Segment Addition Postulate
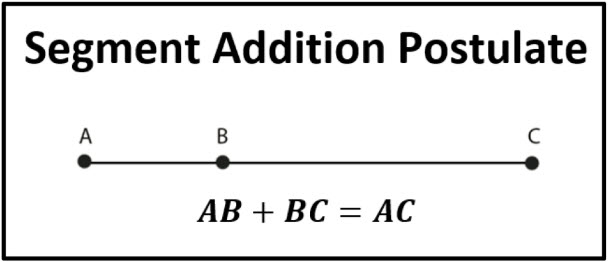
The segment addition postulate in geometry is applicable on a line segment containing three collinear points. It states that if there are two given points on a line segment A and C, then point B lies on the same line segment somewhere between A and C only if the sum of AB and BC is equal to AC.
By applying the segment addition postulate, we can precisely determine the length of a line segment when given specific measurements of its parts. Also, this postulate enables us to divide a line segment into different sections and explore the relation (ratios) between their lengths.
| 1. | |
| 2. | |
| 3. |

Segment Addition Postulate Definition
The segment addition postulate states that if a line segment has two endpoints, A and C, a third point B lies somewhere on the line segment AC if and only if the equation AB + BC = AC is satisfied. Look at the image given below to have a better understanding of this postulate.
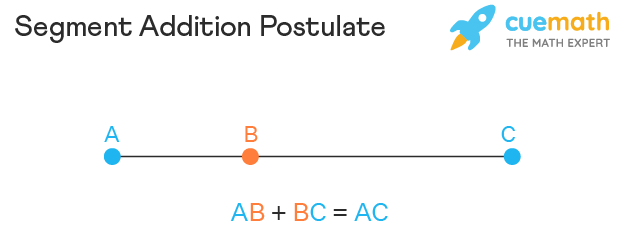
If we carefully look at its name "Segment Addition Postulate", it is very easy to understand.
- A segment, here, means a line segment. It emphasis that this postulate is applicable only on a line segment, and not on a ray or a line . A line segment is part of a line bounded by two defined endpoints. We can have an infinite number of points between the endpoints of a segment.
- The "addition" means that we are adding the distances between points.
- Finally, "postulate" means this axiom is taken as a fact or valid without any proof.
Another way of stating the segment addition postulate is that if point B lies on the line segment AC, then AB + BC = AC.
Segment Addition Postulate Formula
If the end-points of a line segment are denoted as A and C, and there lies a point B on the line segment, then the segment addition postulate formula is given as AB + BC = AC.
Further, extending this theorem to two points, If there are two points B and D on the segment, we will have the formula as AB + BD + DC = AC.
☛ Related Topics:
- Segment Addition Postulate Worksheets
- Difference Between Line and Line Segment
- Line Segment
Segment Addition Postulate Examples
Example 1: In the given figure, if B is the mid-point of line segment AC, find the length of segment AC.

By using the segment addition postulate, we know that the sum of segments AB and BC is equal to AC. It can be written mathematically as AB + BC = AC. Also, B is the midpoint of AC. It implies AB = BC.
⇒ 3x = 4x-6
⇒ 6 = 4x - 3x
Now, put the value of x in the equation AB + BC = AC.
AC = 3x + 4x - 6
⇒ AC = 7x - 6
⇒ AC = 7 × 6 - 6
⇒ AC = 42 - 6
Answer: ∴ The length of the segment AC is 36 units.
Example 2: Find whether Q is the mid-point of segment PR or not, if the length of PR is 45 units. [Refer to the figure below]

Solution: There are three collinear points on the given segment which are points P, Q, and R. By using the segment addition postulate, we know that PQ + QR = PR. Substitute the value of PR as 45 units, we get,
PQ + QR = 45
⇒ 9x + 7 + (-3x+20) = 45
⇒ 9x - 3x + 7 + 20 = 45
⇒ 6x + 27 = 45
Now, let us find the values of PQ and QR.
PQ = 9x + 7 = 9 (3) + 7 = 34 units
QR = -3x+20 = -3 (3) + 20 = 11 units
Answer: ∴ PQ ≠ QR. Q is not the midpoint of segment PR.
Example 3: On a line segment XY, if Z is between X and Y and XY = 25. What will be the expression to find the value of XZ?
Solution: It is given that point Z is between X and Y, so by using the segment addition postulate, we have XZ + ZY = XY. The value of XY is given as 25. So, the expression to find the value of XZ is 25 - ZY.
Answer: ∴ 25 - ZY is the required expression.
go to slide go to slide go to slide

