English Compositions

Preposition in English Grammar with Examples [With PDF]
This is a complete guide on Preposition in English Grammar.

Definition of Preposition:
A preposition is a Part of Speech which is placed before a noun or a pronoun to indicate a direction, method, place, source, etc. In other words, to show the relation of that noun or pronoun with any other word of the sentence.
For example:
- It may join noun to a verb , e.g.: She slipped off the stairs.
- Similarly join one noun to another, e.g.: Joyee was in the kitchen.
- Or join noun to an a d jective , e.g.: We are proud of our country.
Types of Prepositions:
In general, preposition are five types , and those are:
- Simple – in, on, out, for, from.
- Double – into, within, without, onto, upon.
- Disguised – For example, it is 2 o’ clock now.
- Special – We know ‘but’ is used as a conjunction, when ‘but’ means ‘except’ then it is called a special type. For example, he is poor but honest. Or None but a brave man can do this.
- Appropriate – Sourav was accompanied by Ram. If any sentence is in active voice then do not add any preposition. For example, Ram accompanied by Sourav (omit ‘by’ here).

However prepositions are also categorized in the following ways:
- Preposition of Time (At, in, on, by, off, from, away, since, for, towards).
- Preposition of Place (At, from, within, without, inside, outside, in front of, on top of, beyond, between).
- Preposition of Possession (By, of, with).
- Prepositions of direction motion (To, at, from, round, across, against).
- Prepositions of cause, reason, and purpose (Of, for, with).
- Preposition of Agent, Manner or Method (In, on, for, by with, though).
Some Important Points to Remember about Preposition:
- When verbs are placed after a preposition, they should be in gerund [External Link] form except they are used in an infinitive form, for example, she insisted on going to London.
- A clause also an object to a preposition. For example , pay attention to what your teacher said.
- Adverb of place and time can also be the object of a preposition. For example, pay attention to what your teachers say.
- The usages of a noun or pronoun in a preposition in the accusative case [ You can Learn more about Accusative case here (External Links)] For example, the phone in on the table. Here ‘table’ use in the accusative case .
- It sometimes may have one or more than one object, for example, I gave money to Sam and her sister.
- It may govern other parts of speech used as a noun, for example, from here, for good, in short, about to go, before now.
- And also it may govern clauses and phr ases as well, like- I shall go to where you have come from.
Examples of Prepositions:
- Crying out of fear.
- A house for sale.
- To take for granted.
- For god’s sake, help me.
- For all his wealth he is unhappy.
- To sell a thing at three for a rupee.
- Good for health.
- Many men working for the company.
- Time for going out.
- Respect for the elders.
- He cares for nothing.
- A prize for Physics.
- Silent for shame.
- To flee for life.
- Wish for (considering that he is) a boy.
- I speak for (on behalf of) my class.
- He left for home.
- Ready for(against) emergencies.
- Train for Bangalore.
- Bought a car for Rs 3 lakh.
- Change it for another.
- Look for something.
- Send for a doctor.
- They are all for helping the needy.
- Big for his age.
- For five weeks.
- Passengers for Jhargram.
- Get ready for school.
- Go for a walk.
- Read for pleasure.
- Hope for the best.
- Ask for money.
- A taste for music.
- Have a liking for her.
- Unfit for the post.
- Ruined for life.
- A cheque for (not, of) Rs 5000.00.
- I ask for the money.
- I did not expect such treatment at your home.
- John studied at this university.
- The countries are at war or at peace.
- The examination is at hand.
- At 8 o’clock.
- At bed-time.
- At first sight, at noon.
- At night (but not at day), at home
- At the door.
- He studied at this university.
- At a distance.
- At short notice.
- At liberty.
- I did not expect such treatment at your hand.
- Shouted at the boys.
- Look at me.
- Very good at cricket.
- At full speed.
- You will hear and the latest by Saturday.
- At all places.
- To sit at (not under).
- At present (I am busy at present).
- At any moment.
- To sale a thing at three for a rupee.
- At any time.
- At the office.
- At the age of 60.
- I shall see you at Diwali at his house.
- One at a time.
- At the same time.
- At the beginning.
- At the meeting.
- Good at mathematics.
- At the third attempt.
- At regular intervals.
- To travel by boat or rail or car.
- By day (but in the day).
- By or at night (but in the night).
- A machine is driven by steam or petrol or electricity.
- To be destroyed by fire or earthquake.
- To know one by name or sight (I know him by name, I know him by sight).
- To teach by example.
- To life by coaching, teaching, etc.
- Made by machinery.
- By next Sunday.
- To send a letter by post or hand.
- To inform a personal letter or telegram or messenger.
- To sell things by the kilogram are the meter or the dozen (fish is sold here by the kilogram.)
- Cloth is sold by the meter.
- Eggs are sold by the dozen
- To pay by cheque (but in cash or notes).
- Die by poison or accident.
- Done by hand.
- By word of mouth.
- Older by five months.
- It is 10.30 by (not in) my watch.
- By this time.
- Die by thousands.
- Struck by lightning.
- Room ten feet by fifteen.
- Live by the river.
- I did this work all by myself.
- It is 10.30 by my watch.
- I know him by his name.
- In February.
- To be in a place.
- To be in the dark.
- In the sun.
- To be in danger.
- In a difficulty.
- To be in power.
- To be in trouble.
- Ten or twelve in number.
- In a whisper.
- A slope of one in ten.
- In a loud voice.
- In great numbers.
- Rich in minerals.
- Lying in bed.
- Train running in time.
- A lecturer/ reader in (not, on or off) chemistry.
- He is a lecturer in mathematics
- The train is running in time.
- Take the work in hand.
- Speak of him.
- Do not lose sight of the fact.
- Beg a thing of him.
- Made of wood.
- A packet of cigarettes.
- He comes of a good family.
- Born of rich parents.
- Diet of cholera.
- The whole of India.
- The city of Kolkata.
- It was good of you to help me.
- Pressure of English.
- Do not lose sight of the fact.
- He comes of (not from) a good family.
- Professor of English.
- I met him on the road.
- He is on the way to the office.
- I will be at home on Christmas Day.
- I saw the news on T.V.
- On 1 set may.
- On Christmas day.
- On new year.
- To lie on one’s bed.
- To be on the way.
- A speech on the subject.
- Come on holiday.
- A picture on the wall.
- Write on this paper.
- A house on fire.
- To play on a musical instrument.
- Live on rice.
- On a small income.
- Live on capital invested.
- He is on (not in) that committee
- Kolkata is on the Hooghly.
- A house on the main road.
- A ring on his finger.
- Shops on both side.
- Underwater or a tree.
- To be under another.
- Under trial.
- Under sentence.
- A post under government.
- Under repair.
- To be under arms.
- Under consideration.
- About ten percent of the people there under arms.
- Your application is under Consideration.
- Get to bed.
- I go to bed at 10 p.m.
- Add this to that
- Sweet to taste.
- They fought to the last man.
- He did it to his cost.
- Sing to the heart.
- Go to room.
- Six minutes to five.
A Must Watch Video on Preposition:
Open to Your Questions
So there you have it: Pronoun in English Grammar.
Now I would like to know what do you think about this article?
More specifically;
Did this article help you?
Do you have any further queries?
Do let me know by leaving a quick comment below.
References [External Links]:
- Six Preposition Rules | Grammar | EnglishClub
- Mastering Grammar Prepositions – Academic English Online
- Page Content
- Sidebar Content
- Main Navigation
- Quick links
- All TIP Sheets
The Eight Parts of Speech
- Prepositions
- Conjunctions
- Interjections
- Basic Sentence Structure
- Sentence Fragments
- Run-on Sentences and Comma Splices
- Sentence Type and Purpose
- Independent and Dependent Clauses: Coordination and Subordination
- Subject Verb Agreement
- Consistent Verb Tense
- Other Phrases: Verbal, Appositive, Absolute
- Pronoun Reference
- Relative Pronouns: Restrictive and Nonrestrictive Clauses
- Avoiding Modifier Problems
- Transitions
- Would, Should, Could
- Achieving Parallelism
- Definite and Indefinite Articles
- Two-Word Verbs
TIP Sheet THE EIGHT PARTS OF SPEECH
There are eight parts of speech in the English language: noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection. The part of speech indicates how the word functions in meaning as well as grammatically within the sentence. An individual word can function as more than one part of speech when used in different circumstances. Understanding parts of speech is essential for determining the correct definition of a word when using the dictionary.
1. NOUN
- A noun is the name of a person, place, thing, or idea.
man... Butte College... house... happiness
A noun is a word for a person, place, thing, or idea. Nouns are often used with an article ( the , a , an ), but not always. Proper nouns always start with a capital letter; common nouns do not. Nouns can be singular or plural, concrete or abstract. Nouns show possession by adding 's . Nouns can function in different roles within a sentence; for example, a noun can be a subject, direct object, indirect object, subject complement, or object of a preposition.
The young girl brought me a very long letter from the teacher , and then she quickly disappeared. Oh my!
See the TIP Sheet on "Nouns" for further information.
2. PRONOUN
- A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun.
She... we... they... it
A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun. A pronoun is usually substituted for a specific noun, which is called its antecedent. In the sentence above, the antecedent for the pronoun she is the girl. Pronouns are further defined by type: personal pronouns refer to specific persons or things; possessive pronouns indicate ownership; reflexive pronouns are used to emphasize another noun or pronoun; relative pronouns introduce a subordinate clause; and demonstrative pronouns identify, point to, or refer to nouns.
The young girl brought me a very long letter from the teacher, and then she quickly disappeared. Oh my!
See the TIP Sheet on "Pronouns" for further information.
3. VERB
- A verb expresses action or being.
jump... is... write... become
The verb in a sentence expresses action or being. There is a main verb and sometimes one or more helping verbs. (" She can sing." Sing is the main verb; can is the helping verb.) A verb must agree with its subject in number (both are singular or both are plural). Verbs also take different forms to express tense.
The young girl brought me a very long letter from the teacher, and then she quickly disappeared . Oh my!
See the TIP Sheet on "Verbs" for more information.
4. ADJECTIVE
- An adjective modifies or describes a noun or pronoun.
pretty... old... blue... smart
An adjective is a word used to modify or describe a noun or a pronoun. It usually answers the question of which one, what kind, or how many. (Articles [a, an, the] are usually classified as adjectives.)
See the TIP Sheet on "Adjectives" for more information.
5. ADVERB
- An adverb modifies or describes a verb, an adjective, or another adverb.
gently... extremely... carefully... well
An adverb describes or modifies a verb, an adjective, or another adverb, but never a noun. It usually answers the questions of when, where, how, why, under what conditions, or to what degree. Adverbs often end in -ly.
See the TIP Sheet on "Adverbs" for more information.
6. PREPOSITION
- A preposition is a word placed before a noun or pronoun to form a phrase modifying another word in the sentence.
by... with.... about... until
(by the tree, with our friends, about the book, until tomorrow)
A preposition is a word placed before a noun or pronoun to form a phrase modifying another word in the sentence. Therefore a preposition is always part of a prepositional phrase. The prepositional phrase almost always functions as an adjective or as an adverb. The following list includes the most common prepositions:
See the TIP Sheet on "Prepositions" for more information.
7. CONJUNCTION
- A conjunction joins words, phrases, or clauses.
and... but... or... while... because
A conjunction joins words, phrases, or clauses, and indicates the relationship between the elements joined. Coordinating conjunctions connect grammatically equal elements: and, but, or, nor, for, so, yet. Subordinating conjunctions connect clauses that are not equal: because, although, while, since, etc. There are other types of conjunctions as well.
The young girl brought me a very long letter from the teacher, and then she quickly disappeared. Oh my!
See the TIP Sheet on "Conjunctions" for more information.
8. INTERJECTION
- An interjection is a word used to express emotion.
Oh!... Wow!... Oops!
An interjection is a word used to express emotion. It is often followed by an exclamation point.
The young girl brought me a very long letter from the teacher, and then she quickly disappeared. Oh my !
See the TIP Sheet on "Interjections" for more information.
Home | Calendars | Library | Bookstore | Directory | Apply Now | Search for Classes | Register | Online Classes | MyBC Portal MyBC -->
Butte College | 3536 Butte Campus Drive, Oroville CA 95965 | General Information (530) 895-2511
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Parts of speech
The 8 Parts of Speech | Chart, Definition & Examples

