- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
IResearchNet

Self-Presentation
Self-presentation definition.
Self-presentation refers to how people attempt to present themselves to control or shape how others (called the audience) view them. It involves expressing oneself and behaving in ways that create a desired impression. Self-presentation is part of a broader set of behaviors called impression management. Impression management refers to the controlled presentation of information about all sorts of things, including information about other people or events. Self-presentation refers specifically to information about the self.
Self-Presentation History and Modern Usage
Early work on impression management focused on its manipulative, inauthentic uses that might typify a used car salesperson who lies to sell a car, or someone at a job interview who embellishes accomplishments to get a job. However, researchers now think of self-presentation more broadly as a pervasive aspect of life. Although some aspects of self-presentation are deliberate and effortful (and at times deceitful), other aspects are automatic and done with little or no conscious thought. For example, a woman may interact with many people during the day and may make different impressions on each person. When she starts her day at her apartment, she chats with her roommates and cleans up after breakfast, thereby presenting the image of being a good friend and responsible roommate. During classes, she responds to her professor’s questions and carefully takes notes, presenting the image of being a good student. Later that day, she calls her parents and tells them about her classes and other activities (although likely leaving out information about some activities), presenting the image of being a loving and responsible daughter. That night, she might go to a party or dancing with friends, presenting the image of being fun and easygoing. Although some aspects of these self-presentations may be deliberate and conscious, other aspects are not. For example, chatting with her roommates and cleaning up after breakfast may be habitual behaviors that are done with little conscious thought. Likewise, she may automatically hold the door open for an acquaintance or buy a cup of coffee for a friend. These behaviors, although perhaps not done consciously or with self-presentation in mind, nevertheless convey an image of the self to others.

Although people have the ability to present images that are false, self-presentations are often genuine; they reflect an attempt by the person to have others perceive him or her accurately, or at least consistent with how the person perceives himself or herself. Self-presentations can vary as a function of the audience; people present different aspects of themselves to different audiences or under different conditions. A man likely presents different aspects of himself to his close friends than he does to his elderly grandmother, and a woman may present a different image to her spouse than she does to her employer. This is not to say that these different images are false. Rather, they represent different aspects of the self. The self is much like a gem with multiple facets. The gem likely appears differently depending on the angle at which it is viewed. However, the various appearances are all genuine. Even if people present a self-image that they know to be false, they may begin to internalize the self-image and thereby eventually come to believe the self-pres
entation. For example, a man may initially present an image of being a good student without believing it to be genuine, but after attending all his classes for several weeks, visiting the professor during office hours, and asking questions during class, he may come to see himself as truly being a good student. This internalization process is most likely to occur when people make a public commitment to the self-image, when the behavior is at least somewhat consistent with their self-image, and when they receive positive feedback or other rewards for presenting the self-image.
Self-presentation is often directed to external audiences such as friends, lovers, employers, teachers, children, and even strangers. Self-presentation is more likely to be conscious when the presenter depends on the audience for some reward, expects to interact with the audience in the future, wants something from the audience, or values the audience’s approval. Yet self-presentation extends beyond audiences that are physically present to imagined audiences, and these imagined audiences can have distinct effects on behavior. A young man at a party might suddenly think about his parents and change his behavior from rambunctious to reserved. People sometimes even make self-presentations only for themselves. For instance, people want to claim certain identities, such as being fun, intelligent, kind, moral, and they may behave in line with these identities even in private.
Self-Presentation Goals
Self-presentation is inherently goal-directed; people present certain images because they benefit from the images in some way. The most obvious benefits are interpersonal, arising from getting others to do what one wants. A job candidate may convey an image of being hardworking and dependable to get a job; a salesperson may convey an image of being trustworthy and honest to achieve a sale. People may also benefit from their self-presentations by gaining respect, power, liking, or other desirable social rewards. Finally, people make certain impressions on others to maintain a sense of who they are, or their self-concept. For example, a man who wants to think of himself as a voracious reader might join a book club or volunteer at a library, or a woman who wishes to perceive herself as generous may contribute lavishly to a charitable cause. Even when there are few or no obvious benefits of a particular self-presentation, people may simply present an image that is consistent with the way they like to think about themselves, or at least the way they are accustomed to thinking about themselves.
Much of self-presentation is directed toward achieving one of two desirable images. First, people want to appear likeable. People like others who are attractive, interesting, and fun to be with. Thus, a sizable proportion of self-presentation revolves around developing, maintaining, and enhancing appearance and conveying and emphasizing characteristics that others desire, admire, and enjoy. Second, people want to appear competent. People like others who are skilled and able, and thus another sizable proportion of self-presentation revolves around conveying an image of competence. Yet, self-presentation is not so much about presenting desirable images as it is about presenting desired images, and some desired images are not necessarily desirable. For example, schoolyard bullies may present an image of being dangerous or intimidating to gain or maintain power over others. Some people present themselves as weak or infirmed (or exaggerate their weaknesses) to gain help from others. For instance, a member of a group project may display incompetence in the hope that other members will do more of the work, or a child may exaggerate illness to avoid going to school.
Self-Presentation Avenues
People self-present in a variety of ways. Perhaps most obviously, people self-present in what they say. These verbalizations can be direct claims of a particular image, such as when a person claims to be altruistic. They also can be indirect, such as when a person discloses personal behaviors or standards (e.g., “I volunteer at a hospital”). Other verbal presentations emerge when people express attitudes or beliefs. Divulging that one enjoys backpacking through Europe conveys the image that one is a world-traveler. Second, people self-present nonverbally in their physical appearance, body language, and other behavior. Smiling, eye contact, and nods of agreement can convey a wealth of information. Third, people self-present through the props they surround themselves with and through their associations. Driving an expensive car or flying first class conveys an image of having wealth, whereas an array of diplomas and certificates on one’s office walls conveys an image of education and expertise. Likewise, people judge others based on their associations. For example, being in the company of politicians or movie stars conveys an image of importance, and not surprisingly, many people display photographs of themselves with famous people. In a similar vein, high school students concerned with their status are often careful about which classmates they are seen and not seen with publicly. Being seen by others in the company of someone from a member of a disreputable group can raise questions about one’s own social standing.
