
Presentations made painless
- Get Premium

108 Organizational Behavior Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
Inside This Article
Organizational behavior is a fascinating field that examines how individuals, groups, and organizations interact within a work environment. It encompasses a wide range of topics, from leadership and communication to motivation and decision-making. If you're studying organizational behavior and need some inspiration for your next essay, look no further. Here are 108 organizational behavior essay topic ideas and examples to get you started:
- The impact of organizational culture on employee satisfaction
- The role of leadership in shaping organizational behavior
- How diversity and inclusion influence team dynamics
- The importance of emotional intelligence in the workplace
- Strategies for managing conflict in organizations
- The effects of job design on employee motivation
- The relationship between organizational justice and employee performance
- The role of power and politics in organizational behavior
- The impact of technology on organizational communication
- The influence of organizational structure on decision-making processes
- The role of trust in building effective teams
- The effects of stress and burnout on employee well-being
- The impact of organizational change on employee morale
- The relationship between job satisfaction and employee turnover
- Strategies for promoting work-life balance in organizations
- The role of ethics in organizational behavior
- The effects of group dynamics on team performance
- The relationship between personality and organizational behavior
- The impact of globalization on organizational culture
- The role of feedback in employee development
- The effects of job insecurity on employee motivation
- The relationship between leadership style and organizational performance
- The influence of organizational climate on employee engagement
- The role of mentoring in organizational development
- The effects of social media on organizational communication
- The impact of organizational citizenship behavior on team effectiveness
- The relationship between job crafting and employee well-being
- The role of emotional labor in customer service
- The effects of organizational learning on innovation
- The influence of organizational justice on employee trust
- The impact of job characteristics on employee engagement
- The relationship between organizational commitment and job performance
- The role of resilience in overcoming workplace challenges
- The effects of job insecurity on employee productivity
- The importance of psychological safety in team dynamics
- The impact of organizational politics on decision-making processes
- The relationship between job satisfaction and organizational citizenship behavior
- The role of transformational leadership in driving organizational change
- The effects of work-life balance on employee retention
- The influence of organizational culture on employee motivation
- The impact of emotional intelligence on leadership effectiveness
- The relationship between job design and job satisfaction
- The role of organizational justice in shaping employee attitudes
- The effects of diversity and inclusion on team performance
- The importance of communication in building trust within teams
- The impact of job insecurity on employee well-being
- The relationship between leadership style and employee engagement
- The role of feedback in promoting employee development
- The effects of job crafting on job satisfaction
- The influence of organizational climate on team effectiveness
- The impact of organizational learning on innovation
- The relationship between job characteristics and employee motivation
- The role of emotional labor in customer satisfaction
- The effects of organizational citizenship behavior on organizational performance
- The importance of psychological safety in team collaboration
- The impact of organizational politics on decision-making effectiveness
- The role of transformational leadership in organizational development
- The effects of work-life balance on employee engagement
- The influence of organizational culture on team dynamics
- The impact of emotional intelligence on employee well-being
- The relationship between job design and team performance
- The role of organizational justice in shaping organizational behavior
- The effects of diversity and inclusion on employee satisfaction
- The importance of communication in building effective teams
- The impact of job insecurity on job performance
- The relationship between leadership style and organizational culture
- The role of feedback in promoting team cohesion
- The effects of job crafting on team dynamics
- The influence of organizational climate on employee morale
- The impact of organizational learning on team innovation
- The relationship between job characteristics and organizational performance
- The role of emotional labor in employee engagement
- The effects of organizational citizenship behavior on employee motivation
- The importance of psychological safety in team effectiveness
- The impact of organizational politics on employee well-being
- The relationship between job satisfaction and team collaboration
- The role of transformational leadership in building trust within teams
- The effects of work-life balance on organizational performance
- The influence of organizational culture on employee retention
- The impact of emotional intelligence on team dynamics
- The relationship between job design and organizational communication
- The role of organizational justice in shaping team effectiveness
- The effects of diversity and inclusion on organizational culture
- The importance of communication in promoting employee satisfaction
- The impact of job insecurity on team performance
- The relationship between leadership style and job satisfaction
- The role of feedback in driving organizational change
- The effects of job crafting on organizational development
- The impact of organizational learning on team collaboration
- The relationship between job characteristics and team performance
- The role of emotional labor in organizational performance
- The effects of organizational citizenship behavior on team dynamics
- The importance of psychological safety in promoting team cohesion
- The impact of organizational politics on team effectiveness
- The relationship between job satisfaction and organizational communication
- The role of transformational leadership in shaping organizational culture
- The effects of work-life balance on employee morale
- The influence of organizational culture on team collaboration
- The impact of emotional intelligence on organizational performance
- The relationship between job design and employee engagement
- The role of organizational justice in promoting team effectiveness
- The effects of diversity and inclusion on team dynamics
- The importance of communication in building trust within organizations
- The impact of job insecurity on employee satisfaction
- The relationship between leadership style and team performance
- The role of feedback in driving team innovation
These organizational behavior essay topic ideas and examples cover a wide range of issues and concepts within the field. Whether you're interested in exploring the impact of leadership on organizational culture or the effects of job insecurity on employee well-being, there's something here for everyone. So, pick a topic that interests you, conduct some research, and start writing your next organizational behavior essay today!
Want to research companies faster?
Instantly access industry insights
Let PitchGrade do this for me
Leverage powerful AI research capabilities
We will create your text and designs for you. Sit back and relax while we do the work.
Explore More Content
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
© 2024 Pitchgrade
Today’s Most Critical Workplace Challenges Are About Systems
by Ludmila N. Praslova

Summary .
Critical workplace issues — e.g., the problematic quality of leadership within organizations, the threats to employee mental health and well-being, and the lack of belonging and inclusion — are primarily attributable to systemic factors embedded in organizational cultures and processes. And yet, many of these and other issues are still mainly addressed on the individual level. Why do organizations keep investing in remedies that don’t work and have little chance of working? An automatic bias in how we perceive and explain the world is a likely culprit. The author explains how that “superbias” manifests — and what leaders can do to combat it in their organizations.
W. Edwards Deming , a forward-thinking American who helped engineer the Japanese economic miracle and was the father of the continuous quality improvement philosophy, wrote that 94% of issues in the workplace are systemic. Only 6% are attributable to individual-level, idiosyncratic factors. Improvements, therefore, should also focus on systems — not individuals.
Partner Center
Essay on Organizational Behavior
Organizational behavior is the study of how individuals act within groups and how these behaviors impact the organization. Organizational behavior improves business operations such as job performance, increased innovation, high job satisfaction, and encouraging leadership. Organizational performance is considerably related to the employees’ attitudes. Understanding the various aspects of organizational behavior makes it easy for employers to access the feelings, attitudes, and motivation towards their job (Osland et al.,2015). The study introduces people to the concepts and theories about human behavior, which helps replace held notions. Organizational behavior is both a challenge and opportunity to employers due to the study’s focus on reducing absenteeism, increased job satisfaction, and productivity (Osland et al.,2015). The study also guides managers in providing better working conditions, ethical practice, and maximum respect in the workplace.
Every employee is unique, depending on the knowledge and experience they have about the job. Organizational behavior helps leaders to comprehend the motivational tools needed to help their employees reach their full potential (Osland et al.,2015). Leaders must evaluate the organizational structure that acts in the best interests of their employees. For example, recent years have seen corporations such as Google adopt flatter structures that allow employees to operate independently, thus encouraging them to exchange knowledge and acquire more control in decision making.
Performance and Office Characteristics
Behaviors affect employee’s performance. Multiple research pieces provide that employees with positive attitudes are creative and have low-stress levels at work—however, behaviors such as rudeness and gossip lower performance, productivity, and job satisfaction (Pinder, 2014). Organizations with many employees with negative attitudes have conflicts due to miscommunications that reduce overall working morale. The organization and setting of working offices can be a source of good or poor organizational behavior. An open office increases employee’s calmness with crowded offices, causing anxiety and exposure to diseases, breathing problems, among other issues. However, it is unwise to over-densify office spaces because small stations of work make collaboration difficult (Pinder, 2014). Employees take pride in working in successful companies with excellent organizational cultures and have many growth opportunities. A manager’s ability to recognize ways to improve workplace behaviors helps resolve pre-existing problems between workers and promote a healthy working environment.
Organizational behavior does not rely on analysis and conclusions made out of emotions and gut feeling but rather a manager’s ability to collect information concerning an issue in a methodical manner under controlled conditions (Mahek, 2019). The study involves using information and interpreting the findings to analyze the behavior of groups or individuals as desired. Companies exist to fulfill the needs of communities, and for them to survive in today’s competitive world, they must be growth-oriented. Respect for quality, high productivity, and zero errors in these companies ensure their growth merged with great focus on the teams and individuals that run the companies.
Characteristics of Organizational Behavior and Real-Life Application
The study involves rational rather than emotional thinking about individuals. The main aim of organizational behavior lies in explaining, predicting, and understanding human behavior in companies. The study is goal and action-oriented. Also, the study seeks to provide a balance in the technical and human values in the workplace (Mahek, 2019). Organizational behavior achieves productivity by maintaining and constructing worker’s growth, satisfaction, and dignity rather than sacrificing these values. Organizational behavior is an art and science since the study of human behavior leans heavily on science. For instance, modern studies of organizational behavior are critical, experimental, and interpretive, which makes it a revealing science in the search for meaning and knowledge (Mahek, 2019). The study also mixes behavioral sciences such as sociology and psychology, among others. The study has evolved with modern organizational behavior utilizing people’s culture and current events to gain facts and use available paradigms.
Organizational behavior is an important study in real life because it helps one understand their behavior and others (Mahek, 2019). For example, students can use organizational behavior to promote teamwork in school, improve communication, and ultimately promoting a peaceful learning environment. Organizational behavior has helped me understand my views of ethics both in school and in the community. I have always had a problem adapting to new environments and interacting with new people because of my inability to learn behaviors, making it hectic to make friends and express myself while in such places. Having learned about organizational behavior, its characteristics, and the remarkable results the study has on communication, productivity, and attitudes, I now know that I would have handled the situations differently. After the course, new environments and people are no longer a problem since I can effectively utilize the various organizational behavior theories to approach people while understanding their views on some issues, attitudes, and behaviors.
Leadership in Organizational Behavior
In today’s world of business, influential leaders are essential for binding the authority around them. Leadership has countless pitfalls that leaders must learn to avoid since leaders’ mistakes have grave consequences on the societies they lead, businesses, and administrations. Big companies need leadership that harmonizes thousands of people’s energies into a mutual goal, with startup enterprises requiring inspirational leaders that share similar values with their employees (Boekhorst, 2015). Therefore, leadership is a social influence process that aims to increase other people’s efforts in search of a common goal. Different kinds of leadership have different results ranging from effective to chaotic ones. Leaders must assess their personality, strengths, and weaknesses before becoming leaders. A leader in the workplace must connect with the employees and ultimately engage with them to gain their support, cooperation, and respect.
Characteristics and Abilities of Effective Leaders
Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence refers to an individual’s ability to identify their emotions and understand what they are communicating to them. Emotional intelligence also involves a person’s perception of those around you, which creates harmony and respect (Boekhorst, 2015). A leader that does not understand how they feel cannot manage their relationship with others since it is hard for them to relate to their feelings. Emotional intelligence in a leader comprises self-knowledge (awareness), motivation, social skill, empathy, and self-regulation. Each of these facets determines how well a leader gets rounded, thus enabling him/her to excel in the business world.
Self-Awareness
Self-awareness is one of the most important qualities of a leader and trumps all. Every leader, manager, and entrepreneur purposing to make it in business must possess this quality. A leader who has self-awareness knows what motivates them and their decision-making process. When a leader understands their motivation, they can channel the same to the employees to acquire high productivity and harmony (Rao, 2020). Research provides that the energy a leader channels to his/her employees reflects who they are, meaning that a leader who instigates strength to his/her followers Is a strong person who knows their strengths and weaknesses. A self-aware leader is alert to their inner signals, which helps them recognize their feelings and their effects on their job performance. The moral compass helps in decision making, thus deducing the most practical course of action (Rao, 2020). A self-aware leader can see the bigger picture and is genuine about it, giving them the vision to lead and the ability to distinguish between their strengths and weaknesses.
Self-Regulation
Self-regulation refers to the ability to manage one’s emotions in an unrestrained environment. Self-regulation helps leaders to escape the bondage of one’s impulses. Leaders who possess this quality lean toward thoughtfulness and reflection, accepted change and indecision, honesty, and the ability to fight instincts. Self-regulation helps leaders to maintain a positive outlook on life (Rao, 2020). A leader must be able to cool themselves down when upset and cheer themselves up when down. A self-regulated leader is flexible and adapts to various styles or work with their employees and take charge of all situations no matter how challenging. The quality allows one to be an independent actor without needing other people to pull them out of greasy situations or provide the path towards their goals.
A leader cannot be an effective one if they cannot motivate other people. In the workplace, leaders must set goals to ensure a change in their companies and encourage them to follow the same direction (Rao, 2020). Employees mostly do what they have been instructed to do, and without a motivational leader, most would get lost. Successful leaders can motivate people even if it is one of the hardest things to do since people motivate themselves. The secret to being a leader that motivates his/her employees lies in valuing these people than oneself.
Empathy is the strength to relate with and comprehend the needs and views of other people. Empathic leaders can recognize other people’s feelings even when they are not obvious. Empathy sharpens a person’s communication skills in that it guides them on not saying the wrong things when another person is suffering on the inside (Rao, 2020). An empathic leader builds a feeling of importance and belonging to their employees by showing them that their leader cares and is not a heartless detached robot.
Social Skill
The quality refers to a person’s ability to tune into other people’s emotions and comprehend what they think about certain things. This ability helps a leader with team playing, collaboration, and negotiation skills. Active listening and excellent communication skills are important to this quality. Lack of social skills in a leader may result in companies’ collapse due to lack of representation from a coherent external environment (Rao, 2020). The modern world involves leaders assuming that they need to tweet more and send thousands of emails to have social skills, but one needs to be comfortable connecting with other people in person and on social channels.
Leadership Theories
Leadership theories are thoughts that explain why and how certain individuals become leaders. The theories focus on the leader’s characteristics in each school of thought. The theories are:
Great Man Theory
The theory vies leadership as an individual’s heroic act. The theory provides that something special exists about an individual’s combination of abilities and personality traits that sets them up as great leaders, thus distinguishing them from others (Amanchukwu et al., 2015). The theory clings to the fact that leaders are born and not made. Companies tend to focus on persons that possess the ability to inspire others toward a common zeal.
Behavioral Theory
The behavioral theory focuses on the way leaders behave in the workplace. For instance, do leaders just provide rules and expect other people to follow them without question, or do they involve others in the decision-making process (Amanchukwu et al., 2015)? The theory believes leaders can be made from their behaviors and not born as the Great Man Theory holds. Depending on a leader’s behavior, they can become autocratic, democratic, or Laissez-faire leaders.
Situational Theory
The theory focuses on the situational variables without terming one person’s leadership style as better than the others (Amanchukwu et al., 2015). The theory states that different situations call for different leadership styles and the maturity level of the followers.
Transformational Theory
The theory focuses on the relationship between leaders and their followers, emphasizing charismatic and inspirational leaders. The theory focuses on leaders who aim to change their follower’s performance on various tasks (Amanchukwu et al., 2015). Leaders in this theory get motivated by their ability to show their followers that specific tasks are vital and should be highly involved in performing them.
Trait Theory
The theory assumes that leaders are born possessing certain leadership traits, which makes them more suitable for leadership roles than others who lack the natural characteristics (Amanchukwu et al., 2015). The theory upholds the qualities of responsibility, intelligence, accountability, and creativity that make them prosper in leadership.
In conclusion, organizational behavior is a study that focuses on the effect of individual and group behavior in the workplace. The science helps leaders access their employees’ attitudes, feelings, and motivation switches and guide them on their next steps. Through organizational behavior, companies can develop ways to reduce conflicts, improve productivity, build teamwork and create conducive working environments in the workplace. Leadership is a vital concept of organizational behavior and aims at defining the roles, traits, and theories of leadership suitable for different organizational structures and cultures.
Amanchukwu, R. N., Stanley, G. J., & Ololube, N. P. (2015). A review of leadership theories, principles and styles and their relevance to educational management. Management , 5 (1), 6-14.
Boekhorst, J. A. (2015). The role of authentic leadership in fostering workplace inclusion: A social information processing perspective. Human Resource Management , 54 (2), 241-264.
Mahek, S. (2019, September 28). Organisational behaviour: Meaning, scope, nature, models & importance . Economics Discussion. https://www.economicsdiscussion.net/management/organisational-behaviour/31869
Osland, J., Devine, K., & Turner, M. (2015). Organizational behavior. Wiley Encyclopedia of Management , 1-5.
Pinder, C. C. (2014). Work motivation in organizational behavior . psychology press.
Rao, S. (2020, March 23). The mini-guide to effective leadership in the workplace . A Blog About Payroll, Small Business and More | Wagepoint. https://blog.wagepoint.com/all-content/the-mini-guide-to-effective-leadership-in-the-workplace
Cite this page
Similar essay samples.
- Essay on Exploring Climate Memory
- General Principles of Toxicology using Caenorhabditis elegans as a mod...
- How does the tort of negligence protect a patient’s autonomy in resp...
- A critical evaluation of the rule in Wheeldon v. Burrows (1879) 12 Ch ...
- Comparative Study of Human Resource Management Practices in Japan and ...
- Amazon.com Inc.’s SWOT Analysis

Importance & Challenges of Organizational Behavior in the Workplace
In today’s rapidly changing business environment, the success of any organization heavily relies on its employees. Organizational behavior plays a crucial role in managing and understanding human behavior within a workplace, as it encompasses a wide range of topics, including communication, leadership, motivation, and culture. It is therefore crucial to understand the importance of organizational behavior and the challenges it poses.
As the workplace becomes increasingly diverse, the importance of organizational behavior cannot be ignored. It can help organizations create a positive work environment that attracts and retains top talent. Organizational behavior can also help organizations create effective teams and improve communication and collaboration within the organization.
However, there are also challenges associated with organizational behavior, such as resistance to change, conflict management, and maintaining a healthy work-life balance. Overcoming these challenges requires organizations to develop effective strategies and policies that support employees and promote a positive workplace culture.
As the famous HR , Dave Ulrich, once said,
Employees are a company’s greatest asset – they’re your competitive advantage. You want to attract and retain the best; provide them with encouragement, stimulus, and make them feel that they are an integral part of the company’s mission.
In the remaining post, we will discuss the importance and challenges of organizational behavior in detail and explore strategies to create a positive and productive workplace culture.
Table of Contents
Importance of Organizational Behavior
Organizational behavior is critical to the success of a business. It impacts various aspects of a workplace, including employee satisfaction and motivation, communication and collaboration, decision making and problem solving, as well as productivity and efficiency.
Here are some ways that organizational behavior contributes to these factors:
1. Enhancing Employee Satisfaction and Motivation:
Employee satisfaction and motivation are essential factors in driving the success of an organization. It has been established through various studies that companies with highly satisfied and motivated employees tend to have better employee retention rates, higher levels of productivity, and increased profitability.