Book a Free Trial Class
Practice Questions on Segment Addition Postulate
go to slide go to slide
FAQs on Segment Addition Postulate
What is segment addition postulate in geometry.
The segment addition postulate in geometry is the axiom which states that the length of a line segment divided into smaller pieces is the sum of the lengths of all those smaller segments. So, if we have three collinear points A, B, and C on segment AC such that B is somewhere between A and C, then AB + BC = AC. It is a mathematical fact that can be accepted without proof.
What are the Two Conditions of the Segment Addition Postulate?
The two conditions of the segment addition postulate are given below:
- A point P lies on a segment MN if and only if points M, P, and N are collinear taken in order.
- The distance between MP and PN must be equal to MN.
What are the Examples of Segment Addition Postulate?
As per the segment addition postulate, if we have an iron rod of length 30 inches that is cut into two parts where the length of one part is 14 inches, it means the length of the other part of the rod is 30 - 14 = 16 inches.
What is a Segment Addition Postulate Used For?
We can apply this postulate in calculating the missing lengths. It can be used to find the sum of the smaller parts of a segment to find the total length. The segment addition postulate has its applications in construction, architecture, design, etc.
How to Solve for x with Segment Addition Postulate?
If we have a missing length, let's say x, and we know the total length and the length of the other part of the segment, then we can apply the segment addition postulate to find x. For example, if AB = 3, BC = x, and AC = 5, then we can find x by subtracting AB from AC. This implies AC - AB = 5 - 3 = 2 = BC. i.e., x = 2.
How to Use the Segment Addition Postulate to Show that ae=ab+bc+cd+de?
If a segment AE has three points on it, marked as B, C, and D in order, then according to the segment addition postulate, their sum is equal. So, AE = AB + BC + CD + DE. This is possible by applying the postulate for more than one time.
What is Segment Addition Postulate in Proofs?
The segment addition postulate does not require any proof. It is accepted as a mathematical fact. But many times, we use this axiom in stating proofs for line segments. One such proof is given as "If two congruent segments are added to the line segments of the same length, then their sum is also equal."

Segment Addition Postulate: Definition, Formula, Examples, FAQs
What is the segment addition postulate in geometry, how to use segment addition postulate, how to know if three points are collinear, solved examples on segment addition postulate, practice problems on segment addition postulate, frequently asked questions about segment addition postulate.
The segment addition postulate states that if three points A, B, and C are collinear such that B lies between A and C, then the sum of the lengths of segment AB and segment BC is equal to the length of the entire segment AC.
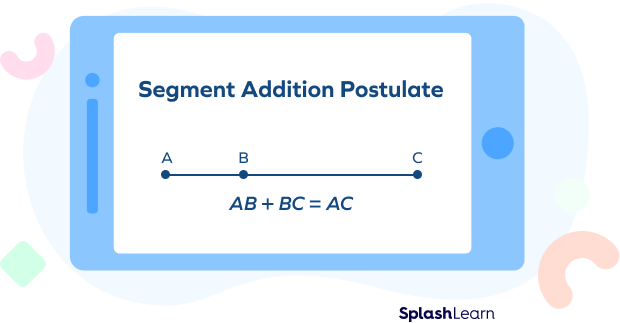
The segment addition postulate (segment addition theorem), in simple words, states that if we divide a line segment into smaller segments, the sum of lengths of the smaller segments will add up to the length of the original segment. It is applicable to the line segments.
The segment addition postulate is an important property of line segments that is used to check if three points are collinear or whether a point lies on a given segment or not.
Recommended Games

Segment Addition Postulate: Definition
The Segment Addition Postulate is a fundamental principle in geometry that states that if three points A, B, and C are collinear such that B lies somewhere on AC, then the sum of the lengths of the segments AB and BC is equal to the length of the entire segment AC.
Recommended Worksheets