Self-Presentation Pitfalls
Self-presentation is most successful when the image presented is consistent with what the audience thinks or knows to be true. The more the image presented differs from the image believed or anticipated by the audience, the less willing the audience will be to accept the image. For example, the lower a student’s grade is on the first exam, the more difficulty he or she will have in convincing a professor that he or she will earn an A on the next exam. Self-presentations are constrained by audience knowledge. The more the audience knows about a person, the less freedom the person has in claiming a particular identity. An audience that knows very little about a person will be more accepting of whatever identity the person conveys, whereas an audience that knows a great deal about a person will be less accepting.
People engaging in self-presentation sometimes encounter difficulties that undermine their ability to convey a desired image. First, people occasionally encounter the multiple audience problem, in which they must simultaneously present two conflicting images. For example, a student while walking with friends who know only her rebellious, impetuous side may run into her professor who knows only her serious, conscientious side. The student faces the dilemma of conveying the conflicting images of rebellious friend and serious student. When both audiences are present, the student must try to behave in a way that is consistent with how her friends view her, but also in a way that is consistent with how her professor views her. Second, people occasionally encounter challenges to their self-presentations. The audience may not believe the image the person presents. Challenges are most likely to arise when people are managing impressions through self-descriptions and the self-descriptions are inconsistent with other evidence. For example, a man who claims to be good driver faces a self-presentational dilemma if he is ticketed or gets in an automobile accident. Third, self-presentations can fail when people lack the cognitive resources to present effectively because, for example, they are tired, anxious, or distracted. For instance, a woman may yawn uncontrollably or reflexively check her watch while talking to a boring classmate, unintentionally conveying an image of disinterest.
Some of the most important images for people to convey are also the hardest. As noted earlier, among the most important images people want to communicate are likeability and competence. Perhaps because these images are so important and are often rewarded, audiences may be skeptical of accepting direct claims of likeability and competence from presenters, thinking that the person is seeking personal gain. Thus, people must resort to indirect routes to create these images, and the indirect routes can be misinterpreted. For example, the student who sits in the front row of the class and asks a lot of questions may be trying to project an image of being a competent student but may be perceived negatively as a teacher’s pet by fellow students.
Finally, there is a dark side to self-presentation. In some instances, the priority people place on their appearances or images can threaten their health. People who excessively tan are putting a higher priority on their appearance (e.g., being tan) than on their health (e.g., taking precautions to avoid skin cancer). Similarly, although condoms help protect against sexually transmitted diseases and unwanted pregnancy, self-presentational concerns may dissuade partners or potential partners from discussing, carrying, or using condoms. Women may fear that carrying condoms makes them seem promiscuous or easy, whereas men may fear that carrying condoms makes them seem presumptuous, as if they are expecting to have sex. Self-presentational concerns may also influence interactions with health care providers and may lead people to delay or avoid embarrassing medical tests and procedures or treatments for conditions that are embarrassing. For example, people may be reluctant to seek tests or treatment for sexually transmitted diseases, loss of bladder control, mental disorders, mental decline, or other conditions associated with weakness or incompetence. Finally, concerns with social acceptance may prompt young people to engage in risky behaviors such as excessive alcohol consumption, sexual promiscuity, or juvenile delinquency.
References:
- Jones, E. E., Pittman, T. S. (1982). Toward a general theory of strategic self-presentation. In J. Suls (Ed.), Psychological perspectives on the self (Vol. 1, pp. 231-260). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
- Leary, M. R. (1996). Self-presentation: Impression management and interpersonal behavior. Boulder, CO: Westview Press.
- Leary, M. R., Tchividjian, L. R., & Kraxberger, B. E. (1994). Self-presentation can be hazardous to your health: Impression management and health risk. Health Psychology, 13, 461-470.
- Schlenker, B. R. (1980). Impression management: The self-concept, social identity, and interpersonal relations. Monterey, CA: Brooks/Cole.
How it works
Transform your enterprise with the scalable mindsets, skills, & behavior change that drive performance.
Explore how BetterUp connects to your core business systems.
We pair AI with the latest in human-centered coaching to drive powerful, lasting learning and behavior change.
Build leaders that accelerate team performance and engagement.
Unlock performance potential at scale with AI-powered curated growth journeys.
Build resilience, well-being and agility to drive performance across your entire enterprise.
Transform your business, starting with your sales leaders.
Unlock business impact from the top with executive coaching.
Foster a culture of inclusion and belonging.
Accelerate the performance and potential of your agencies and employees.
See how innovative organizations use BetterUp to build a thriving workforce.
Discover how BetterUp measurably impacts key business outcomes for organizations like yours.
Daring Leadership Institute: a groundbreaking partnership that amplifies Brené Brown's empirically based, courage-building curriculum with BetterUp’s human transformation platform.

- What is coaching?
Learn how 1:1 coaching works, who its for, and if it's right for you.
Accelerate your personal and professional growth with the expert guidance of a BetterUp Coach.
Types of Coaching
Navigate career transitions, accelerate your professional growth, and achieve your career goals with expert coaching.
Enhance your communication skills for better personal and professional relationships, with tailored coaching that focuses on your needs.
Find balance, resilience, and well-being in all areas of your life with holistic coaching designed to empower you.
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.
Find your coach
-1.png)
Research, expert insights, and resources to develop courageous leaders within your organization.
Best practices, research, and tools to fuel individual and business growth.
View on-demand BetterUp events and learn about upcoming live discussions.
The latest insights and ideas for building a high-performing workplace.
- BetterUp Briefing
The online magazine that helps you understand tomorrow's workforce trends, today.
Innovative research featured in peer-reviewed journals, press, and more.
Founded in 2022 to deepen the understanding of the intersection of well-being, purpose, and performance
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.

For Business
For Individuals

The self presentation theory and how to present your best self

Jump to section
What does self presentation mean?
What are self presentation goals, individual differences and self presentation.
How can you make the most of the self presentation theory at work?
We all want others to see us as confident, competent, and likeable — even if we don’t necessarily feel that way all the time. In fact, we make dozens of decisions every day — whether consciously or unconsciously — to get people to see us as we want to be seen. But is this kind of self presentation dishonest? Shouldn’t we just be ourselves?
Success requires interacting with other people. We can’t control the other side of those interactions. But we can think about how the other person might see us and make choices about what we want to convey.