In fact, according to a study by HBR , motivated employees tend to be 125% more productive than their counterparts who lack motivation.
Organizational behavior is crucial in enhancing employee satisfaction and motivation as it contributes to creating a positive work environment that encourages employee engagement and empowerment. Job design, performance management, and rewards and recognition programs are some of the organizational behavior principles that can aid in creating a work environment that fosters employee satisfaction and motivation. Job design can be used to create more meaningful and challenging work, leading to higher job satisfaction and motivation. In the same vein, performance management systems that provide regular feedback and opportunities for skill development can increase employee engagement and motivation.
2. Improving Communication and Collaboration
Effective communication and collaboration play a vital role in the success of any organization. Inefficient communication can lead to delays, misunderstandings, and reduced productivity. On the other hand, collaboration can help bring together different skills and knowledge to solve complex issues. Organizational behavior principles can assist in improving communication and collaboration by fostering a work environment of trust, respect, and openness.
Organizational behavior theories like social exchange theory and transformational leadership can be used to establish a positive work culture that encourages effective communication and collaboration.
Social exchange theory emphasizes that employees are more likely to participate in positive behaviors like knowledge sharing and collaboration when they perceive that they will receive benefits in return. Similarly, transformational leadership inspires leaders to motivate and encourage their employees by developing a shared vision and a sense of common purpose.
3. Supporting Decision Making and Problem Solving
Making informed decisions and solving complex problems are crucial for the success of an organization. To support these processes, organizational behavior provides frameworks and tools. Decision-making models such as the rational decision-making model and bounded rationality model can aid individuals and teams in making logical decisions by considering all relevant factors.
Similarly, problem-solving techniques such as root cause analysis and brainstorming can be applied to identify underlying causes of problems and generate innovative solutions. Organizational behavior also promotes learning and experimentation culture, enabling individuals and teams to learn from their successes and failures, thereby improving the organization’s decision-making and problem-solving capabilities over time.
4. Increasing Productivity and Efficiency
In today’s highly competitive business environment, organizations need to continuously improve their productivity and efficiency. Organizational behavior offers tools and frameworks that can help achieve this goal by promoting effective time management, resource allocation, and task prioritization.

The Pomodoro Technique is an example of a time management technique that helps individuals and teams work more efficiently by breaking down tasks into manageable work sessions.
Similarly, resource allocation techniques like the critical path method enable organizations to allocate resources more efficiently by identifying critical tasks and activities. Organizational behavior can also foster a culture of continuous improvement by encouraging individuals and teams to seek out and implement process improvements, which can result in significant productivity and efficiency gains over time.
Challenges of Organizational Behavior
Although organizational behavior is an essential component of any business, and has a lot of importance, many organizations still struggle with various challenges in implementing effective organizational behavior strategies. In this section, we will discuss some of the key challenges of organizational behavior.
1. Resistance to Change
One of the biggest challenges of organizational behavior is resistance to change. Change is inevitable, and organizations must constantly adapt to new environments and circumstances to remain competitive. However, employees often resist change, whether it is due to fear of the unknown or a reluctance to let go of familiar processes. This resistance can hinder organizational progress and growth, leading to missed opportunities and lost revenue.
Organizations can mitigate resistance to change by involving employees in the change process, providing training and support, and communicating the reasons for the change clearly and transparently. According to a study by McKinsey & Company , involving employees in the change process can increase the likelihood of success by up to 79%. Furthermore, communication is critical in ensuring that employees understand the changes and are willing to embrace them.
2. Communication Barriers
Achieving effective communication is vital for the success of any organization. However, communication barriers can hamper productivity, collaboration, and decision-making. These obstacles may include language differences, cultural disparities, and physical distance, leading to conflicts, misunderstandings, and lack of trust among team members, thus negatively affecting organizational performance.

Companies can overcome communication barriers by investing in communication tools, offering effective communication skills training to employees, and establishing clear communication channels that encourage honesty, openness, feedback, and clarification.
3. Lack of Trust and Transparency
Building a healthy organizational culture involves trust and transparency, yet some organizations struggle with these components. This can result in disengaged employees, low morale, and high turnover rates. Employees who lack trust in their leaders or feel uninformed may become disillusioned and may not be motivated to put in extra effort.
One way to foster trust and transparency is by involving employees in decision-making processes, promoting accountability, and being candid with employees. According to a study by Edelman , employees who trust their employers are more likely to promote the organization’s products or services, potentially increasing revenue and brand loyalty.
4. Conflicting Values and Goals
Organizations are made up of individuals with different values, beliefs, and goals, which can lead to conflicting interests and priorities. This can create a challenging environment where team members are working at cross-purposes, leading to inefficiencies and missed opportunities. Conflicting values and goals can also create tension and conflict within teams, which can damage relationships and erode trust.
Organizations can address conflicting values and goals by establishing a shared vision and mission that aligns with the organization’s values and goals. Additionally, organizations can foster a culture of collaboration and teamwork, where team members are encouraged to work together to achieve common goals. Deloitte study suggests that organizations that promote a culture of collaboration are five times more likely to be high-performing than those that do not.
Strategies for Overcoming Organizational Behavior Challenges
As seen above, organizational behavior challenges can have a significant impact on a company’s success, but they can be overcome with the right strategies. By addressing issues such as communication barriers, lack of trust, and resistance to change, organizations can create a positive culture that promotes productivity and growth.
1. Encouraging Open Communication
To establish a robust organizational culture, effective communication plays a crucial role as it makes employees feel valued, respected, and listened to. Open communication is linked to increased employee engagement and motivation, leading to improved productivity and profitability. Despite its benefits, communication barriers such as hierarchical structures, cultural differences, and language disparities can impede effective communication.
Organizations can encourage open communication by scheduling regular meetings, feedback sessions, and town halls that provide a secure space for employees to share their thoughts and concerns. This can provide valuable insights to management. Bridging communication gaps can also be achieved by promoting cultural awareness and providing language training.
2. Building Trust and Transparency
Establishing trust and transparency is critical to fostering a positive organizational culture. When leaders are transparent about their decision-making processes and goals, and employees trust that their leaders have their best interests in mind, employees are more likely to be engaged and committed to their work. Conversely, lack of transparency and trust can result in disengagement and skepticism.

To build trust and transparency, organizations can utilize various strategies, such as regularly communicating with employees, sharing company goals and performance metrics, and involving employees in decision-making processes. Additionally, being forthright about obstacles and setbacks and seeking employees’ input on how to address them can promote a sense of responsibility and accountability among employees.
3. Promoting Change Management
Resistance to change is a common organizational behavior challenge. Employees may resist change due to fear of the unknown, lack of understanding, or concerns about job security. However, change is necessary for companies to stay competitive and adapt to evolving markets and technologies.
To promote change management, organizations can communicate the reasons for change clearly and involve employees in the process. By providing training and support, companies can help employees adjust to new processes and technologies. Celebrating successes and recognizing employee contributions can also help build momentum and enthusiasm for change.
4. Fostering a Positive Organizational Culture
A positive organizational culture is key to overcoming organizational behavior challenges. A culture that prioritizes open communication, trust, transparency, and change management can create a sense of purpose and meaning for employees, leading to increased engagement and productivity.
To foster a positive organizational culture, companies can prioritize employee well-being, provide opportunities for growth and development, and celebrate successes. Companies can also create a sense of community and belonging by promoting diversity and inclusivity.
In conclusion, organizational behavior is a crucial aspect of any workplace that can have a significant impact on employee satisfaction, productivity, and efficiency. While there are several benefits of implementing effective organizational behavior strategies, there are also numerous challenges that organizations face when attempting to implement these strategies.
To overcome these challenges, organizations need to implement several strategies that promote effective communication, build trust and transparency, manage change, and foster a positive culture.
By doing so, organizations can create a work environment that promotes employee satisfaction, productivity, and success.
Subscribe Newsletter
Stay Updated with our latest news straight into your inbox!
Latest Posts

5 Steps to Mastering the Art of HR Leadership

Ethical Leadership in HR: Key Traits and Practices

2024 HR Trends – Creating a Culture of Growth & Wellbeing

Top 15 Employee Training Software for Best Training

38 Best Recruitment Tools for Perfect Hiring in 2024
Find us on facebook, know the latest hr trends.
One new article per week.
How to Promote Your Company Culture to Job Seekers

Organizational Behavior and Culture: Understanding the Impact on Employee Motivation & Productivity

How to Encourage Employees to Report Issues

Why Company Culture Matters and How to Improve Yours

- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7

Challenges and Opportunities of Organizational Behavior: Explained
Discover the dynamic world of organisational behaviour and unlock its endless possibilities. This blog delves into the intricacies of organisational behaviour, exploring the challenges it presents and the opportunities it unveils for modern businesses. Discover how organisational behaviour can revolutionise your workplace.

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- BCS Foundation Certificate in IS Project Management
- BCS Professional Certificate in Benefits Planning and Realisation
- BCS Practitioner Certificate in Enterprise and Solution Architecture
- BCS International Diploma in Business Analysis
- BCS Foundation Certificate in Digital Business Change Training

Organisational behaviour can be likened to a complex puzzle, where each piece represents a unique challenge or opportunity. Just as assembling a puzzle requires careful observation, analysis, and strategic thinking, understanding organisational behaviour demands a similar approach.
The challenges within organisational behaviour involve navigating diverse personalities, managing conflicts, and adapting to changing dynamics. Conversely, the opportunities lie in fostering collaboration, enhancing productivity, and creating a harmonious work environment. By unravelling the puzzle of organisational behaviour, businesses can unlock their full potential and achieve remarkable success.
Table of contents
1) What is Organisational Behaviour?
2) Challenges and Opportunities of Organisational Behaviour
a) Enhancing individuals' competencies
b) Enhancing standards and efficiency
c) Comprehensive Quality Control (CQC)
d) Overseeing workforce variety
e) Confronting the impacts of globalisation
f) Empowering employees through delegation
g) Managing transitions
h) Fostering creativity and evolution
i) Enhancing ethical conduct
j) Elevating customer support
3) Conclusion
What is Organisational Behaviour?
Organisational Behaviour (OB) is a field of study that examines the individual, group, and structural aspects of organisations and their impact on behaviour within the workplace. It explores how individuals interact with each other, how groups form and function, and how organisational structures influence employee behaviour and performance. OB encompasses various disciplines, such as psychology, sociology, and management, aiming to understand and improve motivation, communication, leadership, decision-making, and organisational culture. The ultimate goal of organisational behaviour is to enhance organisational effectiveness and the well-being of individuals within the organisation.

Challenges and Opportunities of Organisational Behaviour
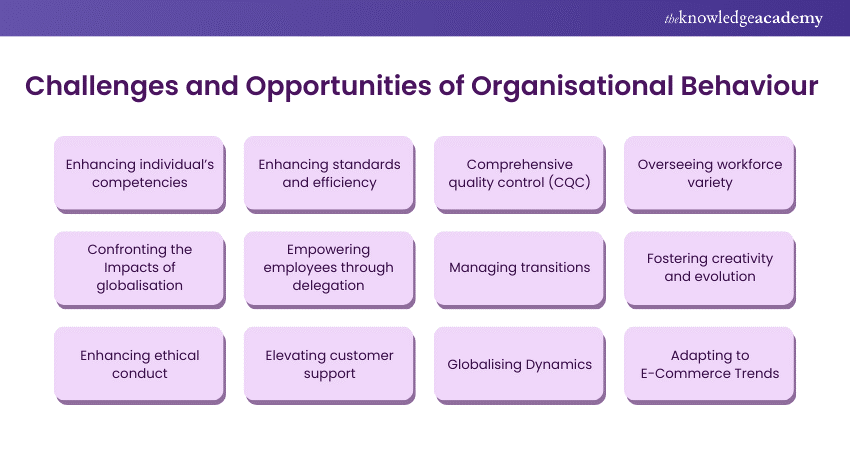
Navigating the department of Organisational Behaviour presents a duality of challenges and opportunities, influencing the dynamics and success of any enterprise. Let’s cover these challenges and opportunities one by one.
Enhancing individuals' competencies
Enhancing individuals' competencies refers to developing and improving employees' skills, knowledge, and abilities within an organisation. This involves providing training and professional development opportunities and fostering a culture of continuous learning. By investing in enhancing individuals' competencies, organisations can improve employee performance, job satisfaction, and overall productivity.
Opportunities:
1) Training and development programs can be designed to address specific skill gaps and promote employee growth.
2) Encouraging employees to pursue additional education and certifications can enhance their competencies.
3) Mentoring and coaching programs can provide guidance and support for individuals to develop new skills.
Enhancing standards and efficiency
Enhancing standards and efficiency involves the challenge of improving processes, systems, and workflows to achieve higher levels of productivity and effectiveness. This requires identifying and eliminating bottlenecks, streamlining operations, and implementing best practices. By enhancing standards and efficiency, organisations can optimise resource utilisation, reduce costs, and deliver better results.
1) Implementing quality management systems such as Six Sigma or Lean methodologies can help identify and eliminate inefficiencies.
2) Embracing technology solutions and automation can streamline processes and improve efficiency.
3) Regular performance evaluations and feedback mechanisms can help identify areas for improvement and set higher standards.
Enhance your knowledge in in Architect roles with our Enterprise and Solution Architecture Course - sign up now!
Comprehensive Quality Control (CQC)
Comprehensive quality control refers to the challenge of ensuring that products, services, and processes meet or exceed customer expectations. It involves establishing quality standards, monitoring performance, and implementing corrective measures when necessary. By prioritising comprehensive quality control, organisations can enhance customer satisfaction, build a positive reputation, and gain a competitive advantage.
1) Implementing quality assurance systems can help identify and prevent quality issues before they arise.
2) Conducting regular audits and inspections can ensure compliance with quality standards.
3) Encouraging a culture of continuous improvement can foster a proactive approach to quality control.
Overseeing workforce variety
Overseeing workforce variety involves managing the challenges and opportunities that arise from having a diverse workforce. It requires promoting inclusivity, managing cultural differences, and leveraging the unique perspectives and strengths of individuals from different backgrounds. By effectively overseeing workforce variety, organisations can foster innovation, creativity, and better decision-making.
1) Implementing diversity and inclusion initiatives can create a positive and inclusive work environment.
2) Encouraging cross-cultural awareness and sensitivity training can help employees understand and appreciate different perspectives.
3) Leveraging diverse teams can lead to a broader range of ideas and solutions.
Confronting the impacts of globalisation
Confronting the impacts of globalisation refers to the challenge of operating in a globalised market and managing the opportunities and threats associated with it. This includes dealing with international competition, cultural diversity, and global supply chains. Organisations must adapt their strategies, processes, and structures to thrive in a globalised economy.
1) Expanding operations to international markets can open new avenues for growth and revenue.
2) Collaborating with global partners and suppliers can enhance competitiveness and access to resources.
3) Developing a global mindset and cultural intelligence can help navigate diverse markets and customer preferences.
Learn the concept of Business Change with our Business Change Course join today!
Empowering employees through delegation
Empowering employees through delegation involves the challenge of entrusting decision-making authority and responsibility to employees at various levels. This requires creating a supportive and empowering work environment, clarifying expectations, and providing employees with the necessary resources and autonomy to make decisions. By empowering employees through delegation, organisations can foster innovation, improve employee engagement, and enhance organisational agility.
1) Delegating authority can free up managers' time to focus on strategic initiatives.
2) Empowering employees can foster a sense of ownership and accountability.
3) Encouraging employee involvement in decision-making can lead to diverse perspectives and better problem-solving.
Managing transitions
Managing transitions refers to the challenge of effectively leading and supporting employees through organisational changes such as mergers, acquisitions, restructuring, or technological advancements. It involves minimising resistance to change, facilitating communication, and providing support during periods of uncertainty. By managing transitions effectively, organisations can minimise disruptions, maintain employee morale, and facilitate successful change implementation.
1) Developing change management strategies and plans can provide a structured approach to navigate transitions.
2) Communicating openly and transparently about changes can help alleviate employee concerns and build trust.
3) Offering training and support to employees can facilitate their adaptation to new roles and responsibilities.
Fostering creativity and evolution
Fostering creativity and evolution involves creating an environment that encourages innovation, experimentation, and continuous improvement. It requires promoting a culture of creativity, providing resources for exploration, and rewarding innovative thinking. By fostering creativity and evolution, organisations can stay ahead of the competition, drive innovation, and adapt to changing market dynamics.
1) Encouraging brainstorming sessions and idea-sharing platforms can stimulate creativity and innovation.
2) Allocating resources for research and development can support the exploration of new ideas and technologies.
3) Recognising and rewarding innovative efforts can motivate employees to think outside the box.
Enhancing ethical conduct
Enhancing ethical conduct involves the challenge of promoting ethical behaviour and decision-making within an organisation. It requires establishing a strong ethical framework, providing ethics training, and fostering a culture of integrity and accountability. By enhancing ethical conduct, organisations can build trust with stakeholders, maintain a positive reputation, and mitigate legal and ethical risks.
1) Developing a comprehensive code of ethics and conduct can provide clear guidelines for employees.
2) Conducting ethics training and workshops can raise awareness and promote ethical decision-making.
3) Encouraging open communication channels can empower employees to report unethical behaviour.
Elevating customer support
Elevating customer support involves the challenge of delivering exceptional customer service and building strong customer relationships. It requires understanding customer needs, providing timely and personalised assistance, and continuously improving the customer experience. By elevating customer support, organisations can enhance customer loyalty, increase customer satisfaction, and drive business growth.
1) Implementing customer relationship management (CRM) systems can help track customer interactions and preferences.
2) Training customer support teams on effective communication and problem-solving can improve customer service skills.
3) Gathering customer feedback and implementing improvements based on their suggestions can enhance the customer experience.
Globalising Dynamics
Globalising dynamics refer to the challenge of operating in a globalised business environment and adapting to international trends and market shifts. It involves staying updated on global economic, political, and technological developments, and adjusting business strategies accordingly. By understanding and responding to globalising dynamics, organisations can seize international opportunities and mitigate potential threats.
1) Conducting market research and analysis can provide insights into global trends and customer preferences.
2) Building strategic partnerships and alliances with international organisations can expand market reach.
3) Investing in technology and infrastructure to support global operations can increase competitiveness.
Adapting to E-Commerce Trends
Adapting to e-commerce trends involves the challenge of leveraging digital technologies and online platforms to meet customer demands and stay competitive in the digital marketplace. It requires developing robust e-commerce strategies, optimising online user experiences, and integrating digital channels with traditional business models. By adapting to e-commerce trends, organisations can reach a wider customer base, improve operational efficiency, and drive online sales growth.
1) Building a user-friendly and secure e-commerce website or mobile app can enhance the customer experience.
2) Implementing data analytics and artificial intelligence tools can provide insights for personalised marketing and product recommendations.
3) Embracing digital marketing strategies such as social media marketing and search engine optimisation can increase online visibility and brand awareness.
Conclusion
Organisational behaviour presents a dynamic view of challenges and opportunities for businesses. By navigating issues such as workforce diversity, globalisation impacts, and ethical conduct, organisations can unlock potential for innovation, efficiency, and customer satisfaction. Embracing these opportunities fosters growth, resilience, and success in today's ever-evolving business environment.
Gain in-depth knowledge of the objectives of governance with our Organisational Behaviour Course!
Frequently Asked Questions
Opportunity types in organisational behaviour include advancement opportunities, learning and development opportunities, leadership opportunities, and networking opportunities.
Opportunities are important because they allow individuals to grow, learn, and advance within their organisation. They foster personal and professional development, enable skill enhancement, and contribute to overall career satisfaction and success.
The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs , videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA .
The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass , a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
The Knowledge Academy offers various Organisational Behaviour including Business Analysis Course, Enterprise and Solution Architecture Course, Project Management Course and Agile Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into BCS Code of Conduct
Our Business Analysis Blogs covers a range of topics related to Scrum, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Business Improvement skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Analysis Resources Batches & Dates
Mon 16th Sep 2024
Mon 18th Nov 2024
Mon 20th Jan 2025
Mon 28th Apr 2025
Mon 30th Jun 2025
Mon 24th Nov 2025
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest summer sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- ISO 9001 Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel Courses
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
1.2 Understanding Organizational Behavior
Learning objectives.
- Learn about the layout of this book.
- Understand what organizational behavior is.
- Understand why organizational behavior matters.
- Learn about OB Toolboxes in this book.
About This Book
The people make the place.
Benjamin Schneider, Fellow of the Academy of Management
This book is all about people, especially people at work. As evidenced in the opening case, we will share many examples of people making their workplaces work. People can make work an exciting, fun, and productive place to be, or they can make it a routine, boring, and ineffective place where everyone dreads to go. Steve Jobs, cofounder, chairman, and CEO of Apple Inc. attributes the innovations at Apple, which include the iPod, MacBook, and iPhone, to people, noting, “Innovation has nothing to do with how many R&D dollars you have.…It’s not about money. It’s about the people you have, how you’re led, and how much you get it” (Kirkpatrick, 1998). This became a sore point with investors in early 2009 when Jobs took a medical leave of absence. Many wonder if Apple will be as successful without him at the helm, and Apple stock plunged upon worries about his health (Parloff, 2008).

