

Your cart is currently empty.
Total: $0.00
Social & Pragmatic Language Goal Bank
- (client) will label emotions/feelings in communication partners or in pictures with 80% accuracy for 3 data collections.
- (client) will use words to express their feelings independently for 80% of opportunities across 3 data sessions.
- (client) will state a logical answer to what another person might be feeling based on a social situation with 80% accuracy for 3 data collections.
- (client) will answer pragmatic questions about social situations during structured activities with 80% accuracy for 3 data collections.
- (client) will identify a problem in a social setting/picture scene with 80% accuracy for 3 data collections.
- (client) will present a solution to a problem independently with 80% accuracy for 3 data collections.
- (client) will label a problem size (small, medium, big) after identifying a problem with 80% accuracy across 5 data collections.
- (client) will make inferences after hearing part of a story/social situation with 80% accuracy for 3 data collections.
- (client) will name a flexible thinking strategy after hearing a problem scenario/social situation in 80% of opportunities across 5 data collections.
- (client) will predict what happens next after hearing part of a story/social situation with 80% accuracy across 5 data collections.
- (client) will identify appropriate/inappropriate behaviors in a story/social situation with 80% accuracy for 3 data collections.
- (client) will describe why a behavior is appropriate/inappropriate in a story/social situation in 80% of opportunities for 3 data collections.
- (client) will use greetings and farewells by looking and verbalizing or by waving "hi"/"goodbye" for 5 consecutive sessions.
- (client) will use appropriate eye contact during a conversational exchange for 5 consecutive sessions.
- (client) orient his eyes toward a speaker/activity after 1 verbal prompt in 80% of opportunities across 3 data collections.
- (client) will look toward a speaker when their name is called in 80% of opportunities for 3 data collections.
- (client) will maintain appropriate body orientation during a single activity for 3 activities per session for 3 data collections.
- (client) will request help independently in 80% of opportunities across 5 data collections.
- (client) will attend to self-directed activity for at least 1 minute without abandoning or transitioning activities across 5 data collections.
- (client) will attend to adult directed activity for at least 1 minute without abandoning activity across 5 data collections.
- (client) will maintain conversation for 3 turns by asking a questions or commenting with no more than 1 verbal prompt for 3 data collections.
- (client) will add an appropriate comment to a topic generated by a communication partner without prompting at least 10x across 3 data collections.
- (client) will ask an appropriate question about topic generated by a communication partner at least 10x across 3 data collections.
- (client) will participate in turn-taking with the therapist for 5 turns per opportunity with a minimum of 5 opportunities across 3 data collections.
- (client) will identify signs of listener boredom or disinterest independently with 80% accuracy for 3 data collections.
- (client) will use age-appropriate vocal characteristics (intonation, volume) for 80% of conversational turns during therapy sessions independently for 3 data collections.
Made with love in Austin, Texas
© 2020 Shine Speech Activities
Product Added To Your Cart
There are 0 Items In Your Cart
Total Price: $0.00
Compare Product
Different By Design Learning
with Shawna Wingert
Social Pragmatic Goals In Speech Therapy: Everything You Need To Know
This overview introduces social pragmatic goals in speech therapy as well as examples of how these goals contribute to your child’s increasing social ability.

When my child was first diagnosed with social pragmatic language disorder, I was not surprised. Part of my college education included a minor in communication disorders, so I was familiar with how a speech-language pathologist would approach his treatment. What did surprise were the actual pragmatic language goals that were put into place as part of his IEP.
Learning Social Language Skills
Table Of Contents
When is child is struggling with pragmatic language, struggle in various language related functions, including:
- conversational turns
- comprehending facial expressions
- body language
- personal space
- understanding figurative language (i.e. metaphor, hyperbole, etc.)
- appropriate eye contact
- visual cues
- verbal prompts
Fluency in conversation exchanges amongst young children is very different than the pragmatic skills necessary for social conversation as a child gets older (and don’t get me started on middle schoolers!). The school setting tends to expose a need for social pragmatics and often leads to speech therapy for social communication skills.

Examples Of Social Skills Goals For Functional Communication
The following is a sample list of goals a speech therapist might establish for social pragmatic learning. Please note, these goals go far beyond the articulation goals that are most frequently a part of speech therapy. You will typically find them as part of an IEP goal bank in speech-language pathology.
- Learner will label emotions/feelings in partners or in pictures with 80% accuracy for 3 sessions.
- Learner will use words to express their feelings independently for 80% of opportunities across 3 sessions.
- Learner will state an answer to what another person might be feeling based about a social situation with 80% accuracy for 3 sessions,
- Learner will answer pragmatic questions about social situations during structured activities with 80% accuracy for 3sessions.
- Learner will identify a problem in a social setting/picture scene with 80% accuracy for 3 sessions.
- Learner will make inferences after hearing part of a story/social situation with 80% accuracy for 3 sessions.
- Learner will use greetings and farewells for 5 consecutive sessions..
- Learner will request help independently in 80% of opportunities across 5 sessions
- Learner will maintain conversation for 3 turns by asking a questions or commenting with no more than 1 verbal prompt for 3 sessions.
- Learner will add an appropriate comment to a topic generated by therapist or partner without prompting at least 10 times across 3 sessions.
- Learner will participate in turn-taking with the therapist for 5 turns per opportunity with a minimum of 5 opportunities across 3 sessions.
- Learner will identify signs of listener boredom or disinterest independently with 80% accuracy for 3 sessions.
These goals are certainly not exhaustive, but do help to measure a child’s progress towards social interaction skills in everyday life.

Autism Spectrum Disorder vs. Social Pragmatic Language Disorder
While there is some overlap, social pragmatic language disorder exists as a diagnosis completely separate from autism spectrum disorder in the DSM-V. Prior to the DSM-V’s release however, the two were considered the same diagnosis – autism spectrum disorder.
According to Attitude Magazine people with social pragmatic language disorder may also struggle with:
- Responding to others
- Using gestures such as waving and pointing
- Taking turns when talking
- Talking about emotions and feelings
- Staying on topic
- Adjusting speech to fit different people and different circumstances
- Asking relevant questions
- Responding with related ideas
- Using words for different purposes, such as greeting people, asking questions, responding to questions, making comments
- Making and keeping friends
Here is a strong comparison of the similarities and differences between the two:
Many of the same symptoms also often overlap with those of other dianoses and learning differences, which can complicate diagnosis (according to a study completed in 2013 .) Part of the diagnostic criteria is designed to rule out other potential factors first.

How Structured Language Activities Support A Child’s Social Relationships
Independent of any diagnosis, the reality is that a child struggling with pragmatic language can benefit greatly from accommodation and intervention.
Social Pragmatic Goals In Speech Therapy
Every one of the goals above corresponds to a need identified as part of the speech evaluations. Conversation skills, problem solving, nonverbal communication, and social cognition are all factored into these goals and how they impact a child’s ability in conversational exchanges.
More Resources For Social Pragmatic Communication
Speech Therapy Goals: A Step By Step Guide
Speech Therapy For An Older Child
Speech Therapy At Home
Fig urative Language Activities
Allusion Sentence Examples And Activities
Shawna Wingert is a former training and development professional turned education specialist, and has homeschooled her two children for the last ten years.Shawna has written four books about homeschooling unique learners and has been featured in homeschooling discussions on Today.com, The Mighty, Simple Homeschool, My Little Poppies and Raising Lifelong Leaners.
You can find her online here at DifferentByDesignLearning.com.
Similar Posts

Occupational Therapy, Speech Therapy and Social Skills Therapy At Home
It is possible to complete occupational therapy, speech therapy, social skills therapy and CBT at home with your children. Here is everything you need to get started. My son was hiding under the chair in the doctor’s office, softly rocking and hitting his head. One minute prior, he had been sitting in the same chair,…

21 Things You Should Know As A Mom In Your First IEP Meeting (real advice from real moms)
If you are a mom headed into your first IEP meeting, please know you are not alone! The following includes crowd-sourced, practical advice, from real moms who have gone before you and are happy to help. For the first time in several years, I sat down in an IEP meeting last Fall. I was overwhelmed,…

Demand Avoidance And Learning: A Real Life Look
Demand avoidance can be a real struggle for neurodiverse children (and their parents!). In this post, I define what demand avoidance really is. I also share examples of what it looks like in our everyday lives and my best advice for how to help. Even if you have never heard the term “Pathological Demand Avoidance,”…
ADHD IEP Goals and Objectives: Everything You Need To Know
Creating appropriate IEP goals and objectives for children with ADHD can provide support and resources for their unique needs. This list of examples will help you get started as you create meaningful and measurable goals for a child with ADHD. Should A Child With ADHD Have An IEP? Because I went to school to be…

My Child Has An IEP: What It’s Really Like
It often surprises people to learn to homeschoolers can also have IEP’s through their school districts. This is our story. This is what it’s really like when your child has an IEP. I recently completed a mid-year IEP meeting for my youngest son. It went about as well as it could go. And it was…

20 Vocabulary Goals For Speech Therapy: Practical Examples For Learning
When creating vocabulary goals for speech therapy, it can be tempting to create a checklist and begin practice drills. The very best approach however, exposes learners to vocabulary practice in everyday life, and gives them strategies for communicating in real life scenarios. Evidence Based Strategies To Strengthen Vocabulary Skills Research shows that a child’s vocabulary…

Problem Solving Goals Speech Therapy

All children are required to solve-problems throughout their school day. Most curricula, be it the Common Core State Standards (CCSS), or various social emotional learning programs, require students to solve problems. Social communication skills also rely heavily on children’s ability to recognize and solve problems. This is why some students have problem solving goals for speech therapy or in the classroom.
Of course, problem-solving looks different at different levels of development, but opportunities to solve problems are embedded all throughout the school day, from preschool to high school.