Self presentation is any behavior or action made with the intention to influence or change how other people see you. Anytime we're trying to get people to think of us a certain way, it's an act of self presentation. Generally speaking, we work to present ourselves as favorably as possible. What that means can vary depending on the situation and the other person.
Although at first glance this may seem disingenuous, we all engage in self-presentation. We want to make sure that we show up in a way that not only makes us look good, but makes us feel good about ourselves.
Early research on self presentation focused on narcissism and sociopathy, and how people might use the impression others have of them to manipulate others for their benefit. However, self presentation and manipulation are distinct. After all, managing the way others see us works for their benefit as well as ours.
Imagine, for example, a friend was complaining to you about a tough time they were having at work . You may want to show up as a compassionate person. However, it also benefits your friend — they feel heard and able to express what is bothering them when you appear to be present, attentive, and considerate of their feelings. In this case, you’d be conscious of projecting a caring image, even if your mind was elsewhere, because you value the relationship and your friend’s experience.
To some extent, every aspect of our lives depends on successful self-presentation. We want our families to feel that we are worthy of attention and love. We present ourselves as studious and responsible to our teachers. We want to seem fun and interesting at a party, and confident at networking events. Even landing a job depends on you convincing the interviewer that you are the best person for the role.
There are three main reasons why people engage in self presentation:
Tangible or social benefits:
In order to achieve the results we want, it often requires that we behave a certain way. In other words, certain behaviors are desirable in certain situations. Matching our behavior to the circumstances can help us connect to others, develop a sense of belonging , and attune to the needs and feelings of others.
Example: Michelle is a new manager . At her first leadership meeting, someone makes a joke that she doesn’t quite get. When everyone else laughs, she smiles, even though she’s not sure why.
By laughing along with the joke, Michelle is trying to fit in and appear “in the know.” Perhaps more importantly, she avoids feeling (or at least appearing) left out, humorless, or revealing that she didn’t get it — which may hurt her confidence and how she interacts with the group in the future.
To facilitate social interaction:
As mentioned, certain circumstances and roles call for certain behaviors. Imagine a defense attorney. Do you think of them a certain way? Do you have expectations for what they do — or don’t — do? If you saw them frantically searching for their car keys, would you feel confident with them defending your case?
If the answer is no, then you have a good idea of why self presentation is critical to social functioning. We’re surprised when people don’t present themselves in a way that we feel is consistent with the demands of their role. Having an understanding of what is expected of you — whether at home, work, or in relationships — may help you succeed by inspiring confidence in others.
Example: Christopher has always been called a “know-it-all.” He reads frequently and across a variety of topics, but gets nervous and tends to talk over people. When attending a networking event, he is uncharacteristically quiet. Even though he would love to speak up, he’s afraid of being seen as someone who “dominates” the conversation.
Identity Construction:
It’s not enough for us to declare who we are or what we want to be — we have to take actions consistent with that identity. In many cases, we also have to get others to buy into this image of ourselves as well. Whether it’s a personality trait or a promotion, it can be said that we’re not who we think we are, but who others see.
Example: Jordan is interested in moving to a client-facing role. However, in their last performance review, their manager commented that Jordan seemed “more comfortable working independently.”
Declaring themselves a “people person” won’t make Jordan’s manager see them any differently. In order to gain their manager’s confidence, Jordan will have to show up as someone who can comfortably engage with clients and thrive in their new role.
We may also use self presentation to reinforce a desired identity for ourselves. If we want to accomplish something, make a change, or learn a new skill , making it public is a powerful strategy. There's a reason why people who share their goals are more likely to be successful. The positive pressure can help us stay accountable to our commitments in a way that would be hard to accomplish alone.
Example: Fatima wants to run a 5K. She’s signed up for a couple before, but her perfectionist tendencies lead her to skip race day because she feels she hasn’t trained enough. However, when her friend asks her to run a 5K with her, she shows up without a second thought.
In Fatima’s case, the positive pressure — along with the desire to serve a more important value (friendship) — makes showing up easy.
Because we spend so much time with other people (and our success largely depends on what they think of us), we all curate our appearance in one way or another. However, we don’t all desire to have people see us in the same way or to achieve the same goals. Our experiences and outcomes may vary based on a variety of factors.
One important factor is our level of self-monitoring when we interact with others. Some people are particularly concerned about creating a good impression, while others are uninterested. This can vary not only in individuals, but by circumstances. A person may feel very confident at work , but nervous about making a good impression on a first date.
Another factor is self-consciousness — that is, how aware people are of themselves in a given circumstance. People that score high on scales of public self-consciousness are aware of how they come across socially. This tends to make it easier for them to align their behavior with the perception that they want others to have of them.
Finally, it's not enough to simply want other people to see you differently. In order to successfully change how other people perceive you, need to have three main skills:
1. Perception and empathy
Successful self-presentation depends on being able to correctly perceive how people are feeling , what's important to them, and which traits you need to project in order to achieve your intended outcomes.
2. Motivation
If we don’t have a compelling reason to change the perception that others have of us, we are not likely to try to change our behavior. Your desire for a particular outcome, whether it's social or material, creates a sense of urgency.
3. A matching skill set
You’ve got to be able to walk the talk. Your actions will convince others more than anything you say. In other words, you have to provide evidence that you are the person you say you are. You may run into challenges if you're trying to portray yourself as skilled in an area where you actually lack experience.
How can you make the most of the self presentation theory at work?
At its heart, self presentation requires a high-level of self awareness and empathy. In order to make sure that we're showing up as our best in every circumstance — and with each person — we have to be aware of our own motivation as well as what would make the biggest difference to the person in front of us.
Here are 6 strategies to learn to make the most of the self-presentation theory in your career:
1. Get feedback from people around you
Ask a trusted friend or mentor to share what you can improve. Asking for feedback about specific experiences, like a recent project or presentation, will make their suggestions more relevant and easier to implement.
2. Study people who have been successful in your role
Look at how they interact with other people. How do you perceive them? Have they had to cultivate particular skills or ways of interacting with others that may not have come easily to them?
3. Be yourself
Look for areas where you naturally excel and stand out. If you feel comfortable, confident, and happy, you’ll have an easier time projecting that to others. It’s much harder to present yourself as confident when you’re uncomfortable.
