culture.
Symbolic interactionism is very common in qualitative research in the social sciences, especially work that involves interviews as a research method.
Symbolic interaction is a theoretical frame that challenges that of functionalism by focusing on microsociology rather than macrosociology .
Whereas functionalists are generally concerned with how social structures, institutions, and concepts have meaning on a social level , symbolic interactionists are concerned with how people make their own meanings of things in their surroundings.
For example, symbolic interactionism argues that people derive their understanding of their world through social interactions and personal experiences and interpretations.
Example of a Study Using a Symbolic Interactionist Framework
A researcher applying symbolic interactionist theory might investigate how medical patients and doctors negotiate understandings of illness during medical consultations. The study would likely involve observations and perhaps recordings of consultations, focusing on the language and symbols used by both parties. A symbolic interactionist approach would highlight how shared meanings and interpretations are built in these interactions, impacting the patient-doctor relationship and treatment decisions.
10. Postmodernism
Scholarly Fields: Sociology, Cultural Studies, Media Studies
Postmodern theory critiques social narratives, beliefs, and definitions, arguing that they’re historically, culturally and socially situated.
A key concept in postmodernism is discourse , which refers to how knowledge is constructed through language. The ways people talk about something constructs normative ideas about it (i.e. ideas, like gender, a socially constructed).
Postmodernists are therefore skeptical of truth-claims made about anything. Their research aims to demonstrate how truth-claims, such as “men are natural-born leaders” emerge through language and social narratives that normalize such as belief.
Postmodernism’s role, therefore. Is to highlight the relativity of truths and social narratives propagated by media and culture.
Example of a Study Using a Postmodern Theoretical Framework
A researcher using a postmodernist framework might conduct a study analyzing the portrayal of reality in contemporary television news. They might examine the selection and presentation of stories, the use of imagery and language, and the underlying assumptions about truth and objectivity. From a postmodernist perspective, the study would not be looking for an objective reality represented in the news but would explore how the news constructs multiple, subjective realities.
List of Additional Theoretical Frameworks
In communication studies.
- Uses and Gratifications Theory
- Agenda-Setting Theory
- Spiral of Silence Theory
- Cultivation Theory
- Muted Group Theory
In Psychology
- Cognitive Development Theory
- Evolutionary psychology
- Socio-cultural Theory
In Sociology
- Social Action Theory
- Poststructuralism
- Labeling Theory
- Strain Theory
- Differential Opportunity Theory
- Differential Association Theory
- Postcolonialism
In Economics
- Keynesian Economics
- Neoclassical Economics
- Marxist Economics
- Behavioral Economics
Choosing a theoretical framework is an early step in developing your research study. Once it is selected, it will go on to inform your research methodology and methods of data collection and analysis. Furthermore, in your analysis chapters of your dissertation, you will be regularly leaning upon the ideas and concepts within your chosen theoretical framework to shed light on your observations. Academic research that uses theoretical frameworks is all about using theory to interpret the world and shed new light on phenomena. With theory, we can develop a cohesive understanding of our subjects and construct detailed, well-thought-out arguments throughout our work.
Anfara Jr, V. A., & Mertz, N. T. (Eds.). (2014). Theoretical frameworks in qualitative research . Sage publications.
Borsboom, D., van der Maas, H. L., Dalege, J., Kievit, R. A., & Haig, B. D. (2021). Theory construction methodology: A practical framework for building theories in psychology. Perspectives on Psychological Science , 16 (4), 756-766.
Connaway, L. S., & Radford, M. L. (2016). Research methods in library and information science . Los Angeles: ABC-CLIO.
Given, L. M. (Ed.). (2008). The Sage encyclopedia of qualitative research methods . Sage publications.
Gelso, C. J. (2006). Applying theories to research. The psychology research handbook: A guide for graduate students and research assistants , 455 .

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 10 Reasons you’re Perpetually Single
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 20 Montessori Toddler Bedrooms (Design Inspiration)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 21 Montessori Homeschool Setups
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 101 Hidden Talents Examples

1 thought on “31 Theoretical Framework Examples”
Dr. Drew: I am glad I found your site and this article on TF. I have found TF to be the most difficult & challenging concept for and for the research process. I will be re-reding it several times today and making sure i completely understand it. Thanks Ken, EdD student
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Conceptual and Theoretical Frameworks for Thesis Studies: What you must know

A theoretical framework is a conceptual model that provides a systematic and structured way of thinking about a research problem or question. It helps to identify key variables and the relationships between them and to guide the selection and interpretation of data. Theoretical frameworks draw on existing theories and research and can be used to develop new hypotheses or test existing ones. They provide a foundation for research design, data collection, and analysis and can help to ensure that research is relevant, rigorous, and coherent. Theoretical frameworks are common in many disciplines, including social sciences, natural sciences, and humanities, and are essential for building knowledge and advancing understanding in a field.
This article explains the importance of frameworks in a thesis study and the differences between conceptual frameworks and theoretical frameworks. It provides guidelines on how to write a thesis framework, definitions of variable types, and examples of framework types.
What is a research framework and why do I need one?
When planning your thesis study, you need to justify your research and explain its design to your readers. This is called the research framework.
When planning your thesis study, you need to justify your research and explain its design to your readers. This is called the research framework. Think of it as the foundation of a building. A good building needs a strong foundation. Similarly, your research needs to be supported by reviewing and explaining the existing knowledge in the field, describing how your research study will fit within or contribute to the existing literature (e.g., it could challenge or test an existing theory or address a knowledge gap), and informing the reader how your study design aligns with your thesis question or hypothesis.
Important components of the framework are a literature review of recent studies associated with your thesis topic as well as theories/models used in your field of research. The literature review acts as a filtering tool to select appropriate thesis questions and guide data collection, analysis, and interpretation of your findings. Think broadly! Apart from reviewing relevant published papers in your field of research, also explore theories that you have come across in your undergraduate courses, other published thesis studies, encyclopedias, and handbooks.
There are two types of research frameworks: theoretical and conceptual .
What is a conceptual framework?
A conceptual framework is a written or visual representation that explains the study variables and their relationships with each other. The starting point is a literature review of existing studies and theories about your topic.
Steps to develop a conceptual framework
- Clarify your study topic by identifying and defining key concepts in your thesis problem statement and thesis question. Essentially, your thesis should address a knowledge gap.
- Perform a literature review to provide a background to interpret and explain the study findings. Also, draw on empirical knowledge that you have gained from personal experience.
- Identify crucial variables from the literature review and your empirical knowledge, classify them as dependent or independent variables, and define them.
- Brainstorm all the possible factors that could affect each dependent variable.
- Propose relationships among the variables and determine any associations that exist between all variables.
- Use a flowchart or tree diagram to present your conceptual framework.
Types of variables
When developing a conceptual framework, you will need to identify the following:
- Independent variables
- Dependent variables
- Moderating variables
- Mediating variables
- Control variables
First, identify the independent (cause) and dependent (effect) variables in your study. Then, identify variables that influence this relationship, such as moderating variables, mediating variables, and control variables. A moderating variable changes the relationship between independent and dependent variables when its value increases or decreases. A mediating variable links independent and dependent variables to better explain the relationship between them. A control variable could potentially impact the cause-and-effect relationship but is kept constant throughout the study so that its effects on the findings/outcomes can be ruled out.
Example of a conceptual framework
You want to investigate the hours spent exercising (cause) on childhood obesity (effect).

Now, you need to consider moderating variables that affect the cause-and-effect relationship. In our example, the amount of junk food eaten would affect the level of obesity.

Next, you need to consider mediating variables. In our example, the maximum heart rate during exercise would affect the child’s weight.

Finally, you need to consider control variables. In this example, because we do not want to investigate the role of age in obesity, we can use this as a control variable. Thus, the study subjects would be children of a specific age (e.g., aged 6–10 years).