Those Darn Squirrels Book Companion for Speech-Language Pathologists
Problem solving – levels of development.
Preschoolers are expected to follow routines, navigate materials, practice turn-taking, self-advocate, share with peers, and manage unexpected changes and feelings. Elementary school students are expected to practice perspective-taking by reading the facial expressions and body language of their peers in order to find kind solutions to problems that may arise with classmates, and to use context clues to infer the meaning of unfamiliar vocabulary to independently support their own reading comprehension. Middle and high school students are expected to identify and describe problems outlined in their reading assignments, solve complex mathematical problems, and comprehend increasingly sophisticated social interactions.
These skills are all forms of problem-solving, and they all have underpinnings in speech, language, and executive functioning – all areas speech therapists are specialized in supporting.
HOW TO WRITE GOALS FOR SPEECH THERAPY
As school-based speech-language pathologists (SLPs), we are ideally positioned to help children with their problem-solving abilities, given that many problem-solving skills are language-based, and because our therapy sessions allow us to teach our students in a small group setting with a small number of peers, or even one-on-one.
Before we dive into writing Individualized Education Program (IEP) goals that are specific to problem-solving, let’s get a quick refresher on best practices when writing speech and language goals in general.
The speech therapy IEP goals we write for our students should target the speech or language challenges they having that are preventing them from reaching the grade-level benchmarks and expectations in their classroom curriculum. The goals we choose should be informed by a good-quality speech and language assessment, which will identify both the specific difficulties a child is having with respect to their speech and language, as well as the ways in which these deficits are manifesting in the classroom.
Once we have developed a good understanding of a student’s speech and language weaknesses, and how this is impacting their academic and social success, we are ready to generate IEP goals for speech and language therapy.
While it can be tempting to recycle IEP goals from other students with similar needs, or to use a goal bank to generate goals, we should be using these sources as a starting point at most when writing long-term goals (and short-term objectives, if applicable); remember that the “I” in IEP stands for “individualized.” Every child is unique, with their own strengths, weaknesses, and personality; and the goals we write for them should reflect this.
The IEP goals we write should be SMART: specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound. Let’s quickly go through what each of these qualifiers mean.
- Specific means that the skill should be observable, and measurable. It should be described using teacher- and parent-friendly language. We can also include any stimuli we’ll provide (prompts, verbal cues, and visual cues) with examples as needed.
- Measurable means we need to outline the criteria and conditions under which we’ll measure the child’s performance. This can include accuracy levels (e.g., percentages, number of trials, the number of consecutive sessions the student will demonstrate the skills), and under what conditions we should measure the child’s ability to demonstrate this skill. For example, if a child is learning how to use a strategy to manage annoying peers that involves going through a set of steps, do we expect them to demonstrate this skill in a busy classroom, or in the context of a quieter therapy room with two other peers?
- Attainable means that we can reasonably expect the child to achieve this goal within the allotted timeframe, based on our clinical judgement, knowledge of developmental norms, and input from other members of the child’s team.
- Relevant means that the goal should be related to supporting the student with a skill they need in order to be more successful in the classroom setting. This can be a skill found in the CCSS or other curricula, or any skill that is part of the expectations for that student in the classroom. Our goal should be a speech or language-based component of a larger skill, and can be a building block towards a more complex skill. Goals can also target a child’s ability to use a compensatory strategy if there is a reason they can’t demonstrate a particular skill in the classroom.
- Time-bound means that we expect the child to reach the goal within 12 months, when the IEP has to be renewed.

How to Write IEP Goals Workbook
Examples of problem solving goals for speech therapy.
Now that we know that SLPs can help to support children with the language- and executive functioning-based underpinnings of problem-solving, and we know how to write SMART IEP goals, let’s look at a few examples.
Liam is a preschooler with expressive language delays. Because of his expressive language challenges, he is not making requests in the classroom to get his basic needs met, such as asking for help putting his shoes on after nap time or asking teacher to open containers like his milk at lunch. Liam gets frustrated and cries often. His teachers would like him to problem-solve by asking for help in times like this. Here is a potential goal we could write for Liam:
“Within one year, Liam will ask for help/desired items using short phrases (e.g., “help me please”, “can I have (item)”, “open please”) in the classroom setting with faded models in 3 out of 4 observed opportunities, over three consecutive school days, as measured by the speech therapist and/or classroom teacher.”
Maya is a third-grader with pragmatic language and executive functioning challenges. She is having a difficult time problem-solving and managing her reactions when she perceives other children in her class to be annoying her. Because of this, Maya is often having big reactions, including aggression, in the classroom where her teacher needs to co-regulate her 1:1, which is taking away from instruction time for the other students and is negatively impacting Maya’s social interactions and friendships with her classmates. Here is a potential goal we could write for Maya:
“By the end of the school year, Maya will correctly use a 5-step strategy (ignore, move away, ask nicely, ask firmly, get a teacher to help) to manage her classmates’ behaviors she finds distracting or annoying independently during role playing scenarios in the therapy room with one to two other peers in 4 out of 5 trials over 5 consecutive sessions, as measured by the speech therapist.”
Malcolm is a sixth-grader who has a language disorder which is impacting a variety of skills, including his reading comprehension. His teacher reported that Malcolm has particular difficulty responding to comprehension questions when there are idioms and metaphors in the text, and he does not know how to use strategies when he encounters this type of language. A comprehensive language assessment confirmed that Malcolm has difficulty comprehending figurative language. Here is a potential goal we could write for Malcolm:
“In one year, Malcom will use context clues in reading passages to choose the correct meaning of 30 previously unfamiliar idioms and 30 previously unfamiliar metaphors, each from a field of 5 multiple choice answers with a minimum of 90% accuracy as measured by the speech therapist.
Remember that your speech therapy goals will look different, based on the specific needs and profile of your student!
CONCLUSION ON PROBLEM SOLVING SPEECH THERAPY GOALS
Problem-solving is an important skill to help children develop, and speech therapists play a key role in helping them achieve their goals. From preschoolers learning how to ask for help when needed, to third graders managing social interactions with peers and sixth graders comprehending complex language structures – problem-solving can be applied across all ages. With the right SMART IEP goal writing strategy and techniques from cognitive neuroscience principles, SLPs are well-equipped to support students of any age to reach their fullest potential. It’s up to us as practitioners to ensure that we provide our clients with the best possible care so they can continue on their road toward success!
The Problem Solving Speech Therapy Goals article was written by Jane Clapp, MA, CCC-SLP. She has worked as a pediatric speech-language pathologist in New York City schools for over 20 years. She is the creator of StoryWhys book companions, which help SLPs provide high-quality, literature-based language therapy with elementary aged students. You can find resources, ideas, and information for busy SLPs on her blog, StoryWhys.com
RELATED POSTS
Social Pragmatics Goals Speech Therapy
List of Strengths and Weaknesses for IEPs
Written Expression IEP Goals
Daily Living Skills – Goals and Objectives
Social Emotional IEP Goals
Behavior IEP Goals
Self Regulation IEP Goals
Executive Function IEP Goals
Fine Motor IEP Goals

Your Therapy Source
Email: [email protected] Phone: (800) 507-4958 Fax: (518) 308-0290


100+ Expressive Language Goals Speech Therapy with Free Goal Bank
Expressive language goals are an important part of speech therapy. Through expressive language goals, we help guide our students in improving their communication abilities.
These goals are designed to build the capacity to convey thoughts, feelings, and information effectively.
Our work in this area is deeply rooted in understanding the specific needs and abilities of each person, tailoring objectives that are both achievable and impactful. Careful assessment and progress tracking underpin our approach to ensure that therapy sessions contribute to meaningful development in speech and language skills.
If you are a speech-language pathologist or teacher looking to learn more about how to write speech therapy goals and for a massive list of expressive language goals, then this blog post was made just for you!
Below is a goal bank of over 100 measurable goals to address expressive language difficulties and hopefully make your work day just a little bit easier!
Enjoy!
Key Takeaways
- Expressive language goals are tailored to improve communication.
- Progress is monitored through careful assessment.
- Strategies & resources are personalized for each individual’s needs.

Understanding Expressive Language Goals
Defining expressive language and its importance.
Expressive language is the ability to communicate thoughts, feelings, and ideas through speech, writing, or other forms of output. It’s a crucial component of day-to-day interactions and a foundational skill for academic success and social integration.
Speech therapy goals aimed at expressive language focus on enhancing the individual’s capacity to convey messages effectively. For individuals with language delays or expressive language difficulties, specific and measurable goals are essential to overcoming their challenges and improving their expressive language skills.
Role of Speech-Language Pathologists in Setting Goals
Our role in goal writing is to tailor objectives that address the unique needs of each person requiring early intervention or ongoing therapy. When setting expressive language goals, we can consider the following:
- Baseline Abilities : Understanding the individual’s current expressive language skills.
- Desired Outcomes : Identifying realistic targets that encourage progress yet remain attainable.
- Measurement Criteria : Establishing clear markers to evaluate progress and adjust goals as needed.
| Assessment | Gather information on expressive language abilities. |
| Target Setting | Determine which language skills to address. |
| Strategy Formulation | Plan intervention techniques and activities. |
| Progress Monitoring | Continually assess the individual’s advancement toward goals. |
We combine our expertise with evidence-based practices to formulate goals that promote meaningful improvements in expressive language.
Components of Effective Goal Setting
When we set out to create successful treatment plans in speech therapy, the goals we establish are crucial landmarks for progress. Our goals need to be well-defined, evidence-based, and tailored to the unique needs of each individual we assist.
SMART Goals Framework
The SMART Goals Framework is essential for establishing clear and achievable targets. Goals must be:
- S pecific: Concrete and clear goals help us provide focused therapy.
- M easurable: We need to track progress objectively.
- A chievable: Goals must be realistic given the individual’s current abilities.
- R elevant: We aim for goals that significantly impact the individual’s communication skills.
- T ime-bound: We set time frames to keep goals within reachable deadlines.
Identifying Specific Areas of Need
To pinpoint the specific areas of need , we:
- Conduct thorough assessments to understand the individual’s baseline abilities.
- Listen to concerns and prioritize goals that align with the individual’s daily communication needs.
Recognizing these areas ensures our treatment plans are directly addressing necessary skills for improvement.

Creating Measurable and Functional Speech Goals
When developing comprehensive goal banks for IEPs, we ensure they are both measurable and functional, directly creating a path for visible progress and practical communication enhancement in various environments.
Sample Goals for Various Language Levels
- Goal: The child will use single words to make requests in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Intermediate:
- Goal: The student will construct 4-word sentences to describe an event in 9 out of 10 trials with minimal prompts.
- Goal: The client will accurately narrate a past event using appropriate tense markers in 90% of observed opportunities.
Adapting Goals to the School Setting
Functional Communication:
- Goal: The child will request assistance during classroom activities using a full sentence in 4 out of 5 instances.
Integration with Academic Content:
- Goal: The student will use complex sentences to summarize a reading passage in oral form with 80% accuracy across four sessions.