4. Be aware that you may mess up
As you work to master new skills and ways of interacting with others, keep asking for feedback . Talk to your manager, team, or a trusted friend about how you came across. If you sense that you’ve missed the mark, address it candidly. People will understand, and you’ll learn more quickly.
Try saying, “I hope that didn’t come across as _______. I want you to know that…”
5. Work with a coach
Coaches are skilled in interpersonal communication and committed to your success. Roleplay conversations to see how they land, and practice what you’ll say and do in upcoming encounters. Over time, a coach will also begin to know you well enough to notice patterns and suggest areas for improvement.
6. The identity is in the details
Don’t forget about the other aspects of your presentation. Take a moment to visualize yourself being the way that you want to be seen. Are there certain details that would make you feel more like that person? Getting organized, refreshing your wardrobe, rewriting your resume, and even cleaning your home office can all serve as powerful affirmations of your next-level self.
Self presentation is defined as the way we try to control how others see us, but it’s just as much about how we see ourselves. It is a skill to achieve a level of comfort with who we are and feel confident to choose how we self-present. Consciously working to make sure others get to see the very best of you is a wonderful way to develop into the person you want to be.
Understand Yourself Better:
Big 5 Personality Test
Allaya Cooks-Campbell
With over 15 years of content experience, Allaya Cooks Campbell has written for outlets such as ScaryMommy, HRzone, and HuffPost. She holds a B.A. in Psychology and is a certified yoga instructor as well as a certified Integrative Wellness & Life Coach. Allaya is passionate about whole-person wellness, yoga, and mental health.
Impression management: Developing your self-presentation skills
6 presentation skills and how to improve them, how to make a presentation interactive and exciting, how to give a good presentation that captivates any audience, what is self-preservation 5 skills for achieving it, how to not be nervous for a presentation — 13 tips that work (really), how self-knowledge builds success: self-awareness in the workplace, self-promotion: how to showcase your skills and experience, 80 affirmations for confidence: combatting self-doubt with self-love, how self-compassion strengthens resilience, how self-efficacy can boost your personal success, what is self-awareness and how to develop it, what i didn't know before working with a coach: the power of reflection, self-advocacy: improve your life by speaking up, building resilience part 6: what is self-efficacy, why learning from failure is your key to success, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform Overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead™
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care®
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case Studies
- Why BetterUp?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Personal Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Labs
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences
Impression Management: Erving Goffman Theory
Charlotte Nickerson
Research Assistant at Harvard University
Undergraduate at Harvard University
Charlotte Nickerson is a student at Harvard University obsessed with the intersection of mental health, productivity, and design.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Saul McLeod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul McLeod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
- Impression management refers to the goal-directed conscious or unconscious attempt to influence the perceptions of other people about a person, object, or event by regulating and controlling information in social interaction.
- Generally, people undertake impression management to achieve goals that require they have a desired public image. This activity is called self-presentation.
- In sociology and social psychology, self-presentation is the conscious or unconscious process through which people try to control the impressions other people form of them.
- The goal is for one to present themselves the way in which they would like to be thought of by the individual or group they are interacting with. This form of management generally applies to the first impression.
- Erving Goffman popularized the concept of perception management in his book, The Presentation of Self in Everyday Life , where he argues that impression management not only influences how one is treated by other people but is an essential part of social interaction.

Impression Management in Sociology
Impression management, also known as self-presentation, refers to the ways that people attempt to control how they are perceived by others (Goffman, 1959).
By conveying particular impressions about their abilities, attitudes, motives, status, emotional reactions, and other characteristics, people can influence others to respond to them in desirable ways.
Impression management is a common way for people to influence one another in order to obtain various goals.
While earlier theorists (e.g., Burke, 1950; Hart & Burk, 1972) offered perspectives on the person as a performer, Goffman (1959) was the first to develop a specific theory concerning self-presentation.
In his well-known work, Goffman created the foundation and the defining principles of what is commonly referred to as impression management.
In explicitly laying out a purpose for his work, Goffman (1959) proposes to “consider the ways in which the individual in ordinary work situations presents himself and his activity to others, the ways in which he guides and controls the impression they form of him, and the kind of things he may or may not do while sustaining his performance before them.” (p. xi)
Social Interaction
Goffman viewed impression management not only as a means of influencing how one is treated by other people but also as an essential part of social interaction.
He communicates this view through the conceit of theatre. Actors give different performances in front of different audiences, and the actors and the audience cooperate in negotiating and maintaining the definition of a situation.
To Goffman, the self was not a fixed thing that resides within individuals but a social process. For social interactions to go smoothly, every interactant needs to project a public identity that guides others’ behaviors (Goffman, 1959, 1963; Leary, 2001; Tseelon, 1992).
Goffman defines that when people enter the presence of others, they communicate information by verbal intentional methods and by non-verbal unintentional methods.
According to Goffman, individuals participate in social interactions through performing a “line” or “a pattern of verbal and nonverbal acts by which he expresses his view of the situation and through this his evaluation of the participants, especially himself” (1967, p. 5).
Such lines are created and maintained by both the performer and the audience. By enacting a line effectively, a person gains positive social value or “face.”
The verbal intentional methods allow us to establish who we are and what we wish to communicate directly. We must use these methods for the majority of the actual communication of data.
Goffman is mostly interested in the non-verbal clues given off which are less easily manipulated. When these clues are manipulated the receiver generally still has the upper hand in determining how realistic the clues that are given off are.
People use these clues to determine how to treat a person and if the intentional verbal responses given off are actually honest. It is also known that most people give off clues that help to represent them in a positive light, which tends to be compensated for by the receiver.
Impression Management Techniques
- Suppressing emotions : Maintaining self-control (which we will identify with such practices as speaking briefly and modestly).
- Conforming to Situational Norms : The performer follows agreed-upon rules for behavior in the organization.
- Flattering Others : The performer compliments the perceiver. This tactic works best when flattery is not extreme and when it involves a dimension important to the perceiver.
- Being Consistent : The performer’s beliefs and behaviors are consistent. There is agreement between the performer’s verbal and nonverbal behaviors.
Self-Presentation Examples
Self-presentation can affect the emotional experience . For example, people can become socially anxious when they are motivated to make a desired impression on others but doubt that they can do so successfully (Leary, 2001).