A part of speech (also called a word class ) is a category that describes the role a word plays in a sentence. Understanding the different parts of speech can help you analyze how words function in a sentence and improve your writing.
The parts of speech are classified differently in different grammars, but most traditional grammars list eight parts of speech in English: nouns , pronouns , verbs , adjectives , adverbs , prepositions , conjunctions , and interjections . Some modern grammars add others, such as determiners and articles .
Many words can function as different parts of speech depending on how they are used. For example, “laugh” can be a noun (e.g., “I like your laugh”) or a verb (e.g., “don’t laugh”).
Table of contents
- Prepositions
- Conjunctions
- Interjections
Other parts of speech
Interesting language articles, frequently asked questions.
A noun is a word that refers to a person, concept, place, or thing. Nouns can act as the subject of a sentence (i.e., the person or thing performing the action) or as the object of a verb (i.e., the person or thing affected by the action).
There are numerous types of nouns, including common nouns (used to refer to nonspecific people, concepts, places, or things), proper nouns (used to refer to specific people, concepts, places, or things), and collective nouns (used to refer to a group of people or things).
Ella lives in France .
Other types of nouns include countable and uncountable nouns , concrete nouns , abstract nouns , and gerunds .
Check for common mistakes
Use the best grammar checker available to check for common mistakes in your text.
Fix mistakes for free
A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun. Pronouns typically refer back to an antecedent (a previously mentioned noun) and must demonstrate correct pronoun-antecedent agreement . Like nouns, pronouns can refer to people, places, concepts, and things.
There are numerous types of pronouns, including personal pronouns (used in place of the proper name of a person), demonstrative pronouns (used to refer to specific things and indicate their relative position), and interrogative pronouns (used to introduce questions about things, people, and ownership).
That is a horrible painting!
A verb is a word that describes an action (e.g., “jump”), occurrence (e.g., “become”), or state of being (e.g., “exist”). Verbs indicate what the subject of a sentence is doing. Every complete sentence must contain at least one verb.
Verbs can change form depending on subject (e.g., first person singular), tense (e.g., simple past), mood (e.g., interrogative), and voice (e.g., passive voice ).
Regular verbs are verbs whose simple past and past participle are formed by adding“-ed” to the end of the word (or “-d” if the word already ends in “e”). Irregular verbs are verbs whose simple past and past participles are formed in some other way.
“I’ve already checked twice.”
“I heard that you used to sing .”
Other types of verbs include auxiliary verbs , linking verbs , modal verbs , and phrasal verbs .
An adjective is a word that describes a noun or pronoun. Adjectives can be attributive , appearing before a noun (e.g., “a red hat”), or predicative , appearing after a noun with the use of a linking verb like “to be” (e.g., “the hat is red ”).
Adjectives can also have a comparative function. Comparative adjectives compare two or more things. Superlative adjectives describe something as having the most or least of a specific characteristic.
Other types of adjectives include coordinate adjectives , participial adjectives , and denominal adjectives .
An adverb is a word that can modify a verb, adjective, adverb, or sentence. Adverbs are often formed by adding “-ly” to the end of an adjective (e.g., “slow” becomes “slowly”), although not all adverbs have this ending, and not all words with this ending are adverbs.
There are numerous types of adverbs, including adverbs of manner (used to describe how something occurs), adverbs of degree (used to indicate extent or degree), and adverbs of place (used to describe the location of an action or event).
Talia writes quite quickly.
Other types of adverbs include adverbs of frequency , adverbs of purpose , focusing adverbs , and adverbial phrases .
A preposition is a word (e.g., “at”) or phrase (e.g., “on top of”) used to show the relationship between the different parts of a sentence. Prepositions can be used to indicate aspects such as time , place , and direction .
I left the cup on the kitchen counter.
A conjunction is a word used to connect different parts of a sentence (e.g., words, phrases, or clauses).
The main types of conjunctions are coordinating conjunctions (used to connect items that are grammatically equal), subordinating conjunctions (used to introduce a dependent clause), and correlative conjunctions (used in pairs to join grammatically equal parts of a sentence).
You can choose what movie we watch because I chose the last time.
An interjection is a word or phrase used to express a feeling, give a command, or greet someone. Interjections are a grammatically independent part of speech, so they can often be excluded from a sentence without affecting the meaning.
Types of interjections include volitive interjections (used to make a demand or request), emotive interjections (used to express a feeling or reaction), cognitive interjections (used to indicate thoughts), and greetings and parting words (used at the beginning and end of a conversation).
Ouch ! I hurt my arm.
I’m, um , not sure.
The traditional classification of English words into eight parts of speech is by no means the only one or the objective truth. Grammarians have often divided them into more or fewer classes. Other commonly mentioned parts of speech include determiners and articles.
- Determiners
A determiner is a word that describes a noun by indicating quantity, possession, or relative position.
Common types of determiners include demonstrative determiners (used to indicate the relative position of a noun), possessive determiners (used to describe ownership), and quantifiers (used to indicate the quantity of a noun).
My brother is selling his old car.
Other types of determiners include distributive determiners , determiners of difference , and numbers .
An article is a word that modifies a noun by indicating whether it is specific or general.
- The definite article the is used to refer to a specific version of a noun. The can be used with all countable and uncountable nouns (e.g., “the door,” “the energy,” “the mountains”).
- The indefinite articles a and an refer to general or unspecific nouns. The indefinite articles can only be used with singular countable nouns (e.g., “a poster,” “an engine”).
There’s a concert this weekend.
If you want to know more about nouns , pronouns , verbs , and other parts of speech, make sure to check out some of our language articles with explanations and examples.
Nouns & pronouns
- Common nouns
- Proper nouns
- Collective nouns
- Personal pronouns
- Uncountable and countable nouns
- Verb tenses
- Phrasal verbs
- Types of verbs
- Active vs passive voice
- Subject-verb agreement
A is an indefinite article (along with an ). While articles can be classed as their own part of speech, they’re also considered a type of determiner .
The indefinite articles are used to introduce nonspecific countable nouns (e.g., “a dog,” “an island”).
In is primarily classed as a preposition, but it can be classed as various other parts of speech, depending on how it is used:
- Preposition (e.g., “ in the field”)
- Noun (e.g., “I have an in with that company”)
- Adjective (e.g., “Tim is part of the in crowd”)
- Adverb (e.g., “Will you be in this evening?”)
As a part of speech, and is classed as a conjunction . Specifically, it’s a coordinating conjunction .
And can be used to connect grammatically equal parts of a sentence, such as two nouns (e.g., “a cup and plate”), or two adjectives (e.g., “strong and smart”). And can also be used to connect phrases and clauses.
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked, what is a collective noun | examples & definition.
- What Is an Adjective? | Definition, Types & Examples
- Using Conjunctions | Definition, Rules & Examples
More interesting articles
- Definite and Indefinite Articles | When to Use "The", "A" or "An"
- Ending a Sentence with a Preposition | Examples & Tips
- What Are Prepositions? | List, Examples & How to Use
- What Is a Determiner? | Definition, Types & Examples
- What Is an Adverb? Definition, Types & Examples
- What Is an Interjection? | Examples, Definition & Types
"I thought AI Proofreading was useless but.."
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
- Parts of Speech
- Sentence Structure
- Sentence Types
- Rules & Usage
- Punctuation
- How to Diagram
- Diagramming Index
- Diagramming Together
- Contact & FAQ
- Stream the Documentary
- Testimonials
Download your free grammar guide here.
What are the parts of speech?
Today's the day for you to learn about this important grammatical concept! But first...let's see what the parts of speech have to do with your clothes.

Imagine that it's laundry day, and you've just finished washing and drying your clothes. You dump the contents of the laundry basket onto your bed, and you begin to organize everything. You fold matching socks together, you create a pile of perfectly folded shirts that you would be proud to show Marie Kondo, and you do the same thing with your pants, jackets, and everything else.
In the same way that we organize our clothes into groups based on each item's function and features, we organize our words into categories based on each word's function and features. We call these categories of words the parts of speech .
Some people categorize words into eight parts of speech, and some people categorize them into nine parts of speech. Neither one is wrong; they're just two ways of looking at things. We'll go over these categories below. Here at English Grammar Revolution, we categorize words into eight groups, but I'll tell you about the ninth one as well.
There's one important thing for you to know before we look at these categories: most words can function as more than one part of speech . They will only do one job at a time, but they can do different things in different sentences. Look at the word love in the following sentences.
My love of grammar inspired me to make this website.
Here, love is functioning as a noun. It's the subject of the sentence.
I love you.
Now, love is acting as a verb ! It's telling us an action.
The only way we can know how to categorize a word is to look at how it's acting within a sentence.
Okay, let's check out the parts of speech!
The 8 Parts of Speech
Nouns name people, places, things, or ideas. They're important parts of our sentences because they perform important jobs (subjects, direct objects, predicate nouns, etc.).
A peacock walked through our yard .
The dog howled during the night , and it woke up our whole family .
Sometimes people get bogged down with this part of speech because there are also many subcategories of nouns. This is similar to the way that we have subcategories for our clothes. You may have a whole drawer full of pants, but you may also have different types of pants that you use for different purposes (workout pants, lounge pants, work pants, etc.). This is similar to the way that we can further categorize nouns into smaller groups.
Here are a few of the subcategories of nouns: proper nouns, common nouns , collective nouns , possessive nouns , and compound nouns.
Tip : Other parts of speech also have subcategories. If you're studying this information for the first time, ignore the subcategories and focus on learning about each broader category.
2. Pronouns
Pronouns take the place of nouns. When most people hear the word pronoun , they think of words like I, we, me, he, she, and they . These are indeed all pronouns, but they're a part of a subcategory called personal pronouns. Know that there are other kinds of pronouns out there as well. Here are some examples: myself, his, someone , and who .
Here are a few of the subcategories of pronouns: reflexive pronouns , indefinite pronouns , possessive pronouns , and relative pronouns .
When we walked across the bridge, we saw someone who knows you .
I will fix the dishwasher myself .
Verbs show actions or states of being. They are integral elements of sentences .
The shuttle will fly into space.
The loving mother comforted and soothed the baby.
In the Montessori tradition of education, they use a large red circle or ball to symbolize a verb, and they often teach children to think of verbs as a sun providing the energy of a sentence. Isn't that a lovely way to think of verbs?
I know that you're getting tired of hearing about subcategories, but linking verbs, action verbs, and helping verbs are described on the verb page here .
Modal verbs are described on that link, and you can learn even more about action verbs and linking verbs from those links.
4. Adjectives
Adjectives describe, or modify , nouns and pronouns. I like to think of them as adding color to language. It would be hard to describe a beautiful sunset or the way a touching story makes us feel without using adjectives.
The wise, handsome owl had orange eyes.
The caring father rocked the baby.
One helpful strategy for learning about and identifying adjectives is to learn how they are diagrammed . Sentence diagrams are pictures of sentences that help us see how all of the words are grammatically related. Since adjectives modify nouns and pronouns, we diagram them on slanted lines under the nouns/pronouns that they are modifying.
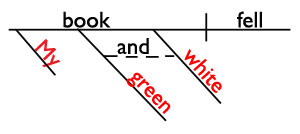
My green and white book fell.
Book is a noun. It's the subject of this sentence. My, green , and white are all adjectives describing book , so we diagram them on slanted lines underneath book . Isn't that a great way to SEE what adjectives do?
Nine Parts of Speech
When people categorize words into eight parts of speech, they say that articles/determiners ( a, an, the, this, that, etc. ) are subcategories of adjectives.
When people categorize words into nine parts of speech, they say that articles/determiners make up their own category and are not a part of the adjective category.
Adverbs modify (describe) verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs. Adverbs are similar to adjectives in that they both modify things.
The extremely cute koala hugged its mom very tightly .
The dog howled loudly .
Sentence diagrams also make it really easy to see what adverbs do. Take a look at this diagram. What do you notice about the way the adverbs are diagrammed?
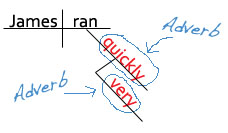
James ran very quickly.
Did you notice that the adverbs are diagrammed on slanted lines under the words that they are modifying?
Ran is a verb. Quickly is an adverb telling us more about the verb ran . Very is an adverb telling us more about the adverb quickly .
Doesn't the diagram make it easier to SEE what adverbs do?
6. Prepositions
Prepositions are probably the most difficult part of speech to explain, but people generally have an easier time understanding them when they look at lots of examples. So...let's start with some examples of commonly used prepositions!
in, for, of, off, if, until
The frog sat in the flower.
The baby cried for a long time.
I'm so convinced that memorizing some of the prepositions will be helpful to you that I'll teach you a preposition song .
Okay, now that we've looked at some examples, let's look at the definition of a preposition.
Prepositions show the relationship between a noun or a pronoun and some other word in the rest of the sentence.
Sentence diagrams will come to the rescue again to help us visualize what prepositions do. Think of prepositions as "noun hooks" or "noun bridges." In the diagram below, notice how the preposition down links the noun tree to the rest of the sentence.
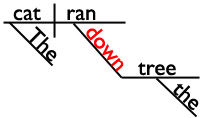
The cat ran down the tree.
Since prepositions always function as "noun hooks," they'll always be accompanied by a noun. The preposition plus its noun is called a prepositional phrase .
If you find a word from the preposition list that's not a part of a prepositional phrase, it's not functioning as a preposition. (You remember that words can function as different parts of speech , right?)
7. Conjunctions
Conjunctions join things together. They can join words or groups of words (phrases and clauses).
The hummingbird sat and waited .
The conjunction and is joining the words sat and waited .
Do you live near the park or near the hospital ?
The conjunction or is joining the phrases near the park and near the hospital.
The two conjunctions we just looked at ( and and or ) belong to a subcategory called coordinating conjunctions, but there are other subcategories of conjunctions as well. The other one that we use most often is subordinating conjunctions . Subordinating conjunctions are a little trickier to learn because they involve a more complicated concept ( dependent adverb clauses ).
For now, just know that all conjunctions, no matter what type they are, connect things together. In fact, let's LOOK at how they do this by looking at a sentence diagram.
Here is a sentence diagram showing how the coordinating conjunction and connects two clauses.

She cooked, and he cleaned.
8. Interjections
Interjections show excitement or emotion.
Wow ! That jump was amazing!
Phew , the baby finally fell asleep.
They are different from the other parts of speech in that they're not grammatically related to the rest of the sentence, and the way that we diagram them reflects that. Look at how we diagram interjections :
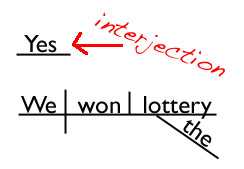
Yes ! We won the lottery!
The interjection yes sit sits there on its own line floating above the rest of the sentence. This helps show that it's not grammatically related to the other words in the sentence.
It's time to review what we covered on this page.
- We can categorize the words that we use into groups based on their functions and features. We call these groups the parts of speech.
- Many words can function as multiple parts of speech. You need to look at each word in the context of a sentence in order to say what part of speech it is.
- The eight parts of speech are nouns, pronouns, adjectives, verbs, adverbs, conjunctions, prepositions, and interjections.
- You just learned about all of the parts of speech. Give yourself a high five!
If you'd like to teach or learn grammar the easy way—with sentence diagrams—check out our Get Smart Grammar Program .
It starts from the very beginning and teaches you grammar and sentence diagramming in easy, bite-size lessons.