100+ Expressive Language Goals for Speech Therapy Goal Bank
Simply scroll to the bottom of this blog post to download a pdf of these 100+ Expressive Language Goals
Speech Therapy Goals for Expressive Language Delay
Utterance expansion, narrative development, gestures/signs, categorizations, similarities, differences, comparisons, multiple meanings, grammar structure, vocabulary definitions.
Given a writing or speaking task, STUDENT will use present progressive-tense verbs (i.g., walking, running, laughing) appropriately in a sentence or conversation with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given a writing or speaking task, STUDENT will use regular/irregular plural markers (i.g., apples/feet) appropriately in a sentence or conversation with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given a writing or speaking task, STUDENT will use article/number agreement (i.g., an apple/the boys) appropriately in a sentence or conversation with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given a writing or speaking task, STUDENT will use present-tense verbs (i.g., give, go, drink) appropriately in a sentence or conversation with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given a writing or speaking task, STUDENT will use future-tense verbs (i.g., will drive, will stop, will park) appropriately in a sentence or conversation with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given a writing or speaking task, STUDENT will use regular/irregular past-tense verbs (i.g., walked/ran) appropriately in a sentence or conversation with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given a picture or story, STUDENT will use nouns to answer WHO or WHAT questions with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given a picture or story, STUDENT will use verbs to tell actions with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given a picture or story, STUDENT will use prepositional phrase to answer WHERE questions with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given a picture or story, STUDENT will use prepositional phrase or adjective to answer HOW questions with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object or picture, STUDENT will use 2 words to call attention to an object (e.g., “this ball”, “my shoe”) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object or picture, STUDENT will use 2 words to show the disappearance of an object (e.g., “no cracker”, “apple all gone”) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object or picture, STUDENT will use 2 words to indicate recurrence of an object (e.g., “more cracker”) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object or picture, STUDENT will use 2 words that contain an adjective and a noun (e.g., “big bear”) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object or picture, STUDENT will use 2 words to show possession of an object (e.g., “Daddy car”) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object or picture, STUDENT will use 2 words to show action object (e.g., “read book”) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object or picture, STUDENT will use 2 words to show the location of an object (e.g., “dog car”) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object or picture, STUDENT will use 2 words to show agent action (e.g., “dog jump”) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object or picture, STUDENT will use 2 words to show emotion (e.g., “baby tired”) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object or picture, STUDENT will use 2 words to achieve the desired end of an object (e.g., “go home”) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object or picture, STUDENT will say 3 to 4-word utterances (e.g., “dog sitting in car”) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an activity, picture, or story, STUDENT will form grammatically correct simple sentences with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an activity, picture, or story, STUDENT will use correct subject-verb agreement in sentences with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an activity, picture, or story, STUDENT will use all necessary propositions in sentences with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an activity, picture, or story, STUDENT will use compound sentences (i.e., and, but, or, etc.) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an activity, picture, or story, STUDENT will use correct subject-verb agreement with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object or picture, STUDENT will use 2-3 word utterances to describe the object or picture with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an opportunity to ask a question/comment/describe, STUDENT will use 4-5 word utterances to ask a question/comment/describe with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an orally presented sentence with missing words, STUDENT will identify missing words (i.e., articles, prepositions. etc.) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an opportunity to ask a question/comment/describe, STUDENT will include all necessary words in a sentence to ask a question/comment/describe with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object or picture, STUDENT will use descriptive words to describe the object or picture with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an opportunity to express a want or need, STUDENT will use complete grammatically correct sentence to express HIS/HER want or need with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an opportunity to tell past events, STUDENT will use simple complete grammatically correct sentence to tell about past events with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an opportunity to express a want or need, STUDENT will use 2-4 words to express HIS/HER want or need with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an opportunity to comment or share information, STUDENT will use2-4 words to express HIS/HER comment or share information with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given a wh-question, STUDENT will use2-4 words to answer simple Wh-questions (i.e., who, what, when, where, why, how) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given visual cues (e.g., sequencing cards) and a story, STUDENT will sequence the story including problem and solution with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given a story or activity, STUDENT will sequence the story or activity that includes # parts with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an opportunity to tell a story, STUDENT will use descriptive language to tell their story with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an opportunity to tell a story from their past, STUDENT will tell their story with the appropriate number of details and in the right order with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given a story or activity, STUDENT will use sequence words to verbally order a story or activity (e.g., first, next, then, after, last) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given a want or request, STUDENT will pair vocalizations with gestures when indicating a want or requesting an object with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given a want for “more”, STUDENT will use words and/or signs to ask for “more” with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given a task or activity, STUDENT will use words and/or signs to indicate HE/SHE is “finished” with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given a difficult task or activity, STUDENT will use words and/or signs to ask for “help” with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given a “yes” or “no” question, STUDENT will use words and/or signs to answer the question with “yes” or “no” with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given 10 common objects or pictures, STUDENT will verbally label the item with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given a common object, noun, or action, STUDENT will verbally label the item in a phrase or sentence with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given 10 common words, STUDENT will verbally name the word with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given 10 common words, STUDENT will verbally name the word in a phrase or sentence with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
SEE ALSO: IEP Goal Bank Posts
Given an object or picture, STUDENT will describe the object or picture by stating the function of the item with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given 10 words, STUDENT will describe the object or picture by stating the function of the word with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given a category, STUDENT will name (3-5) items in that category (e.g., school items, home items, clothing, animals, colors, toys, etc.) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given 3 to 5 items in a category (e.g., dog, cat, fish, etc.), STUDENT will identify the category (e.g., school items, home items, clothing, animals, colors, toys, etc.) and explain their relationships with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given 3 to 5 items, STUDENT will identify the item that does not belong in the group and explain why with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given a category, STUDENT will name (3-5) items in that category and (1) item that does not belong in that category with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given 3 to 5 pictures, STUDENT will select 2 similar pictures and explain the similarities with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given 3 to 5 words verbally, STUDENT will select 2 similar pictures and explain the similarities with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given 3 to 5 pictures, STUDENT will select the different picture and explain the differences with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given a list of 3 to 5 words verbally, STUDENT will identify the different word and explain the differences with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given 3 to 5 words verbally, STUDENT will identify the different word and explain the differences with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given a word pair verbally, STUDENT will explain the primary difference between the two words with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given two object pictures, STUDENT will compare likeness(es) and difference(s) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given two spoken words, STUDENT will compare likeness(es) and difference(s) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given two concepts (e.g. flying vs. driving), STUDENT will compare likeness(es) and difference(s) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given 2 pictures that represent different meanings of the same word , STUDENT will provide a definition for each with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given 2 sentences that represent different meanings of the same word, STUDENT will provide a definition for each with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given a multiple meaning word, STUDENT will provide 2 or more definitions for the multiple meaning word with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object or picture, STUDENT will describe the object or picture by identifying a minimum of (3) attributes (e.g., color, size, number etc.) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object or picture and asked a question, STUDENT will answer the question by identifying a minimum of (5) attributes (e.g., color, size, number etc.) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given 10 items presented verbally, STUDENT will describe the object or picture by identifying a minimum of (3) attributes (e.g., color, size, number etc.) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
SEE ALSO: 179+ Wh Questions Free Printable
Given an object, picture, or story, STUDENT will say a complete sentence using articles (i.e., “a”, “an”, “the”, and “some”) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object, picture, or story, STUDENT will say a complete sentence using demonstrative adjectives (i.e., “this”, “that”, “these”, and “those”) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object, picture, or story, STUDENT will say a complete sentence using plural nouns (i.e., s, es, and irregular plural forms) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object, picture, or story, STUDENT will say a complete sentence using possessive nouns (i.e., “the girl’s book”) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object, picture, or story, STUDENT will say a complete sentence using subject pronouns (i.e., “I”, “he”, “she”, “you”, “we”, “they”) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object, picture, or story, STUDENT will say a complete sentence using object pronouns (i.e., “me”, “him”, “her”, “you”, “us”, “them”) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object, picture, or story, STUDENT will say a complete sentence using possessive pronouns (i.e., “my”, “mine”, “his”, “her/hers”, “you/yours”, “our/ours”, “their/theirs”) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object, picture, or story, STUDENT will say a complete sentence using reflexive pronouns (i.e., “myself”, “himself”, “herself”, “yourself”, “yourselves”, “ourselves”, “themselves”) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object, picture, or story, STUDENT will say a complete sentence using present progressive verb tense (i.e., “The girl is running”) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object, picture, or story, STUDENT will say a complete sentence using past progressive verb tense (i.e., “The girl was running”) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object, picture, or story, STUDENT will say a complete sentence using present tense “s” and “es” marker (i.e., “The girl runs”) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object, picture, or story, STUDENT will say a complete sentence using “has”/”have” (i.e., “The girl has a book”) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object, picture, or story, STUDENT will say a complete sentence using regular past tense (i.e., “The boy waited for the bus.”) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object, picture, or story, STUDENT will say a complete sentence using irregular past tense (i.e., “ran”, “drove”, “drank”) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object, picture, or story, STUDENT will say a complete sentence using conjunctions (i.e., “and”, “or”, “but”, “because”, “if”, “since”) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object, picture, or story, STUDENT will say a complete sentence using future tenses (i.e., “The boy will go to school”) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object, picture, or story, STUDENT will say a complete sentence using negative sentence structures (i.e., “will not/won’t”, “does not/doesn’t”) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object, picture, or story, STUDENT will ask yes/no questions (i.e., “Is the boy hurt?”) in a complete sentence with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object, picture, or story, STUDENT will ask WH questions (i.e., “What is the girl doing?”) in a complete sentence with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object, picture, or story, STUDENT will say a complete sentence using comparatives (i.e., “The kitty is smaller than the tiger”) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object, picture, or story, STUDENT will say a complete sentence using superlatives (i.e., “That is the best cookie.”) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an idiom with a visual cue, STUDENT will accurately describe the meaning of the idiom with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an idiom verbally with no visual cue, STUDENT will accurately describe the meaning of the idiom with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an idiom verbally, STUDENT will identify a social situation where the idiom may be used appropriately with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given 5 words with picture cues, STUDENT will define the word correctly with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object or picture, STUDENT will use 2-3 critical features to describe the object or picture with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an emotional expression picture or story, STUDENT will use vocabulary to clearly describe the feelings, ideas, or experiences with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object, picture, or word, STUDENT will identify synonyms with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object, picture, or word, STUDENT will identify antonyms with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given 5 identified words in sentences, STUDENT will provide a synonym/antonym with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given a story with highlighted words, STUDENT will provide a synonym/antonym for each highlighted word with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given 10 pictures, STUDENT will match opposite pictures in pairs (i.e., happy/sad, up/down) with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object, picture, or word, STUDENT will identify the opposite with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given an object or picture, STUDENT will describe the object or picture by naming the item, identify attributes (color, size, etc.), function, or number with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given a reading task, STUDENT will define unfamiliar words using context clues with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given common academic vocabulary, STUDENT will define prefix and/or suffix with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Given common academic vocabulary, STUDENT will define the vocabulary word using a complete sentence with correct grammar with 80% accuracy in 4 out of 5 opportunities.

Assessment and Progress Tracking
Data collection and utilizing iep goals.
We meticulously collect data on each interaction that pertains to our client’s IEP goals. Crafting a well-structured IEP goal bank allows us to select targets that are measurable and aligned with the client’s specific needs.
As we collect this date, we cross-reference this information with our IEP goal bank to ensure consistency and completeness in our data collection efforts.
If you’re a classroom teacher or speech pathologists in need of data tracking forms while working on your student’s goals for speech-language therapy then be sure to check out my IEP goal data tracking for progress monitoring forms .
Or if you simply want a list of data sheets to choose from then be sure to check out my list of 35 free speech therapy data sheets roundup .
SEE ALSO: 21 Best Reinforcement Games for Speech Therapy

Therapeutic Techniques and Activities
We understand that the efficacy of speech therapy relies heavily on targeted therapeutic techniques and activities. These strategies are meticulously designed to foster language development and improve expressive skills.
Here, we discuss two fundamental approaches: Structured Language Activities and Using Picture Scenes and Cards.
Structured Language Activities
Structured language activities are the cornerstone of our therapeutic approach. These activities provide a controlled environment where we can isolate specific linguistic skills for practice and reinforcement. For instance:
- Modeling : We offer models of correct language use, which clients can recognize and reproduce.
- Repetition : Clients are encouraged to practice specific words or sentence structures repeatedly to build proficiency.
Here are some of our favorite structured language activities to help accomplish speech therapy goals!
- Nobody Hugs A Cactus Structured Narrative Retell by BJT the SLP at Communication Reigns is a short story with specific objectives to build school aged language skills! Short stories play a crucial role in answering verbal prompts to build comprehension. This bundle offer WH Questions and types for fading cues so that all students have their necessary support.
- Speech Therapy: FREE Expressive Language Program by Speech Chick Alissa Halloway is a great way to use visual prompts and verbal prompts in a structured activity. This freebie is highly rated!
- Weekly Agenda / Learning Targets / Student Reflection by Expressive ELA Education is a great resource to add to your treatment plan! Students practice conversational skills and social skills as they are prompted through the plan for the week.
Using Picture Scenes and Cards
Picture scenes and cards elevate the engagement and contextuality of our therapy sessions. These tools help clients visualize and conceptualize language in relatable scenarios.
Picture Scenes : We use detailed scenes to encourage clients to describe activities, tell stories, and develop narrative skills. Picture Cards : These are used for more focused work on specific vocabulary, categorization, and articulation tasks.
Here are some great picture scenes and picture card resources for you!
- FREEBIE! Describing with your Senses Vocabulary/Word Finding Game BOOM CARDS by SLP Style is an engaging picture scene that prompts students to use social language and talk through their senses
- Expressive Language – What do you see at the beach? By Listen Speak Learn offers picture cues to talk about what is seen at the beach.
- Body Parts – Expressive and Receptive Identification by Our Impact is a great way to practice expressive language goals as students practice labeling body parts.