Steve Jobs is known for developing innovative products by hiring the right people for the job and fostering a culture of hard work and creativity.
Wikimedia Commons – CC BY 3.0.
Mary Kay Ash, founder of Mary Kay Inc., a billion-dollar cosmetics company, makes a similar point, saying, “People are definitely a company’s greatest asset. It doesn’t make any difference whether the product is cars or cosmetics. A company is only as good as the people it keeps” [1]
Just like people, organizations come in many shapes and sizes. We understand that the career path you will take may include a variety of different organizations. In addition, we know that each student reading this book has a unique set of personal and work-related experiences, capabilities, and career goals. On average, a person working in the United States will change jobs 10 times in 20 years (U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, 2005). In order to succeed in this type of career situation, individuals need to be armed with the tools necessary to be lifelong learners. So, this book will not be about giving you all the answers to every situation you may encounter when you start your first job or as you continue up the career ladder. Instead, this book will give you the vocabulary, framework, and critical thinking skills necessary for you to diagnose situations, ask tough questions, evaluate the answers you receive, and act in an effective and ethical manner regardless of situational characteristics.
Throughout this book, when we refer to organizations, we will include examples that may apply to diverse organizations such as publicly held, for-profit organizations like Google and American Airlines, privately owned businesses such as S. C. Johnson & Son Inc. (makers of Windex glass cleaner) and Mars Inc. (makers of Snickers and M&Ms), and not-for-profit organizations such as the Sierra Club or Mercy Corps, and nongovernmental organizations (NGOs) such as Doctors Without Borders and the International Red Cross. We will also refer to both small and large corporations. You will see examples from Fortune 500 organizations such as Intel Corporation or Home Depot Inc., as well as small start-up organizations. Keep in mind that some of the small organizations of today may become large organizations in the future. For example, in 1998, eBay Inc. had only 29 employees and $47.4 million in income, but by 2008 they had grown to 11,000 employees and over $7 billion in revenue (Gibson, 2008). Regardless of the size or type of organization you may work for, people are the common denominator of how work is accomplished within organizations.
Together, we will examine people at work both as individuals and within work groups and how they impact and are impacted by the organizations where they work. Before we can understand these three levels of organizational behavior, we need to agree on a definition of organizational behavior.

What Is Organizational Behavior?
Organizational behavior (OB) is defined as the systematic study and application of knowledge about how individuals and groups act within the organizations where they work. As you will see throughout this book, definitions are important. They are important because they tell us what something is as well as what it is not. For example, we will not be addressing childhood development in this course—that concept is often covered in psychology—but we might draw on research about twins raised apart to understand whether job attitudes are affected by genetics.
OB draws from other disciplines to create a unique field. As you read this book, you will most likely recognize OB’s roots in other disciplines. For example, when we review topics such as personality and motivation, we will again review studies from the field of psychology. The topic of team processes relies heavily on the field of sociology. In the chapter relating to decision making, you will come across the influence of economics. When we study power and influence in organizations, we borrow heavily from political sciences. Even medical science contributes to the field of organizational behavior, particularly to the study of stress and its effects on individuals.
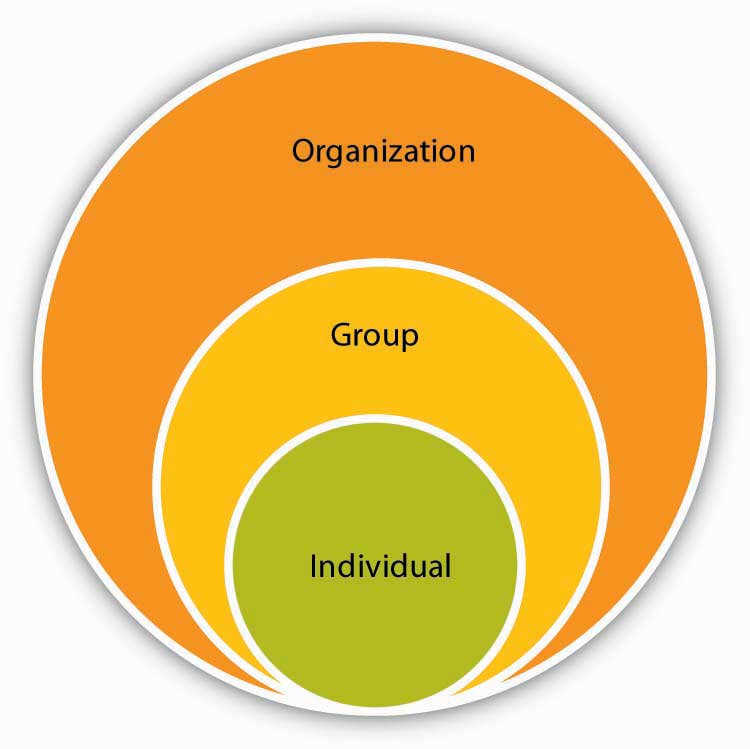
OB spans topics related from the individual to the organization.
Those who study organizational behavior—which now includes you—are interested in several outcomes such as work attitudes (e.g., job satisfaction and organizational commitment) as well as job performance (e.g., customer service and counterproductive work behaviors). A distinction is made in OB regarding which level of the organization is being studied at any given time. There are three key levels of analysis in OB. They are examining the individual, the group, and the organization. For example, if I want to understand my boss’s personality, I would be examining the individual level of analysis. If we want to know about how my manager’s personality affects my team, I am examining things at the team level. But, if I want to understand how my organization’s culture affects my boss’s behavior, I would be interested in the organizational level of analysis.
Why Organizational Behavior Matters
OB matters at three critical levels. It matters because it is all about things you care about. OB can help you become a more engaged organizational member. Getting along with others, getting a great job, lowering your stress level, making more effective decisions, and working effectively within a team…these are all great things, and OB addresses them!
It matters because employers care about OB. A recent survey by the National Association of Colleges and Employers (NACE) asked employers which skills are the most important for them when evaluating job candidates, and OB topics topped the list (NACE 2007 Job Outlook Survey, 2008).
The following were the top five personal qualities/skills:
- Communication skills (verbal and written)
- Honesty/integrity
- Interpersonal skills (relates well to others)
- Motivation/initiative
- Strong work ethic
These are all things we will cover in OB.
Finally, it matters because organizations care about OB. The best companies in the world understand that the people make the place. How do we know this? Well, we know that organizations that value their employees are more profitable than those that do not (Huselid, 1995; Pfeffer, 1998; Pfeffer & Veiga, 1999; Welbourne & Andrews, 1996). Research shows that successful organizations have a number of things in common, such as providing employment security, engaging in selective hiring, utilizing self-managed teams, being decentralized, paying well, training employees, reducing status differences, and sharing information (Pfeffer & Veiga, 1999). For example, every Whole Foods store has an open compensation policy in which salaries (including bonuses) are listed for all employees. There is also a salary cap that limits the maximum cash compensation paid to anyone in the organization, such as a CEO, in a given year to 19 times the companywide annual average salary of all full-time employees. What this means is that if the average employee makes $30,000 per year, the highest potential pay for their CEO would be $570,000, which is a lot of money but pales in comparison to salaries such as Steve Jobs of Apple at $14.6 million or the highest paid CEO in 2007, Larry Ellison of Oracle, at $192.9 million (Elmer-DeWitt, 2008). Research shows that organizations that are considered healthier and more effective have strong OB characteristics throughout them such as role clarity, information sharing, and performance feedback. Unfortunately, research shows that most organizations are unhealthy, with 50% of respondents saying that their organizations do not engage in effective OB practices (Aguirre et al., 2005).
In the rest of this chapter, we will build on how you can use this book by adding tools to your OB Toolbox in each section of the book as well as assessing your own learning style. In addition, it is important to understand the research methods used to define OB, so we will also review those. Finally, you will see what challenges and opportunities businesses are facing and how OB can help overcome these challenges.
Adding to Your OB Toolbox
Your ob toolbox.
OB Toolboxes appear throughout this book. They indicate a tool that you can try out today to help you develop your OB skills.
Throughout the book, you will see many OB Toolbox features. Our goal in writing this book is to create something useful for you to use now and as you progress through your career. Sometimes we will focus on tools you can use today. Other times we will focus on things you may want to think about that may help you later. As you progress, you may discover some OB tools that are particularly relevant to you while others are not as appropriate at the moment. That’s great—keep those that have value to you. You can always go back and pick up tools later on if they don’t seem applicable right now.
The important thing to keep in mind is that the more tools and skills you have, the higher the quality of your interactions with others will be and the more valuable you will become to organizations that compete for top talent (Michaels, Handfield-Jones, & Axelrod, 2001). It is not surprising that, on average, the greater the level of education you have, the more money you will make. In 2006, those who had a college degree made 62% more money than those who had a high school degree (U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics). Organizations value and pay for skills as the next figure shows.
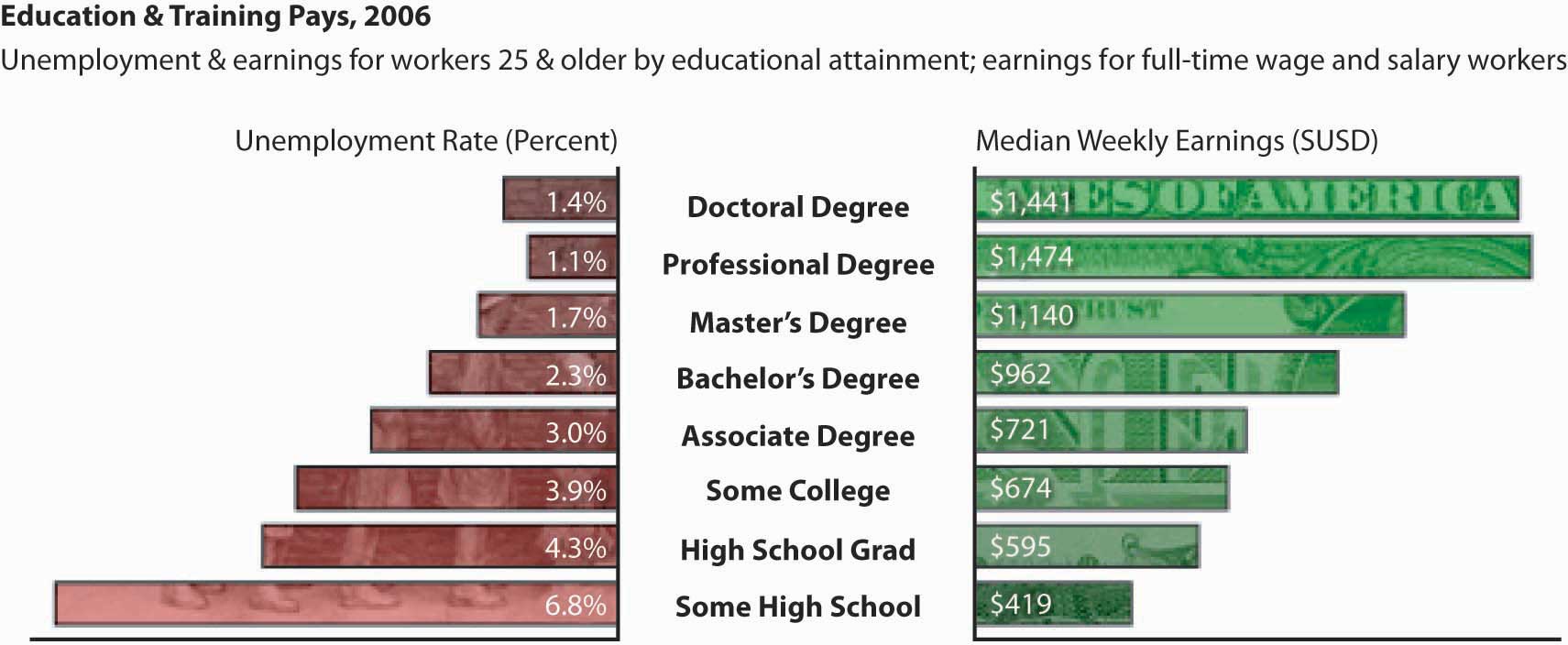
Education and training have financial payoffs as illustrated by these unemployment and earnings for workers 25 and older.
Source: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, http://www.bls.gov .
Tom Peters is a management expert who talks about the concept of individuals thinking of themselves as a brand to be managed. Further, he recommends that individuals manage themselves like free agents (Peters, 1997; Peters, 2004). The following OB Toolbox includes several ideas for being effective in keeping up your skill set.
Your OB Toolbox: Skill Survival Kit
- Keep your skills fresh . Consider revolutionizing your portfolio of skills at least every 6 years.
- Master something . Competence in many skills is important, but excelling at something will set you apart.
- Embrace ambiguity . Many people fear the unknown. They like things to be predictable. Unfortunately, the only certainty in life is that things will change. Instead of running from this truth, embrace the situation as a great opportunity.
- Network . The term has been overused to the point of sounding like a cliché, but networking works. This doesn’t mean that having 200 connections on MySpace, LinkedIn, or Facebook makes you more effective than someone who has 50, but it does mean that getting to know people is a good thing in ways you can’t even imagine now.
- Appreciate new technology . This doesn’t mean you should get and use every new gadget that comes out on the market, but it does mean you need to keep up on what the new technologies are and how they may affect you and the business you are in.
Source: Adapted from ideas in Peters, T. (2007). Brand you survival kit. Fast Company . Retrieved July 1, 2008, from http://www.fastcompany.com/magazine/83/playbook.html .
A key step in building your OB skills and filling your toolbox is to learn the language of OB. Once you understand a concept, you are better able to recognize it. Once you recognize these concepts in real-world events and understand that you have choices in how you will react, you can better manage yourself and others. An effective tool you can start today is journaling , which helps you chart your progress as you learn new skills. For more on this, see the OB Toolbox below.
OB Toolbox: Journaling as a Developmental Tool
- What exactly is journaling ? Journaling refers to the process of writing out thoughts and emotions on a regular basis.
- Why is journaling a good idea ? Journaling is an effective way to record how you are feeling from day to day. It can be a more objective way to view trends in your thoughts and emotions so you are not simply relying on your memory of past events, which can be inaccurate. Simply getting your thoughts and ideas down has been shown to have health benefits as well such as lowering the writer’s blood pressure, heart rate, and decreasing stress levels.
- How do I get started ? The first step is to get a journal or create a computer file where you can add new entries on a regular basis. Set a goal for how many minutes per day you want to write and stick to it. Experts say at least 10 minutes a day is needed to see benefits, with 20 minutes being ideal. The quality of what you write is also important. Write your thoughts down clearly and specifically while also conveying your emotions in your writing. After you have been writing for at least a week, go back and examine what you have written. Do you see patterns in your interactions with others? Do you see things you like and things you’d like to change about yourself? If so, great! These are the things you can work on and reflect on. Over time, you will also be able to track changes in yourself, which can be motivating as well.
Sources: Created based on ideas and information in Bromley, K. (1993). Journaling: Engagements in reading, writing, and thinking . New York: Scholastic; Caruso, D., & Salovey, P. (2004). The emotionally intelligent manager: How to develop and use the four key emotional skills of leadership . San Francisco: Jossey-Bass; Scott, E. (2008). The benefits of journaling for stress management. Retrieved January 27, 2008, from About.com: http://stress.about.com/od/generaltechniques/p/profilejournal.htm .
Isn’t OB Just Common Sense?
As teachers we have heard this question many times. The answer, as you might have guessed, is no—OB is not just common sense . As we noted earlier, OB is the systematic study and application of knowledge about how individuals and groups act within the organizations where they work. Systematic is an important word in this definition. It is easy to think we understand something if it makes sense, but research on decision making shows that this can easily lead to faulty conclusions because our memories fail us. We tend to notice certain things and ignore others, and the specific manner in which information is framed can affect the choices we make. Therefore, it is important to rule out alternative explanations one by one rather than to assume we know about human behavior just because we are humans! Go ahead and take the following quiz and see how many of the 10 questions you get right. If you miss a few, you will see that OB isn’t just common sense. If you get them all right, you are way ahead of the game!
Putting Common Sense to the Test
Please answer the following 10 questions by noting whether you believe the sentence is true or false .
- Brainstorming in a group is more effective than brainstorming alone. _____
- The first 5 minutes of a negotiation are just a warm-up to the actual negotiation and don’t matter much. _____
- The best way to help someone reach their goals is to tell them to do their best. _____
- If you pay someone to do a task they routinely enjoy, they’ll do it even more often in the future. _____
- Pay is a major determinant of how hard someone will work. _____
- If a person fails the first time, they try harder the next time. _____
- People perform better if goals are easier. _____
- Most people within organizations make effective decisions. _____
- Positive people are more likely to withdraw from their jobs when they are dissatisfied. _____
- Teams with one smart person outperform teams in which everyone is average in intelligence. ______
You may check your answers with your instructor.
Key Takeaway
This book is about people at work. Organizations come in many shapes and sizes. Organizational behavior is the systematic study and application of knowledge about how individuals and groups act within the organizations where they work. OB matters for your career, and successful companies tend to employ effective OB practices. The OB Toolboxes throughout this book are useful in increasing your OB skills now and in the future.
- Which type of organizations did you have the most experience with? How did that affect your understanding of the issues in this chapter?
- Which skills do you think are the most important ones for being an effective employee?
- What are the three key levels of analysis for OB?
- Have you ever used journaling before? If so, were your experiences positive? Do you think you will use journaling as a tool in the future?
- How do you plan on using the OB Toolboxes in this book? Creating a plan now can help to make you more effective throughout the term.
Aguirre, D. M., Howell, L. W., Kletter, D. B., & Neilson, G. L. (2005). A global check-up: Diagnosing the health of today’s organizations (online report). Retrieved July 25, 2008, from the Booz & Company Web site: http://www.orgdna.com/downloads/GlobalCheckUp-OrgHealthNov2005.pdf .
Elmer-DeWitt, P. (2008, May 2). Top-paid CEOs: Steve Jobs drops from no. 1 to no. 120. Fortune . Retrieved July 26, 2008, from CNNMoney.com: http://apple20.blogs.fortune.cnn.com/2008/05/02/top-paid-ceos- steve-jobs-drops-from-no-1-to-no-120/ .
Gibson, E. (2008, March). Meg Whitman’s 10th anniversary as CEO of eBay. Fast Company , 25.
Huselid, M. A. (1995). The impact of human resource management practices on turnover, productivity, and corporate financial performance. Academy of Management Journal , 38 , 635-672.
Kirkpatrick, D. (1998). The second coming of Apple. Fortune , 138 , 90.
Michaels, E., Handfield-Jones, H., & Axelrod, B. (2001). The war for talent . Boston: Harvard Business School Publishing.
NACE 2007 Job Outlook Survey. Retrieved July 26, 2008, from the National Association of Colleges and Employers (NACE) Web site: http://www.naceweb.org/press/quick.htm#qualities .
Parloff, R. (2008, January 22). Why the SEC is probing Steve Jobs. Money . Retrieved January 28, 2009, from http://money.cnn.com/2009/01/22/technology/stevejobs_disclosure.fortune/?postversion=2009012216 .
Peters, T. (1997). The brand called you. Fast Company . Retrieved July 1, 2008, from http://www.fastcompany.com/magazine/10/brandyou.html .
Peters, T. (2004). Brand you survival kit. Fast Company . Retrieved July 1, 2008, from http://www.fastcompany.com/magazine/83/playbook.html .
Pfeffer, J. (1998). The human equation: Building profits by putting people first . Boston: Harvard Business School Press.
Pfeffer, J., & Veiga, J. F. (1999). Putting people first for organizational success. Academy of Management Executive , 13 , 37–48.
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. (2005). Retrieved December 8, 2005, from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics Web site: http://www.bls.gov/nls/nlsfaqs.htm#anch5 .
Welbourne, T., & Andrews, A. (1996). Predicting performance of Initial Public Offering firms: Should HRM be in the equation? Academy of Management Journal , 39 , 910–911.
- Retrieved June 4, 2008, from http://www.litera.co.uk/t/NDk1MDA/ . ↵
Organizational Behavior Copyright © 2017 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Organization Behaviour: Challenges and Opportunities