More Worksheets
Segment Addition Postulate: Formula
The formula for the segment addition postulate with respect to three collinear points A, B, C is given by
l(AB) + l(BC) = l(AC)
AB + BC = AC
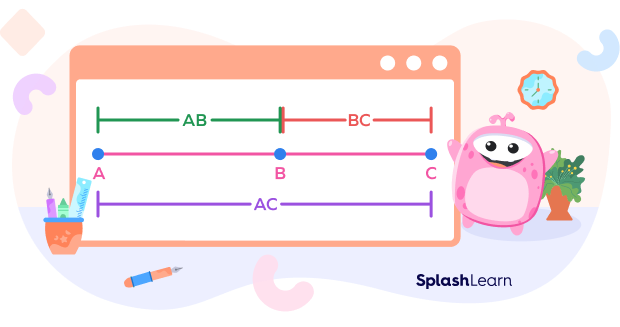
Let’s understand the steps to use the segment addition postulate with the help of an example.
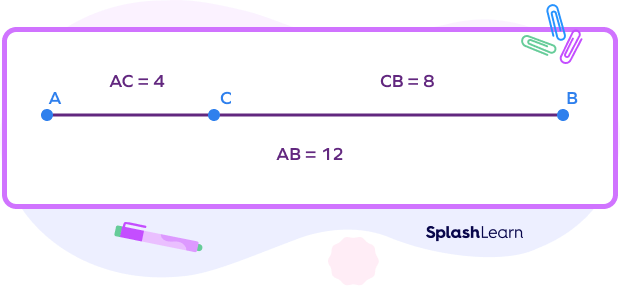
Example: Find the length of the line segment AB.
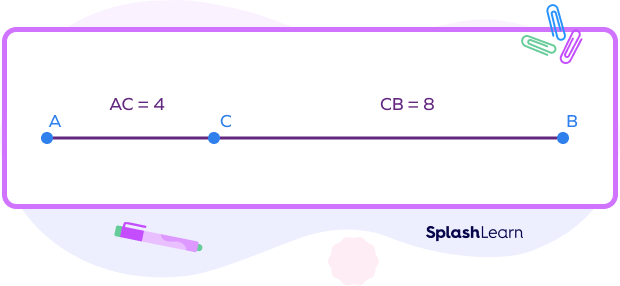
Step 1: Identify the collinear points and note down the given lengths of the line segments.
Here, C lies between A and B.
Step 2: Write the segment addition formula with respect to the given collinear points.
Here, AC + CB = AB
Step 3: Substitute the values and simplify.
AB = 4 + 8 = 12 units
- If the point P lies between A and B, then AP + PB = AB.
- If AP + PB = AB, then P lies between A and B, and the points A, P, and B are collinear.
Facts about Segment Addition Postulate
- The segment addition postulate is not applicable to lines or rays.
- This postulate can identify the midpoint of the line segment. If AB + BC = AC and AB = BC, then B is the midpoint of AC.
In this article, we learned about the segment addition postulate, which is a fundamental property of line segments that helps us to identify collinear points. Let’s solve a few examples and MCQs for better understanding.
1. Does point B lie on segment AC if segment AB = 3 units, BC = 5 units, and AC = 6 units?
Solution:
AB = 3 units, BC = 5 units, and AC = 6 units
Let us calculate the sum of AB and BC .
l ( AB) + l ( BC) = 3 + 5 = 8 units
l (AC) =6 units
l ( AB) + l ( BC)$/neq$ l(AC)
Thus, B does not lie on the line segment AC.
2. In the given diagram, l(AC) = 28 units. Find x.
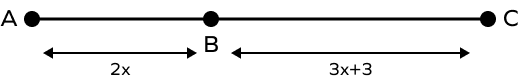
Solution:
B lies between the points A and C.
2x + 3x + 3 = 28
5x + 3 = 28
Thus, the value of x is 5.
3. The point R lies on the line segment PS , where PR = 5x , RS = (6x + 1) , and PS = 56 units. What will be the value of x , PR, RS and PS ?
As point S lies on the line segment PS , the equation will be:
11x + 1 = 56
11x = 56 – 1
$x = \frac{55}{11}$
PR = 5$ \times$ 5 = 25 units
RS = 6(5) + 1=31 units
4. Find GH.
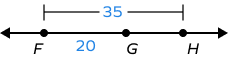
G lies between F and H.
FH = 35 units
GF = 20 units
By segment addition postulate, FG + GH = FH
GH = FH – FG
GH = 35 – 20
GH = 15 units
Attend this quiz & Test your knowledge.
What will be the value of ST if RS = 1 unit and RT = 13 units, and the point S lies on a line segment RT?
If the point y bisects the line segment xz, then, the points ijkl are collinear: ij = 9, jk = 11, and il = 26. what is the length of kl, what will be the value of x if q lies on line segment pr such that pq = 3x - 3, qr = 2x-1, and pr = 11.
How does the segment addition postulate differ from the angle addition postulate?
The Segment Addition Postulate deals with line segments and their lengths. The Angle Addition Postulate deals with the angles and their measures
Where is the segment addition postulate used in daily life?
It is used to find the measurement of walls, small objects with unknown parts of lengths and other similar items.
Can the Segment Addition Postulate be applied to non-collinear points?
No, the postulate specifically applies to collinear points . If the points are not on the same line, the postulate does not hold.
Which algebraic property is the segment addition postulate a part of?
The algebraic property of equality defines the segment addition of equality.
Is it possible to extend the segment addition postulate for more than three collinear points?
Yes, the postulate can be extended to include more than three collinear points. The sum of the lengths of the intermediate line segments would be equal to the length of the entire line segment.
AB + BC + CD = AD
RELATED POSTS
- Like and Unlike Algebraic Terms – Definition, Facts, Examples, FAQs
- Perimeter of a Rhombus – Definition, Formula, Examples, Facts, FAQs
- Line Plot – Definition with Examples
- Corresponding Sides – Definition, Solved Examples, Facts, FAQs
- Edges in Math – Definition With Examples

Math & ELA | PreK To Grade 5
Kids see fun., you see real learning outcomes..
Make study-time fun with 14,000+ games & activities, 450+ lesson plans, and more—free forever.
Parents, Try for Free Teachers, Use for Free
Geometry Worksheets
Practice and master geometry concepts with helpful walkthroughs from our elite math educators, then try practice math problems to sharpen your skills.