Blog Post Resources
Here are all my Speech Therapy Store blog posts for working on expressive language skills that you might also find helpful!
- 33 Most Common Irregular Plurals Flashcards – Download this first post of free irregular plurals with their real-life photos.
- 253+ Yes or No Questions for Speech Therapy – Here is a massive resource working on answering yes or no questions.
- 179+ Wh Questions Free Printable – Grab this freebie to work on answering wh-questions.
- 197+ Best Wh Questions Speech Therapy Activities – If you have a child or student working on wh-question you’ll also want to check out this list of helpful free resources.
- 31+ What Questions for Speech Therapy – Have your child or student watch these wordless videos and then answer the “what” question using the interactive quiz with instant feedback.
- 31 Best Wordless Videos to Work on Answering Questions – Have your student watch these fun animated wordless videos and then answer the included wh-questions.
- Nature Themed Bundle – This bundle includes yes/no questions, wh-questions, pronouns, regular past tense verbs, and irregular past tense verbs.
- Technology Themed Bundle – This bundle also includes yes/no questions, wh-questions, pronouns, regular past tense verbs, and irregular past tense verbs.
Need Other IEP Goals?
Are you a speech language pathologist looking for other effective iep goals for speech? If so, be sure to check out my master list of IEP goals here .
This list of goal writing ideas also includes the following speech pathology goals:
- Figurative Language
- Final Consonants
- Prepositional Phrase
- Context Clues
- Articulation Goals (Single Word Level, Phrase Level, Sentence Level, and Conversation)
- Communication Device – Nonverbal Communication
These are just a few of the possible goal combinations listed on this master list of over 432 IEP goals made for a speech therapist.

<< Fill out the Form to grab your free 100+ Expressive Language Goals PDF >>
Grab your expressive language iep goal bank, frequently asked questions :, expressive language goals for speech therapy.
In this section, we provide a thorough overview of common inquiries surrounding expressive language goals in speech therapy, particularly as they relate to children and early intervention programs.
What objectives are typically included in expressive language goals for speech therapy?
We often target the enhancement of vocabulary, the correct use of grammar, the ability to construct sentences, and the skill of relaying information or needs. Increasing the variety and complexity of spoken language is also a primary objective.
How can one formulate effective long-term goals for expressive language development in speech therapy?
We focus on creating goals that are achievable and measurable, tailored to the child’s current abilities and potential for growth. Goals are plotted out over a period, with milestones that align with the child’s developmental stage.
Can you provide examples of expressive language goals for early intervention programs?
Certainly. We set goals like expanding the child’s vocabulary, encouraging the use of two to three-word phrases, and improving the clarity of speech. Another example is prompting the child to initiate communication.
What strategies are used to establish expressive communication goals in therapy?
We use a detailed assessment of a child’s current language abilities to establish baselines, then leverage those findings to set individualized goals. Strategies may include play-based learning or structured activities.
How do therapists measure progress towards expressive language goals in speech therapy?
Progress is measured through consistent tracking of therapy sessions, using tools such as language samples, direct observation, and standardized tests. We look for signs of improvement in the child’s ability to express themselves.
What are some common goals set for 3-year-olds to enhance expressive language skills?
For 3-year-olds, we often set goals aimed at increasing sentence length, improving story-telling skills, and fostering the use of pronouns and prepositions, reflecting typical language development milestones for this age group.

Want Even More Expressive Language Goals for Speech Therapy?
- Free SLP Planner [Updated Yearly]
- 917+ Best Free Boom Cards for Speech Therapy
- 31 Best Wordless Videos to Teach Problem Solving
- 133+ Categories List for Speech Therapy
- The Best Handout for Phonological Processing Disorder Therapy
Want the Best of the Bests?
Be sure to check out our most popular posts below!
- 21 Best Reinforcement Games for Speech Therapy / Teletherapy
- Best IEP Resources
- 71+ Free Social Problem-Solving Scenarios
- 430+ Free Multisyllabic Words List Activity Bundle
- 432+ Free Measurable IEP Goals and Objectives Bank
- 279+ Free Speech Therapy Digital Materials
- 179+ Free Speech Therapy Wh-Questions Printable
Join Pilot Waitlist

Home » Blog » IEP Goals and Objectives » Effective IEP Goals for Developing Problem-Solving Skills

Effective IEP Goals for Developing Problem-Solving Skills

Special education plays a crucial role in helping students develop essential life skills. One such skill is problem-solving, which has a significant impact on students’ learning, social interactions, and overall wellbeing. In this blog post, we will explore problem-solving skills and how to create effective IEP goals for high school students.
What Are Problem-Solving Skills
Problem-solving skills involve a series of steps students can take to identify, analyze, and resolve issues they encounter. These skills are vital for students’ learning as they help them overcome obstacles and make informed decisions. Additionally, problem-solving skills contribute to students’ social interactions and wellbeing by enabling them to navigate various social situations and maintain healthy relationships.
The Role of Specialists
Various specialists can support the development of problem-solving skills in students:
- Speech-Language Pathologists: They can help students improve their communication abilities, which are crucial for expressing and understanding problems.
- Social Workers: They can provide guidance and resources to help students address social and emotional challenges that may hinder problem-solving.
- Psychologists: They can assist in identifying any underlying cognitive or emotional barriers that may affect students’ problem-solving abilities.
- School Counselors: They can offer support in developing students’ decision-making and coping skills, which are essential components of problem-solving.
IEP Goals for Problem-Solving Skills
Here are some SMART IEP goals to help students develop problem-solving skills:
Goal 1: The student will identify and classify problems as big or small in 90% of situations within six months.
Strategy: Teach students the criteria for differentiating between big and small problems and provide opportunities for practice.
Activity: Role-play scenarios involving various problems and have students classify them as big or small.
Goal 2: The student will generate at least three possible solutions to a given problem in 80% of situations within six months.
Strategy: Teach students brainstorming techniques and encourage them to think creatively when faced with problems.
Activity: Provide problem-solving worksheets that require students to list multiple potential solutions.
Goal 3: The student will evaluate and select the best solution to a given problem in 80% of situations within six months.
Strategy: Teach students how to weigh the pros and cons of each solution and consider potential outcomes.
Activity: Engage students in group discussions where they analyze potential solutions and collectively decide on the best approach.

Implementing and Measuring Progress
To implement these IEP goals, consistently provide students with opportunities to practice problem-solving skills in various settings. Monitor their progress using data collection tools, such as checklists and rating scales, to track their improvement over time. Regularly review and adjust goals as needed, based on the students’ progress and needs.
Developing problem-solving skills is crucial for high school students’ success in learning, social interactions, and overall wellbeing. By setting effective IEP goals and collaborating with specialists, educators can support students in becoming confident problem solvers. We encourage you to apply these IEP goals in your practice and invite you to explore more resources at Everyday Speech Sample Materials .
Related Blog Posts:
Effective iep goals for improving students’ point of view skills.
Introduction In special education, it is essential to address various skills that contribute to the overall development of students. One such significant skill is understanding others' perspectives, which plays a crucial role in fostering healthy social interactions...
Effective IEP Goals for PreK Students: Developing the Target Skill
In special education, it is crucial to identify and address target skills that can significantly impact a student's learning, social interactions, and overall wellbeing. One such essential skill is controlling strong emotions, which enables students to make better...
Effective IEP Goals for Improved Tone of Voice in Middle School Students
Introduction In special education, understanding and addressing the nuances of communication skills, such as tone of voice, is crucial for students' social and emotional development. This blog post will focus on the target skill of using a non-condescending tone of...

FREE MATERIALS
Better doesn’t have to be harder, social skills lessons students actually enjoy.
Be the best educator you can be with no extra prep time needed. Sign up to get access to free samples from the best Social Skills and Social-Emotional educational platform.
Get Started Instantly for Free
Complete guided therapy.
The subscription associated with this email has been cancelled and is no longer active. To reactivate your subscription, please log in.
If you would like to make changes to your account, please log in using the button below and navigate to the settings page. If you’ve forgotten your password, you can reset it using the button below.
Unfortunately it looks like we’re not able to create your subscription at this time. Please contact support to have the issue resolved. We apologize for the inconvenience. Error: Web signup - customer email already exists
Welcome back! The subscription associated with this email was previously cancelled, but don’t fret! We make it easy to reactivate your subscription and pick up right where you left off. Note that subscription reactivations aren't eligible for free trials, but your purchase is protected by a 30 day money back guarantee. Let us know anytime within 30 days if you aren’t satisfied and we'll send you a full refund, no questions asked. Please press ‘Continue’ to enter your payment details and reactivate your subscription
Notice About Our SEL Curriculum
Our SEL Curriculum is currently in a soft product launch stage and is only available by Site License. A Site License is currently defined as a school-building minimum or a minimum cost of $3,000 for the first year of use. Individual SEL Curriculum licenses are not currently available based on the current version of this product.
By clicking continue below, you understand that access to our SEL curriculum is currently limited to the terms above.
- Support My Website

Sunlight Speech Therapy
A place to seek sunlight about speech, language, cognition, and dysphagia