Hello! I'm Elizabeth O'Brien, and my goal is to get you jazzed about grammar.
This is original content from https://www.english-grammar-revolution.com/parts-of-speech.html

Our Free Guide Gives You A Fun Way
To Teach And Learn The Basics v

Elizabeth O'Brien is the creator of Grammar Revolution.
Her lessons are guaranteed to give you more confidence in your communication skills and make you smile. :)
Other Helpful Resources
- Learn more about how Montessori classrooms teach the parts of speech .
Sentences & Diagrams
Shop & log in.
|
|
|
|
Home BLOG SHOP Contact PRIVACY POLICY Your Purchases
Copyright © 2009 - 2024 Grammar Revolution. All Rights Reserved.
JOIN OUR PRIVATE FACEBOOK GROUP RSS INSTAGRAM
Parts of Speech
Perfect english grammar.

- Noun (apple, table, book, beauty, sky, life)
- Verb (be, want, go, do, imagine)

Hello! I'm Seonaid! I'm here to help you understand grammar and speak correct, fluent English.

Read more about our learning method

Parts of Speech
What are the parts of speech, a formal definition.
Table of Contents
The Part of Speech Is Determined by the Word's Function
Are there 8 or 9 parts of speech, the nine parts of speech, (1) adjective, (3) conjunction, (4) determiner, (5) interjection, (7) preposition, (8) pronoun, why the parts of speech are important, video lesson.

- You need to dig a well . (noun)
- You look well . (adjective)
- You dance well . (adverb)
- Well , I agree. (interjection)
- My eyes will well up. (verb)
- red, happy, enormous
- Ask the boy in the red jumper.
- I live in a happy place.
- I caught a fish this morning! I mean an enormous one.
- happily, loosely, often
- They skipped happily to the counter.
- Tie the knot loosely so they can escape.
- I often walk to work.
- It is an intriguingly magic setting.
- He plays the piano extremely well.
- and, or, but
- it is a large and important city.
- Shall we run to the hills or hide in the bushes?
- I know you are lying, but I cannot prove it.
- my, those, two, many
- My dog is fine with those cats.
- There are two dogs but many cats.
- ouch, oops, eek
- Ouch , that hurt.
- Oops , it's broken.
- Eek! A mouse just ran past my foot!
- leader, town, apple
- Take me to your leader .
- I will see you in town later.
- An apple fell on his head .
- in, near, on, with
- Sarah is hiding in the box.
- I live near the train station.
- Put your hands on your head.
- She yelled with enthusiasm.
- she, we, they, that
- Joanne is smart. She is also funny.
- Our team has studied the evidence. We know the truth.
- Jack and Jill went up the hill, but they never returned.
- That is clever!
- work, be, write, exist
- Tony works down the pit now. He was unemployed.
- I will write a song for you.
- I think aliens exist .
Are you a visual learner? Do you prefer video to text? Here is a list of all our grammar videos .
Video for Each Part of Speech
The Most Important Writing Issues
The top issue related to adjectives.
| Don't write... | Do write... |
|---|---|
| very happy boy | delighted boy |
| very angry | livid |
| extremely posh hotel | luxurious hotel |
| really serious look | stern look |
The Top Issue Related to Adverbs
- Extremely annoyed, she stared menacingly at her rival.
- Infuriated, she glared at her rival.
The Top Issue Related to Conjunctions
- Burger, Fries, and a shake
- Fish, chips and peas
The Top Issue Related to Determiners
The Top Issue Related to Interjections
The top issue related to nouns, the top issue related to prepositions, the top issue related to pronouns, the top issue related to verbs.
| Unnatural (Overusing Nouns) | Natural (Using a Verb) |
|---|---|
| They are in agreement that he was in violation of several regulations. | They agree he violated several regulations. |
| She will be in attendance to present a demonstration of how the weather will have an effect on our process. | She will attend to demonstrate how the weather will affect our process. |
- Crack the parts of speech to help with learning a foreign language or to take your writing to the next level.

This page was written by Craig Shrives .
You might also like...
Help us improve....

Was something wrong with this page?

Use #gm to find us quicker .

Create a QR code for this, or any, page.
mailing list
grammar forum
teachers' zone
Confirmatory test.
This test is printable and sendable
expand to full page
show as slides
download as .doc
print as handout
send as homework
display QR code
Parts of Speech
What is a Part of Speech?
We can categorize English words into 9 basic types called "parts of speech" or "word classes". It's quite important to recognize parts of speech. This helps you to analyze sentences and understand them. It also helps you to construct good sentences.
Parts of Speech Table
Parts of speech examples.
- Parts of Speech Quiz
This is a summary of the 9 parts of speech*. You can find more detail if you click on each part of speech.
| part of speech | function or "job" | example words | example sentences |
|---|---|---|---|
| action or state | (to) be, have, do, like, work, sing, can, must | EnglishClub a website. I EnglishClub. | |
| thing or person | pen, dog, work, music, town, London, teacher, John | This is my . He lives in my . We live in . | |
| describes a noun | good, big, red, well, interesting | My dogs are . I like dogs. | |
| limits or "determines" a noun | a/an, the, 2, some, many | I have dogs and rabbits. | |
| describes a verb, adjective or adverb | quickly, silently, well, badly, very, really | My dog eats . When he is hungry, he eats quickly. | |
| replaces a noun | I, you, he, she, some | Tara is Indian. is beautiful. | |
| links a noun to another word | to, at, after, on, but | We went school Monday. | |
| joins clauses or sentences or words | and, but, when | I like dogs I like cats. I like cats dogs. I like dogs I don't like cats. | |
| short exclamation, sometimes inserted into a sentence | oh!, ouch!, hi!, well | ! That hurts! ! How are you? , I don't know. |
- lexical Verbs ( work, like, run )
- auxiliary Verbs ( be, have, must )
- Determiners may be treated as adjectives, instead of being a separate part of speech.
Here are some examples of sentences made with different English parts of speech:
| verb |
|---|
| Stop! |
| noun | verb |
|---|---|
| John | works. |
| noun | verb | verb |
|---|---|---|
| John | is | working. |
| pronoun | verb | noun |
|---|---|---|
| She | loves | animals. |
| noun | verb | noun | adverb |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tara | speaks | English | well. |
| noun | verb | adjective | noun |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tara | speaks | good | English. |
| pronoun | verb | preposition | determiner | noun | adverb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| She | ran | to | the | station | quickly. |
| pron. | verb | adj. | noun | conjunction | pron. | verb | pron. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| She | likes | big | snakes | but | I | hate | them. |
Here is a sentence that contains every part of speech:
| interjection | pron. | conj. | det. | adj. | noun | verb | prep. | noun | adverb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Well, | she | and | my | young | John | walk | to | school | slowly. |
Words with More Than One Job
Many words in English can have more than one job, or be more than one part of speech. For example, "work" can be a verb and a noun; "but" can be a conjunction and a preposition; "well" can be an adjective, an adverb and an interjection. In addition, many nouns can act as adjectives.
To analyze the part of speech, ask yourself: "What job is this word doing in this sentence?"
In the table below you can see a few examples. Of course, there are more, even for some of the words in the table. In fact, if you look in a good dictionary you will see that the word " but " has six jobs to do:
- verb, noun, adverb, pronoun, preposition and conjunction!
| word | part of speech | example |
|---|---|---|
| work | noun | My is easy. |
| verb | I in London. | |
| but | conjunction | John came Mary didn't come. |
| preposition | Everyone came Mary. | |
| well | adjective | Are you ? |
| adverb | She speaks . | |
| interjection | ! That's expensive! | |
| afternoon | noun | We ate in the . |
| noun acting as adjective | We had tea. |
People often ask
FAQ: frequently asked parts of speech questions
Prepositions in English Grammar
Image Source/Getty Images
Simple Prepositions
Complex prepositions, identifying prepositional phrases, ending a sentence with a preposition, prepositions functioning as another part of speech, deverbal prepositions.
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
In English grammar , a preposition is a word that shows the relationship between a noun or pronoun and other words in a sentence. Prepositions are words like in and out , above and below , and to and from, and they're words we use all the time.
How useful are prepositions? Just look at how many prepositions are italicized in this simple sentence from E.B. White's Charlotte's Web : " For the first few days of his life, Wilbur was allowed to live in a box near the stove in the kitchen."
Prepositions are one of the basic parts of speech and are among the words that we use most when composing sentences. They are also a member of a closed word class , meaning that it is very rare for a new preposition to enter the language. There are only about 100 of them in English.
Prepositions often refer to location (" under the table"), direction (" to the south"), or time (" past midnight"). They can also be used to convey other relationships: agency ( by ), comparison ( like, as . . . as ), possession ( of ), purpose ( for ), or source ( from, out of ).
Many prepositions are made up of only one word and are called simple prepositions. These include short and very common words like as, at, by, for, and of. You also use prepositions such as about, between, into, like, onto, since, than, through, with, within, and without to show a relationship between words.
There are many occasions where you might confuse prepositions. For example, sometimes it is difficult to know when you should use in, into, on, or at . This is because their meanings are very similar, so you have to look at the context of the sentence.
Many prepositions have an opposite as well. For instance, you can use before or after, inside or outside, off or on, over or under, and up or down.
Quite a few prepositions express the relationship of things in space. Examples of these include aboard, across, amid, among, around, atop, behind, beneath, beside, beyond, near, over, round, and upon.
Prepositions can also refer to time. Among the most common are after, before, during, till, and until.
Other prepositions have unique uses or can be used in multiple ways. Some of these include about, against, along, despite, regarding, throughout, toward, and unlike.
In addition to the simple prepositions, several word groups can perform the same grammatical function. These are called complex prepositions . They are two- or three-word units that combine one or two simple prepositions with another word.
Within this category, you have phrases like in addition to and such as. Whenever you say thanks to or in between , you are also using a complex preposition.
Prepositions are not in the habit of standing alone. A word group with a preposition at the head followed by an object (or complement) is called a prepositional phrase . The object of a preposition is typically a noun or pronoun: Gus put the horse before the cart.
Prepositional phrases add meaning to the nouns and verbs in sentences. They usually tell us where, when, or how and the words of a prepositional phrase can often be rearranged .
A prepositional phrase may do the work of an adjective and modify a noun: The student in the back row began to snore loudly. It may also function as an adverb and modify a verb: Buster fell asleep during class.
Learning to identify prepositional phrases is often a matter of practice. After some time you will come to realize how frequently we rely on them.
You may have a heard the "rule" that you should never end a sentence with a preposition . This is one of those "rules" that you don't have to put up with. It is based on the etymology of " pre position," from the Greek for "put in front," as well as a false analogy to Latin.
As long ago as 1926, Henry Fowler dismissed the rule about " preposition stranding " as "a cherished superstition" ignored by major writers from Shakespeare to Thackeray. In fact, in "A Dictionary of Modern English Usage" he said, "the remarkable freedom enjoyed by English in putting its prepositions late and omitting its relatives is an important element in the flexibility of the language."
Essentially, you can ignore this rule, and you can cite Fowler to anyone who tells you otherwise. Go ahead and end your sentence with a preposition if you want to.
Just because you see one of the prepositions we've mentioned used, does not mean that they are being used as a preposition. It depends on the circumstances, and this is one of those tricky parts of the English language, so don't let these fool you.
Certain prepositions ( after, as, before, since, until ) serve as subordinating conjunctions when they're followed by a clause :
- You better get out of town before sundown. ( Before is used as a preposition.)
- Many people run out of ideas long before they run out of words. ( Before is used as a conjunction.)
Some prepositions (including about, across, around, before, down, in, on, out, and up ) also moonlight as adverbs . These are sometimes called prepositional adverbs or adverbial particles .
- Beth walked up the driveway. (The preposition up is followed by the object.)
- Beth looked up . (The prepositional adverb up is modifying the verb looked. )
Transitive prepositions that take the same form as -ing participles or -ed participles are called deverbal prepositions. It is a rather short list, but it is important to understand that these are also prepositions.
- according (to)
- allowing (for)
- pertaining (to)
Fowler H. A Dictionary of Modern English Usage. 2nd ed. New York, NY: Oxford University Press; 1965.
- The 9 Parts of Speech: Definitions and Examples
- Pronoun Definition and Examples
- What Is an Adverb in English Grammar?
- Definition and Examples of Interjections in English
- Closed Class Words
- Prepositional Adverbs
- Examples and Usage of Conjunctions in English Grammar
- Postposition (Grammar)
- Understanding the Types of Verbs in English Grammar
- Is It Always Wrong to End a Sentence With a Preposition?
- Definition and Examples of Function Words in English
- Objects in English Grammar
- What Are the Parts of a Prepositional Phrase?
- Understanding the Types of Nouns in English Grammar
- A Definition Plus Helpful Examples of Particles in English Grammar
- Modern English (language)
Parts of Speech: Essential Components of Language
Understanding the parts of speech is essential for anyone looking to improve their grasp on the English language. There are traditionally eight parts of speech, each serving a distinct function within a sentence. By familiarizing oneself with the functions and rules governing each part of speech, one can develop better communication skills, whether it’s through written or spoken language.
Overview of Parts of Speech