Business in today’s world is a hectic and dynamic undertaking. The environment in which organizations operate is ever changing, thereby changing the needs of the organization and internal operations. The concept of organization behaviour is important as it provides insights into organizations’ challenges and opportunities. Although organization behaviour varies from one organization to another, its usefulness is universal. By studying these behaviours organizations become more aware of their business ethics and are able to positively find ways to transfer their employee's attitudes and behaviours into more positive experiences personally and for the company. Most organizations realize that being ethical is good business practice and pays in the long run.
Related Papers
IOSR Journals publish within 3 days
Organizational climate is a meaningful construct with significant implications for understanding human behavior in organizations. Each organization has an organizational climate that clearly distinguishes it from other organizations. This was a descriptive study to examine the effect of organizational climate on organizational performance in Kenya Commercial Bank. A sample of 61 employees was used. Questionnaires were used to collect data. Descriptive statistics and regression analysis were used to analyze data with the help of SPSS. The study found that there was a good organizational climate at KCB indicated by enthusiasm, excitement and happiness of employees. Regression analysis showed that organizational climate is statistically significant (t=5.477, p<0.05). It was concluded that concluded that the quality of environment in workplace may simply determine the level of employee's motivation, productivity and performance in the organization. The study recommends that the bank provide a good working environment for employees so as to enhance their efficiency and productivity. The bank management must also show a high level of commitment to employee objectives, while the employees will also show a high level of commitment to the organization.
The essence of this study effort is to investigate what consequence change has on organizations and how best these consequences can be addressed to ensure that employees' productivity is enhanced. It thus covers major banks and their branches in Rivers State and a randomized population sample of 152 respondents which comprise employees and management staff of these banks were drawn using Taro Yamen sampling formula. The findings derived from the results presented in the analysis of the data indicates that all tested dimensions of organizational change management (Change Communication, Change Identification, Employees' Engagement, Change Implementation and incentives) are significantly associated with the measures of Employees Productivity. It is specifically recommended that Change Communication should be systematic, change implementation should be initiated from the top management and down to the employees in a clear and consistent manner, incentives should be based on organizational contractual policies. Necessary recommendation was also made on getting the employees who will drive the change process to be engaged in the implementation processes in order to achieve employee's productivity.
patson banda
This study was conducted in the City of Lusaka in Zambia at eight public hospitals using a quantitative research design with a post-positivism perspective that employed self-administered closed ended questionnaires for data collecting. The study aims at examining the effect of public sector corporate entrepreneurship dimensions on the performance of the public health sub-sector using the following dimensions that affect organisational performance (1) pro-activeness (2) risk-taking and (3) innovations. In addition, many internal organisational factors moderate the relationship between public sector corporate entrepreneurship dimensions and organisational performance. This study examines three factors: (1) resource availability, (2) supportive organisational structure, (3) rewards/resource reinforcement. Both descriptive and inferential statistics were used to test these relationships. The findings of this study reveal that the dimensions of corporate entrepreneurship-innovation, pro-...
IOSR Journals
Organizations face a highly competitive and continuously evolving business environment.As a result, many companies have been looking for ways to improve their business: that is, providing better services at lower cost, improving customer satisfaction, and staying competitive, in which the successful management of change is crucial to survive and succeed. While organisations often deliberately try to plan change to make it more manageable, organizational realities tend to be more messy and noisy than can be effectively planned for. The findings arising from this essay suggest that middle managers play an important role in facilitating change in organizations. They also suggest that middle managers face major challenges in the organization-wide implementation and adoption of CI including possible resistance by middle management itself.There has, is and probably always will be discourse around middle management and its role in organizational change, where the debate generally evolves around whether middle management can be seen as a strategic asset for change or a blockage to change.
Abstract: Total Quality Management (TQM) is a management philosophy which focuses on customer satisfaction by improving the organisation performance through co-ordination of various processes in all the business units. The purpose of TQM is to provide quality product or service to the customer which inturn provides increased productivity at low cost. TQM is applicable to all manufacturing and service industries. It operates on the principle that cost of prevention is less than the cost of correction. This study focuses on TQM development, performance and sustenance in service industries through effective communication, critical success factors and market orientation. It examines the quality improvement through effective employee communication and the relationship between CSFs and company performance. The study suggests Deming’s Plan-Do-Study-Act (PDSA) cycle based approach to develop and sustain TQM. It articulates the relationship between TQM and market orientation, in terms of both elements (practices) and performance. The study investigates the reasons for TQM failures and proposes guidelines for successful implementation of TQM. Keywords: Critical Success Factors (CSFs), Effective Communication, Market Based Quality, PDSA, TQM Failures, and TQM Implementation
Paul Katuse
Strategic leadership, is an ability by the leader to anticipate, prepare and position for the future; It has also been observed to be the leaders ability to anticipate, create a vision, empower others and exercise flexibility, to create a strategic and viable future of the organization. Leaders who are strategic leaders formulate the goals and strategies for the organization. They do this by developing structures and processes that impact the present and future performance of the organization. They are experienced, senior leaders that are knowledgeable and have the ability to create a vision and execute plans and make significant decisions in the dynamic environment. This study sought to examine the influence of strategic leadership style on academic performance of National Schools in Kenya. The study recommended that the national schools should emphasize the role of strategy leadership styles with view of improving on the academic performance of their schools. However strategy lead...
This research work explores the IT firms' employees' motivation and employees' engagement towards their performance. The study reflects on their attributes and chalked out strategies that generate their performance in the IT industry in Malaysia. They have highlighted the factors that are associated for a firm to be productive in employee performance. This respondents' behavioral research has acquired a definite direction to the IT sector in Malaysia. Thus, the research certainly enlightens the enrichment of materializing the strategy for their productive performance activities in the IT industry for its success over here. To venture this research work in Malaysia, Selangor state has been chosen where a total of one hundred and ninety-eight respondents from the various IT firms have participated to answer the questionnaires which were self-administered and constructed on a basis of five-point Likert Scale. A convenience sampling tool has been used to find out the level of respondents' thoughts and opinions about employees' motivation and their engagement towards their performance in the firms. From this research results with the aid of Pearson Correlation tests, it is found that all the relationships of employee motivation and engagement are found to be positive and significant with the employee performance as all the p-values obtained significance at the 0.01 level for 2-tailed. The results suggest that the respondents pay much importance on the mentioned variables in their practical work place reflecting their performance for a sustainable growth in the firms. At last the multiple regression analysis suggests that all the variables such as employee motivation and employee engagement with the employee performance are significant under the same working environment. Therefore, the descriptive type of research, the findings, and the most enriched recommendations have depicted a vivid scenario about the feasible and significant performance IT sector in the territory of Malaysia.
The business world is now recognizing the significance of ethics and values. The mission, vision and purpose of the organizations are based on the values that have lasted through decades and through highs and lows of business. In the era of global competition, organizations need to adopt ethical standards for organizational excellence and sustenance. Therefore it is found highly desirable, imperative, important and necessary to conduct a study on the effectiveness of organizational ethics which would be useful for the public sector for better service delivery in the state at large. The literature of the study revolves around with the magnitude of democratic ethics, emotional ethics and essence in organizational domain, organizational commitment, waves of ethical values at public sector, relevance of honesty component as a foundation of organizational ethics. The study is based on a research instrument in the nomenclature of "Assessment of Organisational Ethics in Public Department: AOE-PD" scale to arrive at responses towards estimating the findings of the study. The main source of conceptualizing the research scale is formulated with expert opinion comprising both academicians and practicing managers in the industries in Kolkata as well as across the country through primary and secondary collection methods. The study thus, is an attempt to create an enabling tool to reframe and rejuvenate the work life of employees with reinventing new avenues of ethical practices in the Commerce and Industries Department in the Government of West Bengal towards enhancement of productivity in the workplace.
Alonge Ayomide
This paper solely focuses on the fourteen principles established by Henri Fayol and its application in a startup business and further analyze its implications. Published works done previously relating to this study were reviewed extensively. This however produced vigorous on the concept of the principles, better understanding and further modifications. The importance, benefits, strengths and weaknesses of these principles were tested in order to determine how best they are suited in startup businesses. Data was drawn from startups in Lagos, Nigeria which gives this study a directional perspective. Based on literature and results gotten from the data, it was concluded that Fayol’s principles of management are as relevant to startup businesses as they are in other existing organizations. The paper, further recommends thatStartup Organizations should always maintain a sense of direction and carry the staff along by reminding them of the organizations goals and objectives, offer them a ...
This paper aims to review a number of studies on organisational culture and organisational commitment. However, only articles published from 2012-2017 were reviewed. The reviewed literatures showed different conclusions. Most of the studies confirmed that strong significant interactions exist among organisational culture and organisational commitment but in some the association is weak. Other studies showed no association among organisational culture and organisational commitment. This controversy of conclusions emanates from differences in methodology; countries conducted the study and the number of respondents and observations. Therefore, this paper contributed to the understanding the mechanisms through which organisational culture affect organisational commitment by incorporating the concept of different organisational factors. Organisations can retain committed and motivated workforce through fostering a strong culture, which can support employees' affective commitment to the organisation.
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
izidor nwokocha
Seetha Pachchhapur
vakula kumari
Mudzamir Mohamed
IOSR Journals , Sorasak Tangthong
Matthias E Elom
Emem Joseph
IOSR Journal of Business and Management
johny tarore
Susan Wamitu
Sreeramana Aithal
Dr. Kainat Akhtar Usmani
Dr. Akankssha Nigam
Masese Omete Fred
Shweta Lalwani
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- Tools and Resources
- Customer Services
- Affective Science
- Biological Foundations of Psychology
- Clinical Psychology: Disorders and Therapies
- Cognitive Psychology/Neuroscience
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational/School Psychology
- Forensic Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems of Psychology
- Individual Differences
- Methods and Approaches in Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational and Institutional Psychology
Personality
- Psychology and Other Disciplines
- Social Psychology
- Sports Psychology
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Article contents
Organizational behavior.
- Neal M. Ashkanasy Neal M. Ashkanasy University of Queensland
- and Alana D. Dorris Alana D. Dorris University of Queensland
- https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780190236557.013.23
- Published online: 29 March 2017
Organizational behavior (OB) is a discipline that includes principles from psychology, sociology, and anthropology. Its focus is on understanding how people behave in organizational work environments. Broadly speaking, OB covers three main levels of analysis: micro (individuals), meso (groups), and macro (the organization). Topics at the micro level include managing the diverse workforce; effects of individual differences in attitudes; job satisfaction and engagement, including their implications for performance and management; personality, including the effects of different cultures; perception and its effects on decision-making; employee values; emotions, including emotional intelligence, emotional labor, and the effects of positive and negative affect on decision-making and creativity (including common biases and errors in decision-making); and motivation, including the effects of rewards and goal-setting and implications for management. Topics at the meso level of analysis include group decision-making; managing work teams for optimum performance (including maximizing team performance and communication); managing team conflict (including the effects of task and relationship conflict on team effectiveness); team climate and group emotional tone; power, organizational politics, and ethical decision-making; and leadership, including leadership development and leadership effectiveness. At the organizational level, topics include organizational design and its effect on organizational performance; affective events theory and the physical environment; organizational culture and climate; and organizational change.
- organizational psychology
- organizational sociology
- organizational anthropology
Introduction
Organizational behavior (OB) is the study of how people behave in organizational work environments. More specifically, Robbins, Judge, Millett, and Boyle ( 2014 , p. 8) describe it as “[a] field of study that investigates the impact that individual groups and structure have on behavior within organizations, for the purposes of applying such knowledge towards improving an organization’s effectiveness.” The OB field looks at the specific context of the work environment in terms of human attitudes, cognition, and behavior, and it embodies contributions from psychology, social psychology, sociology, and anthropology. The field is also rapidly evolving because of the demands of today’s fast-paced world, where technology has given rise to work-from-home employees, globalization, and an ageing workforce. Thus, while managers and OB researchers seek to help employees find a work-life balance, improve ethical behavior (Ardichivili, Mitchell, & Jondle, 2009 ), customer service, and people skills (see, e.g., Brady & Cronin, 2001 ), they must simultaneously deal with issues such as workforce diversity, work-life balance, and cultural differences.
The most widely accepted model of OB consists of three interrelated levels: (1) micro (the individual level), (2) meso (the group level), and (3) macro (the organizational level). The behavioral sciences that make up the OB field contribute an element to each of these levels. In particular, OB deals with the interactions that take place among the three levels and, in turn, addresses how to improve performance of the organization as a whole.
In order to study OB and apply it to the workplace, it is first necessary to understand its end goal. In particular, if the goal is organizational effectiveness, then these questions arise: What can be done to make an organization more effective? And what determines organizational effectiveness? To answer these questions, dependent variables that include attitudes and behaviors such as productivity, job satisfaction, job performance, turnover intentions, withdrawal, motivation, and workplace deviance are introduced. Moreover, each level—micro, meso, and macro—has implications for guiding managers in their efforts to create a healthier work climate to enable increased organizational performance that includes higher sales, profits, and return on investment (ROE).
The Micro (Individual) Level of Analysis
The micro or individual level of analysis has its roots in social and organizational psychology. In this article, six central topics are identified and discussed: (1) diversity; (2) attitudes and job satisfaction; (3) personality and values; (4) emotions and moods; (5) perception and individual decision-making; and (6) motivation.
An obvious but oft-forgotten element at the individual level of OB is the diverse workforce. It is easy to recognize how different each employee is in terms of personal characteristics like age, skin color, nationality, ethnicity, and gender. Other, less biological characteristics include tenure, religion, sexual orientation, and gender identity. In the Australian context, while the Commonwealth Disability Discrimination Act of 1992 helped to increase participation of people with disabilities working in organizations, discrimination and exclusion still continue to inhibit equality (Feather & Boeckmann, 2007 ). In Western societies like Australia and the United States, however, antidiscrimination legislation is now addressing issues associated with an ageing workforce.
In terms of gender, there continues to be significant discrimination against female employees. Males have traditionally had much higher participation in the workforce, with only a significant increase in the female workforce beginning in the mid-1980s. Additionally, according to Ostroff and Atwater’s ( 2003 ) study of engineering managers, female managers earn a significantly lower salary than their male counterparts, especially when they are supervising mostly other females.
Job Satisfaction and Job Engagement
Job satisfaction is an attitudinal variable that comes about when an employee evaluates all the components of her or his job, which include affective, cognitive, and behavioral aspects (Weiss, 2002 ). Increased job satisfaction is associated with increased job performance, organizational citizenship behaviors (OCBs), and reduced turnover intentions (Wilkin, 2012 ). Moreover, traditional workers nowadays are frequently replaced by contingent workers in order to reduce costs and work in a nonsystematic manner. According to Wilkin’s ( 2012 ) findings, however, contingent workers as a group are less satisfied with their jobs than permanent employees are.
Job engagement concerns the degree of involvement that an employee experiences on the job (Kahn, 1990 ). It describes the degree to which an employee identifies with their job and considers their performance in that job important; it also determines that employee’s level of participation within their workplace. Britt, Dickinson, Greene-Shortridge, and McKibbin ( 2007 ) describe the two extremes of job satisfaction and employee engagement: a feeling of responsibility and commitment to superior job performance versus a feeling of disengagement leading to the employee wanting to withdraw or disconnect from work. The first scenario is also related to organizational commitment, the level of identification an employee has with an organization and its goals. Employees with high organizational commitment, job satisfaction, and employee engagement tend to perceive that their organization values their contribution and contributes to their wellbeing.
Personality represents a person’s enduring traits. The key here is the concept of enduring . The most widely adopted model of personality is the so-called Big Five (Costa & McCrae, 1992 ): extraversion, agreeableness, conscientiousness, emotional stability, and openness. Employees high in conscientiousness tend to have higher levels of job knowledge, probably because they invest more into learning about their role. Those higher in emotional stability tend to have higher levels of job satisfaction and lower levels of stress, most likely because of their positive and opportunistic outlooks. Agreeableness, similarly, is associated with being better liked and may lead to higher employee performance and decreased levels of deviant behavior.