Segment Addition Postulate
By Vighnesh Hemnani
Segment Addition Postulate is a mouthful, but it is a simple concept that is explained simply at Thinkster. Check out our solved example and practice problems for you to work on!
Why is this concept useful?
Where does this concept fit into the curriculum?
Sample Math Problems
- Downloadable PDFs
Practice Math Problems
What is the Segment Addition Postulate?
By definition, the Segment Addition Postulate is a statement that says if we know that there are two points, A and C, along a line segment, then a point B must lie on the same line segment AC if the distances in the following equation add up:
AB + BC = AC
Here’s a simple diagram that depicts this rule:
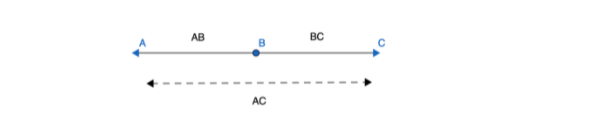
In short, a point B, can only lie in the middle of two points on a line, if the distances in between B, add up to the whole distance – this is pretty intuitive!
How to use this concept?
Segment addition postulate can be used in many ways and you can be asked to solve for a number of missing quantities. The main idea is that often times, a question will ask you to solve for a missing quantity, usually one missing from the following equation:
You can use the above formula from the Segment Addition Postulate to be able to arrive at an answer that will tell you everything about a line segment.
Find the missing length NO given that the total length MO is 9 and MN is 7

By the Segment Addition Postulate, we know that:
MN + NO = MO
If we know that the length AC is 32 and the length BC is 17, then what is the length of AB?

Based on the Segment Addition Postulate, we can say that:
AB + 17 = 32
AB = 32 – 17
In the below diagram, there are some distances provided. In addition, if you know that the total length from A to C is x + 12, then what is the value of x?

Again, the algebraic unknown is just a way to throw people off – if we stick to the Segment Addition Postulate, we should get the following:
6 + 3x + 6 = x + 12
3x + 12 = x + 12
Tip: Just because you got x = 0 doesn’t mean it’s wrong or that there is an error with the question. Remember that the value of x doesn’t directly mean any distance. If you want to calculate the distances, you need to plug x back into either 3x + 6 to get 6, or x + 12 to get 12.
Given the total length from WZ is 20 and the following information, find the value of x:

This time, unlike the previous examples or the definition of Segment Addition Postulate, includes a line with more than 3 points. However, the beauty of this postulate is that it can be extrapolated to more than 3 points. The same concept is just applied again (the sum of each line segment adds up to the length of the whole line segment):
WX + XY + YZ = WZ
2x – 12 + 10 + x – 10 = 20
x – 12 = 20
x = 20 + 12
Download FREE Math Resources
Take advantage of our free downloadable resources and study materials for at-home learning.

8 Math Hacks and Tricks to Turn Your ‘Okay’ Math Student Into a Math Champion!
One thing we teach our students at Thinkster is that there are multiple ways to solve a math problem. This helps our students learn to think flexibly and non-linearly.

How to Make Sure Your Child is Highly Successful and Becomes a Millionaire
As a parent, you hope your child is extremely successful and likely become the next Gates, Zuckerberg, or Meg Whitman. To set your child on the right path, there are many skills and traits that you can start building and nurturing now. Doing so plants the seeds for future success.
1. If you were to know that the length of DG is 5x – 24, then find x based on the following diagram and information provided:

2. Let us say that there is a line upon which there are the collinear points J, K, L, M and N (in that specific order). Supposing that the length of JN is x + 39 and the length of LN is x + 29.
3. Given that the points T, U, V are collinear, those points are in that order on a line segment and the following information, what is the length of TV?
TV = 2x + 1 , TU = x – 2, UV = 14
4. Find the length of QS given the following conditions:
- points Q, R and S are collinear
- R is between point Q and S
Kindergarten
Discover More at the Thinkster Blog
Parents like you are always looking for tips, suggestions, and activities to help their child become the best they can be! Learn more from our expert educators by visiting our blog.