Nouns are words that denote a person, place, or thing. In a sentence, nouns answer the questions who and what. For example, in the sentence “The dog ran after the ball,” there are two nouns: “dog” and “ball.” Nouns can be further classified into common nouns, proper nouns, and collective nouns.
- Common nouns: general names for people, places, or things (e.g., dog, city)
- Proper nouns : specific names of a particular person, place, or thing (e.g., John, London)
- Collective nouns: names for groups of things (e.g., flock, team)
2. Pronouns
Pronouns are words that replace nouns in a sentence. They help avoid repetition and make sentences less monotonous. For example, in the sentence “She gave her book to him,” the pronouns “she,” “her,” and “him” replace the respective nouns. Pronouns can be classified as:
- Personal pronouns : I, you, he, she
- Demonstrative pronouns : this, that, these, those
- Possessive pronouns: mine, yours, his, hers
- Reflexive pronouns: myself, yourself, himself, herself
3. Adjectives
Adjectives are words that describe or modify nouns or pronouns. They provide additional information about the noun/pronoun, such as size, color, or emotion. For example, in the sentence “The red ball is big,” “red” and “big” are adjectives.
Verbs are words that express an action, occurrence, or state of being. They usually indicate what the subject (noun or pronoun) of the sentence is doing. For example, in the sentence “The dog barks,” “barks” is the verb. Verbs can be classified as:
- Action verbs: run, jump, eat, think
- Linking verbs : be, seem, become, appear
- Helping/auxiliary verbs : have, do, will, should
Adverbs are words that modify or describe verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. They provide additional information about the action or quality of an action, such as how, when, or where it took place. For example, in the sentence “The dog barks loudly,” “loudly” is an adverb.
6. Prepositions
Prepositions are words that show the relationship between a noun or a pronoun and other words in a sentence. They usually indicate direction, location, or time. Common prepositions include:
- Direction : to, from, across, through, towards
- Location : in, on, at, under, above
- Time : before, after, during, since, until
7. Conjunctions
Conjunctions are words that connect words or groups of words in sentences. They help form complex sentences and provide a flow of ideas. There are three main types of conjunctions:
- Coordinating conjunctions : and, but, or, for, so (connect words, phrases, or clauses of equal importance)
- Subordinating conjunctions : because, if, although, when (introduce dependent clauses)
- Correlative conjunctions : either…or, neither…nor, both…and (work in pairs to connect similar elements)
8. Interjections
Interjections are short, abrupt words or phrases that express strong emotion or surprise. They are usually set apart from the rest of the sentence by punctuation, such as an exclamation mark or a comma. Examples of interjections include:
- Surprise: oh, wow, ouch
- Agreement: yes, indeed, exactly
- Disagreement: no, nonsense, definitely not
9. Articles
Articles are a type of determiner that precede nouns to specify the noun’s definiteness (whether it is specific or general) and can be classified as:
- Definite article: the (refers to a specific noun)
- Indefinite articles : a, an (refers to a non-specific noun)
Sentence Examples for the 8 Parts of Speech
In this section, we will provide examples of sentences that illustrate the 8 parts of speech in English. The parts of speech include nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections.
| Parts of Speech | Examples |
|---|---|
| Dog | The chased the mailman down the street. |
| Books | Sarah loves reading in the library. |
| She | decided to take up swimming lessons. |
| They | went to the movies together. |
| Jumps | The cat onto the couch. |
| Is | Helen an excellent musician. |
| Happy | The child played with the new toy. |
| Beautiful | She wore a dress to the event. |
| Quickly | The car sped down the road. |
| Softly | She spoke during the presentation. |
| On | The pen is the table. |
| Through | She walked the park. |
| And | She likes pizza pasta. |
| But | I want to go for a run, it’s raining outside. |
| Ouch | That hurt. |
| Wow | What an incredible view. |
Word Classes and Categories
Parts of speech in a language can be subcategorized into word classes and categories, making it easier to study and understand grammar. Word classes can be defined as groups of words that share similar linguistic properties, while categories refer to the roles they play in sentences.
There are generally two basic types of word classes: open and closed. Open word classes are the ones that regularly acquire new words as the language evolves. These include nouns, adjectives, adverbs, and verbs. On the other hand, closed word classes comprise pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions, articles/determiners, and interjections. Closed classes usually remain constant over time, with new words being infrequent additions.
Some major word class categories are:
- Nouns : These represent people, places, things, or ideas. Examples include “dog,” “city,” and “happiness.”
- Verbs : These express actions, states, or occurrences. Examples include “run,” “is,” and “become.”
- Adjectives : These describe qualities or characteristics of nouns. Examples include “tall,” “red,” and “happy.”
- Adverbs : These modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. Examples include “quickly,” “very,” and “well.”
Word classes can be further divided into subcategories based on their specific functions or forms. For instance, nouns can be categorized as proper nouns (e.g., “John”) or common nouns (e.g., “man”), while verbs can be classified as transitive (e.g., “eat”) or intransitive (e.g., “sleep”).
Dictionaries play a crucial role in defining word classes by providing definitions, grammatical information, and usage examples for each word. It helps users understand which category a word belongs to and how it functions in a sentence.
English Language Grammar and Structure
Sentence structure.
In the English language, the foundation of grammar lies in the structure of sentences. A sentence consists of words arranged in a specific order, following a set of rules to convey a complete thought. The basic structure of an English sentence consists of a subject, a verb, and an object. For example:
Furthermore, sentences can be simple, compound, or complex, depending on the number of independent and dependent clauses they contain.
Parts of Speech Relationships
English grammar can be broken down into eight primary parts of speech, each with a unique function in the structure of sentences. These parts of speech are as follows:
- Nouns : They represent people, animals, things, or ideas. Examples: dog, city, love, time.
- Pronouns : These words replace nouns to avoid repetition, such as he, she, they, it, and their.
- Verbs : They describe actions, states, or occurrences, like eat, think, and know.
- Adjectives : Adjectives modify nouns or pronouns, providing more details or descriptions, for instance, red, happy, or large.
- Adverbs : They modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, giving more information about the manner, place, time, or degree. Examples: quickly, very, well.
- Prepositions : These words show the relationship between a noun or pronoun and other words in a sentence, including location or time. Examples: in, on, at, between.
- Conjunctions : They connect words, phrases, or clauses, providing coherence and fluency to sentences. Examples: and, but, because, although.
- Interjections : They express emotions or reactions, often followed by an exclamation point. Examples: oh, wow, ouch, great.
Frequently Asked Questions on Parts of Speech
What are the parts of speech.
The parts of speech are different categories of words based on their usage and role in a sentence. In the English language, there are eight traditional parts of speech: nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections.
Can you provide examples of each part of speech?
Certainly! Here are examples for each part of speech:
- Nouns : cat, book, happiness, city
- Pronouns : he, she, they, whose
- Verbs : run, think, be, have
- Adjectives : happy, large, warm, yellow
- Adverbs : quickly, very, almost, gently
- Prepositions : in, on, of, with
- Conjunctions : and, but, or, yet
- Interjections : ouch, hooray, wow, oh
So interesting page
I love this , let me know can we connect
- Phrases and Clauses
- Parts of a Sentence
- Modal Verbs
- Relative Clauses
- Confusing Words
- Online Grammar Quizzes
- Printable Grammar Worksheets
- Courses to purchase
- Grammar Book
- Grammar Blog
8 Parts of Speech
The 8 parts of speech in English are: Nouns, Adjectives, Adverbs, Verbs, Prepositions, Pronouns, Conjunctions, and Interjections.
A part of speech is a category of words that have similar grammatical functions or properties. In other words, they play similar roles in a sentence. For instance, a verb shows the action of a subject or the subject's state of being.

We'll now look in more detail at the function of each of these parts of speech.
Understanding the 8 Parts of Speech
Nouns are words used to talk about people, places, things, or ideas/concepts. Here are some examples:
- Person: The President
- Place: London
- Thing: Table
- Idea/concept: Neo-liberalism
So it may be naming something we can touch ( e.g. table; book; car ) or something we cannot touch ( e.g. Neo-liberalism; happiness; wish ).
There are both common nouns, used for classes of people, places, things, or ideas/concepts, and proper nouns, which is their given name, always with a capital letter.
Common Nouns
- political party
Proper Nouns
- Chester Avenue
Learn more about the various types of noun >>
Another of the 8 parts of speech are adjectives. They describe nouns or pronouns. They can come before or after the noun/pronoun they describe:
Absolute Adjectives
- The large shopping complex
- The excited child
- She is happy
- It was a shocking film
- Her dress was lovely
- He's a good-looking man
These are absolute adjectives , but they can also be comparative (comparing two or more things) or superlative (showing degree or quality):
Comparative Adjectives
- She's fitter than the others
- Their house is bigger
- I ran faster than you
- Cats are more agile than dogs
- Sue's more tired than Tim
Superlative Adjectives
- She's the fittest
- Their house is the biggest
- I ran the fastest
- Cats are the most agile
- Sue's the most tired
There are various other types of adjective. Learn more about the different types of adjectives >>
Adverbs modify verbs, other adverbs, and adjectives. There are adverbs of manner, time, place and degree . Here are examples of each being modified in relation to verbs, adverbs, and adjectives (the word being modified is underlined):
Adverbs Modifying Verbs
- He runs fast
- Ian quickly left the room
- She spoke slowly
Adverbs Modifying Other Adverbs
- He runs exceptionally fast
- Ian very quickly left the room
- She spoke extremely slowly
Adverbs Modifying Adjectives
- She's really excited
- He's happily married
- The elegantly designed dress is mine
Verbs form part of the predicate of a sentence.
In relation to the subject, they are used to express a physical action (e.g. walk; speak; show) or a mental action (e.g. think; feel; want). They can also express a state of being , mainly with the verb 'to be' but also some others.
Here are some examples:
Physical Action
- He ran home
- They chose the blue one
Mental Activity
- I am thinking about it
- Ian guessed the answer
- She believes in ghosts
State of Being
- She is a police woman
- They seem worried
These though are main verbs. They have many other uses in a sentence so you should read about all the types of verbs further.
Prepositions
Another of the 8 parts of speech are prepositions. These show the relationship between two words or phrases in a sentence. They precede a noun or pronoun.
Commons examples of prepositions are above, up, upon, at, before, behind, since, to, through, under, until, with, within, about, against, along, around, beside, between, down, during, below, by, except, for, from, in, into, like, near, of, off, on, toward.
In these example sentences with prepositions, the two words whose relationship is being expressed are underlined and the prepositions are in bold:
- The book is on the table
- He is the leader of the conservative party
- The boy picked up the toy under the sofa
- This is a present for your mother
Pronouns replace nouns and they prevent us from repeating the noun in a sentence. These are the types of pronouns with some examples:
- Personal e.g. I; you; they; she
- Possessive e.g. mine; yours; his; theirs
- Relative e.g. who; which; that; whom
- Demonstrative e.g. this; these; those
- Reciprocal e.g. one another; each other
- Emphatic / Reflexive e.g. myself; herself; itself; ourselves
- Interrogative e.g. what; which; whom; whose
Here are some examples of these words used in sentences:
- Martha decided she would leave
- Why don't you use his car instead of mine
- Mick is a person who learns quickly
- Shall we buy some of these ?
- They began to argue with each other
- Jenny is pleased with herself
- What time is he coming?
Conjunctions
Conjunctions are the of the 8 parts of speech responsible for joining together words, phrases, or clauses. There are three types:
- Coordinating: and; or; but; so; yet; for; nor
- Correlative: neither/nor; either/or; not only/but also
- Subordinating: e.g. although; because; while; which; where; until
Coordinating Conjunctions
Used to connect like for like words (e.g. noun+noun):
- I like apples and oranges ( 2 nouns )
- His speech was slow but effective ( 2 adjectives )
- Shall I say it loudly or quietly? ( 2 adverbs )
Or simple sentences (independent clauses):
- I find the music annoying but she finds It pleasant
- She came to the lecture late so she missed everything important
- She took her umbrella for it was raining hard
Correlative Conjunctions
Used to join alternative or equal elements:
- He felt neither happy nor sad about it
- Sue had to decide to either quit or carry on
- I went not only to Australia but also to New Zealand
Subordinating Conjunctions
Used to join subordinate clauses to main clauses:
- The government won't vote on the bill until both parties agree
- I'm still not tired although it is late
- I'll eat the dish which you don't like
Interjections
Interjections are words used to express an emotion or a sentiment such as surprise, joy, disgust, fear, excitement, pain, or enthusiasm.
They usually appear at the start of a sentence and are not connected to it grammatically. Here are some examples of interjections in sentences:
- Wow , that's an amazing score!
- Oh , I didn't know you failed the exam
- Well , we better not leave too late
- Ow , that really hurt!
- Ah , I understand now
- Oops , I've forgotten to bring the sandwiches
Learn more about interjections >>
Are there only 8 Parts of Speech?
Sometimes rather than 8 parts of speech, you may see 9 or 10 listed. This is because some people treat articles and determiners as separate categories.
However, when there are only 8 parts of speech considered (as above), this is because as these two types of word modify nouns, they are classified under adjectives.
Now practice what you have learned in our identifying parts of speech quiz
More on Sentence Structure:


Parts of a Sentence: Subject, Verbs, Objects, Predicates, Complements
The main parts of a sentence are subjects, verbs, objects, predicates, and subject complements. All of these have a specific purpose within the structure of a sentence.

Using Object Complements in a Sentence
Using object complements in a sentence enhances your ability to convey specific information about actions and their outcomes.

Types of Clauses in English Grammar - Independent and Dependent Clause
The two types of clauses in English grammar are the independent and dependent clause. Both have a subject and verb which makes them clauses, but while independent clauses express a complete thought, dependent clauses do not. This is the main distinction.