What is a theoretical framework?
A theoretical framework provides a general framework for data analysis. It defines the concepts used and explains existing theories and models in your field of research.
A theoretical framework provides a general framework for data analysis. It defines the concepts used and explains existing theories and models in your field of research. It also explains any assumptions that were used to inform your approach and your choice of specific rationales. Theoretical frameworks are often used in the fields of social sciences.
Purpose of a theoretical framework
- Test and challenge existing theories
- Establish orderly connections between observations and facts
- Predict and control situations
- Develop hypotheses
Steps to develop a theoretical framework
- Identify and define key concepts in your thesis problem statement and thesis question.
- Explain and evaluate existing theories by writing a literature review that describes the concepts, models, and theories that support your study.
- Choose the theory that best explains the relationships between the key variables in your study.
- Explain how your research study fills a knowledge gap or fits into existing studies (e.g., testing if an established theory applies to your thesis context).
- Discuss the relevance of any theoretical assumptions and limitations.
A thesis topic can be approached from a variety of angles, depending on the theories used.
- In psychology, a behavioral approach would use different methods and assumptions compared with a cognitive approach when treating anxiety.
- In literature, a book could be analyzed using different literary theories, such as Marxism or poststructuralism.
Structuring a theoretical framework
The structure of a theoretical framework is fluid, and there are no specific rules that need to be followed, as long as it is clearly and logically presented.
The theoretical framework is a natural extension of your literature review. The literature review should identify gaps in the field of your research, and reviewing existing theories will help to determine how these can be addressed. The structure of a theoretical framework is fluid, and there are no specific rules that need to be followed, as long as it is clearly and logically presented. The theoretical framework is sometimes integrated into the literature review chapter of a thesis, but it can also be included as a separate chapter, depending on the complexity of the theories.
Example of a theoretical framework
The sales staff at Company X are unmotivated and struggling to meet their monthly targets. Some members of the management team believe that this could be achieved by implementing a comprehensive product-training program, but others believe that introducing a sales commission structure will help.
Company X is not achieving their monthly sales targets
To increase monthly sales.
Research question:
How can Company X motivate their sales team to achieve its monthly sales targets?
Sub-questions:
- Why do the sales staff feel unmotivated?
- What is the relationship between motivation and monetary rewards?
- Do the sales staff feel that they have sufficient product knowledge?
Theoretical framework:
A literature search will need to be performed to understand the background of the many different theories of motivation in psychology. For example, Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs (basic human needs—physiological, safety, love/belonging, esteem, and self-actualization—have to be fulfilled before one can live up to their true potential), Vroom’s Theory of Expectancy (people decide upon their actions based on the outcomes they expect), and Locke’s Goal-Setting Theory (goals are a key driver of one’s behavior). These theories would need to be investigated to determine which would be the best approach to increase the motivation of the sales staff in Company X so that the monthly sales targets are met.
A robust conceptual or theoretical framework is crucial when writing a thesis/dissertation. It defines your research gap, identifies your approach, and guides the interpretation of your results.
A thesis is the most important document you will write during your academic studies. For professional thesis editing and thesis proofreading services, check out Enago's Thesis Editing service s for more information.
Editor’s pick
Get free updates.
Subscribe to our newsletter for regular insights from the research and publishing industry!
What type of framework is used in the Humanities and Social Sciences (HSS) domain? +
Theoretical frameworks are typically used in the HSS domain, while conceptual frameworks are used in the Sciences domain.
What is the difference between mediating versus moderating variables? +
The difference between mediators and moderators can be confusing. A moderating variable is unaffected by the independent variable and can increase or decrease the strength of the relationship between the independent and dependent variables. A mediating variable is affected by the independent variable and can explain the relationship between the independent and dependent variables. T he statistical correlation between the independent and dependent variables is higher when the mediating variable is excluded.
What software should I use to present my conceptual framework? +
The software program Creately provides some useful templates that can help you get started. Other recommended programs are SmartDraw , Inkscape , and diagrams.net .
Understanding and solving intractable resource governance problems.
- Conferences and Talks
- Exploring models of electronic wastes governance in the United States and Mexico: Recycling, risk and environmental justice
- The Collaborative Resource Governance Lab (CoReGovLab)
- Water Conflicts in Mexico: A Multi-Method Approach
- Past projects
- Publications and scholarly output
- Research Interests
- Higher education and academia
- Public administration, public policy and public management research
- Research-oriented blog posts
- Stuff about research methods
- Research trajectory
- Publications
- Developing a Writing Practice
- Outlining Papers
- Publishing strategies
- Writing a book manuscript
- Writing a research paper, book chapter or dissertation/thesis chapter
- Everything Notebook
- Literature Reviews
- Note-Taking Techniques
- Organization and Time Management
- Planning Methods and Approaches
- Qualitative Methods, Qualitative Research, Qualitative Analysis
- Reading Notes of Books
- Reading Strategies
- Teaching Public Policy, Public Administration and Public Management
- My Reading Notes of Books on How to Write a Doctoral Dissertation/How to Conduct PhD Research
- Writing a Thesis (Undergraduate or Masters) or a Dissertation (PhD)
- Reading strategies for undergraduates
- Social Media in Academia
- Resources for Job Seekers in the Academic Market
- Writing Groups and Retreats
- Regional Development (Fall 2015)
- State and Local Government (Fall 2015)
- Public Policy Analysis (Fall 2016)
- Regional Development (Fall 2016)
- Public Policy Analysis (Fall 2018)
- Public Policy Analysis (Fall 2019)
- Public Policy Analysis (Spring 2016)
- POLI 351 Environmental Policy and Politics (Summer Session 2011)
- POLI 352 Comparative Politics of Public Policy (Term 2)
- POLI 375A Global Environmental Politics (Term 2)
- POLI 350A Public Policy (Term 2)
- POLI 351 Environmental Policy and Politics (Term 1)
- POLI 332 Latin American Environmental Politics (Term 2, Spring 2012)
- POLI 350A Public Policy (Term 1, Sep-Dec 2011)
- POLI 375A Global Environmental Politics (Term 1, Sep-Dec 2011)
Writing theoretical frameworks, analytical frameworks and conceptual frameworks
Three of the most challenging concepts for me to explain are the interrelated ideas of a theoretical framework, a conceptual framework, and an analytical framework. All three of these tend to be used interchangeably. While I find these concepts somewhat fuzzy and I struggle sometimes to explain the differences between them and clarify their usage for my students (and clearly I am not alone in this challenge), this blog post is an attempt to help discern these analytical categories more clearly.
A lot of people (my own students included) have asked me if the theoretical framework is their literature review. That’s actually not the case. A theoretical framework , the way I define it, is comprised of the different theories and theoretical constructs that help explain a phenomenon. A theoretical framework sets out the various expectations that a theory posits and how they would apply to a specific case under analysis, and how one would use theory to explain a particular phenomenon. I like how theoretical frameworks are defined in this blog post . Dr. Cyrus Samii offers an explanation of what a good theoretical framework does for students .
For example, you can use framing theory to help you explain how different actors perceive the world. Your theoretical framework may be based on theories of framing, but it can also include others. For example, in this paper, Zeitoun and Allan explain their theoretical framework, aptly named hydro-hegemony . In doing so, Zeitoun and Allan explain the role of each theoretical construct (Power, Hydro-Hegemony, Political Economy) and how they apply to transboundary water conflict. Another good example of a theoretical framework is that posited by Dr. Michael J. Bloomfield in his book Dirty Gold, as I mention in this tweet:
In Chapter 2, @mj_bloomfield nicely sets his theoretical framework borrowing from sociology, IR, and business-strategy scholarship pic.twitter.com/jTGF4PPymn — Dr Raul Pacheco-Vega (@raulpacheco) December 24, 2017
An analytical framework is, the way I see it, a model that helps explain how a certain type of analysis will be conducted. For example, in this paper, Franks and Cleaver develop an analytical framework that includes scholarship on poverty measurement to help us understand how water governance and poverty are interrelated . Other authors describe an analytical framework as a “conceptual framework that helps analyse particular phenomena”, as posited here , ungated version can be read here .
I think it’s easy to conflate analytical frameworks with theoretical and conceptual ones because of the way in which concepts, theories and ideas are harnessed to explain a phenomenon. But I believe the most important element of an analytical framework is instrumental : their purpose is to help undertake analyses. You use elements of an analytical framework to deconstruct a specific concept/set of concepts/phenomenon. For example, in this paper , Bodde et al develop an analytical framework to characterise sources of uncertainties in strategic environmental assessments.
A robust conceptual framework describes the different concepts one would need to know to understand a particular phenomenon, without pretending to create causal links across variables and outcomes. In my view, theoretical frameworks set expectations, because theories are constructs that help explain relationships between variables and specific outcomes and responses. Conceptual frameworks, the way I see them, are like lenses through which you can see a particular phenomenon.
A conceptual framework should serve to help illuminate and clarify fuzzy ideas, and fill lacunae. Viewed this way, a conceptual framework offers insight that would not be otherwise be gained without a more profound understanding of the concepts explained in the framework. For example, in this article, Beck offers social movement theory as a conceptual framework that can help understand terrorism . As I explained in my metaphor above, social movement theory is the lens through which you see terrorism, and you get a clearer understanding of how it operates precisely because you used this particular theory.
Dan Kaminsky offered a really interesting explanation connecting these topics to time, read his tweet below.
I think this maps to time. Theoretical frameworks talk about how we got here. Conceptual frameworks discuss what we have. Analytical frameworks discuss where we can go with this. See also legislative/executive/judicial. — Dan Kaminsky (@dakami) September 28, 2018
One of my CIDE students, Andres Ruiz, reminded me of this article on conceptual frameworks in the International Journal of Qualitative Methods. I’ll also be adding resources as I get them via Twitter or email. Hopefully this blog post will help clarify this idea!
You can share this blog post on the following social networks by clicking on their icon.
Posted in academia .
Tagged with analytical framework , conceptual framework , theoretical framework .
By Raul Pacheco-Vega – September 28, 2018
7 Responses
Stay in touch with the conversation, subscribe to the RSS feed for comments on this post .
Thanks, this had some useful clarifications for me!
I GOT CONFUSED AGAIN!
No need to be confused!
Thanks for the Clarification, Dr Raul. My cluttered mind is largely cleared, now.
Thanks,very helpful
I too was/am confused but this helps 🙂
Thank you very much, Dr.
Leave a Reply Cancel Some HTML is OK
Name (required)
Email (required, but never shared)
or, reply to this post via trackback .
About Raul Pacheco-Vega, PhD
Find me online.
My Research Output
- Google Scholar Profile
- Academia.Edu
- ResearchGate
My Social Networks
- Polycentricity Network
Recent Posts
- The value and importance of the pre-writing stage of writing
- My experience teaching residential academic writing workshops
- “State-Sponsored Activism: Bureaucrats and Social Movements in Brazil” – Jessica Rich – my reading notes
- Reading Like a Writer – Francine Prose – my reading notes
- Using the Pacheco-Vega workflows and frameworks to write and/or revise a scholarly book
Recent Comments
- Charlotte on The value and importance of the pre-writing stage of writing
- Raul Pacheco-Vega on The value and importance of the pre-writing stage of writing
- Noni on Developing a structured daily routine for writing and research
- Alan Parker on Project management for academics I: Managing a research pipeline
Follow me on Twitter:
Proudly powered by WordPress and Carrington .
Carrington Theme by Crowd Favorite
- Chapter 1: Home
- Narrowing Your Topic
- Problem Statement
- Purpose Statement
- Conceptual Framework
Designing the Theoretical Framework
Theoretical framework guide, making a theoretical framework, example framework, additional framework resources.
- Quantitative Research Questions This link opens in a new window
- Qualitative Research Questions This link opens in a new window
- Qualitative & Quantitative Research Support with the ASC This link opens in a new window
- Library Research Consultations This link opens in a new window
What is it?
- A foundational review of existing theories.
- Serves as a roadmap or blueprint for developing arguments and supporting research.
- Overview of the theory that the research is based on.
- Can be made up of theories, principles, and concepts.
What does it do?
- Explains the why and how of a particular phenomenon within a particular body of literature.
- Connects the research subject with the theory.
- Specifies the study’s scope; makes it more valuable and generalizable.
- Guides further actions like framing the research questions, developing the literature review, and data collection and analyses.
What should be in it?
- Theory or theories that the researcher considers relevant for their research, principles, and concepts.
- Theoretical Framework Guide Use this guide to determine the guiding framework for your theoretical dissertation research.
How to make a theoretical framework
- Specify research objectives.
- Note the prominent variables under the study.
- Explore and review the literature through keywords identified as prominent variables.
- Note the theories that contain these variables or the keywords.
- Review all selected theories again in the light of the study’s objectives, and the key variables identified.
- Search for alternative theoretical propositions in the literature that may challenge the ones already selected.
- Ensure that the framework aligns with the study’s objectives, problem statement, the main research question, methodology, data analysis, and the expected conclusion.
- Decide on the final framework and begin developing.
- Theoretical Framework Example for a Thesis or Dissertation This link offers an example theoretical framework.
Some additional helpful resources in constructing a theoretical framework for study:
- https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/theoretical-framework/
- https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/theoretical-framework-example/
- https://www.projectguru.in/how-to-write-the-theoretical-framework-of-research/
Theoretical Framework Research
The term conceptual framework and theoretical framework are often and erroneously used interchangeably (Grant & Osanloo, 2014). A theoretical framework provides the theoretical assumptions for the larger context of a study, and is the foundation or ‘lens’ by which a study is developed. This framework helps to ground the research focus understudy within theoretical underpinnings and to frame the inquiry for data analysis and interpretation. The application of theory in traditional theoretical research is to understand, explain, and predict phenomena (Swanson, 2013).
Casanave, C.P.,& Li,Y.(2015). Novices’ struggles with conceptual and theoretical framing in writing dissertations and papers for publication. Publications,3 (2),104-119.doi:10.3390/publications3020104
Grant, C., & Osanloo, A. (2014). Understanding, Selecting, and Integrating a Theoretical Framework in Dissertation Research: Creating the Blueprint for Your “House. ” Administrative Issues Journal: Connecting Education, Practice, and Research, 4(2), 12–26
Swanson, R. (2013). Theory building in applied disciplines . San Francisco: Berrett-Koehler Publishers.
- << Previous: Conceptual Framework
- Next: Quantitative Research Questions >>
- Last Updated: Apr 24, 2024 2:48 PM
- URL: https://resources.nu.edu/c.php?g=1006886

© Copyright 2024 National University. All Rights Reserved.
Privacy Policy | Consumer Information
- Translators
- Graphic Designers
Please enter the email address you used for your account. Your sign in information will be sent to your email address after it has been verified.
6 Steps to Mastering the Theoretical Framework of a Dissertation

As the pivotal section of your dissertation, the theoretical framework will be the lens through which your readers should evaluate your research. It's also a necessary part of your writing and research processes from which every written section will be built.
In their journal article titled Understanding, selecting, and integrating a theoretical framework in dissertation research: Creating the blueprint for your "house" , authors Cynthia Grant and Azadeh Osanloo write:
The theoretical framework is one of the most important aspects in the research process, yet is often misunderstood by doctoral candidates as they prepare their dissertation research study. The importance of theory-driven thinking and acting is emphasized in relation to the selection of a topic, the development of research questions, the conceptualization of the literature review, the design approach, and the analysis plan for the dissertation study. Using a metaphor of the "blueprint" of a house, this article explains the application of a theoretical framework in a dissertation. Administrative Issues Journal
They continue in their paper to discuss how architects and contractors understand that prior to building a house, there must be a blueprint created. This blueprint will then serve as a guide for everyone involved in the construction of the home, including those building the foundation, installing the plumbing and electrical systems, etc. They then state, We believe the blueprint is an appropriate analogy of the theoretical framework of the dissertation.
As with drawing and creating any blueprint, it is often the most difficult part of the building process. Many potential conflicts must be considered and mitigated, and much thought must be put into how the foundation will support the rest of the home. Without proper consideration on the front end, the entire structure could be at risk.