Math Tutor and Coaching Program
With personalized attention from elite math tutors, help your child gain confidence in their math skills.
The Book of Secrets
Learn how to Make Your Child Math Fit for Life.
Related Topics
By Puja Varude
Normal Distribution
By Patricia Martin
Tossing a Coin
By Mandi Elam
Properties of Exponents
By Debi DalPezzo
Solve for x
Your child can improve their math scores by 90% within 3 months.
Our elite math tutors are ready to help make your child a math champion! Sign up for our zero $ free trial to get started today.
Segment Addition Postulate
Andymath.com features free videos, notes, and practice problems with answers! Printable pages make math easy. Are you ready to be a mathmagician?
The segment addition postulate is a formal way of saying the two parts add up to make the whole. It applies to adjacent segments lying on the same line.
\(\textbf{1)}\) If AB\(=10\) and BC\(=25\), what is AC? Show Answer AC\(=35 \)
\(\textbf{2)}\) if ac\(=40\) and bc\(=18\), what is ab show answer the answer is \(ab=22 \) show work \(\,\,\,\,\,\,ab+bc=ac\) \(\,\,\,\,\,\,ab+18=40\) \(\,\,\,\,\,\,ab=22\), \(\textbf{3)}\) if ac\(=52\) and ab\(=10\), what is bc show answer the answer \(bc=42 \) show work \(\,\,\,\,\,\,ab+bc=ac\) \(\,\,\,\,\,\,10+bc=52\) \(\,\,\,\,\,\,bc=42\), \(\textbf{4)}\) if bc\(=28\) and ab\(=9\), what is ac show answer ac\(=37 \), \(\textbf{5)}\) what is the length of ac as an expression show answer ac\(=11x-2 \), \(\textbf{6)}\) if ac\(=10x-4\), what is bc as an expression show answer bc\(=7x-6 \), \(\textbf{7)}\) b is the midpoint of ac. (not drawn to scale) if ab\(=52\) and ac\(=4x+4\), what is the value of x show answer x\(=25 \), see related pages\(\), \(\bullet\text{ geometry homepage}\) \(\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\text{all the best topics…}\), \(\bullet\text{ angle addition postulate}\) \(\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\), \(\bullet\text{ complimentary and supplementary angles}\) \(\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\), measuring the distance between two points: the segment addition postulate can be used to measure the distance between two points on a map or in a physical space. for example, consider a map of a city with two points a and c. to find the distance between a and c, we can use the segment addition postulate to add up the lengths of the segments that make up the path from a to c. designing a building or a bridge: architects and engineers often use the segment addition postulate when designing buildings and bridges. for example, when designing a bridge, engineers may use the segment addition postulate to determine the length of the main span (the distance between the two endpoints of the bridge) by adding up the lengths of the smaller segments that make up the span. survey work: land surveyors use the segment addition postulate to measure distances and angles in the field. for example, they may use a surveyor’s wheel or a laser rangefinder to measure the lengths of segments and use the segment addition postulate to find the total distance between two points. navigation: the segment addition postulate can also be used in navigation to find the distance between two points. for example, when using a gps device, the device may use the segment addition postulate to add up the lengths of the segments between two points to calculate the total distance., about andymath.com, andymath.com is a free math website with the mission of helping students, teachers and tutors find helpful notes, useful sample problems with answers including step by step solutions, and other related materials to supplement classroom learning. if you have any requests for additional content, please contact andy at [email protected] . he will promptly add the content. topics cover elementary math , middle school , algebra , geometry , algebra 2/pre-calculus/trig , calculus and probability/statistics . in the future, i hope to add physics and linear algebra content. visit me on youtube , tiktok , instagram and facebook . andymath content has a unique approach to presenting mathematics. the clear explanations, strong visuals mixed with dry humor regularly get millions of views. we are open to collaborations of all types, please contact andy at [email protected] for all enquiries. to offer financial support, visit my patreon page. let’s help students understand the math way of thinking thank you for visiting. how exciting, related topics to segment addition postulate.

Segment Addition Postulate

As we all know Math concepts build on each other. When it comes to Measuring Segments and the Segment Addition Postulate there are multiple lessons we must pull together to teach this lesson. The videos below do an excellent job of explaining measuring segments using the following methods.
Ruler Postulate –
Segment Addition Postulate –
Pythagorean Theorem –
Distance Formula –
Use a Manipulative to Teach the Measuring Segments
My advice would be to use blocks or cut outs like these to teach this lesson. I think establishing the connection between these real-world things and the algebra behind the geometry make these postulates much easier to learn. If you just go in with and number line and some numbers on the chalk board it probably won’t stick. I even think the measuring segments worksheets you use need to have more realistic pictures and problems in them.
Give them the squares that they can touch and manipulate. They do not have to be anything fancy. You can actually just give them square pieces of precut paper to play around with. Give them a ruler or yard stick, things they can touch and see themselves actually doing in the real world.
The Pythagorean Theorem and the Segment Addition Postulate
We also included a segment addition postulate worksheet below. These will include the problems involving distance formula, the Pythagorean Theorem , and the ruler postulate.
We also are giving you a Measuring Segments Worksheet, Exit Quiz, Bell Work Assignment, a Power Point Presentation, and some Segment Addition Postulate Guided Notes!
These Postulates Come Up Over and Over Again
Make it a lesson they won’t forget because these things come up over and over again in other lessons like…
- Absolute Value
- Constructions
- Operations with Complex Numbers
- Simplifying Radicals
- Irrational Numbers
- Pythagorean Theorem
- Square Roots
The more students hear how to develop strategies, the better they become at doing so.
Seeing these concepts used helps students make connections about the way all math concepts are related.
Here are your Free Resources for this Lesson!
Segment addition postulate worksheet, word docs & powerpoints.
To gain access to our editable content Join the Geometry Teacher Community! Here you will find hundreds of lessons, a community of teachers for support, and materials that are always up to date with the latest standards.
Segment Additions Postulate – Measuring Segments PDFs
1-3 Assignment Student Edition- Measuring Segments ( FREE ) 1-3 Assignment Teacher Edition – Measuring Segments ( Members Only ) 1-3 Bell Work Student Edition – Measuring Segments ( FREE ) 1-3 Bell Work Teacher Edition – Measuring Segments ( Members Only ) 1-3 Exit Quiz Student Edition- Measuring Segments ( FREE ) 1-3 Exit Quiz Teacher Edition – Measuring Segments ( Members Only ) 1-3 Guided Notes SE – Measuring Segments ( FREE ) 1-3 Guided Notes Teacher Edition – Measuring Segments ( Members Only ) 1-3 Lesson Plan – Measuring Segments and the Segment Addition Postulate ( Members Only ) 1-3 Online Activities – Segment Addition Postulate ( Members Only ) 1-3 Slide Show – Measuring Segments ( FREE )
Want access to the rest of the materials on Measuring Segments? To download the rest of the materials for this lesson and get updates via email when new lessons come out simply click the image below to Get All of Our Lessons!