Nominalisation in English Grammar: High Level Writing Tips
Nominalisation is an important aspect of academic writing. This lesson teachers you what this is and how you can use it effectively in your writing.

Subject Complements: Predicate Adjectives and Predicate Nominatives
Here we demystify subject complements, predicate adjectives, and predicate nominatives with simple explanations and examples.

Phrases and Clauses - Building good sentences
Phrases and clauses are the key building blocks of sentences. A clause contains a subject and a verb and can express a complete thought. A phrase does not contain a subject or verb.

How to Use Either and Neither with Examples
Advice on how to use either and neither in English grammar. They can be adjectives, adverbs, pronouns and conjunctions.

Direct and Indirect Objects: The Differences
Direct and indirect objects are key parts of most sentences. A direct object is the receiver of action while indirect object identifies to or for whom or what the action of the verb is performed.

Examples of Parallelism in English Grammar
View examples of parallelism in English grammar that show you correct and incorrect parallel sentences.

Parallelism Grammar Rules (Parallel Structure)
Parallelism is about balancing the grammatical structure of words, phrases and clauses in your sentences. Parallel structure will improve your writing's coherence.
New! Comments
Any questions or comments about the grammar discussed on this page?
Post your comment here.

Sign up for free grammar tips, quizzes and lessons, straight into your inbox
Grammar Rules
Subscribe to grammar wiz:, grammar ebook.

This is an affiliate link
Recent Articles
Gerund or infinitive quiz.
Aug 11, 24 04:34 AM
Use of the Bare Infinitive
Aug 09, 24 01:59 AM
Future Continuous Tense Quiz: Yes/No Questions
Jun 29, 24 11:04 AM
Important Pages
Online Quizzes Grammar Lessons Courses Blog
Connect with Us
Search Site
Privacy Policy / Disclaimer / Terms of Use
Parts of Speech: Definitions, Categories and Examples
By: Author English Study Online
Posted on Last updated: August 28, 2024
Sharing is caring!
In this reference, we will break down each part of speech and provide examples to help you understand their usage. We will also discuss how to identify the different parts of speech in a sentence and provide tips on how to use them correctly. Let’s get started!

Parts of Speech – Created by Englishstudyonline
Table of Contents
What is a Parts of Speech?
A part of speech is a category that describes the role a word plays in a sentence. These roles help you understand how words function in grammar .
There are typically eight main parts of speech in English:
- Nouns : Words that name people, places, things, or ideas.
- Pronouns : Words that replace nouns, such as he, she, it .
- Verbs : Words that describe actions or states, like run, is .
- Adjectives : Words that describe or modify nouns, like blue or quick .
Some grammars list additional parts of speech:
- Adverbs : Words that modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, such as quickly .
- Prepositions : Words that show relationships between a noun (or pronoun) and another word, like in or on .
- Conjunctions : Words that connect clauses, sentences, or words, such as and or but .
- Interjections : Words that express emotion, like wow or oops .
Some sources also include:
- Determiners/Articles : Words that modify nouns and specify which one, like the, a .
Categories of Parts of Speech
Nouns are words that represent people, places, things, or ideas. They are one of the most important parts of speech in English and are used in nearly every sentence. In this section, we will explore the different types of nouns and their functions.
- Common Nouns : General names for people, places, or things. Not capitalized unless at the start of a sentence. Examples : “book,” “city,” “teacher.”
- Proper Nouns : Specific names for people, places, or things. Always capitalized. Examples : “Harry Potter,” “New York City,” “Ms. Johnson.”
- Abstract Nouns : Names for ideas, concepts, or emotions that are intangible. Examples : “love,” “happiness,” “freedom.”
- Collective Nouns : Names for groups of people or things; can be singular or plural. Examples : “team,” “family,” “herd.”
2. Pronouns
Pronouns are words that replace nouns in a sentence. They help avoid repetition and make sentences clearer. Here are different types of pronouns in English:
- Personal Pronouns : Refer to specific people or things and can be subjects or objects. Examples : I/me, you/your/yours, he/him/his, she/her/hers, it/its.
- Demonstrative Pronouns : Point to specific people or things and indicate distance. Examples : this (near), that (far), these (plural, near), those (plural, far).
- Interrogative Pronouns : Used to ask questions. Examples : who (person), whom (person, object), whose (possession).
- Indefinite Pronouns : Refer to non-specific people or things. Examples : anybody, anyone, anything, each, either, everybody, everyone, everything.
- Action Verbs : Describe actions performed by the subject. Examples : Run, Jump, Sing, Dance, Write.
- Linking Verbs : Connect the subject to a noun, pronoun, or adjective that describes it; they do not show action. Examples : Is, Are, Was, Were, Seem.
- Helping Verbs : Work with the main verb to express tense, voice, or mood; they have no meaning on their own. Examples : Am, Is, Are, Was, Were.
4. Adjectives
Adjectives are words that describe or modify nouns or pronouns, giving more information about their qualities, quantity, or identity. Here are three types of adjectives:
- Descriptive Adjectives : Describe the characteristics or qualities of a noun or pronoun. Examples : Beautiful, Tall, Thin, Ugly, Smart, Kind. Sentence Example : “The red car is fast.” (“red” describes the color; “fast” describes the speed).
- Quantitative Adjectives : Indicate the quantity or amount of a noun or pronoun, answering “how much” or “how many.” Examples : Few, Many, Several, Some, All, No. Sentence Example : “I have two apples.” (“two” describes the number of apples).
- Demonstrative Adjectives : Point to specific nouns or pronouns, answering “which one” or “whose.” Examples : This, That, These, Those. Sentence Example : “This book is mine.” (“this” specifies the book).
Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, providing more detail about an action, adverbs of manner, adverbs of place, adverbs of time, adverbs of frequency , adverbs of degree, or intensity.
Examples of adverbs:
- I left my keys here . (Adverb of place)
- She arrived late because she missed the bus. (Adverb of time)
- James visits his grandmother weekly . (Adverb of frequency)
- Please drive carefully on the wet roads. (Adverb of manner)
- She was extremely tired after the long journey. (Adverb of degree)
6. Prepositions
Prepositions are words that show the relationship between a noun or pronoun and other words in a sentence, indicating position, direction, or time.
Prepositions of Time : Indicate when an action takes place. Examples :
- “At” for specific times: “at 2 pm,” “at midnight.”
- “In” for longer periods: “in the morning,” “in October.”
- “On” for dates: “on Monday,” “on July 4th.”
Prepositions of Place : Indicate where something is located. Examples :
- “In” for enclosed spaces: “in the house,” “in the car.”
- “On” for surfaces: “on the table,” “on the floor.”
- “At” for specific locations: “at the park,” “at the beach.”
Prepositions of Direction : Indicate movement from one place to another. Examples :
- “To” for movement towards: “I am going to the store.”
- “From” for movement away: “I am coming from the park.”
- “Towards” for movement in a direction: “I am walking towards the museum.”
7. Conjunctions
Conjunctions are words that connect words, phrases, or clauses in a sentence, helping to create complex sentences and showing relationships between ideas. There are three main types of conjunctions: coordinating, subordinating, and correlative.
Coordinating Conjunctions : Connect words, phrases, or independent clauses of equal importance. Remember them using FANBOYS : for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so. Examples :
- “I like pizza and pasta .”
- “He wanted to go to the beach, but it was raining.”
Subordinating Conjunctions : Connect dependent clauses to independent clauses, showing relationships like cause and effect, time, condition, or contrast. Examples : because, although, while, if, unless, since.
- “Because it was raining, we stayed inside.”
- “While I was studying, my roommate was watching TV.”
Correlative Conjunctions : Work in pairs to connect elements in a sentence, showing a relationship between them. Examples : both…and, either…or, neither…nor, not only…but also.
- “Both my sister and I like to read.”
- “Not only was he late, but he also forgot his homework.”
8. Interjections
In English grammar, interjections are words or phrases that express strong emotions or feelings. They are also known as exclamations and are one of the eight parts of speech in English. Interjections are grammatically independent from the words around them, and they can often be removed from a sentence or context without affecting its basic meaning.
Interjections can be used to express a wide range of emotions, including surprise, joy, anger, frustration, and pain. Some common examples of interjections include “ wow ,” “ ouch ,” “ yay ,” “ oh no ,” and “ oops .” They can be used to add emphasis to a sentence or to convey a particular tone or mood.
9. Articles/Determiners
In English grammar, articles and determiners are words that are used with nouns to provide more information about them. They help us to understand the context and meaning of a sentence.
There are three articles in the English language: “ the ,” “ a, ” and “ an. ” “The” is known as the definite article because it refers to a specific noun that has already been mentioned or is known to the reader. For example, “The cat is sleeping on the sofa.” In this sentence, “the” refers to a specific cat that has already been mentioned or is known to the reader.
“A” and “an” are known as indefinite articles because they refer to any member of a group or class of nouns. “A” is used before words that begin with a consonant sound, while “an” is used before words that begin with a vowel sound. For example, “I need a pen” and “She ate an apple.”
Determiners
Determiners are words that come before a noun to provide more information about it. They can include articles, as well as words like “ this ,” “ that ,” “ these ,” and “ those .”
In addition to these, there are other types of determiners such as possessive determiners (e.g. “my,” “your,” “his,” “her,” “its,” “our,” and “their”), demonstrative determiners (e.g. “this,” “that,” “these,” and “those”), and quantifying determiners (e.g. “some,” “any,” “many,” “few,” “several,” etc.).
Determiners can also be used with adjectives to provide more information about a noun. For example, “She ate the delicious apple” and “I saw that beautiful sunset.”
Examples of Parts of Speech
- Noun – The dog barked loudly.
- Pronoun – They went to the park together.
- Verb – She writes beautiful poetry.
- Adverb – He runs very quickly.
- Adjective – The red car is fast.
- Preposition – The cat is sitting on the sofa.
- Conjunction – She wanted to go for a walk, and he wanted to stay home.
- Interjection – Wow! That was an incredible performance.
Practical Exercises
Exercise 1: Identify the Part of Speech
Read each sentence and identify the underlined word’s part of speech (Noun, Pronoun, Verb, Adverb, Adjective, Preposition, Conjunction, Interjection).
- The beautiful garden is full of flowers.
- She quickly finished her homework.
- Wow! That was a great surprise.
- The cat hid under the bed.
- I want to go out, but it’s raining.
- He is a very talented musician.
- The children play in the park every evening.
- The cake is delicious .
- After lunch, we went for a walk.
- They will arrive at the airport soon.
- Interjection
- Preposition
- Conjunction
Exercise 2: Fill in the Blanks with the Correct Part of Speech
Choose the correct word from the list and fill in the blanks with the appropriate part of speech.
Word List: (and, beautiful, suddenly, them, book, Wow, under, write, she, quickly)
- The weather is so __________ today.
- I have to __________ an essay for my class.
- He ran __________ to catch the bus.
- The ball rolled __________ the table.
- They read a __________ together every night.
- She wanted to go to the park, __________ it started raining.
- Can you give this note to __________?
- __________! That was an amazing goal!
- __________ is going to the market.
- The bird flew away __________.
- beautiful (Adjective)
- write (Verb)
- quickly (Adverb)
- under (Preposition)
- book (Noun)
- and (Conjunction)
- them (Pronoun)
- Wow (Interjection)
- She (Pronoun)
- suddenly (Adverb)
- Recent Posts
- Juridical Process vs. Judicial Process: Understanding the Crucial Differences - December 14, 2023
- Compound Nouns: How to Use Them Effectively in English - November 9, 2023
- English Tenses: A Beginner’s Guide in English - November 6, 2023
The Parts of Speech – Definitions and Examples
The different parts of speech are the breakdown and classification of words in English that show their unique functions and properties. In core language, a single word can function as two or more parts of speech.
Differentiating between the 9 parts of speech is the first step to building your grammar skills and writing tools. Keep reading to learn the definitions and examples of each category!
What are the 9 Basic Parts of Speech?
A noun is any place, person, idea, or thing. Some examples of nouns include:
There are various classifications of nouns you can use in your writing. Proper nouns are specific names for places, persons, ideas, or things. Meanwhile, common nouns are generic class nouns. A possessive noun is another type of noun that demonstrates belonging.
We can also classify this part of speech as an abstract noun, concrete noun, count noun, and uncountable noun.
The placement of the noun in a sentence also determines its function. A noun can be in the nominative or objective case. The nominative functions include subject and subject complement. And the types of objects are direct object, indirect object, and object of a preposition.
A quick introduction to pronouns shows they are classes of words that take the place of nouns. Some examples of pronouns include he, that, whoever, myself.
This quick guide to pronouns shows they can be classified as:
- Personal pronoun (I, he, she, you, etc.)
- Demonstrative pronouns (that, those, these, this, etc.).
- Interrogative pronouns (what, when, why, how, etc.).
- Relative pronouns (who/whom, whose, which, etc.).
- Indefinite pronouns (anybody, everybody, somebody, everything, etc.).
- Reflexive pronouns (myself, yourself, herself, etc.).
- Intensive pronouns (myself, yourself, herself, etc.).
Pronouns can further be divided into first-person pronoun, second-person pronoun, and third-person pronoun.
A verb is a word that conveys time while showing a condition, an action, or the fact that something exists. All complete sentences should contain at least one verb unless using an interjection.
Verbs can be treated as either lexical verbs/action verbs (study, love, drink) or auxiliary verbs (seem, is, have).
A verb phrase combines verbs with linking verbs and lexical categories of verbs. Some examples include:
- Has become.
Phrasal verbs are forms of verbs that consist of two or more words. Here are some examples:
- Put up with.
When you add “up with” after the simple verb “put,” you create a brand-new verb with a new meaning. Therefore, phrasal verbs should be treated as complete verbs because of their unique definitions.
Some verbs are reflexive. A reflexive verb is where the subject and object are one since the sentence uses reflexive pronouns like “himself” or “itself.”
Whether you’re using a lexical or auxiliary verb, this part of the speech always expresses time through the different tenses. For instance, the verb “eats” is a present-tense verb, and its past form is “ate.”
4. Adjective
Another part of speech is the adjective , which modifies or describes a noun or a pronoun. It typically answers the questions “what kind,” “which one,” or “how much.” For example:
The articles “a,” “an,” and “the” are sometimes categorized as adjectives. “The” is a definite article, and “a” and “an” are indefinite articles.
Adjective classes include:
- Absolute adjectives.
- Appositive adjectives.
- Attributive adjectives.
- Predicative adjectives.
- Compound adjectives.
- Qualitative adjectives.
- Denomial adjectives.
- Participial adjectives.
- Demonstrative adjectives.
Adverbs are a word class that modifies adjectives, verbs, and fellow adverbs. One frequent adverb marker is the suffix -ly, such as “healthily,” “badly,” and “swiftly.”
But the discussion of adverbs goes beyond words that describe actions. There are also adverbs of degree, place, time, and frequency. The English language also considers “most days,” “to visit my friend,” “very loudly,” and other adverbial phrases as adverbs.
Adverbial phrases are under the phrasal categories, including verb phrases, adjective phrases, etc.
6. Conjunction
A conjunction is a word that binds words, clauses, and phrases. “And,” “but,” “because,” and “consequently” are some examples of conjunctions.
Conjunctions make it easy to construct more complex sentences because you can easily add new clauses. The category distinctions of this part of speech are:
- Coordinating conjunctions (for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so, etc.)
- Subordinating conjunctions (after, although, unless, since, if, etc.)
- Correlative conjunctions (not only… but also, either… or, etc.)
7. Preposition
Prepositions show relations of space, time, and role between nouns, pronouns, and other words. They are at the start of prepositional phrases. Here are some examples of prepositions:
- Apart from.
8. Determiner
A determiner is like an adjective because it also modifies nouns. However, these words are essential for proper syntax as opposed to adjectives. They can be classified as indefinite and definite. New grammar rules now treat articles as determiners. Examples of determiners include:
- Which.
9. Interjection
The last part of speech is the interjection which may have standalone functions in sentences. “Whoops,” “ouch,” “ah,” and “hooray” can be an entire sentence on their own.
Parts of Speech Chart
Analyzing the parts of speech is different for every individual language. Here’s an overview of the different categories in English.
| Noun | Person, thing, place, or event | She is the new . |
| Pronoun | Replaces a noun | is the new assistant. bag is missing. |
| Verb | Expresses time while demonstrating a condition, action, or the fact that something exists | She the new assistant. I what she that day. |
| Adjective | Modifies a noun or a pronoun | She is the assistant. Jane is selling her apartment. |
| Adverb | Modifies a verb, adjective, or fellow adverb. | remove your makeup. |
| Conjunction | Connects clauses, words, or sentences | I like candles I like reed diffusers. She asked me not to attend she won’t be there. |
| Preposition | Connects a noun to another word | My dog went the neighbor’s house. |
| Determiner | Determines a noun | buzzcut suits your face shape. |
| Interjection | Short exclamation | ! That was an impressive performance. |
When A Word is Also Two Different Kinds of Speech
Sometimes, words have more than one role in the English language. For example, some nouns can also act as adjectives called adjectival nouns. In the phrase “race car,” “race” modifies “car,” so its usage is as an adjective instead of a noun.
A noun can be used in verbal senses. Consider the word “work” in these sentences.
- My new work is more promising than the old one. (noun)
- Shew works in a new industry. (verb)
Open and Closed Word Classes
The two classifications of the parts of speech include open and closed classes. The open classes can be changed and added as the language changes.
- Adjectives.
Meanwhile, closed classes are parts of speech that do not change. These include:
- Prepositions.
- Conjunctions.
- Articles and determiners.
- Interjections.
In some languages, verbs and adjectives form closed classes. This closedness of verbs is common in Basque and Persian verbs .
Linguistics , or the study of language, does not recommend the label “part of speech” anymore. Instead, the discipline favors “syntactic category” or “word class.”
What Part of Speech is With?
In the stricter sense, the only use of “with” is as a preposition. You can find it before a noun or a pronoun to form prepositional phrases. Use it to show togetherness, associations, and connections between people and objects.
What Part of Speech is And?
The conjunction “and” connects words, clauses, and phrases. It can also combine sentences that need to be presented at once.
What Part of Speech is My?
“My” is a possessive pronoun that can also act as an adjective, determiner, or interjection.
Are You Using the Parts of Speech the Right Way?
This guide has shown you the nine parts of speech and their grammatical functions. By now, you should already be able to give definitions and examples of each category, so they make sense.
To correctly use the parts of speech, ask yourself, “what is the function of this word in the sentence?” Keep practicing until you master the traditional grammar rules of English!
Grammarist is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com. When you buy via the links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission at no cost to you.
2024 © Grammarist, a Found First Marketing company. All rights reserved.
Home of English Grammar
Parts of Speech
On the basis of their grammatical behavior the words of a language are divided into several classes. These different classes of words are called the parts of speech . Languages differ in the parts of speech they have. English, for example has eight parts of speech: noun, pronoun, adjective, adverb, preposition, conjunction, verb and interjection.
Some dictionaries recognize more than eight parts of speech. For example, determiners and degree modifiers are also sometimes considered as different parts of speech.
Words are assigned to parts of speech according to their grammatical behavior. For example, words are classified according to the positions in which they can occur in a sentence and the way they change their forms for grammatical reasons.
Words placed together in a single part of speech have important grammatical properties in common, but that doesn’t mean that all the words in a single part of speech have grammatical properties which are entirely identical.
In English, it is possible to assign a single word to two or more parts of speech. For example, book is a noun in the sentence ‘Give me that book’ but a verb in the sentence ‘Book your tickets early’. Similarly fast is an adjective in the sequence ‘a fast car’ but an adverb in the sentence ‘He drove fast’.
A few words exhibit behavior that cannot be assigned to any part of speech at all. English examples include the negative ‘not’ and the polite ‘ please’.