In one paper on self-presentation and emotional experience, Schlenker and Leary (1982) argue that, in contrast to the drive models of anxiety, the cognitive state of the individual mediates both arousal and behavior.
The researchers examine the traditional inverted-U anxiety-performance curve (popularly known as the Yerkes-Dodson law) in this light.
The researchers propose that people are interpersonally secure when they do not have the goal of creating a particular impression on others.
They are not immediately concerned about others’ evaluative reactions in a social setting where they are attempting to create a particular impression and believe that they will be successful in doing so.
Meanwhile, people are anxious when they are uncertain about how to go about creating a certain impression (such as when they do not know what sort of attributes the other person is likely to be impressed with), think that they will not be able to project the types of images that will produce preferred reactions from others.
Such people think that they will not be able to project the desired image strongly enough or believe that some event will happen that will repudiate their self-presentations, causing reputational damage (Schlenker and Leary, 1982).
Psychologists have also studied impression management in the context of mental and physical health .
In one such study, Braginsky et al. (1969) showed that those hospitalized with schizophrenia modify the severity of their “disordered” behavior depending on whether making a more or less “disordered” impression would be most beneficial to them (Leary, 2001).
Additional research on university students shows that people may exaggerate or even fabricate reports of psychological distress when doing so for their social goals.
Hypochondria appears to have self-presentational features where people convey impressions of illness and injury, when doing so helps to drive desired outcomes such as eliciting support or avoiding responsibilities (Leary, 2001).
People can also engage in dangerous behaviors for self-presentation reasons such as suntanning, unsafe sex, and fast driving. People may also refuse needed medical treatment if seeking this medical treatment compromises public image (Leary et al., 1994).
Key Components
There are several determinants of impression management, and people have many reasons to monitor and regulate how others perceive them.
For example, social relationships such as friendship, group membership, romantic relationships, desirable jobs, status, and influence rely partly on other people perceiving the individual as being a particular kind of person or having certain traits.
Because people’s goals depend on them making desired impressions over undesired impressions, people are concerned with the impressions other people form of them.
Although people appear to monitor how they come across ongoingly, the degree to which they are motivated to impression manage and the types of impressions they try to foster varies by situation and individuals (Leary, 2001).
Leary and Kowalski (1990) say that there are two processes that constitute impression management, each of which operate according to different principles and are affected by different situations and dispositional aspects. The first of these processes is impression motivation, and the second is impression construction.
| Impression Motivation | Impression Construction |
|---|---|
| Goal-relevance of impressions | Self-concept |
| Value of desired goals | Desired and undesired identity images |
| Discrepancy between the desired and current image | Role constraints |
Impression Motivation
There are three main factors that affect how much people are motivated to impression-manage in a situation (Leary and Kowalski, 1990):
(1) How much people believe their public images are relevant to them attaining their desired goals.
When people believe that their public image is relevant to them achieving their goals, they are generally more motivated to control how others perceive them (Leary, 2001).
Conversely, when the impressions of other people have few implications on one’s outcomes, that person’s motivation to impression-manage will be lower.
This is why people are more likely to impression manage in their interactions with powerful, high-status people than those who are less powerful and have lower status (Leary, 2001).
(2) How valuable the goals are: people are also more likely to impress and manage the more valuable the goals for which their public impressions are relevant (Leary, 2001).
(3) how much of a discrepancy there is between how they want to be perceived and how they believe others perceive them..
People are more highly motivated to impression-manage when there is a difference between how they want to be perceived and how they believe others perceive them.
For example, public scandals and embarrassing events that convey undesirable impressions can cause people to make self-presentational efforts to repair what they see as their damaged reputations (Leary, 2001).
Impression Construction
Features of the social situations that people find themselves in, as well as their own personalities, determine the nature of the impressions that they try to convey.
In particular, Leary and Kowalski (1990) name five sets of factors that are especially important in impression construction (Leary, 2001).
Two of these factors include how people’s relationships with themselves (self-concept and desired identity), and three involve how people relate to others (role constraints, target value, and current or potential social image) (Leary and Kowalski, 1990).
Self-concept
The impressions that people try to create are influenced not only by social context but also by one’s own self-concept .
People usually want others to see them as “how they really are” (Leary, 2001), but this is in tension with the fact that people must deliberately manage their impressions in order to be viewed accurately by others (Goffman, 1959).
People’s self-concepts can also constrain the images they try to convey.
People often believe that it is unethical to present impressions of themselves different from how they really are and generally doubt that they would successfully be able to sustain a public image inconsistent with their actual characteristics (Leary, 2001).
This risk of failure in portraying a deceptive image and the accompanying social sanctions deter people from presenting impressions discrepant from how they see themselves (Gergen, 1968; Jones and Pittman, 1982; Schlenker, 1980).
People can differ in how congruent their self-presentations are with their self-perceptions.
People who are high in public self-consciousness have less congruency between their private and public selves than those lower in public self-consciousness (Tunnell, 1984; Leary and Kowalski, 1990).
Desired identity
People’s desired and undesired selves – how they wish to be and not be on an internal level – also influence the images that they try to project.
Schlenker (1985) defines a desirable identity image as what a person “would like to be and thinks he or she really can be, at least at his or her best.”
People have a tendency to manage their impressions so that their images coincide with their desired selves and stay away from images that coincide with their undesired selves (Ogilivie, 1987; Schlenker, 1985; Leary, 2001).
This happens when people publicly claim attributes consistent with their desired identity and openly reject identities that they do not want to be associated with.
For example, someone who abhors bigots may take every step possible to not appear bigoted, and Gergen and Taylor (1969) showed that high-status navel cadets did not conform to low-status navel cadets because they did not want to see themselves as conformists (Leary and Kowalski, 1990).
Target value
people tailor their self-presentations to the values of the individuals whose perceptions they are concerned with.
This may lead to people sometimes fabricating identities that they think others will value.
However, more commonly, people selectively present truthful aspects of themselves that they believe coincide with the values of the person they are targeting the impression to and withhold information that they think others will value negatively (Leary, 2001).
Role constraints
the content of people’s self-presentations is affected by the roles that they take on and the norms of their social context.
In general, people want to convey impressions consistent with their roles and norms .
Many roles even carry self-presentational requirements around the kinds of impressions that the people who hold the roles should and should not convey (Leary, 2001).