With this in mind, I'm going to discuss six steps to mastering the theoretical framework section—the "blueprint" for your dissertation. If you follow these steps and complete the checklist included, your blueprint is guaranteed to be a solid one.
Complete your review of literature first
In order to identify the scope of your theoretical framework, you'll need to address research that has already been completed by others, as well as gaps in the research. Understanding this, it's clear why you'll need to complete your review of literature before you can adequately write a theoretical framework for your dissertation or thesis.
Simply put, before conducting any extensive research on a topic or hypothesis, you need to understand where the gaps are and how they can be filled. As will be mentioned in a later step, it's important to note within your theoretical framework if you have closed any gaps in the literature through your research. It's also important to know the research that has laid a foundation for the current knowledge, including any theories, assumptions, or studies that have been done that you can draw on for your own. Without performing this necessary step, you're likely to produce research that is redundant, and therefore not likely to be published.
Understand the purpose of a theoretical framework
When you present a research problem, an important step in doing so is to provide context and background to that specific problem. This allows your reader to understand both the scope and the purpose of your research, while giving you a direction in your writing. Just as a blueprint for a home needs to provide needed context to all of the builders and professionals involved in the building process, so does the theoretical framework of your dissertation.
So, in building your theoretical framework, there are several details that need to be considered and explained, including:
- The definition of any concepts or theories you're building on or exploring (this is especially important if it is a theory that is taken from another discipline or is relatively new).
- The context in which this concept has been explored in the past.
- The important literature that has already been published on the concept or theory, including citations.
- The context in which you plan to explore the concept or theory. You can briefly mention your intended methods used, along with methods that have been used in the past—but keep in mind that there will be a separate section of your dissertation to present these in detail.
- Any gaps that you hope to fill in the research
- Any limitations encountered by past researchers and any that you encountered in your own exploration of the topic.
- Basically, your theoretical framework helps to give your reader a general understanding of the research problem, how it has already been explored, and where your research falls in the scope of it. In such, be sure to keep it written in present tense, since it is research that is presently being done. When you refer to past research by others, you can do so in past tense, but anything related to your own research should be written in the present.
Use your theoretical framework to justify your research
In your literature review, you'll focus on finding research that has been conducted that is pertinent to your own study. This could be literature that establishes theories connected with your research, or provides pertinent analytic models. You will then mention these theories or models in your own theoretical framework and justify why they are the basis of—or relevant to—your research.
Basically, think of your theoretical framework as a quick, powerful way to justify to your reader why this research is important. If you are expanding upon past research by other scholars, your theoretical framework should mention the foundation they've laid and why it is important to build on that, or how it needs to be applied to a more modern concept. If there are gaps in the research on certain topics or theories, and your research fills these gaps, mention that in your theoretical framework, as well. It is your opportunity to justify the work you've done in a scientific context—both to your dissertation committee and to any publications interested in publishing your work.
Keep it within three to five pages
While there are usually no hard and fast rules related to the length of your theoretical framework, it is most common to keep it within three to five pages. This length should be enough to provide all of the relevant information to your reader without going into depth about the theories or assumptions mentioned. If you find yourself needing many more pages to write your theoretical framework, it is likely that you've failed to provide a succinct explanation for a theory, concept, or past study. Remember—you'll have ample opportunity throughout the course of writing your dissertation to expand and expound on these concepts, past studies, methods, and hypotheses. Your theoretical framework is not the place for these details.
If you've written an abstract, consider your theoretical framework to be somewhat of an extended abstract. It should offer a glimpse of the entirety of your research without going into a detailed explanation of the methods or background of it. In many cases, chiseling the theoretical framework down to the three to five-page length is a process of determining whether detail is needed in establishing understanding for your reader.

Use models and other graphics
Since your theoretical framework should clarify complicated theories or assumptions related to your research, it's often a good idea to include models and other helpful graphics to achieve this aim. If space is an issue, most formats allow you to include these illustrations or models in the appendix of your paper and refer to them within the main text.
Use a checklist after completing your first draft
You should consider the following questions as you draft your theoretical framework and check them off as a checklist after completing your first draft:
- Have the main theories and models related to your research been presented and briefly explained? In other words, does it offer an explicit statement of assumptions and/or theories that allows the reader to make a critical evaluation of them?
- Have you correctly cited the main scientific articles on the subject?
- Does it tell the reader about current knowledge related to the assumptions/theories and any gaps in that knowledge?
- Does it offer information related to notable connections between concepts?
- Does it include a relevant theory that forms the basis of your hypotheses and methods?
- Does it answer the question of "why" your research is valid and important? In other words, does it provide scientific justification for your research?
- If your research fills a gap in the literature, does your theoretical framework state this explicitly?
- Does it include the constructs and variables (both independent and dependent) that are relevant to your study?
- Does it state assumptions and propositions that are relevant to your research (along with the guiding theories related to these)?
- Does it "frame" your entire research, giving it direction and a backbone to support your hypotheses?
- Are your research questions answered?
- Is it logical?
- Is it free of grammar, punctuation, spelling, and syntax errors?
A final note
In conclusion, I would like to leave you with a quote from Grant and Osanloo:
The importance of utilizing a theoretical framework in a dissertation study cannot be stressed enough. The theoretical framework is the foundation from which all knowledge is constructed (metaphorically and literally) for a research study. It serves as the structure and support for the rationale for the study, the problem statement, the purpose, the significance, and the research questions. The theoretical framework provides a grounding base, or an anchor, for the literature review, and most importantly, the methods and analysis. Administrative Issues Journal

- Dissertation Coaching
- Qualitative Data Analysis
- Statistical Consulting
- Dissertation Editing
- On-Demand Courses

How to Write a Theoretical Framework: A Step-by-Step Guide
The theoretical framework is an essential component of any research study. It provides the foundation for your research by outlining the key concepts, variables, and relationships that you will explore in your research. In this step-by-step guide, we will walk you through the process of writing a theoretical framework, from understanding the basics to revising and refining your work.
Understanding the Basics of a Theoretical Framework
What is a theoretical framework.
A theoretical framework guides your research by providing a structure for understanding and analyzing your topic.
Having a well-developed theoretical framework is essential because it:
- Provides a basis for analyzing your data and interpreting your findings
- Ensures that your study aligns with existing theories and literature
- Guides the selection of research methods and data collection techniques
- Enhances the credibility and rigor of your research
When you have a strong theoretical framework, you are equipped with a solid foundation that allows you to delve deeper into your research and make a contribution to your field of study. Additionally, a well-developed theoretical framework helps you to identify gaps in existing knowledge and contributes to the advancement of your field. Furthermore, a theoretical framework helps you to establish the context of your research. By grounding your study in established theories and concepts, you demonstrate that your work is built upon an existing body of knowledge.
Key Components of a Theoretical Framework
A theoretical framework typically consists of three key components:
- Conceptual definitions: Clearly defining the main concepts and variables of your study is crucial. This ensures that you and your readers have a shared understanding of the key terms used throughout your research.
- Theoretical assumptions: These are the underlying assumptions or theoretical propositions that guide your study. They provide a theoretical lens through which you will analyze your data and draw conclusions.
- Visual model: This is the graphical or conceptual representation of the relationships between the key concepts and variables in your study. It visually depicts how they interact and influence one another.
Conceptual definitions play a vital role in a theoretical framework as they provide clarity and precision to your research. By clearly defining the main concepts and variables, you ensure that there is no ambiguity among the relationship between concepts in your study. This allows you to communicate your ideas effectively and facilitates a better understanding of your research by both yourself and your readers.
Theoretical assumptions, on the other hand, serve as the foundation upon which your study is built. These assumptions are derived from existing theories and literature and help you to establish a theoretical lens through which you will analyze your data. They guide your research questions, hypotheses, and the overall direction of your study.
Finally, the theoretical model or framework visually represents the relationships between the key concepts and variables in your study. It provides a clear and concise overview of how these elements interact and influence one another. This graphical or conceptual representation aids in understanding the complex dynamics of your research and helps you to identify patterns, trends, and connections.
Preparing to Write Your Theoretical Framework
Before you start writing your theoretical framework, it is important to identify the key concepts and variables that you will plan to study. We recommend starting this process by clearly defining each concept and variable and understanding their relationship to your research question. In doing so, you will be able to ensure that your framework aligns with your research objectives.
Once you have identified your key concepts and variables, conduct a thorough literature review to understand how other researchers have conceptualized and studied these concepts. This will help you build on existing theories and identify any gaps in the literature that your research can address.
Writing Your Theoretical Framework
Articulating Your Assumptions and Hypotheses. Once you have structured your theoretical framework, it is time to articulate your assumptions and hypotheses. Assumptions are statements that you take for granted and form the foundation of your study. They are based on your theoretical framework and inform your research design and methodology. Clearly state your assumptions and explain how they shape your research objectives and approach.
In addition to assumptions, you may also develop hypotheses based on your theoretical framework. Hypotheses are testable predictions or statements about the relationships between variables in your study. They provide a framework for data collection and analysis. Clearly articulate your hypotheses and explain how they align with your theoretical framework and research question.
Explaining Your Choice of Theory. It is essential to provide a clear explanation of why you have chosen a particular theory or model for your research. Discuss the theoretical perspectives or models that informed your choice and explain how they relate to your research question. Justify why this theory or model is appropriate for your study and how it enhances your understanding of the topic.
Support your choice of theory or model with evidence from relevant literature. Show how other researchers have used this theory or model to study similar topics and how it aligns with your research objectives. This will help strengthen the credibility and validity of your theoretical framework.
Revising and Refining Your Theoretical Framework
Once you have completed your initial draft of the theoretical framework, seek feedback from colleagues, mentors, or experts in your field. Ask them to review your framework and provide constructive feedback. Their insights and suggestions can help you identify any potential weaknesses or areas for improvement.
Based on the feedback received, make revisions to your theoretical framework. Incorporate any necessary changes to strengthen the clarity, coherence, and validity of your framework. Repeat this feedback and revision process until you are confident that your theoretical framework effectively supports your research objectives.
Writing a theoretical framework can be a challenging task, but by following this step-by-step guide, you can create a solid foundation for your research. Remember to carefully consider the core components of a theoretical framework and ensure that your structure and language are clear and concise. With a well-developed theoretical framework, your research will be grounded in established theories and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in your field.
Ready to take your research to the next level? Dissertation by Design is here to support you every step of the way. Whether you need personalized guidance on qualitative data analysis, expert statistical consulting, or meticulous dissertation editing, we have the resources to assist you.
Schedule a free consultation today and move forward with clarity and confidence in your academic journey.
Author: Jessica Parker, EdD
Related posts.