Basic English Grammar
Helping People Understand the Eight Parts of Speech!
8 Parts of Speech Definitions With Examples
The 8 parts of speech definitions with examples include nouns, verbs, adjectives, pronouns, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions and interjections.
By using proper grammar in your writing and speaking, you will communicate clearly and effectively with your subject or audience! Moreover, by learning and understanding the 8 parts of speech, you will be able to master proper grammar in your writing and speaking. Below are the 8 parts of speech definitions with examples!

TOC – 8 Parts of Speech Definitions With Examples
- Prepositions
- Conjunctions
- Interjections
Definition of Parts of Speech: A part of speech is a category to which a word is assigned in accordance with its syntactic functions.
To put it very simply, a part of speech identifies a word in accordance with its function in a sentence such as: a noun, a verb, an adjective, a pronoun, an adverb, a preposition, a conjunction and an interjection.
Some Examples of Parts of Speech:
- The driver died in the car accident. (Noun)
- The prisoner escaped from the moving van. (Verb)
- The violent criminal changed his ways in prison. (Adjective)
- The students were late so they ran to class. (Pronoun)
- The bus will leave soon. (Adverb)
- He left his computer in the house. (Preposition)
- David and Jonathan fished all day with no success. (Conjunction)
- Wow! What a magnificent photograph! (Interjection)
Definition of Nouns: Nouns are naming words and they name persons, places, things, animals, qualities, feelings, actions or ideas.
Examples of Nouns:
- Jonathan and Rachel are excellent workers (Naming a Person).
- Australia and New Zealand are island continents in the South Pacific (Naming a Place).
- The boat sank in the river (Naming a Thing).
- The dog jumped the fence (Naming an Animal).
- Courage and bravery are two heroic qualities (Naming a Quality).
- Candice experienced both happiness and sadness at her mother’s funeral (Naming a Feeling).
- He demanded justice for all (Naming an Idea).
Examples of Types of Nouns:
- Jennifer is my best friend (Proper Noun).
- I read several books a week (Common Noun).
- Emma parked her vehicle in the driveway (Concrete Noun).
- His joy overwhelmed the crowd (Abstract Noun).
- I gave my brother a pack of cards for his birthday (Collective Noun).
- My mother-in-law drives a new car (Compound Noun).
- The photographer took a variety of photographs at the school picnic (Countable Noun).
- The jogger brought his water with him (Non-Countable Noun).
- Jonathan’s pickup is being repaired (Possessive Noun).
- His return was a complete surprise (Verbal Noun).
You can learn more about the types of nouns in English grammar by checking out 10 Types of Nouns With Examples. You will find each type of noun explained with several examples so that your skill levels to recognize nouns will increase.
Examples of Functions of Nouns:
- David arrived late to the party (Noun Functions as Subject).
- Rebekah washed the dishes before she went to school (Noun Functions as Direct Object).
- Jonathan taught the students public speaking in class (Noun Functions as Indirect Object).
- Scott is the minister of the local church (Noun Functions as Predicate Nominative).
- The traffic stopped at the lights (Noun Functions as Object of Preposition).
- My assistant, Brad, shared the message on Sunday (Noun Functions as an Appositive).
- Rebekah named her dog Bailey (Noun Functions as Objective Complement).
- Class, it is time for fire drill (Noun Functions as Noun of Direct Address).
You can learn more about the functions of Nouns in English grammar by clicking on The 8 Noun Functions With Examples. You will find each function explained with examples to help you develop your skills in recognizing the different ways nouns function.
Definition of Verbs: Verbs show action or state-of-being.
Examples of Verb Types:
- The dog jumped the fence (Action Verb).
- Rachel is beautiful (State-of-Being Verb).
- Brad hits the ball over the fence (Action Verb).
- The song sounds awful (State-of-Being).
- Emma walked the dog in the park (Action Verb).
Examples of Verb Functions:
- Candice writes a letter to her friend (Transitive Verb).
- Candice writes beautifully (Intransitive Verb).
- David walked the dog in the park (Transitive Verb).
- David walked in the park in the rain (Intransitive Verb).
- Emma became an apprentice hairdresser (Intransitive Verb).
Examples of Verb Voices:
- John rode the bike to school (Active Voice).
- The bike was ridden by John (Passive Voice).
- Jennifer led the worship service (Active Voice).
- The worship service was led by Jennifer (Passive Voice).
- The criminal was punished by the courts (Passive Voice).
You can learn more about how to identify types, functions and voices of verbs by clicking on How To Identify Verbs With Examples. This will help you develop your writing and speaking gifts.
3. Adjectives
Definition of Adjectives: Adjectives are words that describe or modify other words in a sentence thus making your writing and speaking more specific and interesting.
Examples of Several Types Adjectives:
- English grammar will help you develop your writing and speaking skills (Proper Adjective).
- Rachel had beautiful hair (Descriptive Adjective).
- My son bought an expensive car (Qualitative Adjective).
- The black cat ran in front of the car (Attributive Adjective).
- The cat is black (Predicative Adjective).
- My husband has a single focus for life (Quantitative Adjective).
- I can get twenty-four hours of service in our location (Numeral Adjective).
- I want those people charged for robbery (Demonstrative Adjective).
- David wants every person evacuated safely (Distributive Adjective).
- What time will you arrived home from the game (Interrogative Adjective)?
- The students will submit their assignments on time (Possessive Adjective).
- It is a long, narrow, winding road to the mountain top (Sequence Adjectives).
- Emma is a happy and lively person (Coordinate Adjectives).
- That was one nasty old man who drove the school bus this morning (Cumulative Adjectives).
- The murderer is a cold-blooded person (Compound Adjective).
- The builder bought a house in the country (Article Adjectives).
- Jonathan wants a few minutes of your time (Indefinite Adjective).
- The first person in the line collapsed onto the floor (Ordinal Adjective).
- The two men were jailed for life (Cardinal Adjective).
Learning to recognize the different types of adjectives will help you develop your speaking and writing skills so that you can be more specific, interesting and colorful in the way you express yourself.
4. Pronouns
Definition of Pronouns: Pronouns are words that replace nouns in sentence in order to avoid repeating the same noun over and over again.
Examples of Several Types of Pronouns :
- Dad, will you help me with my assignment (Personal Pronoun)?
- These books are mine (Possessive Pronoun).
- Give me that (Demonstrative Pronoun)!
- Some made thousands from the market collapse (Indefinite Pronoun).
- The player who was warmed about his behavior lost his spot on the team (Relative Pronoun).
- Candice saw herself in the mirror (Reflective Pronoun).
- David repairs the car himself (Emphatic Pronoun).
You can learn more about the different types of pronouns in English grammar with examples by clicking on Types of Pronouns With Examples. You will find a brief explanation of each type of pronoun with some examples. This will help you understand how pronouns work in English sentences.