Current or potential social image
People’s public image choices are also influenced by how they think they are perceived by others. As in impression motivation, self-presentational behaviors can often be aimed at dispelling undesired impressions that others hold about an individual.
When people believe that others have or are likely to develop an undesirable impression of them, they will typically try to refute that negative impression by showing that they are different from how others believe them to be.
When they are not able to refute this negative impression, they may project desirable impressions in other aspects of their identity (Leary, 2001).
Implications
In the presence of others, few of the behaviors that people make are unaffected by their desire to maintain certain impressions. Even when not explicitly trying to create a particular impression of themselves, people are constrained by concerns about their public image.
Generally, this manifests with people trying not to create undesired impressions in virtually all areas of social life (Leary, 2001).
Tedeschi et al. (1971) argued that phenomena that psychologists previously attributed to peoples’ need to have cognitive consistency actually reflected efforts to maintain an impression of consistency in others’ eyes.
Studies have supported Tedeschi and their colleagues’ suggestion that phenomena previously attributed to cognitive dissonance were actually affected by self-presentational processes (Schlenker, 1980).
Psychologists have applied self-presentation to their study of phenomena as far-ranging as conformity, aggression, prosocial behavior, leadership, negotiation, social influence, gender, stigmatization, and close relationships (Baumeister, 1982; Leary, 1995; Schlenker, 1980; Tedeschi, 1981).
Each of these studies shows that people’s efforts to make impressions on others affect these phenomena, and, ultimately, that concerns self-presentation in private social life.
For example, research shows that people are more likely to be pro-socially helpful when their helpfulness is publicized and behave more prosocially when they desire to repair a damaged social image by being helpful (Leary, 2001).
In a similar vein, many instances of aggressive behavior can be explained as self-presentational efforts to show that someone is willing to hurt others in order to get their way.
This can go as far as gender roles, for which evidence shows that men and women behave differently due to the kind of impressions that are socially expected of men and women.
Baumeister, R. F. (1982). A self-presentational view of social phenomena. Psychological Bulletin, 91, 3-26.
Braginsky, B. M., Braginsky, D. D., & Ring, K. (1969). Methods of madness: The mental hospital as a last resort. New York: Holt, Rinehart & Winston.
Buss, A. H., & Briggs, S. (1984). Drama and the self in social interaction. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 47, 1310-1324. Gergen, K. J. (1968). Personal consistency and the presentation of self. In C. Gordon & K. J. Gergen (Eds.), The self in social interaction (Vol. 1, pp. 299-308). New York: Wiley.
Gergen, K. J., & Taylor, M. G. (1969). Social expectancy and self-presentation in a status hierarchy. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 5, 79-92.
Goffman, E. (1959). The moral career of the mental patient. Psychiatry, 22(2), 123-142.
- Goffman, E. (1963). Embarrassment and social organization.
Goffman, E. (1978). The presentation of self in everyday life (Vol. 21). London: Harmondsworth.
Goffman, E. (2002). The presentation of self in everyday life. 1959. Garden City, NY, 259.
Martey, R. M., & Consalvo, M. (2011). Performing the looking-glass self: Avatar appearance and group identity in Second Life. Popular Communication, 9 (3), 165-180.
Jones E E (1964) Ingratiation. Appleton-Century-Crofts, New York.
Jones, E. E., & Pittman, T. S. (1982). Toward a general theory of strategic self-presentation. Psychological perspectives on the self, 1(1), 231-262.
Leary M R (1995) Self-presentation: Impression Management and Interpersonal Behaior. Westview Press, Boulder, CO.
Leary, M. R.. Impression Management, Psychology of, in Smelser, N. J., & Baltes, P. B. (Eds.). (2001). International encyclopedia of the social & behavioral sciences (Vol. 11). Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Leary, M. R., & Kowalski, R. M. (1990). Impression management: A literature review and two-component model. Psychological bulletin, 107(1), 34.
Leary M R, Tchvidjian L R, Kraxberger B E 1994 Self-presentation may be hazardous to your health. Health Psychology 13: 461–70.
Ogilvie, D. M. (1987). The undesired self: A neglected variable in personality research. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 52, 379-385.
- Schlenker, B. R. (1980). Impression management (Vol. 222). Monterey, CA: Brooks/Cole.
Schlenker, B. R. (1985). Identity and self-identification. In B. R. Schlenker (Ed.), The self and social life (pp. 65-99). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Schlenker, B. R., & Leary, M. R. (1982). Social anxiety and self-presentation: A conceptualization model. Psychological bulletin, 92(3), 641.
Tedeschi, J. T, Smith, R. B., Ill, & Brown, R. C., Jr. (1974). A reinterpretation of research on aggression. Psychological Bulletin, 81, 540- 563.
Tseëlon, E. (1992). Is the presented self sincere? Goffman, impression management and the postmodern self. Theory, culture & society, 9(2), 115-128.
Tunnell, G. (1984). The discrepancy between private and public selves: Public self-consciousness and its correlates. Journal of Personality Assessment, 48, 549-555.
Further Information
- Solomon, J. F., Solomon, A., Joseph, N. L., & Norton, S. D. (2013). Impression management, myth creation and fabrication in private social and environmental reporting: Insights from Erving Goffman. Accounting, organizations and society, 38(3), 195-213.
- Gardner, W. L., & Martinko, M. J. (1988). Impression management in organizations. Journal of management, 14(2), 321-338.
- Scheff, T. J. (2005). Looking‐Glass self: Goffman as symbolic interactionist. Symbolic interaction, 28(2), 147-166.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
2.3 Perceiving and Presenting Self
Learning objectives.
- Define self-concept and discuss how we develop our self-concept.
- Define self-esteem and discuss how we develop self-esteem.
- Explain how social comparison theory and self-discrepancy theory influence self-perception.
- Discuss how social norms, family, culture, and media influence self-perception.
- Define self-presentation and discuss common self-presentation strategies.
Just as our perception of others affects how we communicate, so does our perception of ourselves. But what influences our self-perception? How much of our self is a product of our own making and how much of it is constructed based on how others react to us? How do we present ourselves to others in ways that maintain our sense of self or challenge how others see us? We will begin to answer these questions in this section as we explore self-concept, self-esteem, and self-presentation.