Download our free guide on how to overcome the top 10 challenges common to doctoral candidates and graduate sooner.
Thank You 🙌
Click here for Graduate Research Workshop on Sept. 8th @ 1pm Central Time
Mary depew resource center for research writing: theoretical frameworks.
- Research Roadmap
- Identifying Scholarly Resources
- Primary Vs. Secondary
- Peer-Reviewed
- Practitioner Vs. Scholarly
- College of Business: Essential Readings
- College of Education: Curriculum & Instruction
- College of Education: Leadership & Administration Essential Readings
- College of Education: Teaching & Learning Essential Readings
- College of Health, Science, and Technology: Essential Readings
- College of Theology, Arts, and Humanities: Division of Research Essential Readings
- Lutheran Education Journal This link opens in a new window
- Concordia University Chicago: Pillars Yearbooks This link opens in a new window
- Martin Luther & the Lutheran Church This link opens in a new window
Theoretical Frameworks
- Navigating Databases
- Journals by Subject
- Online Resources
- Graduate Research Workshop
- APA 7th Ed.
- Expository Paragraph Writing
- Sentence Composition
- Online Writing Labs
- Comprehensive Exam Writing
- Comprehensive Exam Rubric Example
- Comprehensive Exam College of Education, Dept. of Curriculum & Instruction: Rubric Example Parts 1 & 2
- Comprehensive Exam College of Education, Dept. of Ed Leadership: Rubric Example Part 1 & 2
- Comprehensive Exam FAQs This link opens in a new window
- Qualitative Research Focused Journals
- Technology for Data Collection and Analysis
- Research Tools
- Example Dissertations by Epis//Method. Claim
- Dissertation FAQs & Models This link opens in a new window
- Dissertation Ebooks
- Doctoral Defense
- CUC Doc Student Support Groups
- Faculty Publications
- CUC Writing Center This link opens in a new window
- Klinck Library Resources
- Accessibility & Accommodations Services This link opens in a new window
- CougarNet This link opens in a new window
- What are they?
- Strategies for Developing your Framework
- Ed. Leadership Examples
A theoretical framework consists of concepts and, together with their definitions and reference to relevant scholarly literature, existing theory that is used for your particular study. Theoretical frameworks provide a perspective through which to examine a topic, especially when constructing your dissertation. There are many different lenses, which may be used to define specific concepts and explain phenomena. Different lenses can be:
- psychological theories
- social theories
- organizational theories
- economic theories
Sometimes frameworks may come from an area outside of your immediate academic discipline. Using a theoretical framework for your dissertation will help you to better analyze past events by providing a particular set of questions to ask and a perspective to use when examining your topic.
Traditionally, Ph.D. and Applied Degree research must include relevant theoretical framework(s) to frame, or inform, every aspect of the dissertation. Dissertations should make an original contribution to the field by adding support for the theory or demonstrating ways in which the theory may not be as explanatory as originally thought.
It can be difficult to find scholarly work that takes a particular theoretical approach because articles, books, and book chapters are typically described according to the topics they tackle rather than the methods they use to tackle them.
Unfortunately, there is no single database or search technique for locating theoretical information. However, the suggestions below provide techniques for locating possible theoretical frameworks and theorists in the CUC library databases. In addition to your Library research, you should discuss possible theories your Dissertation Chair to ensure they align with your study. You will likely find and discard several potential theoretical frameworks before one is finally chosen.
I. Developing the Framework
Here are some strategies to develop of an effective theoretical framework:
- Examine your thesis title and research problem . The research problem anchors your entire study and forms the basis from which you construct your theoretical framework.
- Brainstorm about what you consider to be the key variables in your research . Answer the question, "What factors contribute to the presumed effect?"
- Review related literature to find how scholars have addressed your research question.
- List the constructs and variables that might be relevant to your study. Group these variables into independent and dependent categories.
- Review key social science theories that are introduced to you in your course readings and choose the theory that can best explain the relationships between the key variables in your study [note the Writing Tip on this page].
- Discuss the assumptions or propositions of this theory and point out their relevance to your research.
A theoretical framework is used to limit the scope of the relevant data by focusing on specific variables and defining the specific viewpoint [framework] that the researcher will take in analyzing and interpreting the data to be gathered. It also facilitates the understanding of concepts and variables according to given definitions and builds new knowledge by validating or challenging theoretical assumptions.
II. Purpose
Think of theories as the conceptual basis for understanding, analyzing, and designing ways to investigate relationships within social systems. To that end, the following roles served by a theory can help guide the development of your framework.
- Means by which new research data can be interpreted and coded for future use,
- Response to new problems that have no previously identified solutions strategy,
- Means for identifying and defining research problems,
- Means for prescribing or evaluating solutions to research problems,
- Ways of discerning certain facts among the accumulated knowledge that are important and which facts are not,
- Means of giving old data new interpretations and new meaning,
- Means by which to identify important new issues and prescribe the most critical research questions that need to be answered to maximize understanding of the issue,
- Means of providing members of a professional discipline with a common language and a frame of reference for defining the boundaries of their profession, and
- Means to guide and inform research so that it can, in turn, guide research efforts and improve professional practice.
Adapted from: Torraco, R. J. “Theory-Building Research Methods.” In Swanson R. A. and E. F. Holton III , editors. Human Resource Development Handbook: Linking Research and Practice . (San Francisco, CA: Berrett-Koehler, 1997): pp. 114-137; Jacard, James and Jacob Jacoby. Theory Construction and Model-Building Skills: A Practical Guide for Social Scientists . New York: Guilford, 2010; Sutton, Robert I. and Barry M. Staw. “What Theory is Not.” Administrative Science Quarterly 40 (September 1995): 371-384.
No framework is necessarily more effective than another. Frameworks serve to provide a conceptual overview, separate from methodologies or implementation. Though there are thousands of theoretical frameworks leveraged in teaching, some of the more popular frameworks are:
- Andragogy/Adult Learning Theory – Theorists like Knowles (1980) believed adults are problem-oriented participants that want to incorporate experience and self-direction into subjects or projects that are relevant to their lives. Andragogic education tends to incorporate methods like constructivism and connectivism, leveraging task-oriented processes and projects, also stressing application.
- Behaviorism – Theorists like Skinner (1953) often focused on observable behavior, believing learning was supported through drill & practice and related reinforcement. Behaviorist instruction tends to be directive, incorporating lectures and practice problems, often leveraging objective assessments including multiple choice questions or other rote approaches.
- Cognitivism – Theorists like Gagné (Gagne, Wager, Golas, & Keller, 2004) focused more on thought processes and structures. For instance, Gagné developed nine events of instruction to describe optimal conditions for learning. Cognitivist instruction often incorporates lecture along with methods like visual tools or organizers to promote retention. It may leverage objective assessments with multiple choice, though also including response or essay activities for learners to demonstrate thought processes.
- Connectivism – Theorists like Siemens & Downes (2009) saw learners as part of many nodes or connections, driving their personal learning by leveraging the knowledge of that network, and contributing to the knowledge infrastructure. Connectivist instruction tends to be self-directed, including a variety of information sources/references and is often used in online education. It could also be considered a constructivist approach.
- Constructivism – Theorists like Piaget (1950) & Brunner (1961) proposed individuals construct knowledge from within, contributing to the process by incorporating personal experience. Constructivist instruction tends to be social and exploratory, sometimes without clearly defined outcomes, often leveraging critical thinking activities, peer review, and/or collaborative projects.
- Objectivism – Theorists or writers like Rand (1943) believed knowledge exists outside the individual as opposed to constructivist perspectives valuing knowledge from within. Objectivist frameworks can describe both behaviorist and cognitivist perspectives. Objectivist instruction tends to be directive and linear, valuing inductive logic, and often leverages objective assessments.
Credit to Central Michigan
- National University: Theoretical Frameworks Sheet
- Grant, C., & Osanloo, A. (2014). Understanding, Selecting, and Integrating a Theoretical Framework in Dissertation Research: Creating the Blueprint for Your “House.” Administrative Issues Journal: Education, Practice & Research, 4(2), 12–26. https://doi.o
- Kumar, S., Dawson, K., Pollard, R., & Jeter, G. (2022). Analyzing Theories, Conceptual Frameworks, and Research Methods in EdD Dissertations. TechTrends: Linking Research & Practice to Improve Learning, 66(4), 721–728. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11528-022-0
- Tegtmeyer, J. (2022). Building a Dissertation Conceptual and Theoretical Framework: A Recent Doctoral Graduate Narrates behind the Curtain Development. Penn GSE Perspectives on Urban Education, 20(1).
- << Previous: Martin Luther & the Lutheran Church
- Next: Lit. Review Resources >>
- Last Updated: Sep 6, 2024 1:28 PM
- URL: https://libguides.cuchicago.edu/research_center
Klinck Memorial Library
Concordia University Chicago 7400 Augusta Street River Forest, Illinois 60305 (708) 209-3050 [email protected] Campus Maps and Directions
- Staff Directory
- Getting Started
- Databases A-Z
- Library Catalog
- Interlibrary Loan
Popular Links
- Research Guides
- Research Help
- Request Class Instruction
© 2021 Copyright: Concordia University Chicago, Klinck Memorial Library
Verify originality of an essay
Get ideas for your paper
Cite sources with ease
Theoretical Framework: Definition, Writing Guide, and Examples
Updated 30 Aug 2024
If you’re crafting a research paper or dissertation, incorporating a theoretical framework can provide a structured approach to organize and document your efforts. Employing this element aids in adhering to established research conventions, potentially enabling you to publish your study and utilize its outcomes for a thesis.
Within this article, we delve into this term definition, highlighting its distinctions from a conceptual framework. We explore the reasons behind including this paragraph in a dissertation or thesis and offer a systematic guide to developing one in six steps. Additionally, we present an illustrative example to assist you in crafting your theoretical framework.
What is a theoretical framework?
This section establishes the theoretical basis and conceptual structure for academic writing. It incorporates essential theories, models, concepts, and ideas from existing literature, offering a framework to interpret findings. Its purpose is to define study scope and boundaries, focusing on relevant aspects and providing a conceptual map for grasping relationships between variables, concepts, and theories. This component is integral for grounding research within a theoretical context, adding depth and significance to study outcomes and insights.
Examples of the most popular frameworks:
Maslow's hierarchy of needs. This theory suggests a hierarchical arrangement of human needs. It starts with fundamental physiological needs at the base, progressing through love, belonging, safety, and esteem, and culminating in self-actualization at the pinnacle. It finds applications across diverse domains like education and psychology.
- Feminist theory. It delves into the interplay between gender and power, shaping cultural, societal, and political dynamics. It underscores the significance of comprehending and questioning oppressive systems.
- Postmodernism. This framework offers a perspective that rejects traditional narratives for a subjective, socially constructed view of reality. It questions norms, highlights language roles, and promotes exploring diverse viewpoints and context impact on meaning.
Why do you need a theoretical framework?
A theoretical framework is like a guidebook for researchers. It lets them explain what they've learned in the context of the topic. It also helps in planning how to conduct the research - which methods to use, how to collect data, and how to analyze it. By outlining the key concepts and assumptions, it helps choose the best research plan. It's like a tool for understanding research results. This part of your dissertation forms the basis for your analysis, aiding in interpreting results and making broader conclusions. The theoretical framework also makes the research more trustworthy. It shows that the study is built on a solid understanding of the theory and clear concepts. Additionally, it gives researchers a common language and structure to communicate effectively. This ensures that everyone is aiming for the same goals and using the same ideas and definitions.
What is the difference between theoretical and conceptual frameworks?
These concepts are frequently used interchangeably. Still, they have distinct differences. A conceptual framework provides a visual or written representation of abstract ideas, while a theoretical framework outlines established theories used to analyze a specific phenomenon. While a conceptual framework is more specific to a particular study, a theoretical framework draws on broader academic theories.
How to write a theoretical framework
As a fundamental element of studies, it provides the structural basis and direction for data analysis and interpretation. To craft a robust paragraph, follow these steps:
- Start by identifying the key concepts and variables relevant to your writing.
- Thoroughly explore existing literature in your field to identify essential theories and concepts, forming the foundation for your framework.
- Utilize your literature review to build a concise conceptual framework outlining fundamental concepts and their relationships.
- Formulate a problem statement, hypotheses, and research questions aligned with your conceptual framework.
- Apply your theoretical framework to research data to identify gaps or weaknesses, enhancing it as needed.
- Present your framework coherently, using suitable terminology and referencing literature to validate and explain your points. It ensures clear conveyance to readers.
How to structure a theoretical framework?
In your dissertation, this paragraph can be integrated within a literature review or established as a distinct section. Generally, if your writing involves intricate theories, it’s advisable to dedicate a separate chapter to the theoretical framework.
Although there isn’t a fixed blueprint for organizing this section, it’s wise to consult your department or institution for specific formatting guidelines. The primary objective is to establish a coherent and intelligible structure. Here are a few approaches:
- Align with your research question , arranging sections around key concepts;
- Organize based on clusters of theories;
- Arrange chronologically.
The clarity of information within your framework is vital for your readers. Consider having a friend review this section or utilize professional proofreading services.
Theoretical framework example
Here is a sample showing how you can organize this paragraph for your dissertation about the impact of social media on consumer behavior, with quotations from scientific sources:
Impact of Social Media on Consumer Behavior
According to the Social Identity Theory, “individuals develop their self-concept and identity based on their association with various social groups” (Tajfel & Turner, 1986). This theory emphasizes people categorize themselves and others into groups, leading to a sense of belonging and social identity. Social media platforms provide an online environment where individuals construct and express their identities through interactions, connections, and content sharing.
Furthermore, the Uses and Gratifications Theory posits that “individuals actively select and utilize media to fulfill specific needs and gratifications” (Katz et al., 1974). This theory aligns with the idea that users engage with social media platforms based on their motivations and desired outcomes. Research by Kim and Lee (2011) highlights that “individuals use social media for various purposes, including information-seeking, social interaction, entertainment, and self-expression.”
Social Comparison Theory should also be considered, emphasizing that “individuals evaluate themselves by comparing their attributes and achievements with those of others” (Festinger, 1954). Through social media, users are exposed to an array of content from their peers, acquaintances, and celebrities, leading to upward or downward social comparisons that influence their self-perception and behavior.
In conclusion, this theoretical framework draws on established social psychology theories to explore how social media usage influences consumer behavior, identity expression, and self-perception. The Social Identity Theory, Uses and Gratifications Theory, and Social Comparison Theory collectively provide a comprehensive lens to understand the complex relationship between social media and consumer behavior.
References:
- Tajfel, H., & Turner, J. C. (1986). The social identity theory of intergroup behavior. In S. Worchel & W. G. Austin (Eds.), Psychology of Intergroup Relations (pp. 7-24). Nelson-Hall.
- Katz, E., Blumler, J. G., & Gurevitch, M. (1974). Utilization of mass communication by the individual. In J. G. Blumler & E. Katz (Eds.), The uses of mass communications: Current perspectives on gratifications research (pp. 19-32). Sage.
- Kim, J., & Lee, J. E. (2011). The Facebook paths to happiness: Effects of the number of Facebook friends and self-presentation on subjective well-being. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 14(6), 359-364.
- Festinger, L. (1954). A theory of social comparison processes. Human Relations, 7(2), 117-140.
Certainly, it's possible to conduct a more comprehensive analysis of these ideas, delving deeper into additional definitions for thorough comparison. Further exploration could involve in-depth discussions of the perspectives put forth by prominent authors and the exploration of various models to exemplify and evaluate diverse concepts. Developing a strong theoretical framework is essential for a solid research foundation, and if you need assistance, you might consider the option to pay for essay services to ensure your framework is well-constructed and thoroughly researched.
Was this helpful?
Thanks for your feedback, related blog posts, dissertation defense: effective strategies for academic success.
One of the pivotal moments in any graduating student's educational path is defending a dissertation. This comprehensive process requires a deep und...
Business Dissertation Topics: 140+ Ideas for Your Research
Selecting the right topic for your business dissertation is a critical step in your academic journey. It not only shapes the direction of your rese...
List of 130+ Dissertation Topics in Education for in-depth Research
As you reach the final stage of your academic journey in education, you'll be required to submit a dissertation. The journey of choosing dissertati...
Join our 150K of happy users
- Get original papers written according to your instructions
- Save time for what matters most