Although the personality traits in the Big Five have been shown to relate to organizational behavior, organizational performance, career success (Judge, Higgins, Thoresen, & Barrick, 2006 ), and other personality traits are also relevant to the field. Examples include positive self-evaluation, self-monitoring (the degree to which an individual is aware of comparisons with others), Machiavellianism (the degree to which a person is practical, maintains emotional distance, and believes the end will justify the means), narcissism (having a grandiose sense of self-importance and entitlement), risk-taking, proactive personality, and type A personality. In particular, those who like themselves and are grounded in their belief that they are capable human beings are more likely to perform better because they have fewer self-doubts that may impede goal achievements. Individuals high in Machiavellianism may need a certain environment in order to succeed, such as a job that requires negotiation skills and offers significant rewards, although their inclination to engage in political behavior can sometimes limit their potential. Employees who are high on narcissism may wreak organizational havoc by manipulating subordinates and harming the overall business because of their over-inflated perceptions of self. Higher levels of self-monitoring often lead to better performance but they may cause lower commitment to the organization. Risk-taking can be positive or negative; it may be great for someone who thrives on rapid decision-making, but it may prove stressful for someone who likes to weigh pros and cons carefully before making decisions. Type A individuals may achieve high performance but may risk doing so in a way that causes stress and conflict. Proactive personality, on the other hand, is usually associated with positive organizational performance.
Employee Values
Personal value systems are behind each employee’s attitudes and personality. Each employee enters an organization with an already established set of beliefs about what should be and what should not be. Today, researchers realize that personality and values are linked to organizations and organizational behavior. Years ago, only personality’s relation to organizations was of concern, but now managers are more interested in an employee’s flexibility to adapt to organizational change and to remain high in organizational commitment. Holland’s ( 1973 ) theory of personality-job fit describes six personality types (realistic, investigative, social, conventional, enterprising, and artistic) and theorizes that job satisfaction and turnover are determined by how well a person matches her or his personality to a job. In addition to person-job (P-J) fit, researchers have also argued for person-organization (P-O) fit, whereby employees desire to be a part of and are selected by an organization that matches their values. The Big Five would suggest, for example, that extraverted employees would desire to be in team environments; agreeable people would align well with supportive organizational cultures rather than more aggressive ones; and people high on openness would fit better in organizations that emphasize creativity and innovation (Anderson, Spataro, & Flynn, 2008 ).
Individual Differences, Affect, and Emotion
Personality predisposes people to have certain moods (feelings that tend to be less intense but longer lasting than emotions) and emotions (intense feelings directed at someone or something). In particular, personalities with extraversion and emotional stability partially determine an individual predisposition to experience emotion more or less intensely.
Affect is also related as describing the positive and negative feelings that people experience (Ashkanasy, 2003 ). Moreover, emotions, mood, and affect interrelate; a bad mood, for instance, can lead individuals to experience a negative emotion. Emotions are action-oriented while moods tend to be more cognitive. This is because emotions are caused by a specific event that might only last a few seconds, while moods are general and can last for hours or even days. One of the sources of emotions is personality. Dispositional or trait affects correlate, on the one hand, with personality and are what make an individual more likely to respond to a situation in a predictable way (Watson & Tellegen, 1985 ). Moreover, like personality, affective traits have proven to be stable over time and across settings (Diener, Larsen, Levine, & Emmons, 1985 ; Watson, 1988 ; Watson & Tellegen, 1985 ; Watson & Walker, 1996 ). State affect, on the other hand, is similar to mood and represents how an individual feels in the moment.
The Role of Affect in Organizational Behavior
For many years, affect and emotions were ignored in the field of OB despite being fundamental factors underlying employee behavior (Ashforth & Humphrey, 1995 ). OB researchers traditionally focused on solely decreasing the effects of strong negative emotions that were seen to impede individual, group, and organizational level productivity. More recent theories of OB focus, however, on affect, which is seen to have positive, as well as negative, effects on behavior, described by Barsade, Brief, and Spataro ( 2003 , p. 3) as the “affective revolution.” In particular, scholars now understand that emotions can be measured objectively and be observed through nonverbal displays such as facial expression and gestures, verbal displays, fMRI, and hormone levels (Ashkanasy, 2003 ; Rashotte, 2002 ).
Fritz, Sonnentag, Spector, and McInroe ( 2010 ) focus on the importance of stress recovery in affective experiences. In fact, an individual employee’s affective state is critical to OB, and today more attention is being focused on discrete affective states. Emotions like fear and sadness may be related to counterproductive work behaviors (Judge et al., 2006 ). Stress recovery is another factor that is essential for more positive moods leading to positive organizational outcomes. In a study, Fritz et al. ( 2010 ) looked at levels of psychological detachment of employees on weekends away from the workplace and how it was associated with higher wellbeing and affect.
Emotional Intelligence and Emotional Labor
Ashkanasy and Daus ( 2002 ) suggest that emotional intelligence is distinct but positively related to other types of intelligence like IQ. It is defined by Mayer and Salovey ( 1997 ) as the ability to perceive, assimilate, understand, and manage emotion in the self and others. As such, it is an individual difference and develops over a lifetime, but it can be improved with training. Boyatzis and McKee ( 2005 ) describe emotional intelligence further as a form of adaptive resilience, insofar as employees high in emotional intelligence tend to engage in positive coping mechanisms and take a generally positive outlook toward challenging work situations.
Emotional labor occurs when an employee expresses her or his emotions in a way that is consistent with an organization’s display rules, and usually means that the employee engages in either surface or deep acting (Hochschild, 1983 ). This is because the emotions an employee is expressing as part of their role at work may be different from the emotions they are actually feeling (Ozcelik, 2013 ). Emotional labor has implications for an employee’s mental and physical health and wellbeing. Moreover, because of the discrepancy between felt emotions (how an employee actually feels) and displayed emotions or surface acting (what the organization requires the employee to emotionally display), surface acting has been linked to negative organizational outcomes such as heightened emotional exhaustion and reduced commitment (Erickson & Wharton, 1997 ; Brotheridge & Grandey, 2002 ; Grandey, 2003 ; Groth, Hennig-Thurau, & Walsh, 2009 ).
Affect and Organizational Decision-Making
Ashkanasy and Ashton-James ( 2008 ) make the case that the moods and emotions managers experience in response to positive or negative workplace situations affect outcomes and behavior not only at the individual level, but also in terms of strategic decision-making processes at the organizational level. These authors focus on affective events theory (Weiss & Cropanzano, 1996 ), which holds that organizational events trigger affective responses in organizational members, which in turn affect organizational attitudes, cognition, and behavior.
Perceptions and Behavior
Like personality, emotions, moods, and attitudes, perceptions also influence employees’ behaviors in the workplace. Perception is the way in which people organize and interpret sensory cues in order to give meaning to their surroundings. It can be influenced by time, work setting, social setting, other contextual factors such as time of day, time of year, temperature, a target’s clothing or appearance, as well as personal trait dispositions, attitudes, and value systems. In fact, a person’s behavior is based on her or his perception of reality—not necessarily the same as actual reality. Perception greatly influences individual decision-making because individuals base their behaviors on their perceptions of reality. In this regard, attribution theory (Martinko, 1995 ) outlines how individuals judge others and is our attempt to conclude whether a person’s behavior is internally or externally caused.
Decision-Making and the Role of Perception
Decision-making occurs as a reaction to a problem when the individual perceives there to be discrepancy between the current state of affairs and the state s/he desires. As such, decisions are the choices individuals make from a set of alternative courses of action. Each individual interprets information in her or his own way and decides which information is relevant to weigh pros and cons of each decision and its alternatives to come to her or his perception of the best outcome. In other words, each of our unique perceptual processes influences the final outcome (Janis & Mann, 1977 ).
Common Biases in Decision-Making
Although there is no perfect model for approaching decision-making, there are nonetheless many biases that individuals can make themselves aware of in order to maximize their outcomes. First, overconfidence bias is an inclination to overestimate the correctness of a decision. Those most likely to commit this error tend to be people with weak intellectual and interpersonal abilities. Anchoring bias occurs when individuals focus on the first information they receive, failing to adjust for information received subsequently. Marketers tend to use anchors in order to make impressions on clients quickly and project their brand names. Confirmation bias occurs when individuals only use facts that support their decisions while discounting all contrary views. Lastly, availability bias occurs when individuals base their judgments on information readily available. For example, a manager might rate an employee on a performance appraisal based on behavior in the past few days, rather than the past six months or year.
Errors in Decision-Making
Other errors in decision-making include hindsight bias and escalation of commitment . Hindsight bias is a tendency to believe, incorrectly, after an outcome of an event has already happened, that the decision-maker would have accurately predicted that same outcome. Furthermore, this bias, despite its prevalence, is especially insidious because it inhibits the ability to learn from the past and take responsibility for mistakes. Escalation of commitment is an inclination to continue with a chosen course of action instead of listening to negative feedback regarding that choice. When individuals feel responsible for their actions and those consequences, they escalate commitment probably because they have invested so much into making that particular decision. One solution to escalating commitment is to seek a source of clear, less distorted feedback (Staw, 1981 ).
The last but certainly not least important individual level topic is motivation. Like each of the topics discussed so far, a worker’s motivation is also influenced by individual differences and situational context. Motivation can be defined as the processes that explain a person’s intensity, direction, and persistence toward reaching a goal. Work motivation has often been viewed as the set of energetic forces that determine the form, direction, intensity, and duration of behavior (Latham & Pinder, 2005 ). Motivation can be further described as the persistence toward a goal. In fact many non-academics would probably describe it as the extent to which a person wants and tries to do well at a particular task (Mitchell, 1982 ).
Early theories of motivation began with Maslow’s ( 1943 ) hierarchy of needs theory, which holds that each person has five needs in hierarchical order: physiological, safety, social, esteem, and self-actualization. These constitute the “lower-order” needs, while social and esteem needs are “higher-order” needs. Self-esteem for instance underlies motivation from the time of childhood. Another early theory is McGregor’s ( 1960 ) X-Y theory of motivation: Theory X is the concept whereby individuals must be pushed to work; and theory Y is positive, embodying the assumption that employees naturally like work and responsibility and can exercise self-direction.
Herzberg subsequently proposed the “two-factor theory” that attitude toward work can determine whether an employee succeeds or fails. Herzberg ( 1966 ) relates intrinsic factors, like advancement in a job, recognition, praise, and responsibility to increased job satisfaction, while extrinsic factors like the organizational climate, relationship with supervisor, and salary relate to job dissatisfaction. In other words, the hygiene factors are associated with the work context while the motivators are associated with the intrinsic factors associated with job motivation.
Contemporary Theories of Motivation
Although traditional theories of motivation still appear in OB textbooks, there is unfortunately little empirical data to support their validity. More contemporary theories of motivation, with more acceptable research validity, include self-determination theory , which holds that people prefer to have control over their actions. If a task an individual enjoyed now feels like a chore, then this will undermine motivation. Higher self-determined motivation (or intrinsically determined motivation) is correlated with increased wellbeing, job satisfaction, commitment, and decreased burnout and turnover intent. In this regard, Fernet, Gagne, and Austin ( 2010 ) found that work motivation relates to reactions to interpersonal relationships at work and organizational burnout. Thus, by supporting work self-determination, managers can help facilitate adaptive employee organizational behaviors while decreasing turnover intention (Richer, Blanchard, & Vallerand, 2002 ).
Core self-evaluation (CSE) theory is a relatively new concept that relates to self-confidence in general, such that people with higher CSE tend to be more committed to goals (Bono & Colbert, 2005 ). These core self-evaluations also extend to interpersonal relationships, as well as employee creativity. Employees with higher CSE are more likely to trust coworkers, which may also contribute to increased motivation for goal attainment (Johnson, Kristof-Brown, van Vianen, de Pater, & Klein, 2003 ). In general, employees with positive CSE tend to be more intrinsically motivated, thus additionally playing a role in increasing employee creativity (Judge, Bono, Erez, & Locke, 2005 ). Finally, according to research by Amabile ( 1996 ), intrinsic motivation or self-determined goal attainment is critical in facilitating employee creativity.
Goal-Setting and Conservation of Resources
While self-determination theory and CSE focus on the reward system behind motivation and employee work behaviors, Locke and Latham’s ( 1990 ) goal-setting theory specifically addresses the impact that goal specificity, challenge, and feedback has on motivation and performance. These authors posit that our performance is increased when specific and difficult goals are set, rather than ambiguous and general goals. Goal-setting seems to be an important motivational tool, but it is important that the employee has had a chance to take part in the goal-setting process so they are more likely to attain their goals and perform highly.
Related to goal-setting is Hobfoll’s ( 1989 ) conservation of resources (COR) theory, which holds that people have a basic motivation to obtain, maintain, and protect what they value (i.e., their resources). Additionally there is a global application of goal-setting theory for each of the motivation theories. Not enough research has been conducted regarding the value of goal-setting in global contexts, however, and because of this, goal-setting is not recommended without consideration of cultural and work-related differences (Konopaske & Ivancevich, 2004 ).
Self-Efficacy and Motivation
Other motivational theories include self-efficacy theory, and reinforcement, equity, and expectancy theories. Self-efficacy or social cognitive or learning theory is an individual’s belief that s/he can perform a task (Bandura, 1977 ). This theory complements goal-setting theory in that self-efficacy is higher when a manager assigns a difficult task because employees attribute the manager’s behavior to him or her thinking that the employee is capable; the employee in turn feels more confident and capable.
Reinforcement theory (Skinner, 1938 ) counters goal-setting theory insofar as it is a behaviorist approach rather than cognitive and is based in the notion that reinforcement conditions behavior, or in other words focuses on external causes rather than the value an individual attributes to goals. Furthermore, this theory instead emphasizes the behavior itself rather than what precedes the behavior. Additionally, managers may use operant conditioning, a part of behaviorism, to reinforce people to act in a desired way.
Social-learning theory (Bandura, 1977 ) extends operant conditioning and also acknowledges the influence of observational learning and perception, and the fact that people can learn and retain information by paying attention, observing, and modeling the desired behavior.
Equity theory (Adams, 1963 ) looks at how employees compare themselves to others and how that affects their motivation and in turn their organizational behaviors. Employees who perceive inequity for instance, will either change how much effort they are putting in (their inputs), change or distort their perceptions (either of self or others in relation to work), change their outcomes, turnover, or choose a different referent (acknowledge performance in relation to another employee but find someone else they can be better than).
Last but not least, Vroom’s ( 1964 ) expectancy theory holds that individuals are motivated by the extent to which they can see that their effort is likely to result in valued outcomes. This theory has received strong support in empirical research (see Van Erde & Thierry, 1996 , for meta-analytic results). Like each of the preceding theories, expectancy theory has important implications that managers should consider. For instance, managers should communicate with employees to determine their preferences to know what rewards to offer subordinates to elicit motivation. Managers can also make sure to identify and communicate clearly the level of performance they desire from an employee, as well as to establish attainable goals with the employee and to be very clear and precise about how and when performance will be rewarded (Konopaske & Ivancevich, 2004 ).
The Meso (Group) Level of Analysis
The second level of OB research also emerges from social and organizational psychology and relates to groups or teams. Topics covered so far include individual differences: diversity, personality and emotions, values and attitudes, motivation, and decision-making. Thus, in this section, attention turns to how individuals come together to form groups and teams, and begins laying the foundation for understanding the dynamics of group and team behavior. Topics at this level also include communication, leadership, power and politics, and conflict.
A group consists of two or more individuals who come together to achieve a similar goal. Groups can be formal or informal. A formal group on the one hand is assigned by the organization’s management and is a component of the organization’s structure. An informal group on the other hand is not determined by the organization and often forms in response to a need for social contact. Teams are formal groups that come together to meet a specific group goal.
Although groups are thought to go through five stages of development (Tuckman, 1965 : forming, storming, norming, performing, and adjourning) and to transition to effectiveness at the halfway mark (Gersick, 1988 ), group effectiveness is in fact far more complex. For example, two types of conformity to group norms are possible: compliance (just going along with the group’s norms but not accepting them) and personal acceptance (when group members’ individual beliefs match group norms). Behavior in groups then falls into required behavior usually defined by the formal group and emergent behavior that grows out of interactions among group members (Champoux, 2011 ).
Group Decision-Making
Although many of the decisions made in organizations occur in groups and teams, such decisions are not necessarily optimal. Groups may have more complex knowledge and increased perspectives than individuals but may suffer from conformity pressures or domination by one or two members. Group decision-making has the potential to be affected by groupthink or group shift. In groupthink , group pressures to conform to the group norms deter the group from thinking of alternative courses of action (Janis & Mann, 1977 ). In the past, researchers attempted to explain the effects of group discussion on decision-making through the following approaches: group decision rules, interpersonal comparisons, and informational influence. Myers and Lamm ( 1976 ), however, present a conceptual schema comprised of interpersonal comparisons and informational influence approaches that focus on attitude development in a more social context. They found that their research is consistent with the group polarization hypothesis: The initial majority predicts the consensus outcome 90% of the time. The term group polarization was founded in Serge Moscovici and his colleagues’ literature (e.g., Moscovici & Zavalloni, 1969 ). Polarization refers to an increase in the extremity of the average response of the subject population.
In other words, the Myer and Lamm ( 1976 ) schema is based on the idea that four elements feed into one another: social motivation, cognitive foundation, attitude change, and action commitment. Social motivation (comparing self with others in order to be perceived favorably) feeds into cognitive foundation , which in turn feeds into attitude change and action commitment . Managers of organizations can help reduce the negative phenomena and increase the likelihood of functional groups by encouraging brainstorming or openly looking at alternatives in the process of decision-making such as the nominal group technique (which involves restricting interpersonal communication in order to encourage free thinking and proceeding to a decision in a formal and systematic fashion such as voting).
Elements of Team Performance
OB researchers typically focus on team performance and especially the factors that make teams most effective. Researchers (e.g., see De Dreu & Van Vianen, 2001 ) have organized the critical components of effective teams into three main categories: context, composition, and process. Context refers to the team’s physical and psychological environment, and in particular the factors that enable a climate of trust. Composition refers to the means whereby the abilities of each individual member can best be most effectively marshaled. Process is maximized when members have a common goal or are able to reflect and adjust the team plan (for reflexivity, see West, 1996 ).
Communication