Definition of Adverbs: Adverbs are words or a group of words that modify verbs, adjectives or other adverbs. They usually tell when, where, how or to what extent an action is performed or it may indicate the quality or degree of the action.
Examples of Different Types of Adverbs:
- She worked slowly and carefully on the building site (Adverb of Manner).
- David will be home soon (Adverb of Time).
- Candice put her book there (Adverb of Place).
- We are extremely hungry (Adverb of Degree).
- She never cleans her room (Adverb of Frequency).
- He gave little to charity (Adverb of Quantity).
- He fell forward on the parade ground (Adverb of Direction).
- Hopefully, I will be able to attend class today (Adverb of Uncertainty).
- Rachel went shopping; however, she didn’t buy anything (Conjunctive Adverb).
- Yes, I will be coming to the game tomorrow (Adverb of Affirmation).
You can learn more about adverbs and how they are used in English sentences by clicking on What is an Adverb? Adverb can be confusing at times because they perform differently roles and they can be inserted at different place in English sentences. By learning to recognize the types of adverbs and how they function in sentences, you will certainly increase your ability to write and speak with interesting to your audiences.
6. Prepositions
Definition of Prepositions: Prepositions consist of words or groups of words that show the relationship between nouns or pronouns with other words in sentences.
Examples of Several Types of Prepositions:
- Emma arrived on Saturday afternoon (Preposition of Time).
- The book is on the table (Preposition of Place).
- David will ride his bike to the game on Saturday (Preposition of Movement).
- Rebekah goes to work by bus (Preposition of Manner).
- Jonathan is sawing the timber with his new saw (Preposition of Agent).
- The hardware store sells electrical cord by the meter (Preposition of Measure).
- Candace received her weekly wage from her workplace (Preposition of Source).
- This is the property of my late wife (Preposition of Possession).
You can learn more about the 8 types of prepositions with examples by clicking on 8 types of prepositions with examples. Once you identify the 8 types of preposition and how they function in sentence, you will become more creative in your writing and speaking skills.
7. Conjunctions
Definition of Conjunctions: Conjunctions are words or groups of words that show how ideas are related to each other in English sentences.
Examples of Several Types of Conjunctions:
- Rachel and Darcy traveled to the zoo during the holidays (Coordinating Conjunction).
- Unless the drought breaks soon, many farmers will find it very difficult to continue farming (Subordinating Conjunction).
- David is both discreet and considerate (Correlative Conjunctions).
- We have been good friends; however, I think at times you take me for granted (Conjunctive Adverb).
- The stray dog not only destroyed the chicken pen but also killed the chickens (Correlative Conjunctions).
You can learn more about the 4 types of conjunctions with examples by clicking on 4 Types of Conjunctions With Examples. By learning these 4 types of conjunctions with examples, you will be able to identify how words, phrases and clauses relate to each other in English sentences.
8. Interjections
Definition of Interjections: Interjections are used to express feelings and emotions in English sentences.
Examples of Interjections:
- Oh, you can’t be serious!
- Wow! That’s was excellent.
- Ah, I needed that cuppa!
- I won the lottery, wahoo!
- It stinks, hey, I will never do that again!
You can learn more about interjections by clicking on What is an Interjection?
The more you understand the 8 parts of speech in English grammar with examples, the better you will be able to write and speak to your designated audience. Enjoy!
Master comma placement by learning the 8 simple comma rules with examples.
8 Parts of Speech Definitions For Kids!
Articles of Interest

What are the 7 Subjective Pronouns?

Possessive Adjectives vs Possessive Pronouns

What are the 7 Possessive Adjectives?

What is a Simple Sentence With Examples?

Predicate Nominative Vs Predicate Adjective

4 Types of Sentence Structures With Examples
Parts of Speech in English
Learn through the article!
Pass a language test
Check the results
Subscribe to reach fluency!

Learning English can be a challenge, especially if it's not your native language. One of the hardest concepts to grasp is the role of words in sentences. It's important to understand any part of speech and how it’s used. This article will provide a handy reference on the different parts of speech with examples to help you better understand the ideas.
Parts of Speech Chart
The first step to understanding the different parts of speech is to know what they are and how they are used. The parts of speech chart is a great tool for understanding different words and how they interact with each other.
Use it as your reference for parts of speech examples!
| Part of Speech | Definition | Example |
| Identifies a person, place, thing, or idea | The store, John, America | |
| Describes or modifies a noun or pronoun | Big, red, sunny | |
| Expresses an action, occurrence, or state of being | Run, walk, be | |
| Describes a verb, adjective, or another adverb | Quickly, actually, almost | |
| Stands in place of a noun or noun phrase | He, she, them | |
| Introduces a noun or noun phrase | store, gym, elephant | |
| Expresses a relationship between two other words in a sentence | Inside, between, in front of | |
| Connects words or groups of words | After, because, when | |
| Expresses emotion or surprise | Wow! Huh! Oh! |
Now that you can identify the different parts of speech, let's dive a little deeper into each one.
Adjectives help us describe or modify a noun or pronoun. For example, in the sentence "The big, red balloon," the words "big" and "red" are adjectives because they are used to describe the noun “balloon.”
Examples of using adjectives :
- Compare two things. For example, in the sentence "She is taller than her brother," the word "taller" is an adjective because it is used to compare two people.
- Describe the quantity of something. For example, in the sentence "She ate five cookies," the word "five" is an adjective used to describe the quantity of cookies.
- Describe feelings or emotions. For example, in the sentence "He was angry," the word "angry" is an adjective that is used to describe the feeling of anger.
- Show the size of something. For example, in the sentence "The elephant was huge," the word "huge" is an adjective because it describes the size of the elephant.
- Show the shape of something. For example, in the sentence "The triangle was sharp," the word "sharp" is an adjective because it is used to describe the shape of the triangle.
- Show the color of something. For example, in the sentence "The sky was blue," the word "blue" is an adjective because it is used to describe the color of the sky.
Adverbs help us describe or modify a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. For example, in the sentence "She quickly ran to the store," the word "quickly" is an adverb because it is used to describe the verb “ran.”
Examples of using adverbs :
- Describe the manner in which something is done. For example, in the sentence "He spoke softly," the word "softly" is an adverb that describes the manner in which he spoke.
- Describe the frequency of something. For example, in the sentence "He often goes to the store," the word "often" is an adverb used to describe the frequency with which he goes to the store.
- Describe the degree of something. For example, in the sentence "He was very tired," the word "very" is an adverb used to describe the degree of his tiredness.
- Describe the time of something. For example, in the sentence "She arrived late," the word "late" is an adverb used to describe the time of her arrival.
Verbs are words that are used to express an action, occurrence, or state of being. For example, in the sentence "She walked to the store," the word "walked" is a verb because it is used to express the action of walking.
Examples of using verbs:
- Express a physical sensation. For example, in the sentence "He felt sick," the word "felt" is a verb because it is used to express the physical sensation of being sick.
- Express a mental state. For example, in the sentence "She was confused," the word "was" is a verb because it is used to express the mental state of confusion.
- Express an opinion. For example, in the sentence "They thought it was a good idea," the word "thought" is a verb used to express the opinion that it was a good idea.
- Express a desire. For example, in the sentence "He wanted to go home," the word "wanted" is a verb because it is used to express the desire to go home.
Nouns are words that help us identify a person, place, thing, or idea. For example, in the sentence "The store was busy," the word "store" is a noun because it is used to identify a place.
Examples of using nouns:
- Refer to a specific object. For example, in the sentence "She bought a book," the word "book" is a noun because it is used to refer to a specific object.
- Refer to an abstract concept or idea. For example, in the sentence "He wanted freedom," the word "freedom" is a noun because it is used to refer to an abstract concept.
- Refer to a person's occupation. For example, in the sentence "She is a teacher," the word "teacher" is a noun because it is used to refer to a person's occupation.
- Refer to a feeling or emotion. For example, in the sentence "He felt sadness," the word "sadness" is a noun because it is used to refer to a feeling or emotion.
Pronouns are words used instead of a noun or noun phrase. For example, in the sentence "She went to the store," the word "she" is a pronoun because it is used in place of the noun “woman.”
Examples of using pronouns:
- Refer to a specific person or thing. For example, in the sentence "He gave it to them," the word "it" is a pronoun because it refers to a specific thing.
- Refer to groups of people or things. In the sentence "They went to the store," the word "they" is a pronoun because it refers to a group.
- Refer to a place or thing that has already been mentioned. For example, in the sentence "She went to the store and then came back," the word "it" is a pronoun because it is used to refer to the store that has already been mentioned.
- Refer to a person or thing whose gender is unknown. For example, in the sentence "Someone left their bag," the word "their" is a pronoun because it refers to a person or thing whose gender is unknown.
Articles are words that are used to introduce a noun or noun phrase. For example, in the sentence "A store was busy," the word "a" is an article because it is used to introduce the noun “store.”
Examples of using articles:
- Refer to a specific person or thing. For example, in the sentence "She bought the book," the word "the" is an article because it is used to refer to a specific book.
- Refer to groups of people or things. For example, in the sentence "The students went to the store," the word "the" is an article because it refers to a group of people.
- Refer to a place or thing that has already been mentioned. For example, in the sentence "He went to the store, but I didn't," the word "the" is an article because it is used to refer to the store that has already been mentioned.
Prepositions
Prepositions are words that are used to express a relationship between two other words in a sentence. For example, in the sentence "She went to the store," the word "to" is a preposition because it is used to express the relationship between the words "she" and “store.”
Examples of using prepositions:
- Express a location. For example, in the sentence "The store is across the street," the word "across" is a preposition because it is used to express the location of the store.
- Express time. For example, in the sentence "She went to the store yesterday," the word "yesterday" is a preposition because it is used to express the time that she went to the store.
- Express the direction of something. For example, in the sentence "She walked up the stairs," the word "up" is a preposition because it is used to express the direction of her walk.
- Express a cause. For example, in the sentence "She was late because of the traffic," the word "because" is a preposition because it is used to express the cause of her lateness.
Conjunctions
Conjunctions help us connect words or groups of words. For example, in the sentence "She went to the store and then came back," the word "and" is a conjunction because it helps us connect the two clauses.
Examples of using conjunctions:
- Show contrast. For example, in the sentence "He wanted to go home, but he stayed," the word "but" is a conjunction that we use to show contrast between the two clauses.
- Express a cause or purpose. For example, in the sentence "She was late because she missed the bus," the word "because" is a conjunction that we use to express the cause of her lateness.
- Express an alternative. For example, in the sentence "She went to the store or she went to the park," the word "or" is a conjunction because it is used to express an alternative.
- Express a result. For example, in the sentence "She was tired so she went to bed," the word "so" is a conjunction that helps express the result of her being tired.
Interjections
Interjections are words that express emotion or surprise. For example, in the sentence "Wow, the store was really busy!" the word "wow" is an interjection because it is used to express surprise.
Examples of using interjections:
- Express joy. For example, in the sentence "Yay, I got an A!" the word "yay" is an interjection because it is used to express joy.
- Express disappointment. For example, in the sentence "Oh, I didn't get the job," the word "oh" is an interjection because it is used to express disappointment.
- Express surprise. For example, in the sentence "Oh my gosh, I can't believe it!" the phrase "oh my gosh" is an interjection because it is used to express surprise.
- Express excitement. For example, in the sentence "Yippee, I got the job!" the word "yippee" is an interjection because it is used to express excitement.

Learning English can be a challenge, but understanding the different parts of speech is an important step in becoming a proficient speaker. After enough practice, you will be able to easily identify what are some parts of speech in English without having to think about them.
Check out specific references for each part you’re interested in to learn more about them!
Make your next step to fluency with Promova