Transcription Service for Your Academic Paper
Start Transcription now
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources
Your Step to Success
Transcription Service for Your Paper
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
Example Of A Theoretical Framework In A Dissertation
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

An example of a theoretical framework anchors a research paper to a specific theory. Researchers use theoretical frameworks in various fields to provide a premise for the ideas proposed in a research publication. It typically entails the key concepts, theories, and ideas that shape the methodology and research question. This article delves into an example of a theoretical framework, exploring how it functions as an integral component of research design, leading to the conclusion.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Example of a Theoretical Framework – In a Nutshell
- 2 Definition: Example of a theoretical framework
- 3 Example of a theoretical framework – Problem statement & research questions
Example of a Theoretical Framework – In a Nutshell
- An example of a theoretical framework outlines the theory-based approach taken when conducting research.
- The example of a theoretical framework comprises the problem statement , research question, and relevant literature review .
- A well formulated example of a theoretical framework is essential to guide your research and methodology to explain and summarize your findings convincingly.
In what format are you currently required to submit your thesis?
Definition: Example of a theoretical framework
An example of a theoretical framework is a structure that defines the main ideas in a thesis or dissertation . It limits the breadth of the study by narrowing the focus to key variables and their relationship. Theoretical frameworks also give a researcher the specific structure that guides the collection and interpretation of the relevant data in a research proposal .
Printing Your Thesis With BachelorPrint
- High-quality bindings with customizable embossing
- 3D live preview to check your work before ordering
- Free express delivery
Configure your binding now!
to the print shop
Example of a theoretical framework – Problem statement & research questions
The example of a theoretical framework is based on:
- The problem statement – involves contextualizing the research problem . The researcher describes the specific issue that the study seeks to address and justifies the study’s relevance and primary objectives.
- The research questions – are focused on a specific issue, and they should be feasible and researchable using various credible sources.
- The literature review – is an overview of published works about a certain topic, and it outlines what is currently known versus the existing gaps.
Examples of a problem statement and research questions
Find an example of a research question and problem statement below:
An insurance company is having a hard time cross-selling its products. The sales department has realized that most of the customers hold just one policy, although the company offers over ten unique policies. The company would like to have its customers purchase more than one policy since it is clear most customers are purchasing other policies from other companies.
The sales and marketing department wants to increase product awareness. They have concluded that more product awareness will improve the uptake of other products by the existing customers.

To analyze this problem, you have formulated a problem statement, objective, and a research question as follows:
- Problem: Many customers are purchasing additional policies from other companies.
- Objective: Selling more products to existing customers.
- Research question: How can customer product awareness be improved to increase cross-selling of insurance products?
In this study, the concept of “product awareness” is the main focus, alongside the chances that it will improve sales across other products. The example of a theoretical framework should analyze this concept and propose theories that discuss the relationship between the two variables.
- What is the relationship between product awareness and sales ?
- How informed are the existing customers about the company’s products?
- Which factors determine product awareness?
Example of a theoretical framework
In the following example, we define the concept of product awareness mentioned above.
| Explains product awareness as the degree to which customers are familiar with a company's product. She further emphasizes that product awareness is an important step in selling a new product and informing customers about other products or services sold by a company. | |
| States that product awareness is the lever that associates a particular product with a company. She associates product awareness with visual cues that identify a product in the marketplace without a product name. | |
| Offers a more detailed definition of product awareness, identifying prior knowledge of a product as a strong sales driver. He states that the first step in any purchase is knowing that the product exists in a company's product line. He continues to identify the impact of targeted marketing to ensure the right products are marketed to the right potential customers. |
Spacey’s description is more compatible with the study as it highlights the importance of conscious marketing strategies to improve product awareness. Although Kopp and Marrs clearly define product awareness, they don’t propose an actionable step in analyzing product awareness.
The insurance company wants to maximize product awareness as part of its long-term strategy. As a result, targeted marketing will ensure the products are divided and advertised to the most potential buyers.
Spacey’s Product Awareness Work Plan
According to Spacey, the more aware your target customer base is of your range of products, the easier it is to sell more products to an individual customer. Spacey explains that product awareness simplifies promoting your products through different mediums, introducing new products, building a strong reputation, and retaining customers.
What is an example of a theoretical framework based on?
An example of a theoretical framework is based on the problem statemen t, research questions , and review of literature sources . These essential elements guide data collection , analysis, and generalization of the findings.
What is a research question?
A research question is a component of an example of a theoretical framework in research. It is the specific question that forms the basis of the solution proposed by a researcher at the end of a study.
When do you need an example of a theoretical framework?
You need an example of a theoretical framework when undertaking a study with several existing theories. The theoretical framework assists you in reviewing your sources and creating the most relevant research questions.
How do you create an example of a theoretical framework?
Begin by identifying your main concepts and variables. Evaluate and summarize probable theories and show how your findings correspond to the identified theories.
- ✓ Post a picture on Instagram
- ✓ Get the most likes on your picture
- ✓ Receive up to $300 cash back
Bachelor Print is the most amazing company ever to print or bind academic work...
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Anbieter | Eigentümer dieser Website, |
| Zweck | Speichert die Einstellungen der Besucher, die in der Cookie Box von Borlabs Cookie ausgewählt wurden. |
| Cookie Name | borlabs-cookie |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1 Jahr |
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Anbieter | Bachelorprint |
| Zweck | Erkennt das Herkunftsland und leitet zur entsprechenden Sprachversion um. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | ip-api.com |
| Cookie Name | georedirect |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1 Jahr |
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Anbieter | Playcanvas |
| Zweck | Display our 3D product animations |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | playcanv.as, playcanvas.as, playcanvas.com |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1 Jahr |
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Zweck | Cookie von Google zur Steuerung der erweiterten Script- und Ereignisbehandlung. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Cookie Name | _ga,_gat,_gid |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 2 Jahre |
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Meta Platforms Ireland Limited, 4 Grand Canal Square, Dublin 2, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Facebook-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .facebook.com |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird zum Entsperren von Google Maps-Inhalten verwendet. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .google.com |
| Cookie Name | NID |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 6 Monate |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Meta Platforms Ireland Limited, 4 Grand Canal Square, Dublin 2, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Instagram-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .instagram.com |
| Cookie Name | pigeon_state |
| Cookie Laufzeit | Sitzung |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Openstreetmap Foundation, St John’s Innovation Centre, Cowley Road, Cambridge CB4 0WS, United Kingdom |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um OpenStreetMap-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .openstreetmap.org |
| Cookie Name | _osm_location, _osm_session, _osm_totp_token, _osm_welcome, _pk_id., _pk_ref., _pk_ses., qos_token |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1-10 Jahre |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Twitter International Company, One Cumberland Place, Fenian Street, Dublin 2, D02 AX07, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Twitter-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .twimg.com, .twitter.com |
| Cookie Name | __widgetsettings, local_storage_support_test |
| Cookie Laufzeit | Unbegrenzt |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Vimeo Inc., 555 West 18th Street, New York, New York 10011, USA |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Vimeo-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | player.vimeo.com |
| Cookie Name | vuid |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 2 Jahre |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um YouTube-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | google.com |
| Cookie Name | NID |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 6 Monate |
Privacy Policy Imprint
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates
Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates
Published on June 7, 2022 by Tegan George . Revised on November 21, 2023.
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical early steps in your writing process . It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding the specifics of your dissertation topic and showcasing its relevance to your field.
Generally, an outline contains information on the different sections included in your thesis or dissertation , such as:
- Your anticipated title
- Your abstract
- Your chapters (sometimes subdivided into further topics like literature review, research methods, avenues for future research, etc.)
In the final product, you can also provide a chapter outline for your readers. This is a short paragraph at the end of your introduction to inform readers about the organizational structure of your thesis or dissertation. This chapter outline is also known as a reading guide or summary outline.
Table of contents
How to outline your thesis or dissertation, dissertation and thesis outline templates, chapter outline example, sample sentences for your chapter outline, sample verbs for variation in your chapter outline, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about thesis and dissertation outlines.
While there are some inter-institutional differences, many outlines proceed in a fairly similar fashion.
- Working Title
- “Elevator pitch” of your work (often written last).
- Introduce your area of study, sharing details about your research question, problem statement , and hypotheses . Situate your research within an existing paradigm or conceptual or theoretical framework .
- Subdivide as you see fit into main topics and sub-topics.
- Describe your research methods (e.g., your scope , population , and data collection ).
- Present your research findings and share about your data analysis methods.
- Answer the research question in a concise way.
- Interpret your findings, discuss potential limitations of your own research and speculate about future implications or related opportunities.
For a more detailed overview of chapters and other elements, be sure to check out our article on the structure of a dissertation or download our template .
To help you get started, we’ve created a full thesis or dissertation template in Word or Google Docs format. It’s easy adapt it to your own requirements.
Download Word template Download Google Docs template