Find and Use Slopes of Lines
Teaching midpoint and distance in the coordinate plane, teaching congruent figures, triangle congruence by asa and aas, teaching perpendicular and angle bisectors, teaching bisectors in triangles, best geometry books for kids, proving theorems in geometry, how to prove lines are parallel, teaching logic in geometry, teaching angle pairs, proofs with uno cards, valentine’s day math activity – classifying quadrilaterals, christmas math worksheets, thanksgiving worksheet for geometry – happy turkey day, halloween geometry activities high school, how to teach classifying polygons, points lines and planes, tessellation project, the unit circle – hand trick, introduction to trigonometry, pi day top 5 for geometry teachers, polygons in the coordinate plane – how to use geogebra, teaching tessellations to your geometry class, 3 ways to make your life easier as a geometry teacher without more geometry worksheets, reasoning and proof, geometry games – dance dance transversal, midsegments of triangles, planning a proof, triangle congruence by sss and sas, pythagorean theorem – nfl and geometry, inequalities in one triangle, parallel lines cut by a transversal – colorful flip book notes, measuring angles putt-putt course design project, how to teach tangent lines – graphic organizer, two tips to teach volumes of prisms and cylinders, parallel lines and transversals, nets and drawings for visualizing geometry – geometry nets project, ratios and proportions – bad teacher, hybrid flipped classroom model, how to teach perimeter and area of similar figures – in jay leno’s garage, how to create a jeopardy game, 5 tips for new teachers, 8 teacher discounts you don’t want to miss this summer, your students are cheating with this math app, how to setup and use google classroom and google forms to teach geometry, special right triangles – the foundation of everything trig, how to use google forms and word clouds to help your students master their geometry vocabulary, interactive geometry teaching techniques, the magic octagon – understand congruence in terms of rigid motions, attention getters to keep your geometry class locked in, teaching strategies for your inclusion geometry class without an intervention specialist, how to teach the properties of quadrilaterals, how to make geometry interesting, how to teach circles using the common core standards, full year of geometry lesson plans, how a rock star geometry teacher uses the ipad to educate, are you a geometry teacher with no textbooks or geometry worksheets, how to deal with a class clown – classroom management strategies, geometry lessons | the game has changed | common core standards, teaching dimensions with super mario – geometry, lesson for the first day of geometry class, freebie pre-requisite resources for this lessons.
The Distributive Property – Cupcakes and Algebra
- Factoring to Solve Quadratic Equations – Know Your Roots
Pythagorean Theorem – NFL and Geometry
- Adding and Subtracting Fractions – Cut the Cheese
How to Teach Simplifying Radicals
The Order of Operations – Don’t ask your Calculator

Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to email this to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pocket (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window)
- Teachers Pay Teachers
- Privacy Policy
How to Teach the Segment Addition Postulate

Geometry can be a tricky thing to teach, especially when you have to start off with topics like the segment addition postulate. I’ve got your back though, so don’t worry. Let’s go over how to teach the segment addition postulate.

How to teach the segment addition postulate part 1: Background Information
Before you teach the segment addition postulate there are some concepts you need to make sure your students understand. Hopefully you have gone over the building blocks of geometry such as points, lines, planes, and segments. You also must make sure that your students can solve basic equations! Specifically, they really need to be comfortable solving equations with variables on both sides and combining like terms.
Warm-Up Idea
I would recommend a warm-up activity where your students review basic vocabulary and solve a few equations. Make a desmos activity builder with a vocab card-sort as the first slide and follow it up with some equations! Desmos activity builders are great for combining a few different topics together in a warm-up. If you haven’t tried it out, it’s really easy to get started! Give it a shot!

https://teacher.desmos.com/
How to teach the segment addition postulate part 2: Lesson
Ok, so you made it through the warm-up and your students know their vocabulary and can solve equations. Let’s get started! I think the segment addition postulate is pretty easy to grasp for students if you start small. I like to hold up expo markers and connect them while having the students count out how many total markers are connected.

If I have two markers here, and three markers here, and I stick them together, how many do I have? Five, of course! It’s a great way to get the students connecting prior knowledge to the current concept. Thats when you introduce the actual AB+BC=AC. Start off with some simple examples before growing into more complicated algebra. After doing a few more problems together, it’s time for the students to practice.
Practice Idea
I love getting students practicing their skills together with their peers, so here’s where I would use a partner activity! https://www.teacherspayteachers.com/Product/Segment-Addition-Postulate-Partner-Activity-8116893
I currently have this activity listed for free on my Teachers Pay Teachers, so try it out! Students love working together. They’ll each solve their own problems, but then check with their partner. No prep for you!