Self-Concept
Self-concept refers to the overall idea of who a person thinks he or she is. If I said, “Tell me who you are,” your answers would be clues as to how you see yourself, your self-concept. Each person has an overall self-concept that might be encapsulated in a short list of overarching characteristics that he or she finds important. But each person’s self-concept is also influenced by context, meaning we think differently about ourselves depending on the situation we are in. In some situations, personal characteristics, such as our abilities, personality, and other distinguishing features, will best describe who we are. You might consider yourself laid back, traditional, funny, open minded, or driven, or you might label yourself a leader or a thrill seeker. In other situations, our self-concept may be tied to group or cultural membership. For example, you might consider yourself a member of the Sigma Phi Epsilon fraternity, a Southerner, or a member of the track team.

Men are more likely than women to include group memberships in their self-concept descriptions.
Stefano Ravalli – In control – CC BY-NC-SA 2.0.
Our self-concept is also formed through our interactions with others and their reactions to us. The concept of the looking glass self explains that we see ourselves reflected in other people’s reactions to us and then form our self-concept based on how we believe other people see us (Cooley, 1902). This reflective process of building our self-concept is based on what other people have actually said, such as “You’re a good listener,” and other people’s actions, such as coming to you for advice. These thoughts evoke emotional responses that feed into our self-concept. For example, you may think, “I’m glad that people can count on me to listen to their problems.”
We also develop our self-concept through comparisons to other people. Social comparison theory states that we describe and evaluate ourselves in terms of how we compare to other people. Social comparisons are based on two dimensions: superiority/inferiority and similarity/difference (Hargie, 2011). In terms of superiority and inferiority, we evaluate characteristics like attractiveness, intelligence, athletic ability, and so on. For example, you may judge yourself to be more intelligent than your brother or less athletic than your best friend, and these judgments are incorporated into your self-concept. This process of comparison and evaluation isn’t necessarily a bad thing, but it can have negative consequences if our reference group isn’t appropriate. Reference groups are the groups we use for social comparison, and they typically change based on what we are evaluating. In terms of athletic ability, many people choose unreasonable reference groups with which to engage in social comparison. If a man wants to get into better shape and starts an exercise routine, he may be discouraged by his difficulty keeping up with the aerobics instructor or running partner and judge himself as inferior, which could negatively affect his self-concept. Using as a reference group people who have only recently started a fitness program but have shown progress could help maintain a more accurate and hopefully positive self-concept.
We also engage in social comparison based on similarity and difference. Since self-concept is context specific, similarity may be desirable in some situations and difference more desirable in others. Factors like age and personality may influence whether or not we want to fit in or stand out. Although we compare ourselves to others throughout our lives, adolescent and teen years usually bring new pressure to be similar to or different from particular reference groups. Think of all the cliques in high school and how people voluntarily and involuntarily broke off into groups based on popularity, interest, culture, or grade level. Some kids in your high school probably wanted to fit in with and be similar to other people in the marching band but be different from the football players. Conversely, athletes were probably more apt to compare themselves, in terms of similar athletic ability, to other athletes rather than kids in show choir. But social comparison can be complicated by perceptual influences. As we learned earlier, we organize information based on similarity and difference, but these patterns don’t always hold true. Even though students involved in athletics and students involved in arts may seem very different, a dancer or singer may also be very athletic, perhaps even more so than a member of the football team. As with other aspects of perception, there are positive and negative consequences of social comparison.
We generally want to know where we fall in terms of ability and performance as compared to others, but what people do with this information and how it affects self-concept varies. Not all people feel they need to be at the top of the list, but some won’t stop until they get the high score on the video game or set a new school record in a track-and-field event. Some people strive to be first chair in the clarinet section of the orchestra, while another person may be content to be second chair. The education system promotes social comparison through grades and rewards such as honor rolls and dean’s lists. Although education and privacy laws prevent me from displaying each student’s grade on a test or paper for the whole class to see, I do typically report the aggregate grades, meaning the total number of As, Bs, Cs, and so on. This doesn’t violate anyone’s privacy rights, but it allows students to see where they fell in the distribution. This type of social comparison can be used as motivation. The student who was one of only three out of twenty-three to get a D on the exam knows that most of her classmates are performing better than she is, which may lead her to think, “If they can do it, I can do it.” But social comparison that isn’t reasoned can have negative effects and result in negative thoughts like “Look at how bad I did. Man, I’m stupid!” These negative thoughts can lead to negative behaviors, because we try to maintain internal consistency, meaning we act in ways that match up with our self-concept. So if the student begins to question her academic abilities and then incorporates an assessment of herself as a “bad student” into her self-concept, she may then behave in ways consistent with that, which is only going to worsen her academic performance. Additionally, a student might be comforted to learn that he isn’t the only person who got a D and then not feel the need to try to improve, since he has company. You can see in this example that evaluations we place on our self-concept can lead to cycles of thinking and acting. These cycles relate to self-esteem and self-efficacy, which are components of our self-concept.
Self-Esteem
Self-esteem refers to the judgments and evaluations we make about our self-concept. While self-concept is a broad description of the self, self-esteem is a more specifically an evaluation of the self (Byrne, 1996). If I again prompted you to “Tell me who you are,” and then asked you to evaluate (label as good/bad, positive/negative, desirable/undesirable) each of the things you listed about yourself, I would get clues about your self-esteem. Like self-concept, self-esteem has general and specific elements. Generally, some people are more likely to evaluate themselves positively while others are more likely to evaluate themselves negatively (Brockner, 1988). More specifically, our self-esteem varies across our life span and across contexts.

Self-esteem varies throughout our lives, but some people generally think more positively of themselves and some people think more negatively.