It can be easy to fall into a pattern of overusing the same words or sentence constructions, which can make your work monotonous and repetitive for your readers. Consider utilizing some of the alternative constructions presented below.
Example 1: Passive construction
The passive voice is a common choice for outlines and overviews because the context makes it clear who is carrying out the action (e.g., you are conducting the research ). However, overuse of the passive voice can make your text vague and imprecise.
Example 2: IS-AV construction
You can also present your information using the “IS-AV” (inanimate subject with an active verb ) construction.
A chapter is an inanimate object, so it is not capable of taking an action itself (e.g., presenting or discussing). However, the meaning of the sentence is still easily understandable, so the IS-AV construction can be a good way to add variety to your text.
Example 3: The “I” construction
Another option is to use the “I” construction, which is often recommended by style manuals (e.g., APA Style and Chicago style ). However, depending on your field of study, this construction is not always considered professional or academic. Ask your supervisor if you’re not sure.
Example 4: Mix-and-match
To truly make the most of these options, consider mixing and matching the passive voice , IS-AV construction , and “I” construction .This can help the flow of your argument and improve the readability of your text.
As you draft the chapter outline, you may also find yourself frequently repeating the same words, such as “discuss,” “present,” “prove,” or “show.” Consider branching out to add richness and nuance to your writing. Here are some examples of synonyms you can use.
| Address | Describe | Imply | Refute |
| Argue | Determine | Indicate | Report |
| Claim | Emphasize | Mention | Reveal |
| Clarify | Examine | Point out | Speculate |
| Compare | Explain | Posit | Summarize |
| Concern | Formulate | Present | Target |
| Counter | Focus on | Propose | Treat |
| Define | Give | Provide insight into | Underpin |
| Demonstrate | Highlight | Recommend | Use |
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Anchoring bias
- Halo effect
- The Baader–Meinhof phenomenon
- The placebo effect
- Nonresponse bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
When you mention different chapters within your text, it’s considered best to use Roman numerals for most citation styles. However, the most important thing here is to remain consistent whenever using numbers in your dissertation .
The title page of your thesis or dissertation goes first, before all other content or lists that you may choose to include.
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical first steps in your writing process. It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding what kind of research you’d like to undertake.
- Your chapters (sometimes subdivided into further topics like literature review , research methods , avenues for future research, etc.)
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2023, November 21). Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved September 3, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/dissertation-thesis-outline/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, dissertation table of contents in word | instructions & examples, figure and table lists | word instructions, template & examples, thesis & dissertation acknowledgements | tips & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Multidiscip Healthc
- PMC11345462
Theoretical Domains Framework: A Bibliometric and Visualization Analysis from 2005-2023
1 Department of Gastroenterology, Children’s Hospital of Fudan University, National Children’s Medical Center, Shanghai, 201102, People’s Republic of China
Yuyan Huang
Yingwen wang.
2 Centre for Clinical Practice Guideline Production and Evaluation, Children’s Hospital of Fudan University, National Children’s Medical Center, Shanghai, 201102, People’s Republic of China
Xiaofeng Xu
3 Nursing Department, Children’s Hospital of Fudan University, National Children’s Medical Center, Shanghai, 201102, People’s Republic of China
Associated Data
All the data used in this study are available from the corresponding author Ying Gu.
The Theoretical Domains Framework (TDF) is among the most extensively utilised foundational frameworks in implementation science. It was developed from 33 psychological theories, with the latest version identifying 14 domains encompassing 84 theoretical constructs. These domains and constructs capture the complexity of factors that affect behaviours, making the framework a valuable tool for designing and implementing interventions within health and social care settings.
To summarise the development, hot topics, and future trends in TDF-related research and provide implementation practitioners with more information on the application of TDF.
We used TDF as the topic and searched the ISI Web of Science Core Collection, identifying 1382 relevant publications. We used analytical tools such as Excel, Tableau, VOSviewer, and Citespace to conduct a bibliometric analysis of the relevant publication.
We identified the United Kingdom as the primary contributor, with University College London as the key institution. Susan Michie ranked highest in total citations. The analysis highlighted cancer and stroke as primary clinic medicine-related topics using TDF. Emerging themes encompass abuse, violence, maternal health, antenatal care, patient involvement, and trauma-informed care et al. “Nurse” and “qualitative research” emerged as recent and enduring hotspots, possibly indicating future research trends.
This article represents the first attempt to summarise the TDF using bibliometric analysis. We suggest this method can be used to analyse other theoretical frameworks in scientific implementation of its objectivity and quantifiability. Overall, the application scope of TDF is shifting from public health towards more specialised clinical directions, although its application in the field of public health is continuously expanding. In the future, the number of users of TDF is also expected to expand from implementation scientists to professional technical personnel.
Introduction
Theoretical Domains Framework (TDF) is one of the most widely used foundational theoretical frameworks in the field of implementation science. 1 The development and validation of the TDF went through two phases. The first phase involved the establishment of a comprehensive theoretical framework consisting of 12 domains and 128 explanatory constructs by a team of behavioural scientists and implementation researchers. 2 In the second phase, Cane et al refined the TDF in 2012 after validation, identifying 14 domains covering 84 theoretical constructs. The 14 domains include Knowledge, Skills, Social/Professional Role and Identity, Beliefs about Capabilities, Optimism, Beliefs about Consequences, Reinforcement, Intentions, Goals, Memory, Attention and Decision Processes, Environmental Context and Resources, Social Influences, and Emotion and Behavioral Regulation. 3 Also in 2012, French et al published an article on the four steps for developing intervention measures using the TDF, guiding researchers in comprehensive intervention strategy design. 4 In 2017, Atkins published a guide with the aim of assisting the implementation community in achieving their implementation goals using TDF. 5 Over the past decade, TDF has been extensively utilised in the global healthcare arena. Its application has bolstered the confidence of healthcare professionals in carrying out projects. 6
The topic of TDF-related research encompasses evidence-based guidelines implementation, 7 health check initiatives execution, 8 vaccinations, 9 health promotion app utilisation, 10 school-based daily physical activity, 11 and others. The study population is inclusive of administrators, healthcare practitioners, patients, and the general populace. Research settings span across various contexts, including hospitals, communities, households, and schools et al. Qualitative research predominates, with the primary research method utilising interviews and focus groups. 5 Several systematic reviews have synthesised existing research findings, addressing specific research questions such as how to apply the TDF to design interventions for behaviour change in healthcare practitioners and the general population. 12–14 Other studies have summarised the application of TDF in identifying barriers and facilitators in areas like guideline implementation,15 medication adherence,16 sustainable practices in operating theatres, 15 and pressure injury prevention. 16 It is essential to access these publications to evaluate their impact on research and development.
Bibliometric analysis is a valuable research methodology that provides quantitative insights into the publication landscape of a particular field. 17 Compared to systematic reviews, it does not require an in-depth interpretation of each literature piece, allowing for a larger volume of literature inclusion. It focuses on quantitative analysis of citations and co-citations, offering a macroscopic view of research field hotspots and trends. At this level, it can serve as a valuable complement to systematic reviews. Notably, there is currently a dearth of bibliometric studies about the TDF. We aim to offer valuable insights for future research by conducting a bibliometric analysis of literature centred around the TDF.
Materials and Methods
Retrieval strategies.
The data for the study was obtained from the Web of Science Core Collection (WOSCC, Clarivate Analytics, Philadelphia, PA, USA), recognised as one of the most commonly utilised databases for bibliometric studies. The search was conducted on December 27, 2023, using “Theoretical Domains Framework” as the topic. We also included an article by Cane et al in our search strategy, as this article formed the original version of the TDF, but the full text does not mention the term “ Theoretical Domains Framework”. To ensure comprehensive retrieval, we added the article’s title to our search strategy. Therefore, our search term was: (TS=(“Theoretical Domains Framework”)) OR TI=(“Making psychological theory useful for implementing evidence-based practice: a consensus approach”).
The data utilised in this study are publicly accessible and do not contain protected health information. Therefore, no approval was sought from the Ethics Committee of Fudan University Affiliated Children’s Hospital. This study adheres to the BIBLIO checklist for reporting the bibliometric reviews of the biomedical literature.
Analytical Tool
Excel (version 16.49) developed by Microsoft company was used to display the annual number of publications.
Tableau (version 2023.2.1), 18 developed by Christian Chabot, Chris Stolte and Pat Hanrahan, was utilised for presenting global publishing density and high-frequency keywords.
VOSviewer (version 1.6.19) is a software for creating, visualising and exploring bibliometric maps of science literature developed by the team of Professor Ludo Waltman and Nees-Jan van Eck (Leiden University). 19 We used it to visualise (1) the citations of articles, (2) the top institutions by the number of publications, and (3) the collaboration network of authors and countries.
CiteSpace, developed by Professor Chen Chaomei’s team (version 6.1.R6), serves as an additional software for bibliometric analysis and visualization. 20 The graphs generated by Citespace are more diverse, including (1) the keywords with the strongest citation bursts. The figure will display six columns of data, namely keywords, year (the years in which the keywords appear), strength (burst strength), begin (the start time of keyword burst), end (the end time of keyword burst), and a timeline of the burst; (2). The Timezone of keywords.
Here are all the metrics used in the tables: (1) Total citation(TC) is a noteworthy metric that denotes the frequency with which an article has been referenced by other publications since its publication. Total link strength(TLS) refers to the cumulative strength of connections between nodes in a network or graph.
The graphs generated using VOSviewer to analyse data present three key elements: nodes, lines, and colours. nodes represent the analysed elements, such as institutions and countries. The size of the nodes represents the quantity or frequency. For instance, when analysing the literature citation, a larger node representing a particular document indicates a higher frequency of citations. Lines represent the relationships between two nodes, with thicker edges indicating greater collaboration or more frequent co-occurrences between the two elements. Nodes of the same colour signify that they belong to the same cluster.
Annual Number of Articles on TDF
A total of 1382 articles were included in the study. Figure 1 illustrates a consistent upward trend in the annual publication count of articles focused on TDF from 2005 to 2023. Based on the currently available data, the lowest counts were observed in 2005 and 2009, each with one publication. From 2012 onwards, the annual publication count on TDF exceeded 10 articles, reaching its peak at 301 in 2023.