Goal Bank Speech Therapy for SNF
Goal Bank for speech therapists working in a skilled nursing facility. Goals for Cognition, Memory, Attention, Problem Solving, Aphasia, Dysarthria, Voice, Swallowing, Tracheostomy, and Skilled Maintenance. For an all in one download please see end of document.
ST Goal Bank
Cuing Hierarchy
Independent
Setup/cleanup assistance
Supervision or touching assistance
Partial/mod assist
Substantial/maximal assistance
- Pt will complete further cognitive assessment (SLUMS/RIPA/ALFA/ACA) in order to assess cognitive communication skills by (DATE).
- Pt will be able to verbally express compensatory strategies to improve cognition in order to return to PLOF.
Long-Term Goal
- Pt will increase memory abilities to (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) demonstrating improved (orientation, basic functional recall of everyday activities, biographical information, safety precautions) in order to (return to PLOF/increase independent on nursing unit).
- Pt will increase memory to (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) demonstrating independence with (functional memory tasks, use of compensatory strategies and precautions, recall of medication schedule) in order to (return to PLOF/increase independence on nursing unit).
Short-Term Goal
- Pt will complete further memory assessment with (SLUMS/RIPA) in order to determine current cognitive level and goal set appropriately.
- Pt will utilize memory book with ___% accuracy with (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist) in order to assist with everyday functional recall.
- Pt will utilize external/internal memory strategies to solve functional (immediate/short-term/working) memory tasks at (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist) with ___% accuracy to return to PLOF.
- Pt will complete (alternating/sustained/selective) attention activities with (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) in order to increase independence with functional activities.
- Pt will complete alternating attention tasks with ___% accuracy given (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) cues to attend in a noisy environment in order to increase independence during functional tasks.
- Pt will sustain attention to (visual information/auditory information/activity) for ___ minutes in a quiet environment given (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) to increase independence during functional tasks.
- Pt will selectively attend to (visual/auditory information/activity) for __ minutes given (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) to attend to functional activities.
PROBLEM SOLVING
- Pt will demonstrate problem solving skills with (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) or higher, demonstrating improved (insight, safety, executive functioning, reasoning, functional problem solving) in order to return to (IADL’s, increase independence on nursing unit).
- Pt will demonstrate problem solving skills with (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) or higher, demonstrating improve problem solving required for independence with basic ADL’s and safety.
- Pt will complete ALFA assessment in order to determine patients’ problem-solving functioning to goal set appropriately.
- Pt will complete basic problem-solving tasks related to safety (use of call light/walker/O2 precautions) at __% accuracy with (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) cues in order to (return to PLOF/increase independence on nursing unit).
- Pt will sequence functional activities with ___% with (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) in order to (return to PLOF/increase independence on nursing unit).
- Pt will complete higher-level problem-solving tasks r/t IADL’s at ___% accuracy given (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) cues in order to (return to PLOF).
SOCIAL INTERACTION
- Pt will increase social interaction to (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) demonstrating increased ability to (manage emotions, cope, engage in social communication, maintain topic, use appropriate pragmatics, turn-take).
- Pt will increase social interaction to (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) or higher demonstrating improved (behavior, pragmatics, eye contact, emotional regulation, coping with anxiety/depression.
- Caregivers/Staff will be able to teach back pt behavioral plan to manage (agitation/restlessness/anxiety/depression) in order to improve quality of care.
- Pt will demonstrate techniques of emotional regulation to manage negative ideation and behavior (deep breathing, positive thinking, mindfulness) with (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent in order to benefit quality of life.
- Pt will communicate in social interactions given (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) for (turn taking, eye contact, pragmatics, appropriateness) in order to increase appropriate social interactions with staff/residents/family.
APHASIA RECEPTIVE
- Pt will demonstrate (verbal/written) expression skills with (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) concerning improved (motor speech, word finding, fluency, voice, initiation, pragmatics) in order to express (simple wants/needs/higher level/complex ideas).
- Pt will answer simple biographical yes/no questions presented (verbally/visually) with ___% accuracy with (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) cues in order to increase ability to communicate simple biographical information.
- Pt will follow (simple/complex 1-step commands/2-step commands) with ___% accuracy given (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) cues in order to increase ability to complete functional tasks.
- Pt will identify the correct picture in a field of (2/4/6) when presented with the word (verbally/visually) at ___% accuracy given (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) cues in order to increase ability to recognize functional language.
- Pt will read (sentences/paragraphs) and answer comprehension questions with ___% accuracy given (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) cues in order to improve functional communication.
APHASIA EXPRESSIVE
Long-Term Goals
- Pt will be able to communicate using (simple/complex) (words/phrases/sentences) with ( independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) in order to increase ability to express (simple/complex) (wants/needs/ideas/feelings).
Short-Term Goals
- Pt will name common objects at __% accuracy with (independence/mod assist/max assist) given (phonemic/orthographic/semantic) cues in order to increase ability to express wants/needs.
- Pt will generate sentences with 3 or more words in response to a situation with __% accuracy with (independence/mod assist/max assist) given (phonemic/orthographic/semantic) in order to increase ability to communicate basic wants and needs.
- Pt will participate in (simple/complex) conversation with ___% accuracy with situation with __% accuracy with (independence/mod assist/max assist) given (phonemic/orthographic/semantic) in order to increase ability to communicate complex thoughts, feelings, and needs.
- Pt will produce (vowels/phrases/paragraphs/conversation) with appropriate intelligibility given (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) cues in order to increase ability to express wants and needs.
- Pt will produce (vowels/phrases/paragraphs) with appropriate voicing in ___% of opportunities given ( independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) cues in order to increase ability to express wants and needs.
- Pt will produce phrases with (5 or fewer words/7 or more) in one breath in __% of opportunities with (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) cues in order to increase ability to express wants/needs.
- Pt will produce phrases with appropriate stress in __% of opportunities given ( independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) cues in order to increase ability to express wants/needs.
- Pt will produce (words/phrases) with appropriate voicing with (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) in order to express wants/needs.
- Pt will produce (easy onset/non-nasal/tense vowels/minimal pairs) words with appropriate voicing in ___% of opportunities with ( independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) cues in order to increase ability to express wants/needs.
- Pt will produce (words/phrases) at (70dB/80dB) vocal loudness with ( independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) cues in order to increase ability to express wants/needs.
- Pt will improve MPT to __ml with (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) to demonstrate increased breath support req for voicing.
COMPREHENSION
- Pt will d/c with ( independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) in order to increase comprehension (reading/expression) of (simple/complex) ideas and instruction.
- Pt will d/c with ( independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) (reading/expression) in order to increase comprehension of functional information.
- Pt will follow (1/2/3) step directions at ( independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) level with ___% accuracy in order to complete functional activities.
- Pt will respond to (simple/complex) questions at ( independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) level with __% accuracy in order to increase ability to participate in functional communication.
- Pt will respond to (simple/complex) questions at independent level with __% accuracy demonstrating improved auditory processing/comprehension
- Pt will answer paired Y/N questions at with __% accuracy at ( independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) in order to increase ability to participate in functional communication.
- Pt will identify (object/pic/word) in a field of (2/4/6) with ___% accuracy with (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) in order to participate in functional activities.
Pt will be able to use (low tech/high tech) AAC device with (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) cues in order to communicate basic wants/needs.
Pt will (type/identify) single (words/icons) with ___% accuracy given ( independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) cues in order to communicate basic wants/needs.
Pt will answer simple biographical questions at __% accuracy given (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) cues in order to increase functional communication.
Pt will be able to navigate device with ___% accuracy given ( independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) cues in order to increase independence with device.
Pt will be able to add new (icons/vocabulary) to AAC device with ___% accuracy with (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) cues in order to increase functional communication.
- Pt will d/c on IDDSI diet of (Regular-7/Easy to Chew-7b/Soft and Bite Size-6/Minced and Moist-5/Puree-4) (Thin/Nectar Thick) liquids) with (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) use of swallow strategies in order to improve (oral/pharyngeal) swallowing safety and improve (nutrition/hydration)
- Pt will d/c on PO diet maintaining nutritional needs PO requiring no alternative means of nutrition (IV/PEG/NG).
- Pt/caregiver will demonstrate/verbalize understanding of diet recommendations, swallowing strategies, swallowing exercises for (home/facility) maintenance program.
- Pt will complete instrumental swallow evaluation to assess swallow function and determine appropriate diet level.
- Pt/caregiver will demonstrate understanding of oral care and be able to follow oral care program with (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) in order to benefit oral health.
- Pt will decrease (oral pocketing/anterior labial spillage) with ___% accuracy with (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) to reduce risk of aspiration.
- Pt will manage trials of (Regular-7/Easy to Chew-7b/Soft and Bite Size-6/Minced and Moist-5/Puree-4) following swallowing strategies with ___% accuracy with (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) in order to decrease s/s of aspiration.
- Pt will complete (pharyngeal/oral motor exercises) with (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) in order to increase swallow function.
TRACH/DECANNULATION
Secretion Management/Suctioning Goal
- Pt will independently manage secretions as demonstrated by requiring no suction (deep or oral suction) over __hr period.
- Pt will utilize quad cough at spv level to clear deep secretions and req no deep suction over __hr period.
- Pt with demonstrate ability to clear pharyngeal secretions without need for deep suction over __period.
- Pt will independently utilize yanker to clear oral secretions
- Pt will decrease anterior spillage of saliva req __ cueing to clear secretions
- Pt will increase awareness of drooling req __ cues in __ min/sessions to wipe/mng secretions
- Pt will improve labial seal in order to decrease anterior spillage of secretions by meeting IOPI peak of __ kPa when measuring lip strength
- Pt will improve lingual strength req to mng secretions as demonstrated by IOPI peak of __kPa when measuring base of tongue strength.
DECANNULATION
- Pt will meet decannulation goals in order to increase independence to return to PLOF.
- Pt will tolerate uncuffed trach for __ hrs/days in order to demonstrate readiness for passy muir speaking valve
- Pt will down size to _ size trach in order to tolerate PMSV/demonstrate readiness for capping trials
- Pt will tolerate PMSV for __hrs in order to increase independence with verbal communication
- Pt will tolerate PMSV for __hrs in order to demonstrate readiness for capping trials and decannulation
- Pt will tolerate capping trials for __min/hrs in order to work towards decannulation
- Pt will be decannulated in order to improve swallow function/in order to improve verbal communication
- Pt and family will demonstrate understanding of trach related goals
- Pt/family will demonstrate understanding of trach/pmsv care (placement/clearing)
- Pt will meet incentive spirometer peak of __ ml to demonstrate improved breath support req for decannulation
- Pt will meet __ syllables per breath over 3 trials demonstrating improved breath support req for decannulation
- Pt will meet MPT of ___ sec over 3 trials to demonstrate breath support req for decannulation
- Pt will digitally occlude (stoma/trach) to improve breath support req for intelligible speech at __ level.
SKILLED MAINTENANCE
- Pt will maintain cog/communication skills at level of (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) with implementation of __% verbal cues and environmental modifications to decrease risk of cognitive decline.
- Pt will maintain comprehension skills at (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) with implementation of min cues during discussion of familiar topics to decrease risk of social isolation and to facilitate communication opportunities.
- Pt will maintain current diet with pleasure feedings with SLP in order to benefit quality of life.
- Pt will maintain safe swallow function while consuming (thin liquids/texture) by (spoon/cup/straw) with SLP only for pleasure feedings.
- Pt will continue to engage in 3-minute social interactions with staff during daily care in order to maintain communication skills.
- Pt will maintain short-term memory skills using a memory book and verbal cues from staff in 80% of opportunities.
- Pt will maintain ability to recall self-relevant pieces of information at __% accuracy with verbal/visual cues to maintain ability to recall events and leisure activities scheduled.
- Pt will maintain current reasoning skills at ___% accuracy and occasional (min/mod) cues to prevent cognitive decline and to maintain independence within this environment.
- Pt will maintain thought organizational skills at __% accuracy and occasional cues with task modifications as needed to prevent cognitive decline within this environment.
- Pt will maintain ability to respond to yes/no questions at __% accuracy with implementation of verbal cues to increase ability to engage in meaningful interactions.
- Pt will demonstrate ability to use verbal and non-verbal communication to make decisions related to preferences during care tasks and daily routine with (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) to facilitate highest level of independence in current environment.
- Pt will maintain ability to complete 3 conversational exchanges related to direct and observable topics using multisensory stimuli in order to reduce risk of social isolation.
- Pt will maintain current level of cognitive-communication to actively participate (following along with handout, switching between tasks, singing along, etc) in weekly activity with (independence/setup/supervision/mod assist/max assist/dependent) in order to maintain quality of life and highest level of independence with leisure activities of choice.
Share this:
You might also like.