In order to build high-performing work teams, communication is critical, especially if team conflict is to be minimized. Communication serves four main functions: control, motivation, emotional expression, and information (Scott & Mitchell, 1976 ). The communication process involves the transfer of meaning from a sender to a receiver through formal channels established by an organization and informal channels, created spontaneously and emerging out of individual choice. Communication can flow downward from managers to subordinates, upward from subordinates to managers, or between members of the same group. Meaning can be transferred from one person to another orally, through writing, or nonverbally through facial expressions and body movement. In fact, body movement and body language may complicate verbal communication and add ambiguity to the situation as does physical distance between team members.
High-performance teams tend to have some of the following characteristics: interpersonal trust, psychological and physical safety, openness to challenges and ideas, an ability to listen to other points of view, and an ability to share knowledge readily to reduce task ambiguity (Castka, Bamber, Sharp, & Belohoubek, 2001 ). Although the development of communication competence is essential for a work team to become high-performing, that communication competence is also influenced by gender, personality, ability, and emotional intelligence of the members. Ironically, it is the self-reliant team members who are often able to develop this communication competence. Although capable of working autonomously, self-reliant team members know when to ask for support from others and act interdependently.
Emotions also play a part in communicating a message or attitude to other team members. Emotional contagion, for instance, is a fascinating effect of emotions on nonverbal communication, and it is the subconscious process of sharing another person’s emotions by mimicking that team member’s nonverbal behavior (Hatfield, Cacioppo, & Rapson, 1993 ). Importantly, positive communication, expressions, and support of team members distinguished high-performing teams from low-performing ones (Bakker & Schaufeli, 2008 ).
Team Conflict
Because of member interdependence, teams are inclined to more conflict than individual workers. In particular, diversity in individual differences leads to conflict (Thomas, 1992 ; Wall & Callister, 1995 ; see also Cohen & Bailey, 1997 ). Jehn ( 1997 ) identifies three types of conflict: task, relationship, and process. Process conflict concerns how task accomplishment should proceed and who is responsible for what; task conflict focuses on the actual content and goals of the work (Robbins et al., 2014 ); and relationship conflict is based on differences in interpersonal relationships. While conflict, and especially task conflict, does have some positive benefits such as greater innovation (Tjosvold, 1997 ), it can also lead to lowered team performance and decreased job satisfaction, or even turnover. De Dreu and Van Vianen ( 2001 ) found that team conflict can result in one of three responses: (1) collaborating with others to find an acceptable solution; (2) contending and pushing one member’s perspective on others; or (3) avoiding and ignoring the problem.
Team Effectiveness and Relationship Conflict
Team effectiveness can suffer in particular from relationship conflict, which may threaten team members’ personal identities and self-esteem (Pelled, 1995 ). In this regard, Murnighan and Conlon ( 1991 ) studied members of British string quartets and found that the most successful teams avoided relationship conflict while collaborating to resolve task conflicts. This may be because relationship conflict distracts team members from the task, reducing team performance and functioning. As noted earlier, positive affect is associated with collaboration, cooperation, and problem resolution, while negative affect tends to be associated with competitive behaviors, especially during conflict (Rhoades, Arnold, & Jay, 2001 ).
Team Climate and Emotionality
Emotional climate is now recognized as important to team processes (Ashkanasy & Härtel, 2014 ), and team climate in general has important implications for how individuals behave individually and collectively to effect organizational outcomes. This idea is consistent with Druskat and Wolff’s ( 2001 ) notion that team emotional-intelligence climate can help a team manage both types of conflict (task and relationship). In Jehn’s ( 1997 ) study, she found that emotion was most often negative during team conflict, and this had a negative effect on performance and satisfaction regardless of the type of conflict team members were experiencing. High emotionality, as Jehn calls it, causes team members to lose sight of the work task and focus instead on the negative affect. Jehn noted, however, that absence of group conflict might also may block innovative ideas and stifle creativity (Jehn, 1997 ).
Power and Politics
Power and organizational politics can trigger employee conflict, thus affecting employee wellbeing, job satisfaction, and performance, in turn affecting team and organizational productivity (Vigoda, 2000 ). Because power is a function of dependency, it can often lead to unethical behavior and thus become a source of conflict. Types of power include formal and personal power. Formal power embodies coercive, reward, and legitimate power. Coercive power depends on fear. Reward power is the opposite and occurs when an individual complies because s/he receives positive benefits from acting in accordance with the person in power. In formal groups and organizations, the most easily accessed form of power is legitimate because this form comes to be from one’s position in the organizational hierarchy (Raven, 1993 ). Power tactics represent the means by which those in a position of power translate their power base (formal or personal) into specific actions.
The nine influence tactics that managers use according to Yukl and Tracey ( 1992 ) are (1) rational persuasion, (2) inspirational appeal, (3) consultation, (4) ingratiation, (5) exchange, (6) personal appeal, (7) coalition, (8) legitimating, and (9) pressure. Of these tactics, inspirational appeal, consultation, and rational persuasion were among the strategies most effective in influencing task commitment. In this study, there was also a correlation found between a manager’s rational persuasion and a subordinate rating her effectively. Perhaps this is because persuasion requires some level of expertise, although more research is needed to verify which methods are most successful. Moreover, resource dependence theory dominates much theorizing about power and organizational politics. In fact, it is one of the central themes of Pfeffer and Salancik’s ( 1973 ) treatise on the external control of organizations. First, the theory emphasizes the importance of the organizational environment in understanding the context of how decisions of power are made (see also Pfeffer & Leblebici, 1973 ). Resource dependence theory is based on the premise that some organizations have more power than others, occasioned by specifics regarding their interdependence. Pfeffer and Salancik further propose that external interdependence and internal organizational processes are related and that this relationship is mediated by power.
Organizational Politics
Political skill is the ability to use power tactics to influence others to enhance an individual’s personal objectives. In addition, a politically skilled person is able to influence another person without being detected (one reason why he or she is effective). Persons exerting political skill leave a sense of trust and sincerity with the people they interact with. An individual possessing a high level of political skill must understand the organizational culture they are exerting influence within in order to make an impression on his or her target. While some researchers suggest political behavior is a critical way to understand behavior that occurs in organizations, others simply see it as a necessary evil of work life (Champoux, 2011 ). Political behavior focuses on using power to reach a result and can be viewed as unofficial and unsanctioned behavior (Mintzberg, 1985 ). Unlike other organizational processes, political behavior involves both power and influence (Mayes & Allen, 1977 ). Moreover, because political behavior involves the use of power to influence others, it can often result in conflict.
Organizational Politics, Power, and Ethics
In concluding this section on power and politics, it is also appropriate to address the dark side, where organizational members who are persuasive and powerful enough might become prone to abuse standards of equity and justice and thereby engage in unethical behavior. An employee who takes advantage of her position of power may use deception, lying, or intimidation to advance her own interests (Champoux, 2011 ). When exploring interpersonal injustice, it is important to consider the intent of the perpetrator, as well as the effect of the perpetrator’s treatment from the victim’s point of view. Umphress, Simmons, Folger, Ren, and Bobocel ( 2013 ) found in this regard that not only does injustice perceived by the self or coworkers influence attitudes and behavior within organizations, but injustice also influences observer reactions both inside and outside of the organization.
Leadership plays an integrative part in understanding group behavior, because the leader is engaged in directing individuals toward attitudes and behaviors, hopefully also in the direction of those group members’ goals. Although there is no set of universal leadership traits, extraversion from the Big Five personality framework has been shown in meta-analytic studies to be positively correlated with transformational, while neuroticism appears to be negatively correlated (Bono & Judge, 2004 ). There are also various perspectives to leadership, including the competency perspective, which addresses the personality traits of leaders; the behavioral perspective, which addresses leader behaviors, specifically task versus people-oriented leadership; and the contingency perspective, which is based on the idea that leadership involves an interaction of personal traits and situational factors. Fiedler’s ( 1967 ) contingency, for example, suggests that leader effectiveness depends on the person’s natural fit to the situation and the leader’s score on a “least preferred coworker” scale.
More recently identified styles of leadership include transformational leadership (Bass, Avolio, & Atwater, 1996 ), charismatic leadership (Conger & Kanungo, 1988 ), and authentic leadership (Luthans & Avolio, 2003 ). In a nutshell, transformational leaders inspire followers to act based on the good of the organization; charismatic leaders project a vision and convey a new set of values; and authentic leaders convey trust and genuine sentiment.
Leader-member exchange theory (LMX; see Graen & Uhl-Bien, 1995 ) assumes that leadership emerges from exchange relationships between a leader and her or his followers. More recently, Tse, Troth, and Ashkanasy ( 2015 ) expanded on LMX to include social processes (e.g., emotional intelligence, emotional labor, and discrete emotions), arguing that affect plays a large part in the leader-member relationship.
Leadership Development
An emerging new topic in leadership concerns leadership development, which embodies the readiness of leadership aspirants to change (Hannah & Avolio, 2010 ). In this regard, the learning literature suggests that intrinsic motivation is necessary in order to engage in development (see Hidi & Harackiewicz, 2000 ), but also that the individual needs to be goal-oriented and have developmental efficacy or self-confidence that s/he can successfully perform in leadership contexts.
Ashkanasy, Dasborough, and Ascough ( 2009 ) argue further that developing the affective side of leaders is important. In this case, because emotions are so pervasive within organizations, it is important that leaders learn how to manage them in order to improve team performance and interactions with employees that affect attitudes and behavior at almost every organizational level.
Abusive Leadership
Leaders, or those in positions of power, are particularly more likely to run into ethical issues, and only more recently have organizational behavior researchers considered the ethical implications of leadership. As Gallagher, Mazur, and Ashkanasy ( 2015 ) describe, since 2009 , organizations have been under increasing pressure to cut costs or “do more with less,” and this sometimes can lead to abusive supervision, whereby employee job demands exceed employee resources, and supervisors engage in bullying, undermining, victimization, or personal attacks on subordinates (Tepper, 2000 ).
Supervisors who are very high or low in emotional intelligence may be more likely to experience stress associated with a very demanding high-performance organizational culture. These supervisors may be more likely to try to meet the high demands and pressures through manipulative behaviors (Kilduff, Chiaburu, & Menges, 2010 ). This has serious implications for employee wellbeing and the organization as a whole. Abusive supervision detracts from the ability for those under attack to perform effectively, and targets often come to doubt their own ability to perform (Tepper, 2000 ).
The Macro (Organizational) Level of Analysis
The final level of OB derives from research traditions across three disciplines: organizational psychology, organizational sociology, and organizational anthropology. Moreover, just as teams and groups are more than the sum of their individual team members, organizations are also more than the sum of the teams or groups residing within them. As such, structure, climate, and culture play key roles in shaping and being shaped by employee attitudes and behaviors, and they ultimately determine organizational performance and productivity.
Organizational Structure
Organizational structure is a sociological phenomenon that determines the way tasks are formally divided and coordinated within an organization. In this regard, jobs are often grouped by the similarity of functions performed, the product or service produced, or the geographical location. Often, the number of forms of departmentalization will depend on the size of the organization, with larger organizations having more forms of departmentalization than others. Organizations are also organized by the chain of command or the hierarchy of authority that determines the span of control, or how many employees a manager can efficiently and effectively lead. With efforts to reduce costs since the global financial crisis of 2009 , organizations have tended to adopt a wider, flatter span of control, where more employees report to one supervisor.
Organizational structure also concerns the level of centralization or decentralization, the degree to which decision-making is focused at a single point within an organization. Formalization is also the degree to which jobs are organized in an organization. These levels are determined by the organization and also vary greatly across the world. For example, Finnish organizations tend to be more decentralized than their Australian counterparts and, as a consequence, are more innovative (Leiponen & Helfat, 2011 ).
Mintzberg ( 1979 ) was the first to set out a taxonomy of organizational structure. Within his model, the most common organizational design is the simple structure characterized by a low level of departmentalization, a wide span of control, and centralized authority. Other organizational types emerge in larger organizations, which tend to be bureaucratic and more routinized. Rules are formalized, tasks are grouped into departments, authority is centralized, and the chain of command involves narrow spans of control and decision-making. An alternative is the matrix structure, often found in hospitals, universities, and government agencies. This form of organization combines functional and product departmentalization where employees answer to two bosses: functional department managers and product managers.
New design options include the virtual organization and the boundaryless organization , an organization that has no chain of command and limitless spans of control. Structures differ based on whether the organization seeks to use an innovation strategy, imitation strategy, or cost-minimization strategy (Galunic & Eisenhardt, 1994 ). Organizational structure can have a significant effect on employee attitudes and behavior. Evidence generally shows that work specialization leads to higher employee productivity but also lower job satisfaction (Porter & Lawler, 1965 ). Gagné and Deci emphasize that autonomous work motivation (i.e., intrinsic motivation and integrated extrinsic motivation) is promoted in work climates that are interesting, challenging, and allow choice. Parker, Wall, and Jackson ( 1997 ) specifically relate job enlargement to autonomous motivation. Job enlargement was first discussed by management theorists like Lawler and Hall ( 1970 ), who believed that jobs should be enlarged to improve the intrinsic motivation of workers. Today, most of the job-design literature is built around the issue of work specialization (job enlargement and enrichment). In Parker, Wall, and Jackson’s study, they observed that horizontally enlarging jobs through team-based assembly cells led to greater understanding and acceptance of the company’s vision and more engagement in new work roles. (In sum, by structuring work to allow more autonomy among employees and identification among individual work groups, employees stand to gain more internal autonomous motivation leading to improved work outcomes (van Knippenberg & van Schie, 2000 ).
The Physical Environment of Work
Ashkanasy, Ayoko, and Jehn ( 2014 ) extend the topic of organizational structure to discuss, from a psychological perspective, how the physical work environment shapes employee attitudes, behaviors, and organizational outcomes. Elsbach ( 2003 ) pointed out that the space within which employees conduct their work is critical to employees’ levels of performance and productivity. In their study, Ashkanasy and his colleagues looked at the underlying processes influencing how the physical environment determines employee attitudes and behaviors, in turn affecting productivity levels. They base their model on affective events theory (Weiss & Cropanzano, 1996 ), which holds that particular “affective” events in the work environment are likely to be the immediate cause of employee behavior and performance in organizations (see also Ashkanasy & Humphrey, 2011 ). Specifically, Ashkanasy and colleagues ( 2014 ) looked at how this theory holds in extremely crowded open-plan office designs and how employees in these offices are more likely to experience negative affect, conflict, and territoriality, negatively impacting attitudes, behaviors, and work performance.
- Organizational Climate and Culture
Although organizational structure and the physical environment are important determinants of employee attitudes and behaviors, organizational culture and climate lie at the heart of organizational interactions (Ashkanasy & Jackson, 2001 ). Organizational culture derives from an anthropological research tradition, while organizational climate is based on organizational psychology.
A central presumption of culture is that, as Smircich ( 1983 ) noted, organizational behavior is not a function of what goes on inside individual employees’ heads, but between employees, as evidenced in daily organizational communication and language. As such, organizational culture allows one organization to distinguish itself from another, while conveying a sense of identity for its members.
Organizational Climate and its Relation to Organizational Culture
Organizational culture creates organizational climate or employees’ shared perceptions about their organization and work environment. Organizational climate has been found to facilitate and/or inhibit displays of certain behaviors in one study (Smith-Crowe, Burke, & Landis, 2003 ), and overall, organizational climate is often viewed as a surface-level indicator of the functioning of the employee/organizational environment relationship (Ryan, Horvath, Ployhart, Schmitt, & Slade, 2000 ). For instance, a more restrictive climate may inhibit individual decision-making in contrast to a more supportive climate in which the organization may intervene at the individual level and in which the ability/job performance relationship is supported (James, Demaree, Mulaik, & Ladd, 1992 ). In a study focused on safety climate, Smith-Crowe and colleagues found that organizational climate is essential in determining whether training will transfer to employee performance, and this is most likely because organizational climate moderates the knowledge/performance relationship. Gibbs and Cooper ( 2010 ) also found that a supportive organizational climate is positively related to employee performance. They specifically looked at PsyCap, the higher-order construct of psychological capital first proposed by Luthans and Youssef ( 2004 ).
Organizational Change
The final topic covered in this article is organizational change. Organizational culture and climate can both be negatively impacted by organizational change and, in turn, negatively affect employee wellbeing, attitudes, and performance, reflecting onto organizational performance. Often, there is great resistance to change, and the success rate of organizational change initiatives averages at less than 30% (Al-Haddad & Kotnour, 2015 ). In order to overcome this resistance, it is important that managers plan ahead for changes and emphasize education and communication about them. As organizations becoming increasingly globalized, change has become the norm, and this will continue into the future.
Additionally, as organizations become increasingly globalized, organizational changes often involve mergers that have important organizational implications. In this regard, Kavanagh and Ashkanasy ( 2006 ) found that, for a merger to be successful, there needs to be alignment between the individual values and organizational cultures of merging partners. Managers during a merger situation need to be especially cognizant of how this organizational change affects the company’s original organizational culture.
Organizational development (OD), a collection of planned change interventions, may be the way to improve organizational performance and increase employee wellbeing. OD focuses on employees respecting one another, trust and support, equal power, confrontation of problems, and participation of everyone affected by the organizational change (Lines, 2004 ). Moreover, when an organization already has an established climate and culture that support change and innovation, an organization may have less trouble adapting to the change.