Annual number of published articles of TDF from 2005 to 2023 on Web of Science.
National Publication Count
Figure 2 displays the publication counts for each country from 2005 to 2023. A total of 73 countries were included in the analysis, with higher publication counts concentrated in Europe, North America, and Australia. The top ten countries by publication count are as follows: England (N=656), Australia (N=353), Canada (N=337), USA (N=182), Ireland (N=83), Netherlands (N=53), Germany (N=36), New Zealand (N=24), People’s Republic of China (N=24), and Denmark (N=20).

National publication count. The countries within the red boxes were the top ten countries in terms of publication numbers.
TC of Included Articles
We set the VOSviewer filter to a minimum TC of 50, 59 articles were included in the analysis, as shown in Figure 3 . Table 1 presents the highest 10 citations based on the document’s citation analysis. In most fields, an article is considered a classic citation if it exceeds 100. The top 10 cited articles in TDF range from a minimum of 182 to a maximum of 2167 citations. Notably, the two articles share the same first author, Susan Michie, a key founder of the TDF. Six articles were published in the same journal, Implementation Science, a leading publication dedicated to presenting evidence on methods to integrate research findings into regular healthcare practices and health policies. The earliest article, published in 2005 and ranked second in citation count, introduced the original version of TDF. The most-cited article, published by James Cane in 2012, involved validating and refining the original version. The latest article, published in 2017, provides practical guidelines for using the TDF to assess implementation issues and design interventions.
Top 10 Cited Articles in TDF Research Between 2005 and 2023
| Rank | Title | First author | Journal | Publication year | Total citation | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Validation of the theoretical domains framework for use in behaviour change and implementation research | James Cane | Implementation science | 2012 | 2167 | UK |
| 2 | Making psychological theory useful for implementing evidence based practice: A consensus approach | Susan Michie | Quality & safety in health care | 2005 | 1842 | UK |
| 3 | Making sense of implementation theories, models and frameworks | Per Nilsen | Implementation science | 2015 | 1769 | Sweden |
| 4 | A guide to using the theoretical domains framework of behaviour change to investigate implementation problems | Lou Atkins | Implementation science | 2017 | 1125 | UK |
| 5 | Developing theory-informed behaviour change interventions to implement evidence into practice: A systematic approach using the theoretical domains framework | Simon D French | Implementation science | 2012 | 733 | Australia |
| 6 | Behaviour change techniques: The development and evaluation of a taxonomic method for reporting and describing behaviour change interventions (a suite of five studies involving consensus methods, randomised controlled trials and analysis of qualitative data) | Susan Michie | Health technology assessment | 2015 | 301 | UK |
| 7 | Theories of behaviour change synthesised into a set of theoretical groupings: Introducing a thematic series on the theoretical domains framework | Jill J Francis | Implementation science | 2012 | 264 | UK |
| 8 | From lists of behaviour change techniques (bcts) to structured hierarchies: Comparison of two methods of developing a hierarchy of bcts | James Cane | British journal of health psychology | 2015 | 207 | UK |
| 9 | Implementation mapping: Using intervention mapping to develop implementation strategies | Maria E Fernandez | Frontiers in public health | 2019 | 197 | USA |
| 10 | Discriminant content validity of a theoretical domains framework questionnaire for use in implementation research | Johanna M Huijg | Implementation science | 2014 | 182 | Netherlands |

Articles total cited more than 50 times.
Contribution of the Institutions
A total of 1770 institutions were analysed. By applying the VOSviewer filter to include only institutions with a minimum document count of 10, 87 institutions met the criteria (refer to Figure 4 ). These institutions were categorised into 5 clusters. The largest cluster, highlighted in red, encompasses 31 institutions, with University College London (UCL) playing a central role. The second-largest green cluster includes 26 institutions, with key contributors such as the University of Melbourne, the University of Sydney, and Monash University. The third-largest blue cluster comprises 20 institutions, prominently featuring the University of Toronto, the University of Ottawa, and the Ottawa Hospital Research Institute. The smaller yellow and purple clusters each contain 5 institutions. Table 2 presents the top 10 institutions based on publication count, with half hailing from Canada, three from the UK, and two from Australia.
Top 10 Institution by Number of Publication
| Rank | Institution | Country | Number of publication | Total citation | Total link strength |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | University of Ottawa | Canada | 111 | 3802 | 4718 |
| 2 | University College London | UK | 103 | 7740 | 6237 |
| 3 | University of Toronto | Canada | 101 | 2027 | 2567 |
| 4 | Monash University | Australia | 79 | 5247 | 4701 |
| 5 | University of Sydney | Canada | 71 | 689 | 1241 |
| 6 | University of Melbourne | Australia | 68 | 1434 | 1870 |
| 7 | Ottawa Hospital Research Institute | Canada | 64 | 2048 | 2665 |
| 8 | Ottawa Hospital | Canada | 57 | 775 | 1866 |
| 9 | City University London | UK | 54 | 1282 | 1709 |
| 10 | Newcastle University | UK | 49 | 5455 | 4583 |

Top 87 institutions by number of publications.
Contribution of the Countries
Co-authorship offers insights into how collaboration and knowledge exchange occur within and across scientific fields. We included the top 100 authors by publication count in the collaborative network analysis ( Figure 5 ) and found that these 100 authors were divided into 11 clusters represented by different colours. Authors from the same country and institution tend to collaborate more closely. The largest cluster, in red, includes 26 authors, most from Canada. The second-largest cluster, in green, consists of 21 authors, most from the UK, radiating outward with key figures such as Susan Michie, Jill J Francis, and Fabiana Lorencatto. Overall, authors within the green and red clusters tend to collaborate more closely, while their collaboration with other clusters is less tight. The yellow cluster, represented by Luke Wolfenden, collaborates closely with the red cluster, and the purple cluster, represented by Natalie Taylor from Australia, also collaborates closely but has fewer connections with other authors.

Collaboration network of top 100 authors.
Co-Authorship of Countries
We included the top 35 countries by publication count in the co-authorship analysis, revealing three clusters (see Figure 6 ). The largest cluster is represented in red, and although the connections between clusters appear relatively thin, indicating a lower degree of collaboration, the countries within this cluster are widely distributed, spanning North America, South America, Asia, Africa, and Europe. The 15 countries in this cluster include the USA, Brazil, India, Kenya, Malaysia, Nigeria, People’s Republic of China, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, South Africa, Spain, Switzerland, United Arab Emirates, and Wales (which belongs to the UK). The USA, Canada, and England (part of the UK) establish close and intensive collaborative relationships. The second-largest cluster is green, consisting of 12 European countries: Austria, Belgium, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Italy, Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, and Sweden. The third-largest cluster in blue includes five countries, boasting the highest publication count and demonstrating close collaboration with other clusters. This cluster comprises Australia, Canada, the UK (England, North Ireland, and Scotland), Iran, Ireland, and New Zealand.

Collaboration network of countries.
High-Frequency Keywords
High-frequency keywords serve as crucial indicators of core concepts and hotspots. Analyzing these terms provides valuable insights into the field’s dynamics, focal points, and major trends, guiding researchers in understanding its structure and knowledge network. Figure 7 illustrates the top 35 keywords with the highest occurrence frequency in TDF. Apart from TDF, the top five keywords are qualitative research, barriers and facilitations, behaviour change, implementation, and primary care.

The top 35 high-frequency keywords in TDF.
TDF has been widely utilized in the field of clinical medicine. We screened disease keywords with a minimum occurrence of 5, and ultimately, 21 keywords were included in the analysis (see Figure 8 ). From the figure, it is evident that TDF is most frequently employed in the field of cancer, followed by stroke, diabetes mellitus, COVID-19, dementia, obesity, asthma, low back pain, depression, aphasia, COPD, chronic illness, chronic kidney disease, osteoarthritis, pressure ulcer, chronic pain, diabetic retinopathy, HIV, severe mental illness, hypertension, and traumatic brain injury.

21diseases-related keywords.
Top 50 Keywords with the Strongest Citation Bursts
Keyword bursts map reflects a sudden increase in the citation frequency of a particular keyword during a specific period, providing a comprehensive insight into the evolving trends of hot topics in the TDF research field. The stronger the burst intensity and the longer its duration, the greater the attention and research output received by the topic. We utilized CiteSpace’s burst detection algorithm to analyze keywords in 1382 TDF-related articles from 2005 to 2023. (see Figure 9 )

Top 50 keywords with the strongest citation burst.
In the charts generated by CiteSpace, the timeline is depicted in blue, with the intervals of keyword bursts highlighted in red at specific positions along the blue timeline. Specific details regarding burst keywords, burst intensity, and the start and end years can also be found in Figure 9 . The top three keywords with the highest burst intensity are highlighted: behaviour change intervention (8.33), implementation science (5.87), and psychological theory (5.32). The top three keywords with the longest burst time are: complex intervention (8 years), nurse (5 years), psychological theory (4 years), health care professional (4 years), general practitioner (4 years), prevalence (4 years), health promotion (4 years), implementation science (4 years), qualitative research (4 years). The keywords burst until 2023 include nurse (from 2019 to 2023) and qualitative (from 2020 to 2023).
Timezone of Keywords
The Timezone of keywords, depicted in Figure 10 , is of significant importance as it traces the evolution of research hotspots, identifies emerging trends, and evaluates the dynamics of a research field over time. It has the capability to unveil words that might not have reached a significant burst strength but represent emerging research areas. These less frequently occurring terms, often overlooked by researchers, can offer valuable directions for further exploration. In the figure, the size of the circles represents the frequency of occurrences, with the horizontal axis denoting time and the vertical axis indicating the keywords corresponding to specific time points. The curves reveal the developmental and declining patterns of keywords.