You can see here that both partners have room to solve their own equations, but should get the same value for x. If they disagree, have them switch and solve the other side to see where their work went wrong. You’ll be able to walk around the room and supervise and help the truly stuck students. Easy!
How to teach the segment addition postulate part 3: Wrap-Up
If your students didn’t get through all of the practice, don’t worry. Worksheets like that make great homework assignments as well. Or maybe you have your own homework assignment you want to assign! The last thing I would make sure you do to solidify the lesson is going back to the letters. Sometimes students get really locked in on the algebra and forget about using the points to state the relationship, such as AB+BC=AC. Have an exit ticket where students have to write these relationships out a few times just to drive it home! It’ll be a welcome break after working through some tough equations.
If you feel like your students didn’t quite get it, check out my old post on my favorite review ideas! https://mathwithfriends.org/top-ways-for-math-teachers-to-review/

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.
- Standard 1a: Identify, name, draw, and apply basic facts about points, lines, segments, rays, and planes
- What are the dimensions of a point? of a line?
- What are colinear points?
- What are coplanar points?
- Identifying lines and points in a plane
- Assignment 1-1: Part A Pg. 8 #8-10, 14-16, 17-22, 24, 27-30 Part B #56-64
- Screencast
- Screencast Quiz
- Mid-Chapter Review
- Standard 1b: Copy and compare segments for congruence.
- Standard 1c: Use the Segment Addition Postulate to solve for missing segment lengths.
- Distance or Length of a Line Segment
- Algebra Review: Absolute Value & Distance, and Solving for a Variable
- Segment Addition Postulate
- Solving for Missing Line Segment Lengths
- Assignment 1-2: Pg 10 #65-68, Pg. 16 #9-12, 29, 31, 32, 36
- Standard 1d: Use the Midpoint Formula to find midpoints and bisectors of line segments
- Standard 1e: Use the Distance Formula and the Pythagorean Theorem segment lengths using midpoints and segment bisectors
- The Pythagorean Theorem
- Distance between points
- Horizontal Distance (x)
- Vertical Distance (y)
- Finding segment lengths using midpoints and segment bisectors
- The Distance Formula
- Midpoint Formula
- Assignment 1-3: Part A Pg. 24 #1-10, 16-30 even, 36-40 Part B Pg. 26 #41, 42, 45
- Screencast Quiz
- Standard 1f: Classify polygons
- Standard 1g: Find perimeters and areas of polygons in the coordinate plane.
- Classifying Polygons
- Using the Distance Formula to Classify a Polygon
- Using Slope to Classify a Polygon in the coordinate plane
- Assignment 1-4: Pg. 34 #3-10, 13-22, 30
- Standard 1h: Name, measure, and classify angles.
- Standard 1i: Identify congruent angles and equal angle measures.
- Standard 1j: Use the Angle Addition Postulate to solve for angle measures.
- Standard 1k: Construct and Bisect Angles.
- Constructing an Angle with a Protractor and/or Compass
- Replicating an angle with a compass
- Constructing a right angle
- Constructing acute and obtuse angles
- Angle Addition Postulate
- Assignment 1-5: Pg. 43 #4-12 even, 23, 24, 26, 27, 34, 38, 39 Part B #31, 32
- Standard 1l: Identify complementary and supplementary angles. Identify linear pairs and vertical angles.
- Standard 1m: Identify and solve for complementary and supplementary angles.
- Standard 1n: Identify and solve for linear pairs and vertical angles.
- Adjacent Angles
- Linear Pairs
- Vertical Angles
- Complimentary Angles
- Supplementary Angles
- Constructing Angles
- Constructing a Linear Pair
- Constructing Adjacent Angles
- Assignment 1-6: Part A Pg 52 #3-6, 8, 10, 11-18, 20 Part B #29, 30