Organizational change research encompasses almost all aspects of organizational behavior. Individuals and employees are motivated to achieve success and be perceived as successful. In this regard, each of the individual differences—personality, affect, past experiences, values, and perceptions—plays into whether individuals can transcend obstacles and deal with the barriers encountered along the journey toward achievement. Teams are similarly motivated to be successful in a collective sense and to prove that they contribute to the organization as a whole. In addition to individual differences, team members deal with bringing all those individual differences together, which can wreak havoc on team communication and cause further obstacles in terms of power differences and conflicts in regard to decision-making processes. Last, at the organizational level of organizational behavior, it is important to account for all of these micro- and meso-level differences, and to address the complexity of economic pressures, increasing globalization, and global and transnational organizations to the mix. This is at the top level of sophistication because, as emphasized before, just as groups equal much more than the sum of individual members, organizations are much more than the sum of their teams. The organizational structure, the formal organization, the organizational culture, and climate and organizational rules all impact whether an organization can perform effectively. Organizational behavior, through its complex study of human behavior at its very conception, offers much-needed practical implications for managers in understanding people at work.
- Adams, J. S. (1963). Towards an understanding of inequity. Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology , 67 , 422–436.
- Al-Haddad, S. , & Kotnour, T. (2015). Integrating the organizational change literature: A model for successful change. Journal of Organizational Change Management , 28 , 234–262.
- Amabile, T. M. (1996). Creativity in context: Update to the social psychology of creativity . Boulder, CO: Westview Press.
- Anderson, C. , Spataro, S. E. , & Flynn, F. J. (2008). Personality and organizational culture as determinants of influence. Journal of Applied Psychology , 93 , 702–710.
- Ardichivili, A. , Mitchell, J. A. , & Jondle, D. (2009). Characteristics of ethical business cultures. Journal of Business Ethics , 85 , 445–451.
- Ashforth, B. E. , & Humphrey, R. H. (1995). Emotion in the workplace: A reappraisal. Human Relations , 48 , 97–125.
- Ashkanasy, N. M. (2003). Emotions in organizations: A multilevel perspective. In F. Danserau & F. J. Yammarino (Eds.), Research in multilevel issues (Vol. 2, pp. 9–54). Oxford: Elsevier.
- Ashkanasy, N. M. , & Ashton-James, C. E. (2008). Affective events theory: A strategic perspective. In W. J. Zerbe , C. E. J. Härtel , & N. M. Ashkanasy (Eds.), Research on emotion in organizations (Vol. 4, pp. 1–34). Bingley, U.K.: Emerald Group Pub.
- Ashkanasy, N. M. , Ayoko, O. B. , & Jehn, K. A. (2014). Understanding the physical environment of work and employee behavior: An affective events perspective. Journal of Organizational Behavior , 35 , 1169–1184.
- Ashkanasy, N. M. , & Dasborough, M. T. (2003). Emotional awareness and emotional intelligence in leadership teaching. Journal of Education in Business , 79 , 18–22.
- Ashkanasy, N. M. , Dasborough, M. T. , & Ascough, K. W. (2009). Developing leaders: Teaching about emotional intelligence and training in emotional skills. In S. J. Armstrong & C. V. Fukami (Eds.), The Sage handbook of management learning, education and development (pp. 161–185). London: SAGE.
- Ashkanasy, N. M & Daus, C. S. (2002). Emotion in the workplace: The new challenge for managers. Academy of Management Executive , 16 , 76–86.
- Ashkanasy, N. M. , & Härtel, C. E. J. (2014). Emotional Climate and culture: The good, the bad, and the ugly. In B. Schneider & K. Barbera (Eds.), The Oxford handbook of organizational culture and climate (pp. 136–152). New York: Oxford University Press.
- Ashkanasy, N. M. , & Humphrey, R. H. (2011). Current research on emotion in organizations. Emotion Review , 3 , 214–224.
- Ashkanasy, N. M. , & Jackson, C. R. A. (2001). Organizational culture and climate. In N. Anderson , D. S. Ones , H. K. Sinangil , & C. Viswesvaran (Eds.), Handbook of work and organizational psychology (pp. 398–415). London: SAGE.
- Bakker, A. B. , & Schaufeli, W. B. (2008). Positive organizational behavior: Engaged employees in flourishing organizations. Journal of Organizational Behavior , 29 , 147–154.
- Bandura, A. (1977). Social learning theory . Alexandria, VA: Prentice Hall.
- Barsade, S. G. , Brief, A. P. , & Spataro, S. E. (2003). The affective revolution in organizational behavior: The emergence of a paradigm. In J. Greenberg (Ed.), Organizational behavior: The state of the science (pp. 3–50). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
- Bass, B. M. , Avolio, B. J. , & Atwater, L. E. (1996). The transformational and transactional leadership of men and women. Applied Psychology: An International Review , 45 , 5–34.
- Bono, J. E. , & Colbert, A. E. (2005). Understanding responses to multi‐source feedback: The role of core self‐evaluations. Personnel Psychology , 58 , 171–203.
- Bono, J. E. , & Judge, T. A. (2004). Personality and transformational and transactional leadership: a meta-analysis. Journal of Applied Psychology , 89 , 901–910.
- Boyatzis, R. E. , & McKee, A. (2005). Resonant leadership: Renewing yourself and connecting with others through mindfulness, hope, and compassion . Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Brady, M. K. , & Cronin, J. J., Jr. (2001). Customer orientation: Effects on customer service perceptions and outcome behaviors. Journal of Service Research , 3 , 241–251.
- Britt, T. W. , Dickinson, J. M. , Greene-Shortridge, T. M. , & McKibbin, E. S. (2007). Self-engagement at work. In D. L. Nelson & C. L Cooper (Eds). Positive Organizational Behavior (pp. 143–158). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Brotheridge, C. , & Grandey, A. (2002). Emotional labor and burnout: Comparing two perspectives of “people work.” Journal of Vocational Behavior , 60 , 17–39.
- Castka, P. , Bamber, C. J. , Sharp, J. M. , & Belohoubek, P. (2001). Factors affecting successful implementation of high performance teams. Team Performance Management: An International Journal , 7 (7/8), 123–134.
- Champoux, J. E. (2011). Organizational behavior: Integrating individuals, groups and organizations (4th ed.). Florence: Routledge.
- Cohen, S. G. , & Bailey, D. E. (1997). What makes teams work? Group effectiveness research from the shop floor to the executive suite. Journal of Management , 23 , 239–290.
- Conger, J. A. , & Kanungo, R. N. (1988). Charismatic leadership. The elusive factor in organizational effectiveness . San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
- Costa, P. T., Jr. , & McCrae, R. R. (1992). Revised NEO personality inventory (NEO-PI-R) and NEO five-factor inventory (NEO-FFI) manual . Odessa, FL: Psychological Assessment Resources.
- De Dreu, C. K. W. , & Van Vianen, A. E. M. (2001). Managing relationship conflict and the effectiveness of organizational teams. Journal of Organizational Behavior , 22 , 309–3278.
- Diener, E. , Larsen, R. J. , Levine, S. , Emmons, R. (1985). Intensity and frequency: Dimensions underlying positive and negative affect. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 28 , 1253–1265.
- Druskat, V. U. , & Wolff, S. B. (2001). Building the emotional intelligence of groups. Harvard Business Review , 79 , 81–90.
- Elsbach, K. D. (2003). Relating physical environment to self-categorizations: Identity threat and affirmation in a non-territorial office space. Administrative Science Quarterly , 48 , 622–654.
- Erickson, R. J. , & Wharton, A. S. (1997). Inauthenticity and depression: Assessing the consequences of interactive service work. Work and Occupations , 24 , 188–213.
- Feather, N. T. , & Boeckmann, R. J. (2007). Beliefs about gender discrimination in the workplace in the context of affirmative action: Effects of gender and ambivalent attitudes in an Australian sample. Sex Roles , 57 , 31–42.
- Fernet, C. , Gagne, M. , & Austin, S. (2010). When does quality of relationships with coworkers predict burnout over time? The moderating role of work motivation. Journal of Organizational Behavior , 31 , 1163–1180.
- Fiedler, F. E. (1967). A theory of leadership effective ness. New York: McGraw-Hill.
- Fritz, C. , Sonnentag, S. , Spector, P. E. , & McInroe, J. (2010). The weekend matters: Relationships between stress recovery and affective experiences. Journal of Organizational Behavior , 31 , 1137–1162.
- Galunic, D. C. , & Eisenhardt, K. M. (1994). Renewing the strategy-structure-performance paradigm. In B. M. Staw & L. L. Cummings (Eds.), Research in organizational behavior (Vol. 16, pp. 215–255). Greenwich, CT: JAI Press.
- Gallagher, E. C. , Mazur, A. K. , & Ashkanasy, N. M. (2015). Rallying the troops or beating the horses? How project-related demands can lead to either high performance or abusive supervision. Project Management Journal , 46 (3), 10–24.
- Gersick, C. J. G. (1988). Time and transition in work teams: Toward a new model of group development. Academy of Management Journal , 31 , 9–41.
- Gibbs, P. C. , & Cooper, C. L. (2010). Fostering a positive organizational culture and climate in an economic downturn. In N. M. Ashkanasy , C. P. M. Wilderom , & M. F. Peterson , The handbook of organizational culture and climate (2d ed., pp. 119–137). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Graen, G. B. , & Uhl-Bien, M. (1995). Development of LMX theory of leadership over 25 years: Applying a multi-level, multi-domain perspective. Leadership Quarterly , 6 , 219–247.
- Grandey, A. (2003). When the show must go on: Surface and deep acting as predictors of emotional exhaustion and service delivery. Academy of Management Journal , 46 , 86–96.
- Groth, M. , Hennig-Thurau, T. , & Walsh, G. (2009). Customer reactions to emotional labor: The roles of employee acting strategies and customer detection accuracy. Academy of Management Journal , 52 , 958–974.
- Hannah, S. T. , & Avolio, B. J. (2010). Ready or not: How do we accelerate the developmental readiness of leaders? Journal of Organizational Behavior , 31 , 1181–1187.
- Hatfield, E. , Cacioppo, J. T. , & Rapson, R. L. (1993). Emotional contagion: Current directions. Psychological Science , 2 , 96–99.
- Herzberg, F. (1966). Work and the nature of man . Cleveland, OH: World Publishing.
- Hidi, S. , & Harackiewicz, J. M. (2000). Motivating the academically unmotivated: A critical issue for the 21st century. Review of Educational Research , 70 , 151–179.
- Hobfoll, S. E. (1989). Conservation of resources: A new attempt at conceptualizing stress. American Psychologist , 44 , 513–524.
- Hochschild, A. R. (1983). The managed heart: Commercialization of human feeling . Berkeley: University of California Press.
- Holland, J. (1973). Making vocational choices: Q theory of careers . Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
- Janis, I. L. , & Mann, L. (1977). Decision making: A psychological analysis of conflict, choice, and commitment . New York: Free Press.
- James, L. R. , Demaree, R. G. , Mulaik, S. A. , & Ladd, R. T. (1992). Validity generalization in the context of situational models. Journal of Applied Psychology , 77 , 3–14.
- Jehn, K. A. (1997). A qualitative analysis of conflict types and dimensions in organizational groups. Administrative Science Quarterly , 42 , 538–566.
- Johnson, E. C. , Kristof-Brown, A. L , van Vianen, A. E. M. , de Pater, I. E. , & Klein, M. R. (2003). Expatriate social ties: Personality antecedents and consequences for adjustment. International Journal of Selection and Assessment , 11 , 277–288.
- Judge, T. A. , Bono, J. E. , Erez, A. , & Locke, E. A. (2005). Core self-evaluations and job and life satisfaction: The role of self-concordance and goal attainment. Journal of Applied Psychology , 90 , 257–268.
- Judge, T. A. , Higgins, C. A. , Thoresen, C. J. , & Barrick, M. R. (2006). The Big Five personality traits, general mental ability, and career success across the life span. Personnel Psychology , 52 , 621–652.
- Judge, T. A. , Ilies, R. , & Scott, B. A. (2006). Work-family conflict and emotions: Effects at work and home. Personnel Psychology , 59 , 779–814.
- Kahn, W. A. (1990). Psychological conditions of personal engagement and disengagement at work. Academy of Management Journal , 33 , 692–724.
- Kavanagh, M. H. , & Ashkanasy, N. M. (2006). The impact of leadership and change management strategy on organizational culture and individual acceptance of change during a merger. British Journal of Management , 17 , S81–S103.
- Kilduff, M. , Chiaburu, D. S. , & Menges, J. I. (2010). Strategic use of emotional intelligence in organizational settings: Exploring the dark side. Research in Organizational Behavior , 30 , 129–152.
- Konopaske, R. , & Ivancevich, J. M. (2004). Global management and organizational behavior: Text, readings, cases, and exercises . New York: McGraw-Hill.
- Latham, G. P. , & Pinder, C. C. (2005). Work motivation theory and research at the dawn of the twenty-first century. Annual Review of Psychology , 56 , 485–516.
- Lawler, E. E. , & Hall, D. T. (1970). Relationship of job characteristics to job involvement, satisfaction, and intrinsic motivation. Journal of Applied psychology , 54 , 305–312.
- Leiponen, A. , & Helfat, C. E. (2011). Location, decentralization, and knowledge sources for innovation. Organization Science , 22 , 641–658.
- Lines, R. (2004). Influence of participation in strategic change: Resistance, organizational commitment and change goal achievement. Journal of Change Management , 4 (3), 193–215.
- Locke, E. A. , & Latham, G. P. (1990). A theory of goal setting and task performance . Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
- Luthans, F. , & Avolio, B. J. (2003). Authentic leadership development. In K. S. Cameron , J. E. Dutton , & R. E. Quinn (Eds.), Positive organizational scholarship: Foundations of a new discipline (pp. 241–261). San Francisco: Barrett-Koehler.
- Luthans, F. , & Youssef, C. M. (2004). Human, social, and now positive psychological capital management. Organizational Dynamics , 33 , 143–160.
- Martinko, M. J. (1995). The nature and function of attribution theory within the organizational sciences. In. M. J. Martinko (Ed.), Advances in attribution theory: An organizational perspective (pp. 7–14). Delray Beach, FL: St. Lucie Press.
- Maslow, A. H. (1943). A theory of human motivation. Psychological Review , 50 , 370–396.
- Mayer, J. D. , & Salovey, P. (1997). What is emotional intelligence? In P. Salovey & D. J. Sluyter (Eds.), Emotional development and emotional intelligence: Educational implications (pp. 3–31). New York: Basic Books.
- Mayes, B. T. , & Allen, R. W. (1977). Toward a definition of organizational politics. Academy of Management Journal , 2 , 635–644.
- McGregor, D. (1960). The human side of enterprise . New York: McGraw-Hill.
- Mintzberg, H. (1979). The structuring of organizations: A synthesis of the research . Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
- Mintzberg, H. (1985). The organization as a political arena. Journal of Management Studies , 22 , 133–154.
- Mitchell, T. R. (1982). Motivation: New directions for theory, research, and practice. Academy of Management Review , 7 , 80–88.
- Moscovici, S. , & Zavalloni, M. (1969). The group as a polarizer of attitudes. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 12 , 125–135.
- Murnighan, J. K. , & Conlon, D. E. (1991). The dynamics of intense workgroups: A study of British string quartets. Administrative Science Quarterly , 36 , 165–186.
- Myers, D. G. , & Lamm, H. (1976). The group polarization phenomenon. Psychological Bulletin , 83 , 602–627.
- Ozcelik, H. (2013). An empirical analysis of surface acting in intra-organizational relationships. Journal of Organizational Behavior , 34 , 291–309.
- Ostroff, C. , & Atwater, L. E. (2003). Does whom you work with matter? Effects of referent group and age composition on managers’ compensation. Journal of Applied Psychology , 88 , 725–740.
- Parker, S. K. , Wall, T. D. , & Jackson, P. R. (1997). “That's not my job”: Developing flexible employee work orientations. Academy of Management Journal , 40 , 899–929.
- Pelled, L. H. (1995). Demographic diversity, conflict, and work group outcomes: An intervening process theory. Organization Science , 7 , 615–631.
- Pfeffer, J. , & Leblebici, H. (1973). Executive recruitment and the development of interfirm organizations. Administrative Science Quarterly , 18 , 449–461.
- Pfeffer, J. , & Salancik, G. R. (1973). The external control of organizations: A resource dependence perspective . Palo Alto, CA: Stanford University Press.
- Porter, L. W. , & Lawler, E. E. (1965). Properties of organization structure in relation to job attitudes and job behavior. Psychological Bulletin , 64 , 23–51.
- Rashotte, L. S. (2002). What does that smile mean? The meaning of nonverbal behaviors in social interaction. Social Psychology Quarterly , 65 , 92–102.
- Raven, B. H. (1993). The bases of power: Origins and recent developments. Journal of Social Issues , 49 , 227–251.
- Richer, S. , Blanchard, C. , & Vallerand, R. J. (2002). A motivational model of work turnover. Journal of Applied Social Psychology , 32 , 2089–2113.
- Rhoades, J. A. , Arnold, J. , & Jay, C. (2001). The role of affective traits and affective states in disputants’ motivation and behavior during episodes of organizational conflict. Journal of Organizational Behavior , 22 , 329–345.
- Robbins, S. P. , Judge, T. A. , Millett, B. , & Boyle, M. (2014). Organisational behaviour (7th ed.). French’s Forest, NSW, Australia: Pearson Education.
- Ryan, A. M. , Horvath, M. , Ployhart, R. E. , Schmitt, N. , & Slade, L. A. (2000). Hypothesizing differential item functioning in global employee opinion surveys. Personnel Psychology , 53 , 531–562.
- Scott, W. G. , & Mitchell, T. R. (1976). Organization theory: A structural and behavioral analysis . Homewood, IL: Irwin.
- Skinner, B. F. (1938). The behavior of organisms: An experimental analysis . New York: Appleton-Century-Crofts.
- Smircich, L. (1983). Concepts of culture and organizational analysis. Administrative science quarterly , 28 , 339–358.
- Smith-Crowe, K. , Burke, M. J. , & Landis, R. S. (2003). Organizational climate as a moderator of safety knowledge-safety performance relationships. Journal of Organizational Behavior , 24 , 861–876.
- Staw, B. M. (1981). The escalation of commitment to a course of action. Academy of Management Review , 6 , 577–587.
- Tepper, B. J. (2000). Consequences of abusive supervision. Academy of Management Journal , 43 , 178–190.
- Thomas, K. W. (1992). Conflict and negotiation processes in organizations. In M. D. Dunnette , & L. M. Hough (Eds.), Handbook of industrial and organizational psychology (2d ed., Vol. 3, pp. 652–717). Mountain View, CA: Consulting Psychologist Press.
- Tjosvold, D. (1997). Networking by professionals to manage change: Dentists’ cooperation and competition to develop their business. Journal of Organizational Behavior , 18 , 745–752.
- Tse, H. M. M. , Troth, A. M. , & Ashkanasy, N. M. (2015). Leader-member exchange and emotion in organizations. In B. Erdogan & T. N. Bauer (Eds.), The Oxford handbook of leader-member exchange (pp. 209–225). New York: Oxford University Press.
- Tuckman, B. (1965). Developmental sequence in small groups. Psychological Bulletin , 63 , 384–399.
- Umphress, E. E. , Simmons, A. L. , Folger, R. , Ren, R. , & Bobocel, R. (2013). Observer reactions to interpersonal injustice: The roles of perpetrator intent and victim perception. Journal of Organizational Behavior , 34 , 327–349.
- Van Erde, W. , & Thierry, H. (1996). Vroom’s Expectancy models and work-related criteria: A meta-analysis. Journal of Applied Psychology , 81 , 576–588.
- Van Knippenberg, D. , & Van Schie, E. L. S. (2000). Foci and correlates of organizational identification. Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology , 73 , 137–147.
- Vigoda, E. (2000). Organizational politics, job attitudes, and work outcomes: Exploration and implications for the public sector. Journal of Vocational Behavior , 57 , 326–347.
- Vroom, V. H. (1964). Work and motivation . New York: Wiley.
- Wall, J. , & Callister, R. (1995). Conflict and its management. Journal of Management , 21 , 515–558.
- Wallach, M. A. , Kogan, N. , & Bem D. J. (1964). Diffusion of responsibility and level of risk taking in groups. Journal of Abnormal Social Psychology , 68 , 263–274.
- Watson, D. (1988). The vicissitudes of mood measurement: Effects of varying descriptors, time frames, and response formats on measures of positive and negative affect. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 55 , 128–141.
- Watson, D. , & Tellegen, A. (1985). Toward a consensual structure of mood. Psychological Bulletin , 98 , 219–235.
- Watson, D. , & Walker, L. M. (1996). The long-term stability and predictive validity of trait measures of affect. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 70 , 567–577.
- Weiss, H. M. (2002). Deconstructing job satisfaction: Separating evaluations, beliefs and affective experiences. Human Resource Management Review , 12 , 173–194.
- Weiss, H. M. , & Cropanzano, R. (1996). Affective events theory: A theoretical discussion of the structure, causes and consequences of affective experiences at work. In B. M. Staw & L. L. Cummings (Eds.), Research in organizational behavior (Vol. 18, pp. 1–74). Westport, CT: JAI Press.
- West, M. (1996). Reflexivity and work group effectiveness: A conceptual integration. In M. A. West (Ed.), The handbook of work group psychology (pp. 555–579). Chichester, U.K.: Wiley.
- Wilkin, C. L. (2012). I can’t get no job satisfaction: Meta-analysis comparing permanent and contingent workers. Journal of Organizational Behavior , 34 , 47–64.
- Yukl, G. , & Tracey, J. B. (1992). Consequences of influence tactics used with subordinates, peers, and the boss. Journal of Applied Psychology , 77 , 525–535.
Related Articles
- Organizational Sensemaking
- Human Resource Management and Organizational Psychology
- Overqualification in the Workplace
- Communication and Intergroup Relations
- Justice in Teams
- Training from an Organizational Psychology Perspective
- Dual Process Models of Persuasion
Printed from Oxford Research Encyclopedias, Psychology. Under the terms of the licence agreement, an individual user may print out a single article for personal use (for details see Privacy Policy and Legal Notice).
date: 08 September 2024
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
- [185.126.86.119]
- 185.126.86.119
Character limit 500 /500
COVID-19: Organizational Challenges and Opportunities
[Additional essays and videocasts regarding psychological ramifications of the COVID-19 virus outbreak can be found at: https://communitiescollaborating.com/[
Kevin Weitz, Psy.D. and LarryHiner, Psy.D.
Societies around the world must address the challenge of COVID-19 at multiple levels–personal, family, friends and colleagues, team, organizational and societal. The Global Psychology Task Force has found that many of the psychological ramifications of this virus are first recognized, understandably, at the personal and family levels. We wonder about our own suseptibility to this pandemic virus and to the welfare of other members of our family. It would seem, however, that increasing concerns about the impact of the virus on the larger sectors: teams, organizations and social systems are likely to emerge in future months.
In keeping with this likely increase in concern about one of these sectors (organizations), William Bergquist interviewed two members of the Global Psychology Task Force, Kevin Weitz and Larry Hiner. Both have extensive experience in consulting to and working inside many organizations around the world (see a brief description of their backgrounds below).
Organizational Structures and Operations
Bergquist recorded three Zoom-based interviews with Drs. Weitz and Hiner. The first focused on the opportunities emerging in the radical rethinking of organizational structures and operations.