The Timezone of keywords.
The figure illustrates a substantial influx of high-frequency keywords around the 12-year mark, persisting until 2020 and beyond. Around 2023, a surge in low-frequency keywords, such as “abuse”, “violence”, “maternal health”, and “antenatal care”, becomes apparent. These may signify potential research focal points in the coming years.
As healthcare knowledge evolves and evidence-based medicine advances, researchers no longer rely solely on experience and assumptions in implementation research. Using theory and framework to understand the mechanisms behind behaviour, implement intervention measures, and promote behaviour change has gained increasing recognition among researchers. However, given the richness of behavioural psychology theories, there is a risk of overlooking important factors that may determine behaviour when conducting behaviour change research and intervention designs based on only one or a few theories. Researchers often face challenges when selecting and applying the most appropriate theory.
The TDF was first established by Michie et al in 2005. 2 Its core strength lies in attempting a comprehensive coverage of behaviour change theories, integrating various complex psychological theories that were previously disparate. It integrates 33 relevant psychological theories into 128 constructs organized into 12 domains. This simplification of theory application in behaviour change research addresses researchers’ dilemmas.
From 2005 to 2012, there was relatively limited research using “TDF” as a keyword. It was not until 2012, when James Cane’s team validated and refined the TDF, resulting in a version with 84 constructs sorted into 14 domains. 3 Over the past decade, articles with TDF as the main topic have shown a rising trend, and according to the fitted formula based on data from 2005 to 2022, it is projected to surpass 1000 articles per year on the Web of Science by 2030. TDF places emphasis on individual factors while also taking into account social and environmental aspects. Its application affords healthcare professionals a broad perspective for discerning barriers and facilitators, augmenting their confidence in project implementation.
The UK leads by a significant margin in terms of publications, followed by Australia and Canada. These three countries also exhibit the highest intensity of collaboration among themselves, with domestic research institutions actively participating in international research projects and sharing experiences and resources with other countries and organisations. For example, Newcastle University forms a cluster with Australian universities such as the University of Melbourne, University of Sydney, Monash University, and Griffith University (see Figure 5 ), indicating a close collaboration that contributes to advancing the implementation of science and research globally. China is the only Asian country in the top ten for publication volume, and the application of TDF in China has garnered increasing attention. From 2016 to 2013, there were 20 articles in China’s primary literature database, the Wanfang Database.
From our analysis of citation bursts for key terms, two keywords have exhibited significant bursts in recent years, persisting until 2023, namely “nurse” and “qualitative research.” Qualitative research first appeared in 2013 and has emerged as the primary research methodology in TDF applications. This prominence continued through 2020 and persist into 2023, establishing itself as a focal point and trend in TDF research for the foreseeable future. The emergence of “nurse” is a novel finding in this study. Nurses, playing a crucial role in primary health care, have garnered increasing attention regarding their behaviours and experiences. Examples include enhancing nurses’ capabilities in correctly utilizing electronic medication management systems, 21 identifying factors influencing nurse and pharmacist prescriber management of respiratory tract infections, 22 and exploring the components of nurse-patient therapeutic engagement in acute mental health wards. 23 The primary motivation behind our research is to explore the application of TDF in conducting implementation research at our centre, addressing clinical issues, and extending the findings to China.
Cancer is a primary focus in TDF research, and our study reveals that TDF research in the field of cancer is concentrated on cancers of the male and female reproductive and urinary systems, such as prostate cancer, cervical cancer, and bladder cancer. For example, identifying factors inconsistent with guidelines for staging clinical prostate cancer and designing guideline-concordant intervention measures, 24 , 25 explores modifiable influences on medication-taking behaviour in women with breast cancer, 26 Evaluating women’s perspectives on human papillomavirus (HPV) self-sampling is another aspect of the research. 27
Beyond cancer, there is a wealth of TDF research in stroke rehabilitation. Various chronic diseases are also the key topics, including diabetes mellitus, 28–31 chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), 32 , 33 chronic kidney disease (CKD), 34–36 chronic pain, 37 , 38 and pressure ulcers, among others. Given the global impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on healthcare systems, a considerable portion of research attempts to address issues related to COVID-19 vaccination using TDF. 39 , 40 Furthermore, low back pain is another crucial disease topic, and it was one of the earliest areas where an improved version of TDF was applied in clinical practice.
Through the Timezone of keywords, we observed a significant emergence of conceptual keywords related to implementation science in 2012, including “clinical practice guideline”, “behaviour change intervention”, “complex intervention”, and “clinical behaviour”, among others. Notably, there were no specific disease-related terms during this period. In 2020, there was a surge in disease and healthcare-related terms, encompassing public health topics such as “immunisation” and “food”, as well as specific diseases like “muscle tension dysphonia”, “ventilator-associated pneumonia”, “Parkinson’s disease”, “bloodstream infection”, and others. Additionally, emerging topics in recent years include “end-of-life”, “violence”, “abuse”, and “binge drinking”. While most of these terms have not reached the ‘burst’ level, they reflect the expanding application of TDF across various medical specialities, a trend expected to continue.
The limitations of this study include a potential publication bias, as it solely relies on literature indexed in the WOSCC. The focus on English-language publications may also introduce language bias, neglecting valuable contributions in other languages. While providing a macro-level overview, the bibliometric analysis may lack depth in qualitative understanding of specific TDF applications. Furthermore, the study’s cross-sectional nature captures a snapshot in time, potentially overlooking evolving trends. Despite these limitations, the study offers valuable insights into TDF-related research’s current state and trends.
This study is the first attempt to apply bibliometric analysis to the TDF, offering insights into its development, hot topics, and future trends. By identifying key research articles, major contributors, and emerging themes, we provide a comprehensive overview of the TDF’s impact and application scope. The findings highlight the TDF’s evolving role from public health to more specialised clinical directions, while its use in public health continues to expand.
Researchers can leverage bibliometric analysis to explore the evolving landscape of implementation science more effectively. By identifying influential works, key contributors, and collaboration networks, researchers can better strategize their studies to address current and future challenges in the field. The emergence of new topics such as abuse, violence, maternal health, and trauma-informed care suggests that future research may increasingly focus on these areas, expanding the TDF’s applicability.
Future research should consider interdisciplinary applications, particularly in areas where understanding behaviour change is crucial. Exploring the integration of TDF with emerging technologies, such as digital health interventions and artificial intelligence, can enhance the design and implementation of behaviour change strategies. Moreover, Strengthening international collaborations, developing and refining methodological approaches for different cultural and healthcare settings, and conducting longitudinal studies to evaluate the long-term impact of TDF-based interventions will provide deeper insights into their sustainability and effectiveness.
Funding Statement
This research was supported by funds from the Scientific Research Foundation of Shanghai Local High-Level University Construction Project–Evidence-based Nursing Innovation Research Institute: Multi-center evidence-based innovation practice project (No. FNDGJ201904).
Data Sharing Statement
Institutional review board statement.
The data utilized in this study are publicly accessible and do not contain protected health information. Therefore, no approval was sought from the Ethics Committee.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Author Contributions
All authors made a significant contribution to the work reported, whether that is in the conception, study design, execution, acquisition of data, analysis and interpretation, or in all these areas; took part in drafting, revising or critically reviewing the article; gave final approval of the version to be published; have agreed on the journal to which the article has been submitted; and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Sample theoretical framework. Below is a simplified example showing how you can describe and compare theories in your thesis or dissertation. In this example, we focus on the concept of customer satisfaction introduced above. ... Theoretical Framework Example for a Thesis or Dissertation. Scribbr. Retrieved September 3, 2024, from https://www ...
A theoretical framework guides the research process like a roadmap for the study, so you need to get this right. Theoretical framework 1,2 is the structure that supports and describes a theory. A theory is a set of interrelated concepts and definitions that present a systematic view of phenomena by describing the relationship among the variables for explaining these phenomena.
Example Theoretical Framework of a Dissertation or Thesis. Published on 8 July 2022 by Sarah Vinz. Revised on 10 October 2022. Your theoretical framework defines the key concepts in your research, suggests relationships between them, and discusses relevant theories based on your literature review. A strong theoretical framework gives your ...
Theoretical Framework. Definition: Theoretical framework refers to a set of concepts, theories, ideas, and assumptions that serve as a foundation for understanding a particular phenomenon or problem. It provides a conceptual framework that helps researchers to design and conduct their research, as well as to analyze and interpret their findings.
Revised on 10 October 2022. A theoretical framework is a foundational review of existing theories that serves as a roadmap for developing the arguments you will use in your own work. Theories are developed by researchers to explain phenomena, draw connections, and make predictions. In a theoretical framework, you explain the existing theories ...
A theoretical framework is a foundational review of existing theories that serves as a roadmap for developing the arguments you will use in your own work. Theories are developed by researchers to explain phenomena, draw connections, and make predictions. In a theoretical framework, you explain the existing theories that support your research ...
Theoretical framework vs conceptual framework. As you can see, the theoretical framework and the conceptual framework are closely related concepts, but they differ in terms of focus and purpose. The theoretical framework is used to lay down a foundation of theory on which your study will be built, whereas the conceptual framework visualises ...
Understanding, Selecting, and Integrating a Theoretical ...
The theoretical framework - the 'toolbox' - details the theories, propositions, hypotheses (if you're using them) and concepts - the 'tools' - that you will use to address or make sense of this problem. The list of potential explanations for why responses differ is enormous. You could approach this question with a focus on ...
The theoretical framework strengthens the study in the following ways: An explicit statement of theoretical assumptions permits the reader to evaluate them critically. The theoretical framework connects the researcher to existing knowledge. Guided by a relevant theory, you are given a basis for your hypotheses and choice of research methods.
The Theoretical Frameworks research guide at National University Library includes an online tutorial on researching theoretical and conceptual frameworks. Grant, Cynthia, and Azadeh Osanloo. " Understanding, Selecting, and Integrating a Theoretical Framework in Dissertation Research: Creating the Blueprint for Your 'House.'".
Resources About Theory and Theoretical Frameworks. Challenging Ideas: Theory and Empirical Research in the Social Sciences and humanities Edited by Maren Lytje, Torben K. Nielsen, and Martin Ottovay Jørgensen. Call Number: Ebook, click link to view. ISBN: 9781443887373. Publication Date: 2015.
In a thesis or dissertation, a theoretical framework is a section where the writer evaluates or discusses the most relevant theories to their study. The purpose of this section is to: Define the key concepts. Combine and evaluate relevant models and theories. Explain expectations and assumptions that guide the project.
Postmodernists look at the world and see how language and discourse shape belief systems. When selecting a theoretical framework, we're making a conscious decision about our approach and focus. For example, 'feminism' and ' critical theory ' are theoretical frameworks that will focus on how power functions in society.
A theoretical framework is a conceptual model that provides a systematic and structured way of thinking about a research problem or question. ... theoretical frameworks. It provides guidelines on how to write a thesis framework, definitions of variable types, and examples of framework types. ... A robust conceptual or theoretical framework is ...
A theoretical framework, the way I define it, is comprised of the different theories and theoretical constructs that help explain a phenomenon. A theoretical framework sets out the various expectations that a theory posits and how they would apply to a specific case under analysis, and how one would use theory to explain a particular phenomenon.
The term conceptual framework and theoretical framework are often and erroneously used interchangeably (Grant & Osanloo, 2014). A theoretical framework provides the theoretical assumptions for the larger context of a study, and is the foundation or 'lens' by which a study is developed. This framework helps to ground the research focus ...
Complete your review of literature first. In order to identify the scope of your theoretical framework, you'll need to address research that has already been completed by others, as well as gaps in the research. Understanding this, it's clear why you'll need to complete your review of literature before you can adequately write a theoretical ...
A theoretical framework guides your research by providing a structure for understanding and analyzing your topic. Having a well-developed theoretical framework is essential because it: Provides a basis for analyzing your data and interpreting your findings. Ensures that your study aligns with existing theories and literature.
Using a theoretical framework for your dissertation will help you to better analyze past events by providing a particular set of questions to ask and a perspective to use when examining your topic. Traditionally, Ph.D. and Applied Degree research must include relevant theoretical framework(s) to frame, or inform, every aspect of the dissertation.
This section establishes the theoretical basis and conceptual structure for academic writing. It incorporates essential theories, models, concepts, and ideas from existing literature, offering a framework to interpret findings. Its purpose is to define study scope and boundaries, focusing on relevant aspects and providing a conceptual map for ...
Example Of A Theoretical Framework | Definition | Problem statement | Research question | Examples ~ read more. Free 24h Customer Service:724 281 3937. When ordering within:----:----:---- ... An example of a theoretical framework is a structure that defines the main ideas in a thesis or dissertation. It limits the breadth of the study by ...
Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates. Published on June 7, 2022 by Tegan George.Revised on November 21, 2023. A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical early steps in your writing process.It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding the specifics of your dissertation topic and showcasing its relevance to ...
The first phase involved the establishment of a comprehensive theoretical framework consisting of 12 domains and 128 explanatory constructs by a team of behavioural scientists and implementation researchers. 2 In the second phase, Cane et al refined the TDF in 2012 after validation, identifying 14 domains covering 84 theoretical constructs.