Documentation Systems in SNF Setting

Dementia Goal Bank for Speech Therapy

Speech Therapist Interview Questions for SNF
One thought on “ goal bank speech therapy for snf ”.
- Pingback: Dementia Goal Bank for Speech Therapy - Sunlight Speech Therapy
Comments are closed.
Privacy Overview
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
Now Hiring: Speech Language Pathologists! Learn more ->
Speech-Language Pathology IEP Goals: A Complete Guide and Goal Bank

Introduction
Effective communication is the cornerstone of a student's education and overall development. For some students facing unique communication challenges, Speech-Language Pathologists (SLPs) play a crucial role in paving the way toward proficient communication. Individualized Education Program (IEP ) goals in Speech-Language Pathology serve as powerful tools, uniquely tailored to address each student's specific communication needs. These goals guide educators, therapists, and parents toward a shared destination: empowering students to communicate confidently, express themselves authentically, and navigate both academic and social environments.
In this comprehensive guide we:
- Provide practical insights into crafting meaningful objectives
- Offer a goal bank with real-world examples
- Emphasize collaborative efforts needed to support students on their communication journeys
Understanding Speech-Language Pathology IEP Goals
The term "IEP goals" carries profound significance. An IEP, or Individualized Education Plan, is a personalized blueprint designed to ensure that every student, regardless of their unique challenges, receives an education tailored to their needs. At its heart, IEP goals are the compass guiding this journey, directing educators and specialists toward specific objectives that will help students flourish academically and socially.
Defining IEP Goals: Personalized Pathways to Success
IEP goals are precise, measurable objectives that chart a student's progress in various domains of education. They are not one-size-fits-all; instead, they are meticulously tailored to address the individual strengths and challenges of each student. These goals encompass a wide spectrum of skills, ranging from academic achievements to specialized areas such as Speech-Language Pathology (SLP).
The Role of Speech-Language Pathology (SLP)
Speech-Language Pathology (SLP) offers support for students facing communication difficulties. SLP professionals, known as Speech-Language Pathologists, possess the expertise to diagnose and treat a wide range of speech and language disorders, articulation difficulties, fluency disorders, voice disorders, and more. Their role extends beyond merely helping students articulate words clearly; it encompasses fostering effective communication in all its forms.
The Significance of IEP Goals in Speech-Language Pathology
Within the context of SLP services, IEP goals serve as the foundation upon which Speech-Language Pathologists build their intervention plans. Whether addressing articulation issues, language delays, or social communication challenges, SLPs rely on IEP goals to ensure that their strategies align with the specific needs of each student.
In the sections that follow, we will delve deeper into the art of crafting meaningful and impactful IEP goals in Speech-Language Pathology. We'll explore the intricacies of goal setting, share practical insights into aligning goals with students' unique communication profiles, and provide real-world examples that showcase the transformative power of well-crafted IEP goals.
Certainly! Here's an expanded Section 2 for your blog post on Speech-Language Pathology (SLP) IEP Goals:
The IEP Process: From Referral to Evaluation:
The journey of crafting and implementing Speech-Language Pathology (SLP) IEP goals is intricately woven into the larger landscape of the Individualized Education Program (IEP) process. Understanding this process, step by step, is essential to appreciate the vital role SLPs play in ensuring students' communication needs are met comprehensively.
The IEP Process Unveiled
The IEP process is a structured approach designed to identify, evaluate, and support students with diverse needs. It encompasses several key stages, each playing a pivotal role in shaping the educational experience of the student.
1.Referral: The process begins with a referral, where a student's unique needs are brought to the attention of educators and specialists. This stage is often initiated by teachers, parents, or other professionals who observe challenges in a student's communication skills.
SLP's Role : Speech-Language Pathologists may be among the first to identify communication difficulties and initiate the referral process. Their expertise in assessing speech and language disorders equips them to identify students who would benefit from SLP services.
2. Evaluation : Following the referral, a comprehensive evaluation is conducted to assess the student's strengths and challenges. This assessment involves a multidisciplinary team , which may include the SLP, working together to gather data, conduct tests, and analyze the student's communication abilities.
SLP's Role : In the evaluation stage, SLPs play a crucial role in assessing the student's speech and language skills. They contribute valuable insights into the nature and extent of communication difficulties, helping to inform the development of IEP goals tailored to the student's needs.
3. Eligibility Determination : Based on the evaluation results, the IEP team determines whether the student is eligible for specialized services. If eligibility is established, the team proceeds to create the student's individualized education plan, which includes SLP-related goals.
SLP's Role : SLPs provide critical input during the eligibility determination process, drawing on their expertise to advocate for students who require speech and language support. Their insights guide the team in making informed decisions about the student's eligibility.
4. Goal Setting : With eligibility confirmed, the IEP team, including the SLP, collaborates to set specific, measurable, and achievable goals for the student. These goals are at the heart of the IEP and serve as the foundation for intervention strategies.
SLP's Role : Speech-Language Pathologists take a lead role in crafting communication-related goals that address the student's individual needs. These goals are designed to enhance the student's speech production, language comprehension, or social communication skills.
5. IEP Implementation : Once the IEP is developed, it is put into action. SLPs work closely with the student, educators, and other professionals to implement the strategies and interventions outlined in the plan.
SLP's Role : SLPs are instrumental in delivering specialized services as outlined in the IEP. They employ evidence-based techniques and interventions to support the student in achieving their communication goals.
6. Progress Monitoring : Regular progress monitoring is essential to ensure that the student is making meaningful strides toward their goals. Adjustments to the IEP may be made based on the student's progress and evolving needs.
SLP's Role : Speech-Language Pathologists play a central role in tracking the student's communication progress. They use assessment data and ongoing observations to gauge the effectiveness of interventions, adapting strategies as necessary.
7. Collaboration: Throughout the IEP process, collaboration is key. This extends not only to the professionals involved but also to parents and caregivers who play a vital role in supporting the student's journey.
SLP's Role : SLPs foster collaboration by engaging with parents and other professionals to ensure a holistic approach to communication support. They provide insights, guidance, and resources to empower families in helping their child succeed.
Crafting Effective SLP IEP Goals
In Speech-Language Pathology (SLP), the path to effective communication starts with clear, purposeful goals. These goals act as guides for educators, specialists, and students, leading them toward proficient communication. To do this effectively, create SMART SLP IEP goals—ones that are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
1. Specific : Tailored to the student's unique needs.
2. Measurable : Trackable for progress.
3. Achievable : Realistic and attainable.
4. Relevant: Address specific communication challenges.
5. Time-bound : Set clear deadlines.
Common SLP IEP Goal Areas
Speech-Language Pathologists (SLPs) play a pivotal role in helping students overcome a wide array of communication challenges. To appreciate the breadth of their expertise, let's explore some of the common domains in which SLPs work their magic:
1. Articulation and Phonology
- Goal : Improve the clarity of speech sounds.
- Example : The student will correctly produce the /s/ and /z/ sounds in words and sentences with 80% accuracy in three consecutive therapy sessions.
2. Expressive Language
- Goal : Enhance the ability to express thoughts and ideas.
- Example : The student will use complete sentences to describe a picture or event, incorporating appropriate vocabulary and grammar.
3. Receptive Language
- Goal : Strengthen comprehension skills.
- Example : The student will follow two-step directions in the classroom environment, demonstrating understanding by completing tasks accurately.
4. Fluency (Stuttering)
- Goal: Improve speech fluency and reduce stuttering behaviors.
- Example: The student will employ smooth, uninterrupted speech patterns during oral presentations, with the ability to self-monitor and implement fluency techniques.
- Goal : Enhance vocal quality and resonance.
- Example: The student will use appropriate pitch and volume levels during conversational exchanges, maintaining vocal health and clarity.
6. Social Communication and Pragmatics
- Goal : Develop effective social interaction skills.
- Example : The student will engage in reciprocal conversations with peers, demonstrating turn-taking, active listening, and appropriate body language.
These are just a few of the areas where SLPs make a profound impact. Each goal is carefully tailored to the unique needs of the student, ensuring that interventions address specific challenges while promoting confidence and proficiency in communication.
In the next sections, we'll delve deeper into these domains, providing further insights and practical examples to illuminate the path toward achieving these goals.
IEP Goal Bank for Speech-Language Pathology
Articulation and phonology.
Preschool (Ages 3-5):
- The student will correctly produce the /k/ and /g/ sounds in initial and final word positions with 90% accuracy in spontaneous speech, as measured by audio recording and analysis.
- The student will reduce tongue thrust patterns, achieving 80% accuracy in structured speech tasks, as measured by audio recording and analysis.
Elementary (Ages 6-8):
- The student will use age-appropriate speech sounds when describing pictures, achieving 100% intelligibility among peers, as measured by peer evaluations.
- The student will maintain appropriate oral posture for speech production, reducing jaw tension and strain, as measured by an SLP's visual observation.
Middle School (Ages 9-12):
- The student will generalize correct /s/ and /z/ sounds from structured activities to conversational speech, as measured by audio recording and analysis.
- The student will improve the production of blends (e.g., "bl," "fl," "sn") in words and sentences, achieving 80% accuracy in structured speech tasks, as measured by audio recording and analysis.
Expressive Language
- The student will use basic vocabulary to express needs and preferences in sentences with 4-5 words, as measured by language samples.
- The student will increase the use of action verbs in spoken sentences and describe sequential events, demonstrating a 100-word vocabulary, as measured by language samples.
- The student will construct complex sentences with conjunctions (e.g., "although," "while") in written assignments, achieving 85% accuracy.
- The student will expand vocabulary by using synonyms, antonyms, and figurative language appropriately in oral and written language, as measured by vocabulary assessments.
- The student will improve narrative skills by generating original stories with a clear beginning, middle, and end, incorporating descriptive details, achieving 90% accuracy, as measured by narrative assessments.
- The student will use persuasive language and argumentative strategies in written essays, demonstrating effective communication of ideas, as measured by written compositions.
Receptive Language
- The student will follow one-step and two-step directions related to daily routines, such as "pick up the crayons and put them in the box," with 85% accuracy, as measured by teacher observations.
- The student will identify objects, actions, and spatial concepts in pictures and respond to "wh" questions (e.g., "Where is the cat?") with 80% accuracy, as measured by language samples.
- The student will listen to short stories and answer complex comprehension questions, including inferential questions, with 90% accuracy, as measured by reading comprehension assessments.
- The student will demonstrate improved auditory memory by recalling and summarizing spoken information, including main ideas and details, as measured by recall exercises.
- The student will use effective listening strategies, such as paraphrasing and asking clarifying questions, during classroom discussions and lectures, as measured by teacher feedback.
- The student will identify figurative language elements (e.g., similes, metaphors, idioms) in written texts and explain their meanings, achieving 85% accuracy, as measured by reading comprehension assessments.
Fluency (Stuttering)
- The student will reduce instances of stuttering by using easy onsets and light contacts during speech, achieving 95% fluency in structured speaking tasks, as measured by audio recording and analysis.
- The student will increase self-awareness of stuttering behaviors and use self-correction strategies, as measured by self-monitoring logs.
- The student will participate in classroom activities that involve speaking in front of peers, demonstrating improved fluency and control, as measured by teacher observations.
- The student will confidently engage in peer conversations, including open discussions and debates, demonstrating consistent fluency, as measured by peer evaluations and recorded conversations.
- The student will use appropriate pitch and resonance in speech, achieving a balanced vocal tone, as measured by audio recording and analysis.
- The student will employ vocal techniques to convey emotions and intentions effectively in spoken language, as measured by audience understanding and feedback.
- The student will improve vocal hygiene practices, reducing vocal strain and hoarseness, as measured by an SLP's visual observation and self-reporting.
Social Communication and Pragmatics:
- The student will initiate and maintain conversations with peers, incorporating turn-taking and active listening skills, as measured by peer evaluations and recorded conversations.
- The student will use polite language and request clarification appropriately during social interactions, demonstrating effective communication, as measured by teacher observations.
- The student will interpret non-verbal cues, such as body language and facial expressions, to understand social contexts and adjust behavior accordingly, as measured by comprehension of non-verbal cues in social interactions.
- The student will engage in cooperative group activities, demonstrating the ability to negotiate, compromise, and resolve conflicts with peers, as measured by teacher observations.
- The student will engage in role-play scenarios to practice problem-solving and conflict resolution in social situations, as measured by performance in role-play exercises.
- The student will use appropriate communication strategies in academic settings, such as seeking clarification from teachers and participating in classroom discussions, as measured by teacher feedback.
In the world of Speech-Language Pathology (SLP), the importance of setting clear and purposeful goals cannot be overstated. These goals act as guiding lights, directing educators, specialists, and students toward the destination of proficient and effective communication. Crafting Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART) SLP IEP goals is a transformative step, promoting personalized growth.
Effective communication profoundly influences students' academic and social success. As advocates for students' speech and language needs, we encourage you to champion well-crafted IEP goals. By doing so, we empower students to navigate their educational journey confidently, armed with the indispensable ability to communicate effectively. Together, let's ensure every student's voice is not only heard but celebrated in their journey of growth and achievement.
Want more? Subscribe for access to all free resources
79+ districts thriving with parallel.