https://psychology.zoom.us/rec/share/6MlyHYrt8TNIWZXD-FrHVPJiLNneT6a82nQfqPdexUnSKBp3zxmNgIvDoOiSHcYr?startTime=1587061957000
Organizational Culture
The second interview was primarily concerned with the challenges faced by organizations in moving at least temporarily to a virtual culture–with many if not all employees working from their home. More broadly, this interview dealt with the culture in which organizations will now operate during (and perhaps after) the virus’s invasion.
https://psychology.zoom.us/rec/share/6MlyHYrt8TNIWZXD-FrHVPJiLNneT6a82nQfqPdexUnSKBp3zxmNgIvDoOiSHcYr?startTime=1587063567000
Organizational Leadership
The third interview was wide ranging with Weitz and Hiner being asked to consider what they would do as CEO of an organization with which they have consulted or in which they have offered professional coaching services.
https://psychology.zoom.us/rec/share/6MlyHYrt8TNIWZXD-FrHVPJiLNneT6a82nQfqPdexUnSKBp3zxmNgIvDoOiSHcYr?startTime=1587064705000
Kevin Weitz, Psy.D.
Dr. Kevin Weitz specializes in helping leaders define and align their organization’s culture and day-to-day behaviors with business strategy to execute effectively. Recently, his work has focused on shaping behaviors to reduce “insider threats” to highly confidential company information and cybersecurity. Kevin Weitz has almost thirty years’ experience leading organizational transformation and change projects, with expertise in building leadership teams to drive change. He has global experience with multinational organizations in the US, Canada, Kazakhstan, Latin America and South Africa. Dr. Weitz has authored a Kindle e-book about organizational culture change entitled The House of Culture.
Larry Hiner, Psy.D.
Deacon Larry is co-founder and Executive Advisor for WorkforceEQ, a not-for-profit instituted to Enhance the Value of Dignity for All Persons in the Workplace. He earned his Doctorate in Psychology from the Professional School of Psychology in 2007, having previously earned a Masters in Counseling and Human Development from the Johns Hopkins University in 1980. He has experience in Clinical as well as Organizational practices. Dr. Hiner was Ordained as a Deacon in the Roman Catholic tradition in June of 2014, having completed 5 years of Seminary studies and discerning his call to the Diaconate. Deacon Larry has been married for 45 years and is the proud father to four sons and their families.
- Related Articles
- More By Kevin Weitz
- More In Organizational Behavior / Dynamics
I Dreamed I Was Flying: A Developmental Representation of Competence
John trumper and susan price: working with members of the navaho nation, snuggling in: what makes us comfortable when we sleep, multiple moments of positivity in the workplace: organizational culture and strategy, in search of truth i: hubris and narcissism, the neuroscience of organizational culture, performing in a vuca-plus world, organizational consultation xxxii: the appreciative leader: from a 21st century perspective, leading into the future xib: holding the center while innovating and opening boundaries, leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Many companies struggle to implement new business strategies because they underestimate ho…
- Counseling / Coaching
- Health / Biology
- Sleeping/Dreaming
- Personality
- Developmental
- Cognitive and Affective
- Psychobiographies
- Disclosure / Feedback
- Influence / Communication
- Cooperation / Competition
- Unconscious Dynamics
- Intervention
- Child / Adolescent
- System Dynamics
- Organizational Behavior / Dynamics
- Development / Stages
- Organizational Types / Structures
- System Dynamics / Complexity
- Assessment / Process Observation
- Intervention / Consulting
- Cross Cultural
- Behavioral Economics
- Technologies
- Edge of Knowledge
- Organizational
- Laboratories
- Field Stations
- In Memoriam
Organizational Challenges in the 21st Century Analytical Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Introduction
Reference list.
In light with the developments of the 21 st century, the business world has been in the heart of the revolutions. The key concepts of technology, liberalizations of markets and globalization have really transformed the world. As a result of these transformations, increased activity in the commercial and industrial sectors has been witnessed.
The world is presently operating as one village, whereby people are able to communicate efficiently and conveniently with one another. This has been facilitated by the growth of computer and internet technology. The growth of air transport has also been of significant influence to the enhancement of transport. With these developments, communication and transport have been heightened thus enhancing global relations in terms of business and other activities.
Nevertheless, the growth of globalization has not come singly, whereby it has been associated with various limitations. In this case, the issue of global recession is a factor of globalization, whereby nations directly depend on one another for business. This is unlike years, whereby nations operated independently.
With regards to the emergence of global recession, which refers to global economic slowdown, business organizations are obligated to undertake the most competitive leadership strategies so as to counter the situation. This is in response to the lost business and the diminishing market potentiality.
As noted by Northouse (2007: 101), business organizations have been significantly impacted by the issue of global recession. This refers to a period of global economic slowdown or down turn, whereby nations experience limited economic growth rates of 3% of less.
Combination of this situation with the overwhelming competition in the international markets, business organizations find it hard to survive. The situation can only be countered by adoption of the most efficient leadership styles. A good example is Nokia which has in the recent faced it rough in the technology and mobile phone industry.
The challenges facing the company are based on the issue of global recession and growth of competition in the industry it is operating in (Isaksen and Tidd 2006: 102). In reaction to the situation, the company is forced to adopt the most competitive and leadership techniques so as to overcome the challenges.
A study by Kotter (1996: 68) indicated that good leadership is the only solution to the challenges faced by business in the height of global recession among other challenges like increased competition. In this case, transformational leadership has been highlighted as the most appropriate leadership approach for organizations in recent days. Transformational leadership has been defined as a form of leadership style whereby leaders and their followers align themselves to higher moral and motivational levels (Fisher and Ury 1992: 29).
This is attained through impacting visions and personality among all individuals in the organizations. With regards to this leadership style, leaders have the obligation of inspiring their followers to change their perceptions and expectations.
With the challenges of global recession, this leadership style stands to be very efficient in the sense that it will bring every individual in the organization into focus and adjust to the prevailing situation. A point worth of consideration is that this leadership style demands leaders to motivate employees towards attaining a common goal (Weinstein et al 2004: 71). By so doing, the challenges facing the business will be countered.
Cherry (2011: 1) indicated that transformational leadership style is guided by various components which makes it efficient in countering business challenges. Firstly, the concept of intellectual stimulation is highly embraced in this leadership approach. In this case, the leaders do not only challenge the status quo, but also instill creativity among the employees.
Hacker and Roberts (2003: 45) depicted that leaders should encourage followers to be innovative and do things in new ways thus exploiting available opportunities. In the case of Nokia the company has in the recent been in its endeavors to intellectually stimulate its employees. This is an efficient approach in countering the economic slowdown, whereby new strategies of doing business as well as products will be attained.
The concept of individualized consideration is also addressed in this leadership style. In this case, leaders should offer encouragement and support to all individuals within the organizations. A point worth of consideration is that leaders should foster supportive relationships through open communication, where followers are free to share and seek ideas (Bass and Riggio 2006: 78). By undertaking these approaches, organizations will be able to acquire unique ideas and contributions from their followers.
Chase et al (2001: 49) depicted that leaders in the contemporary society should offer inspirational motivation to their employees. This is acquired through the provision of a clear vision which will help in guiding the followers. By inspiring the followers, leaders will help their followers to experience same motivation and passion which will help in realizing the common goal. Another core component of transformational leadership is the issue of idealized influence.
Yukl (2001: 93) argued that leaders should be a role model to their followers. This concept can not be exempted from leadership in the contemporary society based the numerous challenges faced by businesses. Schein (1992: 62) noted that followers respect and trust their leaders and they will simply emulate them.
With this in mind, business organizations will be able to overcome the challenges they are facing in the height of global recession. Global recession is leading to loss of business hence calling for the adoption of best leadership strategies.
Alongside the adoption of transformational leadership style, the concept of total quality management (TQM) can not be exempted from organizational management in recent days. As noted by Hakes (2001: 22) the issue of quality and product leadership has been identified as key aspects of success.
With this in mind, business organizations are obligated to ensure that their products and services are of the best quality in the market. Every business organization should keep a watch of the products and services of its competitors (Wilson 2005: 102). The concept of TQM basically refers to an approach of management which entails on managing entire organization so as to produce quality goods and services. In the case of mobile phone industry, quality of the products has been of great importance.
In this case, each company is seeking to improve its services and products. In the midst of global recession, Nokia is obligated to ensure optimum quality of its products (Bass and Riggio 2006: 78). Based on this scenario, the adoption of TQM is inevitable for the success of Nokia during this period of economic slow down.
Pekar (2005: 42) outlined that employee involvement in the running of an organizations in recent days is inevitable. Employee involvement is a key element of TQM, whereby they are able to prevent problems before they occur. Organizations are also obligated to focus on their customers so as to determine the actual wants and needs of the customers.
This will help an organization to offer quality products and services which meet the needs of customers. In the case of Nokia, the need for Smartphone has been an overwhelming market trend in recent days. In order for the company to realize its dreams and counter the market challenges it has no obligation of adopting the market demands. This is part of TQM, whereby the company’s operations and product specifications are dictated by the market demands (Pekar 2005: 42).
The concept of benchmarking is also a key leadership and business management approach that can not be down looked. As observed by Hakes (2001: 22) benchmarking is an element of TQM in which an organization seeks out other organizations it is operating with. An organization uses the products and services of other companies as its benchmark or standard, thus being able to judge its performance.
It is also worth noting that organizations are also required to adapt as well as improve processes adopted by other organizations. This will help an organization to attain the high quality and efficient products, thus being able to win the market. Presently, TQM has proved to be an efficient leadership and management approach which has helped many businesses to endure market excellence (Hakes 2001: 22).
In consideration with the discussion and analysis of the business environment in the 21 st century, it has been clearly evident that business organizations are faced with numerous challenges. The issues of global recession and increased competition in the corporate world have been overwhelming in recent days. In response to these challenges, business organizations are obligated to adopt the most efficient leadership styles.
In this case, the concepts f transformational leadership and TQM have been highlighted as the most suitable for business organizations in recent days. This will help business organization to be efficient and steadfast in offering the best products and services. For instance, the case of Nokia has been overwhelming, whereby it is facing numerous challenges following the issue of global recession and competition in the mobile industry. In response to this scenarios, the company is obligated to adopting the above highlighted leadership approaches.
Bass, B. and Riggio, R. (2006). Transformational Leadership . New York: Routldge, 78-102.
Chase, R. et al. (2001). Operations Management for Competitive Advantage . New York: McGraw Hill Press, 49-81.
Cherry, K. (2011). Transformational Leadership. Retrieved from: https://www.verywellmind.com/what-is-transformational-leadership-2795313
Fisher, R. and Ury, W. (1992). Getting to Yes: Classic text on negotiation . New York McGraw Hill, 29-51.
Hacker, S. and Roberts, T. (2003). Transformational Leadership: Creating Organizations of Meaning. London: Routldge, 45-63.
Hakes, C. (2001), Total Quality Management: The Key to Business Improvemen t. London: Routldge, 22-36.
Isaksen, S. and Tidd, J. (2006). Meeting the Innovation Challenge: Leadership for Transformation and Growth . London: Wiley & Sons, 102-132.
Kotter, J,.P (1996). Leading Change . New York: Harvard Business School Press, 68-97
Northouse, P. (2007). Leadership: Theory and Practice . London: Sage Publications, 101-151.
Pekar, J. (2005). Total Quality Management: Guiding Principles for Application . New York: Wiley & Sons Press, 42-53.
Schein, E. (1992). Organizational culture and leadership: Core leadership text . New York: McGraw Hill, 62-80.
Weinstein, S. et al. (2004) Transformational Leadership: Vision, Persuasion, and Team Building for the Development Professional. New York: Wiley & Sons Press, 71-86.
Wilson, J. (2005) An Historical Perspective on Operations Management, Production and Inventory Management. London: Wiley & Sons Press, 102- 137.
Yukl, G, A. (2001). Leadership in Organizations . New York: Wiley & Sons Press, 93-103.
- Gender Differences in Leadership Styles
- Sustainability Reporting Benefits
- Managing Supply Chain of Nokia
- How to Create a Brand Extension of Nokia Phones With Nokia I-Phones
- Nokia Incentives Over the Last 10 Years
- TQM in Dubai Metro System
- Repairing Jobs that Fail to Satisfy: DrainFlow Case
- Are Workers Motivated Mainly by Money?
- Airport Security Program (Airports Management)
- Management Information Systems: Effective Decision-Making and Security
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2019, April 25). Organizational Challenges in the 21st Century. https://ivypanda.com/essays/organizational-challenges-in-the-21st-century-essay/
"Organizational Challenges in the 21st Century." IvyPanda , 25 Apr. 2019, ivypanda.com/essays/organizational-challenges-in-the-21st-century-essay/.
IvyPanda . (2019) 'Organizational Challenges in the 21st Century'. 25 April.
IvyPanda . 2019. "Organizational Challenges in the 21st Century." April 25, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/organizational-challenges-in-the-21st-century-essay/.
1. IvyPanda . "Organizational Challenges in the 21st Century." April 25, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/organizational-challenges-in-the-21st-century-essay/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Organizational Challenges in the 21st Century." April 25, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/organizational-challenges-in-the-21st-century-essay/.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here are 108 organizational behavior essay topic ideas and examples to get you started: The impact of organizational culture on employee satisfaction. The role of leadership in shaping organizational behavior. How diversity and inclusion influence team dynamics. The importance of emotional intelligence in the workplace.
Today's Most Critical Workplace Challenges Are About ...
13 challenges and opportunities of organizational behavior are; Improving People's Skills. Improving Quality and Productivity. Total Quality Management (TQM) Managing Workforce Diversity. Responding to Globalization. Empowering People. Coping with Temporariness. Stimulating Innovation and Change.
Organizational behavior is both a challenge and opportunity to employers due to the study's focus on reducing absenteeism, increased job satisfaction, and productivity (Osland et al.,2015). The study also guides managers in providing better working conditions, ethical practice, and maximum respect in the workplace.
Corporate mission, vision and objective statements. Management is the monitoring and adjusting the se activities in order to achieve the greatest effectiveness and efficiency in achieving the organization goal. It is very important because it involves the planning, organizing, controlling, monitoring, revising and modifying the organization ...
Organizational behaviour could be defined as the study and use of information associated with peoples behaviours at workplaces. Normally it focuses on certain features which include; individual, group, structure, technology and environment features (Hackman and Oldham, 1975). Get a custom essay on Management and Organizational Behavior.
organizations operate is ever changing, thereby changing the needs of the organization and internal operations. The concept of organization behaviour is important as it provides insights into organizations' challenges and opportunities. Although organization behaviour varies from one organization to another, its usefulness is universal.
Apparently, the issue of professionalism and privacy is a behavioral challenge that requires well-articulated solutions. ... By using real-life examples and outlining issues and concepts espoused in the field of organizational behaviour, the essay plays an instrumental role in elevating the understanding that marketing scholars have in ...
1. Resistance to Change. One of the biggest challenges of organizational behavior is resistance to change. Change is inevitable, and organizations must constantly adapt to new environments and circumstances to remain competitive. However, employees often resist change, whether it is due to fear of the unknown or a reluctance to let go of ...
Opportunities: 1) Developing a comprehensive code of ethics and conduct can provide clear guidelines for employees. 2) Conducting ethics training and workshops can raise awareness and promote ethical decision-making. 3) Encouraging open communication channels can empower employees to report unethical behaviour.
1.2 Understanding Organizational Behavior
Organizational challenges are difficulties employees face that prevent them from accomplishing their goals. In the workplace, problems can manifest in the environment and among team members and management. A company's operations can change over time, requiring employees to adjust to new policies and find productive ways to work together.
A Study On Organizational Behavior Management Essay. Organizational behavior is a field concerned with study of the relationship between the organization and the individuals in the workforce. In particular it entails studying how the organization influences the behavior of its workers and how as a result those individuals are able to influence ...
tially profound. Fortunately, the data collected and used within organizations can also be repurposed for organizational research, opening new ways to measure behavior and study people at work (Salganik, 2019). The rise of people analytics in organizations is associated with new. 0191-3085/© 2023 The Author.
Innovation with field experiments: Studying organizational behaviors in actual organizations. Organizational scholarship centers on understanding organizational context, usually captured through eld studies, as well as determining causality, typically with laboratory fi experiments. We argue that eld experiments can bridge these approaches ...
The findings arising from this essay suggest that middle managers play an important role in facilitating change in organizations. They also suggest that middle managers face major challenges in the organization-wide implementation and adoption of CI including possible resistance by middle management itself.There has, is and probably always will ...
Abstract. Diversity management is a process intended to create and maintain a positive work environment where the similarities and differences of individuals are valued. The literature on diversity management has mostly emphasized on organization culture; its impact on diversity openness; human resource management practices; institutional ...
Challenges That Face The Organizational Behaviour Business Essay. Employee and customer satisfaction are the vital elements of an organisation to survive in the continuous changing world. To function effectively, the organisation must understand the culture and the diversity of the employees. Organisations must adapt to the changes of ...
Organizational Behavior
Kevin Weitz, Psy.D. and LarryHiner, Psy.D. Societies around the world must address the challenge of COVID-19 at multiple levels-personal, family, friends and colleagues, team, organizational and societal. The Global Psychology Task Force has found that many of the psychological ramifications of this virus are first recognized, understandably ...
Change management in the organisational behaviour textbook by (King, D., & Lawley, S. 2016) is defined as 'Any form of effort or initiative undertaken to alter a particular aspect of the organisation'. This relates to one of the most famous theories of change management by Kurt Lewin (1890-1947). Change is something that is always happening ...
Yukl (2001: 93) argued that leaders should be a role model to their followers. This concept can not be exempted from leadership in the contemporary society based the numerous challenges faced by businesses. Schein (1992: 62) noted that followers respect and trust their leaders and they will simply emulate them.
Open Document. Challenges and opportunities for Organizational behavior 1. Responding to Globalization Globalization has transformed the world into a global village wherein the organizations are no longer restricted to their national borders. Challenges-managers has to face the difficult task of interacting with people from different nations ...