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The segment addition postulate states that if a line segment has two endpoints, A and C, a third point B lies somewhere on the line segment AC if and only if the equation AB + BC = AC is satisfied. Look at the image given below to have a better understanding of this postulate. If we carefully look at its name "Segment Addition Postulate", it is very easy to understand.
Example: Find the length of the line segment AB. Step 1: Identify the collinear points and note down the given lengths of the line segments. Here, C lies between A and B. AC = 4. BC = 7. Step 2: Write the segment addition formula with respect to the given collinear points. Here, AC + CB = AB. Step 3: Substitute the values and simplify.
The Segment Addition Postulate Date_____ Period____ Find the length indicated. ... Write a segment addition problem using three points (like question 11) that asks the student to solve for x but has a solution x . Many possibilities: AB = x, BC = , AC = ...
3) Using the Segment Addition Postulate, and letting x equal the number of stories above John's floor, we have 19 + x = 64 and so x = 45. 4) There are a few ways to find BC, and we will outline ...
This time, unlike the previous examples or the definition of Segment Addition Postulate, includes a line with more than 3 points. However, the beauty of this postulate is that it can be extrapolated to more than 3 points. The same concept is just applied again (the sum of each line segment adds up to the length of the whole line segment):
Use the segment addition postulate to answer each question. MATH MONKS — 3x 32 13 10 and BC = — 8 and AC = BC = 7) EF= 27 14 23 2) DE = 18 and 5) LM = x + 4, MN — 25 8) ST = 59 25 2x, 3) GH — 6 and HJ = 6) I-IJ = 18, HI 12, RS = SEGMENT ADDITION POSTULATE Use the segment addition postulate to answer each question.
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like line segment, congruent segments, congruent and more.
In Summary. The segment addition postulate is a fundamental principle in geometry that states that given two line segments with a common endpoint and slope, the sum of the lengths of the two segments is equal to the length of the line segment formed by the two segments taken together. This principle is often used to find the lengths of unknown ...
College. Students learn the segment addition postulate and the definition of a midpoint, as well as the definitions of congruent segments and segment bisectors. Students then use algebra to find missing segment lengths and answer various other questions related to midpoints, congruent segments, and segment bisectors. We help you determine the ...
Segment Addition Postulate Sum of the parts equal the whole. 1. Find AC 2. Find AB if AC = 15 3. Find AB and BC if AC = 25 4. Find AB if B is the midpoint of line segment AC 5. Find the value of x and AC AB + BC = AC A B C 5 15 A B C x 12 A B C x 2x + 4 A B C 5x - 27 2x + 3 A B C 4x - 3 2x + 3 A M C.
Solve for the missing length indicated. 23. Solve for the missing length indicated. 15. Solve for the missing length indicated. 24. Solve for the missing length indicated. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like 10, 11, 3 and more.
We also included a segment addition postulate worksheet below. These will include the problems involving distance formula, the Pythagorean Theorem, and the ruler postulate. We also are giving you a Measuring Segments Worksheet, Exit Quiz, Bell Work Assignment, a Power Point Presentation, and some Segment Addition Postulate Guided Notes!
Business Contact: [email protected] Mathgotservedhttps://mathgotserved.com/geometryGeometry Unit 1 Foundations1.2 Segment Addition Postulate https://...
Ruler Postulate: Write an equation for the length of AB. Segment Addition Postulate: Write an equation for the length of AC. Check Your Understanding: 1. Find the length of ST. 2. Write an equation explaining the relationship between Rs, ST, and RT. 3. Use segment addition to write an equation and then solve for x. Click here for more practice ...
Segment Addition Postulate Protractor Postulate Ruler Postulate Postulates Sep 511:48 AM exit ticket 1. Explain how you think the Segment Addition Postulate could be used in real life. 2. Sketch and label the following objects: a. A point exterior to an obtuse angle b. The midpoint of the segment joining (0,2) and (4,6)
1 To find the lengths of segments. Examples. 1 Comparing Segment Lengths. 2 Using the Segment Addition Postulate. 3 Using the Midpoint. Math Background. A one-to-one correspondence, as used in the Ruler Postulate, is one way to show that two sets are equivalent when their elements cannot be counted.
Explains the Ruler Postulate and the Segment Addition Postulate in under 3 minutes. Click Create Assignment to assign this modality to your LMS. We have a new and improved read on this topic.
Draw the picture of the segment described, then write the Segment Addition Postulate for the points described.. 1. S is between D and P 2. J is between S and H 3. C is between Q and R 4. T is between M and N C is between A and E. For each problem, draw a picture representing the three points and the information given.
Worksheet by Kuta Software LLC 15) G I H 2 x + 30 2x + 34 16 16) Q S R 2x + 26 3 x + 19 17) L N M 8 6 x − 1 3 + 8 x 18) J L K x − 5 11 2 x − 1 19) F H G 2 x + 3 5 3 x + 4 20) T V U x + 5 5
Write the Segment Addition Postulate for each problem. Also use Segment Addition Postulate to solve the following problems. 1. If AB = 12 and BC = 7, then find the length of AC. A B C 2. If AB = 4x + 9, BC = 5x + 2, and AC = 56, then find the value for x, AB, BC. A B C 3.
How to teach the segment addition postulate part 3: Wrap-Up. If your students didn't get through all of the practice, don't worry. Worksheets like that make great homework assignments as well. Or maybe you have your own homework assignment you want to assign! The last thing I would make sure you do to solidify the lesson is going back to ...
Use the Segment Addition Postulate. variables and lengths of line segments. Use the Angle Addition Postulate to. and measures of angles. Use properties of complementary and supplementary angles to. determine the value of variables and measures of angles. Print pages 3 & 4 double sided and make enough copies for your students.
Standard 1c: Use the Segment Addition Postulate to solve for missing segment lengths. Outline. Distance or Length of a Line Segment; Algebra Review: Absolute Value & Distance, and Solving for a Variable ... Assignment 1-3: Part A Pg. 24 #1-10, 16-30 even, 36-40 Part B Pg. 26 #41, 42, 45; Screencast; Screencast Quiz; Powerpoint; PDF Slides; Desmos;