Kelsey Breen
Special Education Coordinator, Illinois Valley Central School District

The professionals you need, the flexibility you want
With live-online services we are able to find related service professionals that will not compete against your ability to hire individuals in-district. We can reach IEP and 504 students from multiple sites, and offer flexible scheduling and pricing options.

Related articles

The Ultimate IEP Goal Guide for SLPs

Parallel Behind the Scenes: Natalie Bianco, M.A. CCC-SLP/L

Navigating Successful IEP Transitions: Planning for Students with Disabilities
Empowering School Districts with World-Class Providers, Fast
The power of partnership: canton union school district #66.
Students served by Parallel SLPs
Psychoeducational Assessments conducted
Total service hours provided
Unlock the case study

Empowering Excellence: Porterville Unified School District
Increase in SLPs
Increase in services delivered by Parallel

Contact & Support
Follow on Facebook
Connect on LinkedIn
Follow on Instragram
Subscribe on Youtube
All clinical services are provided by licensed physicians and clinicians practicing within independently owned and operated professional practices. For patients in New York and Connecticut, this is known as “Parallel Behavioral Health, P.C.” Parallel Learning, Inc. does not itself provide any physician, behavioral health professional, or other healthcare provider services.
How to Write Neurodiversity-Affirming Speech Therapy Goals [with goal bank]
Neurodiversity-affirming speech goals should include language and communication strategies that respect and acknowledge the diverse ways in which people think, learn, and communicate. This article discusses considerations when writing goals and includes complete goal examples.
What is Neurodiversity?
The concept of neurodiversity acknowledges that brain differences are natural and that conditions like autism, adhd, or stuttering are variations of the human brain, not deficits..
This concept is crucial to recognize in our field, as many speech-language pathologists (SLPs) treat individuals who identify as neurodivergent and are also the ones who provide support to their caregivers/families.
More recently, many SLPs have deliberately made the "switch" to a neurodiversity-affirming approach, which obviously includes goal writing! Part of implementing this approach involves educating oneself on the meaning and scope of neurodivergence and the experiences of neurodivergent individuals.
A message for clinicians who are exploring this approach for the first time: If you are unfamiliar with neurodiversity-affirming principles, that is okay! Changing a method of therapy that you’ve been accustomed to and formally educated on can take time and understanding. Many, if not all of us have been there. The important thing is that you are here and that you are interested in learning more to better your practice and increase your connection with your clients. Here, you can read more about what it means to be a neurodiversity-affirming therapist!

Tips for Writing Neurodiversity-Affirming Speech Therapy Goals
In the world of speech therapy, adopting a neurodiversity-affirming approach is not just a method but a philosophy that respects and values the differences in how individuals communicate and perceive the world. Therefore, it is important to remember that there isn’t a ‘set’ rule of thumb as to how neurodiversity-affirming goals should be written, but more of a general guideline of principles to consider when you sit down to write your goals . These principles focus on ways to look through a lens that highlights our client’s differences as strengths versus acknowledging these differences as disorders that need to be fixed.
Considerations when writing neurodiversity-affirming goals:
Goals should be…
Personalized to the individual
- Goals should focus on what is most meaningful and useful to the individual (this translates to: target what is most functional, and/or skill areas the client expresses interest in working on ). For instance, how can you write a goal for a client who expresses an interest in better understanding social cues so they can feel more comfortable knowing when to exit a conversation? Perhaps try one that involves learning to make environmental inferences. Why? For one, it is a functional skill that can be applied across contexts and secondly, this may also support the client’s understanding of the different variations of body language/phrases that are consistent with leaving an interaction.
Empowerment-focused versus "normalizing":
- Goals should refrain from pushing neurodivergent clients to conform to "typical" speech patterns and focus on empowering them to communicate in ways that are most effective for them. For example, a client who has had limited success with therapy goals that solely focus on communicating via oral language (verbally), may benefit from exploring augmentative and alternative communication (AAC), such as a speech-generating device . This client may have an increased quality of communication and effectiveness when using other communication modalities that are more suitable for their needs.
Inclusive and collaborative:
- Whenever possible, involve the client and/or their families in the development of their goals/treatment plan! This collaboration can contribute to a sense of assurance with a focus on goals that are aligned with the client’s individualized aspirations and needs. The role of the client and family ensures that the plan is individualized, goal-oriented, culturally and contextually relevant and that it empowers the client within their unique communication journey. We like to use our PDF fillable ethnographic interview to help obtain some of this personal information about our clients' home lives and routines.
Flexible and adaptable (if needed):
- Goals should be worded/sequenced in a way that recognizes that needs and preferences can change over time. Therefore, goals should balance between being adaptable while also recognizing that future goals may go in a different direction. In addition to goals being adaptable, we as clinicians should also be adaptable! For example, you may have a client who has an interest relating to baking; however, you’ve received input from his family that this interest has recently decreased. Rather than writing the client’s goal to say, [Name] will notify an adult by stating/pointing to an unexpected problem/unexpected event, within a kitchen/food prep setting, in 4 out of 5 opportunities , you may want to consider making it more adaptable to other contexts/settings. You could try something like, [Name] will notify an adult by stating/pointing to an unexpected problem/unexpected event, within a natural home setting (e.g., kitchen, living room, bedroom, etc.), in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Writing Neurodiversity-Affirming Goals
In this article, we focus on writing goals speech therapy goals that are consistent with a neurodiversity-affirming approach. Below we have provided goals that reflect a traditional (sometimes referred to as ableist ) approach to treatment, followed by those that are neurodiversity-affirming. First, we will dive into how these goals can be structured:
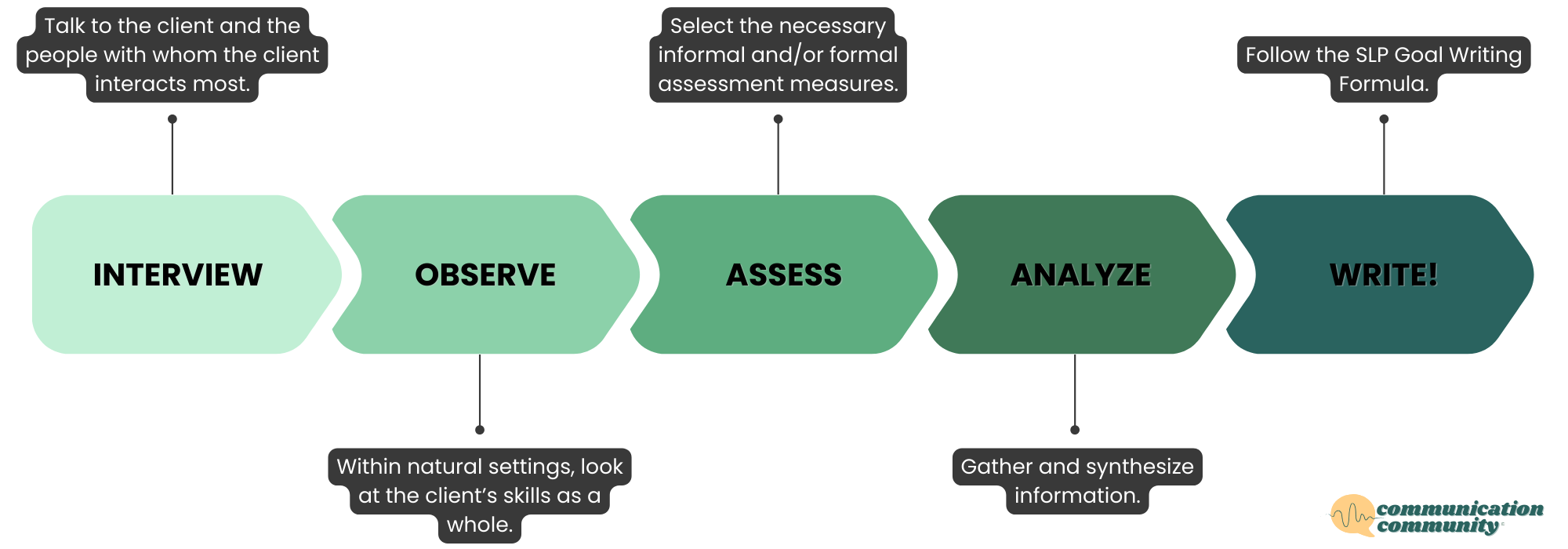
As seen above, speech goals should be written with 3* components in mind: the DO statement, the CONDITION statement, and the CRITERION statement.
*Also commonly included is consistency (we incorporate this!). Aka does the individual have to meet a specific criterion more than once? A common example of this may include across 3 consecutive sessions. This is usually something understood by the therapy organization/service provider and is sometimes/sometimes not included in the written goal itself. This is to ensure that the skill has been generalized and provides more reliable data that the skill has been properly mastered.
DO Statement
What the client is actually going to DO and the specific skill they will be working towards.
Example : will request additional information related to a subject area of interest
CONDITION Statement
The specific setting and/or context your client will work on this skill.
Example : within different academic environments (e.g., classroom setting)
CRITERION Statement
How the client’s performance will be measured.
Example : in 80% of opportunities
DO + CONDITION + CRITERION
Complete example : [Client] will request for additional information related to a subject area of interest, within varied academic environments (e.g., classroom setting), in 80% of opportunities.
There you have it! An example using our Goal Writing Formula containing the DO + CONDITION + CRITERION (don’t forget to think about consistency!) for writing neurodiversity-affirming goals.
Neurodiversity-Affirming Speech Therapy Goal Bank
Below, check out some of our neurodiversity-affirming goals for various areas of treatment. They include what a traditional approach to writing the goal may look like, followed by neurodiversity-affirming examples.
Perspective Taking
Traditional Approach : Teach standard ways of interpreting social situations and only consider the perspectives of others.
Neurodiversity-Affirming: Speech Therapy Goal Example 1
[Client] will identify their opinion about a particular subject/topic, when asked their perspective and when provided with a visual support, in 8 out of 10 opportunities.
Neurodiversity-Affirming: Speech Therapy Goal Example 2
[Client] will state their perspective related to a particular subject/topic, then state the (suspected) perspective of their communication partner, following a group conversation activity, in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
Body Autonomy (AAC)
Traditional Approach : The clinician uses an AAC prompting hierarchy that involves hand-over-hand prompts to target/achieve a communication goal.
[Client] will use a multimodal communication approach to express information about a preferred topic/interest, within varied contexts and settings, in 90% of opportunities.
[Client] will use the phrase “I need help,” to request assistance, following a clinician’s model, during routine tasks/activities, in 80% of opportunities.
Problem-Solving
Traditional Approach : Incorporates “problem” targets that are solely focused on ableist perspectives (e.g., Teaching that not having friends and/or eating lunch alone is considered a problem needing a solution).
[Client] will identify problems related to community safety, when presented with real picture scenes, in 8 out of 10 trials.
[Client] will state the cause of a functional problem, then state 1-2 preventative techniques, during therapy tasks, with 90% accuracy.
Self-Regulation
Traditional Approach : Teach outdated self-regulation techniques (e.g., eliminate stimming behaviors), irrespective of individual sensory preferences.
[Client] will identify (e.g., point to) settings where they feel most comfortable, when presented with a visual, in 75% of opportunities.
[Client] will state how they are feeling and if there is anything they need (e.g., “I feel anxious. I need my fidget.”), during a feeling scan activity or spontaneously, in 4 out of 5 of opportunities.
Self-Advocacy
Traditional Approach : Focus on adapting the individual to existing environments without necessarily advocating for personal needs or changes.
[Client] will request an accommodation related to work/school, within familiar settings (e.g., internship), in 80% of opportunities.
[Client] will state if she did not understand her communication partner’s message and request for clarification/repetition/ rephrasing, within conversational interactions, in 90% of opportunities.
Self-Awareness
Traditional Approach : Aim to increase awareness of how one's actions are perceived only according to neurotypical standards and expectations.
[Client] will state foods that they like, dislike, or have an allergy/food sensitivity to, when presented with menu options, across structured/unstructured settings, in 90% of opportunities.
[Client] will identify academic areas that they would like to improve or access more information about, during college preparation tasks, 4 times per treatment quarter.
Traditional Approach : Concentrate primarily on achieving fluent speech.
[Client] will research stuttering support channels (e.g., Instagram accounts of people who stutter [PWS]) and indicate if they are helpful/not helpful, within a clinical setting or as a home task, 5 times during the treatment period.
[Client] will complete a self-reflection about his stuttering experience across the week, within his home or educational setting, at least 1 time each week.
Social Communication
Traditional Approach : Only introduce neurotypical social communication norms and "appropriate" behaviors.
[Client] will introduce a conversational topic surrounding a shared interest between him and his communication partner, during various social interactions, in 4 out of 5 opportunities.
[Client] will describe a personal special interest to an unfamiliar/familiar communication partner, within leisure/social settings, with 80% opportunities.
While neurodiversity-affirming approaches are valuable, it's important to recognize that some neurodivergent (or neurotypical) individuals may prefer more traditional methods of therapy instruction or communication. For example, you may have a client who stutters and would prefer to work on increasing fluency. Every individual is unique, and what works best and is preferred by one person may not be the same for another. It's crucial to respect these preferences and tailor approaches accordingly. For some, traditional methods might provide a sense of structure or familiarity that is comforting or more effective in meeting their specific needs. Ultimately, the choice of therapy method should be guided by the individual's personal comfort, needs, and preferences, ensuring that they feel supported and empowered in their journey. A neurodiversity-affirming approach honors just that!
Looking for MORE neurodiversity-affirming goals and resources?
Check out our 5-star ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ comprehensive Self-Determination Goal Bank , covering the areas of:
- Choice & decision making
- Goal setting
- Problem solving
- Self-advocacy
- Self-awareness
- Self-efficacy
- Self-regulation
This goal content AND hundreds of pages of other resources (like our Ethnographic Interview ) are now available in our time, energy, and cost-saving Premium Community !