More helpful articles:
Parts of Speech | English Grammar for Class 6 PDF Download
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? |
What are Parts of Speech?
- In a sentence, words are the basic units that each have their own meanings.
- We can group words into different types , called parts of speech, based on how they are used and what they do.
- A single word can act as more than one part of speech depending on how it's used.
- Knowing the parts of speech helps us understand the exact meaning of a word.
- There are eight parts of speech in English: noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection.
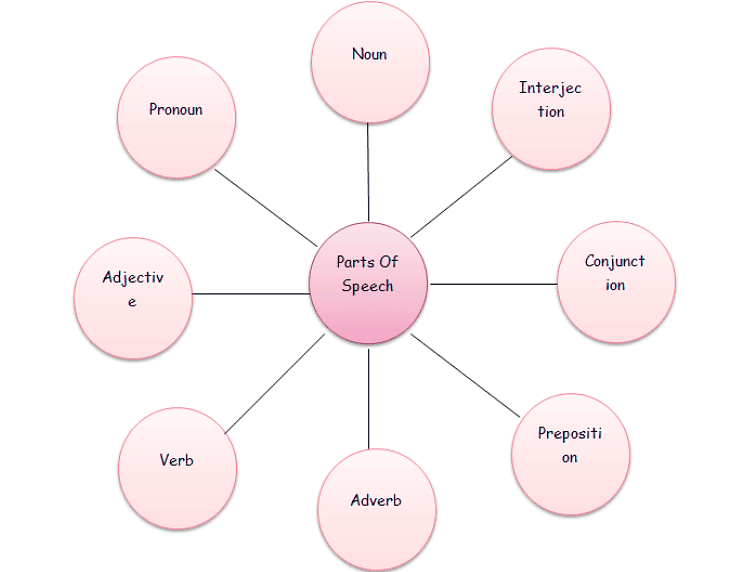
1. The Noun
- This part of speech refers to words that are used to name persons, places, things, events, or ideas . All nouns are naming words.
- Example : Alex, woman, child (person); lion, rabbit, bear (animal); dove, crow, eagle (bird); Paris, Tokyo, Australia (place); laptop, phone, book (thing); bravery, wisdom (idea), etc.
- Whatever we can see, feel, or think and have names are considered nouns.
Sample Sentences:
- Amanda lives in Paris .
- John uses a fountain pen for writing.
- Lisa is very talented.
- Marcus is looking very dashing.
- Today is Emma’s birthday.
- My sister is moving to Tokyo .
2. The Pronoun
- This part of speech refers to a word that replaces a noun.
- They eliminate the need for repetition.
- A pronoun is usually substituted for a specific noun, which is called its antecedent.
- Example : I, you, he, she, we, ours, mine, yours, his, her, him, hers, they, them, theirs, it, etc.
- Kevin is a very diligent student. He always works hard.
- The biggest portion is yours .
- They are Canadian.
- The coach gave all of us instructions.
- Sarah gave her notebook to Maya.
- His house is bigger than ours .
3. The Adjective
- This part of speech refers to a word that modifies, describes , or gives more information about a noun or pronoun .
- Adjectives are describing words and normally come before the nouns.
- Example : fast, quiet, useful, much, pretty, old, blue, smart, beautiful, big, sad, red, young, fun, crazy, three, etc.
- The tiny girl had a red kite.
- The diligent worker received "A" grade.
- I have three bikes.
- Wow! That pizza is amazing .
- She is a young teacher.
- Max is a clever boy.
4. The Verb
- This part of speech refers to a word that tells us what the subject does , or what happens to it, or what state it is in, or what possesses.
- Examples : am, is, was, are, were, have, has, had, do, does, did, be, am, is, are, was, were, being, been, should, could, will, would, might, can, may, must, shall, ought (to), go, speak, run, eat, play, live, walk, like, etc.
- They are always prepared for any situation.
- Nora is charming.
- Jake runs every day.
- I enjoy chocolate ice-cream.
- We had a nutritious meal.
- I believe that he is right.
5. The Adverb
- This part of speech refers to a word that modifies a verb, an adjective, or another adverb .
- Adverbs tell us how, when, where, how often, and to what degree (extent) something happens or takes place. Adverbs often end in -ly.
- Examples : gently, quickly, extremely, carefully, well, slowly, quietly, very, always, never, too, tomorrow, here, etc.
- He ate his cake quickly .
- The chef carefully prepared the dish.
- Liam was extremely happy about his new toy.
- She danced beautifully .
- We are leaving tomorrow .
- He looked everywhere for his glasses.
The word "quickly" describes how the action of finishing the homework was done, making it an adverb.
6. The Preposition
- This part of speech refers to a word or a group of words that shows its relation with another noun or pronoun or a verb.
- Therefore, it can also be called a ‘ relation ’ word and comes before a noun or a pronoun in a sentence.
- They are used to indicate time, place, direction, or relationship.
- Example : in, on, into, at, by, upon, across, beside, between, of, out of, for, above, below, throughout, outside, before, near, etc.
- Mia’s cat is lying under the chair.
- She placed her bag on the desk.
- He sat on the rug.
- They will meet at 3 o’clock in the afternoon.
- Look behind the couch.
7. The Conjunction (Connectors or Linking Words)
This part of speech refers to a word that joins two or more words, phrases, or clauses. There are three kinds of conjunctions:
- Coordinating Conjunctions: These are the words that join words, phrases, and clauses of equal grammatical importance in the sentence. Example: and, but, or, so, nor, for, yet.
- Correlative Conjunctions: These are the words that join equally important ideas, but they work in pairs. Example: either...or, both...and, not only...but also, neither…nor, whether…or, either…or.
- Subordinating Conjunctions: These are the words that join words, phrases, and clauses that are not equal. Example: because, although, while, since, after, as, as if, before, even if, even though, if, so that, though, unless, until, when, whenever, where, wherever, whether.
- He wants to leave, but he cannot.
- She is kind and diligent.
- Would you prefer a cup of coffee or tea?
- He didn’t pass the exam because he wasn’t ready.
- We were thirsty, so we ordered lemonade.
- I was tired but I still finished my project.
8. The Interjection
- This part of speech refers to a word or phrase that expresses strong, sudden emotions.
- It expresses strong feelings of joy, sadness, surprise, appreciation, condemnation, etc.
- Since interjections are commonly used to convey strong emotions, they are usually followed by an exclamation mark but in case of mild interjections, a comma is placed after the interjection.
- Example : Ouch!, Alas!, Oh!, Bravo!, Fantastic!, Gorgeous!, Wow!, Hurrah!, Pooh!, Pshaw!, Fie!, Gosh!
- Ouch ! I hurt my foot.
- Hurray ! Next week is a vacation.
- Hey ! You made a mistake.
- Oh , we’re late for the meeting.
- Oh ! I’m late for my appointment.
- Wow ! I passed the driving test.
The word "beautiful" describes the noun "flowers," so it is an adjective.
Note 1: Articles and determiners like a, an, the, some, any, etc., are also adjectives but they are studied separately due to their importance in modifying the meaning of the word they qualify.
Note 2: Same Word – Several Parts of Speech
There are words that can be used in more than one way. This implies that a word can function as several different parts of speech. The function of a word in a sentence decides to which part of speech it belongs.
Note the highlighted words in the following sentences:
- She likes to watch plays on TV. (noun)
- He plays basketball during his free time. (verb)
- I would like a drink . (noun)
- They drink too much soda. (verb)
- Alex bought a new sofa for his living room. (noun)
- She is planning to buy a sofa bed for her guest room. (adjective)
Parts of Speech With Examples
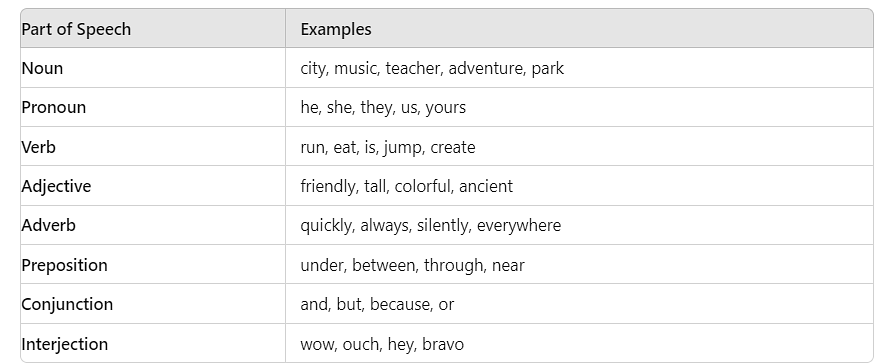
Sentences with All Parts of Speech
The (article) friendly (adjective) grey (adjective) cat (noun) sleeps (verb) under (preposition) the (article) big (adjective) tree (noun).
He (pronoun) cheerfully (adverb) sings (verb) the (article) song (noun) every (adjective) night (noun) in (preposition) the (article) moonlight (noun).
The (article) young (adjective) woman (noun) shares (verb) her (pronoun) knowledge (noun) with (preposition) the (article) students (noun).
Our (pronoun) cousin (noun) rarely (adverb) cooks (verb) delicious (adjective) meals (noun) in (preposition) his (pronoun) free (adjective) time (noun).
Before (preposition) the (article) movie (noun), they (pronoun) ate (verb) at (preposition) the (article) restaurant (noun) and (conjunction) enjoyed (verb) a (article) dessert (noun).
She (pronoun) was (verb) extremely (adverb) excited (adjective) when (conjunction) she (pronoun) found (verb) the (article) rare (adjective) book (noun).
We (pronoun) carefully (adverb) packed (verb) our (pronoun) bags (noun) with (preposition) warm (adjective) clothes (noun) for (preposition) the (article) trip (noun).
The (article) experienced (adjective) chef (noun) demonstrated (verb) the (article) intricate (adjective) recipe (noun) to (preposition) the (article) cooks (noun) patiently (adverb).
At (preposition) the (article) park (noun), they (pronoun) usually (adverb) have (verb) a (article) picnic (noun) near (preposition) the (article) lake (noun).
I (pronoun) have (verb) always (adverb) admired (verb) such (adjective) a (article) stunning (adjective) sculpture (noun) in (preposition) our (pronoun) gallery (noun).
| |172 docs|44 tests |
Top Courses for Class 6
FAQs on Parts of Speech - English Grammar for Class 6
| 1. What is the function of a noun in a sentence? |
| 2. Can you provide an example of a pronoun and explain its purpose? |
| 3. How do adjectives enhance the meaning of a noun in a sentence? |
| 4. What is the difference between an adverb and an adjective? |
| 5. How do conjunctions help connect different parts of a sentence or ideas? |
| Last updated |
Sample Paper
Previous year questions with solutions, parts of speech | english grammar for class 6, past year papers, mock tests for examination, important questions, study material, extra questions, practice quizzes, semester notes, objective type questions, shortcuts and tricks, viva questions, video lectures.

Parts of Speech Free PDF Download
Importance of parts of speech, parts of speech notes, parts of speech class 6 questions, study parts of speech on the app.
| cation olution |
| Join the 10M+ students on EduRev |
Welcome Back
Create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Unattempted tests, change country, practice & revise.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Courses on Khan Academy are always 100% free. Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: https://www.khanacademy.org/humanities/grammar/parts-of-speech-...
Just like y is sometimes a vowel and sometimes a consonant, there are words that are sometimes one part of speech and other times another. Here are a few examples: "I went to work " (noun). "I work in the garden" (verb). "She paints very well " (adverb). "They are finally well now, after weeks of illness" (adjective).
Prepositions are words that show the relationship between elements in a sentence. They can express relationships of place, time, direction, and other abstract or logical connections. A preposition is usually located directly before the word or phrase that it relates to - the object of the preposition. We walked to the shop.
This is a complete guide on Preposition in English Grammar. Definition of Preposition: A preposition is a Part of Speech which is placed before a noun or a pronoun to indicate a direction, method, place, source, etc. In other words, to show the relation of that noun or pronoun with any other word of the sentence.
There are eight parts of speech in the English language: noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection. The part of speech indicates how the word functions in meaning as well as grammatically within the sentence. An individual word can function as more than one part of speech when used in different ...
Also known as word classes, these are the building blocks of grammar. Every sentence you write or speak in English includes words that fall into some of the nine parts of speech. These include nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, articles/determiners, and interjections. (Some sources include only eight parts ...
The parts of speech are classified differently in different grammars, but most traditional grammars list eight parts of speech in English: nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. Some modern grammars add others, such as determiners and articles. Many words can function as different parts of ...
The eight parts of speech are nouns, pronouns, adjectives, verbs, adverbs, conjunctions, prepositions, and interjections. You just learned about all of the parts of speech. Give yourself a high five! If you'd like to teach or learn grammar the easy way—with sentence diagrams—check out our Get Smart Grammar Program.
When we talk about 'parts of speech', what we mean is whether a word is a noun or a verb or an adjective or a preposition or something else. Here are some different word categories that we use when we're talking about English grammar. Click on each category for more information. Noun (apple, table, book, beauty, sky, life)
The 9 parts of speech are adjectives, adverbs, conjunctions, determiners, interjections, nouns, prepositions, pronouns, and verbs. (These are also known as "word classes.") A Formal Definition. A "part of speech" is a category to which a word is assigned in accordance with its syntactic functions. In English, the main parts of speech are noun ...
Words with More Than One Job. Many words in English can have more than one job, or be more than one part of speech. For example, "work" can be a verb and a noun; "but" can be a conjunction and a preposition; "well" can be an adjective, an adverb and an interjection.
Explore the intricacies of English grammar in this comprehensive video on the "Parts of Speech." Learn with clear examples as we delve into the fundamental b...
Prepositions in English Grammar . Prepositions are one of the basic parts of speech and are among the words that we use most when composing sentences. They are also a member of a closed word class, meaning that it is very rare for a new preposition to enter the language. There are only about 100 of them in English.
The parts of speech are different categories of words based on their usage and role in a sentence. In the English language, there are eight traditional parts of speech: nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections.
Ouch! I cut my finger. Oh, you moved to Manhattan. In English grammar, there are a total of 9 parts of speech: nouns, pronouns, verbs, adverbs, adjectives, articles (or determiners), prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. This article provides definitions and examples of all of them!
The 8 parts of speech in English are: Nouns, Adjectives, Adverbs, Verbs, Prepositions, Pronouns, Conjunctions, and Interjections. A part of speech is a category of words that have similar grammatical functions or properties. In other words, they play similar roles in a sentence. For instance, a verb shows the action of a subject or the subject ...
What is a Parts of Speech? A part of speech is a category that describes the role a word plays in a sentence.These roles help you understand how words function in grammar.. There are typically eight main parts of speech in English: Nouns: Words that name people, places, things, or ideas.; Pronouns: Words that replace nouns, such as he, she, it.; Verbs: Words that describe actions or states ...
The first step in building a strong understanding of grammar is knowing all the parts of a sentence, because every word in every sentence fills a role. In th...
For instance, the verb "eats" is a present-tense verb, and its past form is "ate.". 4. Adjective. Another part of speech is the adjective, which modifies or describes a noun or a pronoun. It typically answers the questions "what kind," "which one," or "how much.". For example: Blue.
Courses on Khan Academy are always 100% free. Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: https://www.khanacademy.org/humanities/grammar/parts-of-speech-...
Languages differ in the parts of speech they have. English, for example has eight parts of speech: noun, pronoun, adjective, adverb, preposition, conjunction, verb and interjection. Some dictionaries recognize more than eight parts of speech. For example, determiners and degree modifiers are also sometimes considered as different parts of speech.
By BEGG. The 8 parts of speech definitions with examples include nouns, verbs, adjectives, pronouns, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions and interjections. By using proper grammar in your writing and speaking, you will communicate clearly and effectively with your subject or audience! Moreover, by learning and understanding the 8 parts of ...
Parts of Speech Chart. The first step to understanding the different parts of speech is to know what they are and how they are used. The parts of speech chart is a great tool for understanding different words and how they interact with each other. Use it as your reference for parts of speech examples! Part of Speech. Definition.
Full syllabus notes, lecture and questions for Parts of Speech - English Grammar for Class 6 - Class 6 ... There are eight parts of speech in English: noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection. 1. The Noun. This part of speech refers to words that are used to name persons, places, things, events, or ...