References/further resources
Burch, J. (2023, November 9). Affirming neurodivergence: no more ‘quiet hands.’ The ASHA LeaderLive. Retrieved November 30, 2023, from https://leader.pubs.asha.org/do/10.1044/leader.MIW.28112023.slp-neurodiverse-treatment.30/full/
Cleveland Clinic. (2022, June 2). Neurodivergent. Retrieved from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/23154-neurodivergent
Communication Community. (2023, December 1). How to be a neurodiversity-affirming speech therapist? Retrieved from https://www.communicationcommunity.com/how-to-be-a-neurodiversity-affirming-speech-therapist/
Communication Community. (2023, February). Self-Determination and Self-Advocacy Goals and Resources. Retrieved from https://www.communicationcommunity.com/self-determination-and-self-advocacy-goals-and-resources/
Communication Community. (2023, April 21). What is neurodiversity? Retrieved from https://www.communicationcommunity.com/what-is-neurodiversity/
Cross Country. (2023, September). SLP Goals: Neurodiversity-Affirming Speech Therapy. Retrieved from https://www.crosscountry.com/blog/slp-goals-neurodiversity-affirming-speech-therapy?
DeThorne, L., & Searsmith, K. (2020). Autism and neurodiversity: Addressing concerns and offering implications for the school-based speech-language pathologist. Perspectives of the ASHA Special Interest Groups, 6, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1044/2020_PERSP-20-00188
Dodd, A. (2023, April 19). Neurodiverse applicants are revolutionizing the hiring process. Quartz. Retrieved from https://qz.com/work/1981466/neurodiverse-applicants-are-revolutionizing-the-hiring-process/
Forbes Business Council. (2023, March 7). Why it's important to embrace neurodiversity in the workplace and how to do it effectively. Forbes. Retrieved from https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbesbusinesscouncil/2023/03/07/why-its-important-to-embrace-neurodiversity-in-the-workplace-and-how-to-do-it-effectively/?sh=6417d0eb4669
National Autism Resource and Information Center, & Autistic Self Advocacy Network. (n.d.). A curriculum for self advocates. Retrieved from https://autisticadvocacy.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/CurriculumForSelfAdvocates_r7.pdf
Sauers, J. (2023, November). Incorporating neurodiversity-affirming approaches. The Respectful SLP.
Therapist Neurodiversity Collective. (2023, July 17). Reassessing autistic social intelligence: Challenging the status quo of social skills training. Retrieved from https://therapistndc.org/therapy/social-skills-training/
Yu, B., & Sterponi, L. (2022). Toward neurodiversity: How conversation analysis can contribute to a new approach to social communication assessment. Language Speech and Hearing Services in Schools, 54(1), 27–41. https://doi.org/10.1044/2022_LSHSS-22-00041
You might also like

Cognition and Speech Therapy: Addressing Cognitive-Communicative Deficits

Research Outlines and Summaries for Speech Therapists
Supporting Carryover in Speech Therapy

Using AI to Enhance Speech Therapy Sessions

Data Collection in Speech Therapy: Why It's Important and Tips for Success
Subscribe to new posts., subscribe to be notified of new content and support communication community, help keep this site independent..


IMAGES
COMMENTS
Add these IEP problem solving goals for speech therapy to your goal bank for social language communication.
Speech therapy goal bank for social and pragmatic language, including dozens of goals to improve communication. Speech language therapy goal bank. List of words for each speech sound! Free speech therapy goal bank for articulation, phonology, speech sounds.
Your Goal Bank for Adult Speech Therapy comes with 150+ ready-made goals. Click for aphasia goals, dysarthria goals, memory goals, AAC goals—and much more.
#4 Problem Solving Make a smart guess about how a character will solve a problem. How will they fix that? This skill leads fantastically into size of the problem activities and solving problems in the real world! Photographs are perfect to work on social inferences in speech therapy.
During a 5-minute conversation with the speech language pathologist, [name] will identify and repair communication breakdowns in 3/4 of opportunities across three consecutive probing sessions.
If you want to save yourself time writing your IEP's you've come to the right place. Here is a 432+ free IEP goal bank to make your life easier writing your speech therapy goals and to save you time.
The Role of Speech Language Pathologists (SLPs) SLPs play a vital role in addressing pragmatic language goals. With their expertise and training, they can assess, diagnose, and provide intervention for individuals with pragmatic language difficulties. SLPs work collaboratively with other professionals, such as educators, psychologists, and occupational therapists, to ensure a holistic approach ...
Thus, pragmatic goals for speech therapy should target a child's social and communication skills in addition to their language development. Listed below are 4 examples of pragmatic goals for speech therapy: Increasing the use of eye contact: Eye contact is important for communication, as it can help show interest and attention.
Your in-depth guide to writing excellent, person-centered speech therapy goals. Comes with a mini goal bank.
Social Pragmatic Goals In Speech Therapy. Every one of the goals above corresponds to a need identified as part of the speech evaluations. Conversation skills, problem solving, nonverbal communication, and social cognition are all factored into these goals and how they impact a child's ability in conversational exchanges.
As school-based speech-language pathologists (SLPs), we are ideally positioned to help children with their problem-solving abilities, given that many problem-solving skills are language-based, and because our therapy sessions allow us to teach our students in a small group setting with a small number of peers, or even one-on-one.
Every SLP encounters obstacles in speech therapy. This post outlines 10 tools for speech therapists to use for clinical problem solving with students.
21 practical cognitive tasks to improve attention, memory, and problem solving. Read the article for ready-to-go speech therapy treatment ideas and our most popular free PDF!
It involves understanding and using language appropriately, interpreting nonverbal cues, initiating and maintaining conversations, understanding figurative language, and problem-solving in social interactions. Pragmatic language goals, therefore, are specific objectives that individuals set to improve their pragmatic language skills.
Expressive language is the ability to communicate thoughts, feelings, and ideas through speech, writing, or other forms of output. It's a crucial component of day-to-day interactions and a foundational skill for academic success and social integration. Speech therapy goals aimed at expressive language focus on enhancing the individual's ...
Cognition goals for speech therapy include the areas of attention, memory, problem-solving, executive functions, and using compensatory strategies. Individuals with cognitive-communicative deficits may benefit from speech therapy to address these areas and improve cognitive functioning.
Learn about effective IEP goals for high school students based on problem-solving skills and how specialists can support their development.
My middle school speech language therapy goal bank will give you ideas for speech therapy student goals, including social skills and conversation.
Goal Bank for speech therapists working in a skilled nursing facility. Goals for Cognition, Memory, Attention, Problem Solving, Aphasia, Dysarthria, Voice, Swallowing, Tracheostomy, and Skilled Maintenance.
In this post, you'll learn how to modify speech therapy goals for adults, with plenty of examples. Plus, you'll get a bonus Mini Goal Bank PDF! For even more help writing excellent goals, download our free Mini Goal Bank PDF! For evidence-based speech therapy materials, check out our bestselling Adult Speech Therapy Starter Pack! Visit Our ...
Here are 20 sample IEP goals for pragmatic language skills: Turn-Taking in Conversations: By [date], when engaged in conversation with peers, [student] will take turns speaking and listening, waiting for others to finish speaking before responding, in [percentage] of opportunities.
IEP goals are essential for students with speech and language disorders. This blog post provides a complete guide to writing effective IEP goals, as well as a bank of sample goals for a variety of speech and language areas.
Neurodiversity-affirming speech goals should include language and communication strategies that respect and acknowledge the diverse ways in which people think, learn, and communicate. This article discusses considerations when writing goals and includes complete goal examples.