RHiNO NEAL – [trophy] – CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
How we judge ourselves affects our communication and our behaviors, but not every negative or positive judgment carries the same weight. The negative evaluation of a trait that isn’t very important for our self-concept will likely not result in a loss of self-esteem. For example, I am not very good at drawing. While I appreciate drawing as an art form, I don’t consider drawing ability to be a very big part of my self-concept. If someone critiqued my drawing ability, my self-esteem wouldn’t take a big hit. I do consider myself a good teacher, however, and I have spent and continue to spend considerable time and effort on improving my knowledge of teaching and my teaching skills. If someone critiqued my teaching knowledge and/or abilities, my self-esteem would definitely be hurt. This doesn’t mean that we can’t be evaluated on something we find important. Even though teaching is very important to my self-concept, I am regularly evaluated on it. Every semester, I am evaluated by my students, and every year, I am evaluated by my dean, department chair, and colleagues. Most of that feedback is in the form of constructive criticism, which can still be difficult to receive, but when taken in the spirit of self-improvement, it is valuable and may even enhance our self-concept and self-esteem. In fact, in professional contexts, people with higher self-esteem are more likely to work harder based on negative feedback, are less negatively affected by work stress, are able to handle workplace conflict better, and are better able to work independently and solve problems (Brockner, 1988). Self-esteem isn’t the only factor that contributes to our self-concept; perceptions about our competence also play a role in developing our sense of self.
Self-Efficacy refers to the judgments people make about their ability to perform a task within a specific context (Bandura, 1997). As you can see in Figure 2.2 “Relationship between Self-Efficacy, Self-Esteem, and Self-Concept” , judgments about our self-efficacy influence our self-esteem, which influences our self-concept. The following example also illustrates these interconnections.
Figure 2.2 Relationship between Self-Efficacy, Self-Esteem, and Self-Concept
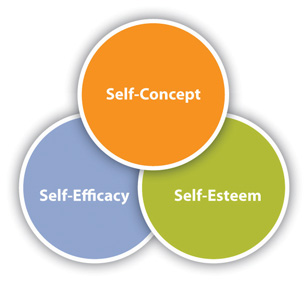
Pedro did a good job on his first college speech. During a meeting with his professor, Pedro indicates that he is confident going into the next speech and thinks he will do well. This skill-based assessment is an indication that Pedro has a high level of self-efficacy related to public speaking. If he does well on the speech, the praise from his classmates and professor will reinforce his self-efficacy and lead him to positively evaluate his speaking skills, which will contribute to his self-esteem. By the end of the class, Pedro likely thinks of himself as a good public speaker, which may then become an important part of his self-concept. Throughout these points of connection, it’s important to remember that self-perception affects how we communicate, behave, and perceive other things. Pedro’s increased feeling of self-efficacy may give him more confidence in his delivery, which will likely result in positive feedback that reinforces his self-perception. He may start to perceive his professor more positively since they share an interest in public speaking, and he may begin to notice other people’s speaking skills more during class presentations and public lectures. Over time, he may even start to think about changing his major to communication or pursuing career options that incorporate public speaking, which would further integrate being “a good public speaker” into his self-concept. You can hopefully see that these interconnections can create powerful positive or negative cycles. While some of this process is under our control, much of it is also shaped by the people in our lives.
The verbal and nonverbal feedback we get from people affect our feelings of self-efficacy and our self-esteem. As we saw in Pedro’s example, being given positive feedback can increase our self-efficacy, which may make us more likely to engage in a similar task in the future (Hargie, 2011). Obviously, negative feedback can lead to decreased self-efficacy and a declining interest in engaging with the activity again. In general, people adjust their expectations about their abilities based on feedback they get from others. Positive feedback tends to make people raise their expectations for themselves and negative feedback does the opposite, which ultimately affects behaviors and creates the cycle. When feedback from others is different from how we view ourselves, additional cycles may develop that impact self-esteem and self-concept.
Self-discrepancy theory states that people have beliefs about and expectations for their actual and potential selves that do not always match up with what they actually experience (Higgins, 1987). To understand this theory, we have to understand the different “selves” that make up our self-concept, which are the actual, ideal, and ought selves. The actual self consists of the attributes that you or someone else believes you actually possess. The ideal self consists of the attributes that you or someone else would like you to possess. The ought self consists of the attributes you or someone else believes you should possess.
These different selves can conflict with each other in various combinations. Discrepancies between the actual and ideal/ought selves can be motivating in some ways and prompt people to act for self-improvement. For example, if your ought self should volunteer more for the local animal shelter, then your actual self may be more inclined to do so. Discrepancies between the ideal and ought selves can be especially stressful. For example, many professional women who are also mothers have an ideal view of self that includes professional success and advancement. They may also have an ought self that includes a sense of duty and obligation to be a full-time mother. The actual self may be someone who does OK at both but doesn’t quite live up to the expectations of either. These discrepancies do not just create cognitive unease—they also lead to emotional, behavioral, and communicative changes.

People who feel that it’s their duty to recycle but do not actually do it will likely experience a discrepancy between their actual and ought selves.
Matt Martin – Recycle – CC BY-NC 2.0.
When we compare the actual self to the expectations of ourselves and others, we can see particular patterns of emotional and behavioral effects. When our actual self doesn’t match up with our own ideals of self, we are not obtaining our own desires and hopes, which can lead to feelings of dejection including disappointment, dissatisfaction, and frustration. For example, if your ideal self has no credit card debt and your actual self does, you may be frustrated with your lack of financial discipline and be motivated to stick to your budget and pay off your credit card bills.
When our actual self doesn’t match up with other people’s ideals for us, we may not be obtaining significant others’ desires and hopes, which can lead to feelings of dejection including shame, embarrassment, and concern for losing the affection or approval of others. For example, if a significant other sees you as an “A” student and you get a 2.8 GPA your first year of college, then you may be embarrassed to share your grades with that person.
When our actual self doesn’t match up with what we think other people think we should obtain, we are not living up to the ought self that we think others have constructed for us, which can lead to feelings of agitation, feeling threatened, and fearing potential punishment. For example, if your parents think you should follow in their footsteps and take over the family business, but your actual self wants to go into the military, then you may be unsure of what to do and fear being isolated from the family.
Finally, when our actual self doesn’t match up with what we think we should obtain, we are not meeting what we see as our duties or obligations, which can lead to feelings of agitation including guilt, weakness, and a feeling that we have fallen short of our moral standard (Higgins, 1987). For example, if your ought self should volunteer more for the local animal shelter, then your actual self may be more inclined to do so due to the guilt of reading about the increasing number of animals being housed at the facility. The following is a review of the four potential discrepancies between selves:
- Actual vs. own ideals. We have an overall feeling that we are not obtaining our desires and hopes, which leads to feelings of disappointment, dissatisfaction, and frustration.
- Actual vs. others’ ideals. We have an overall feeling that we are not obtaining significant others’ desires and hopes for us, which leads to feelings of shame and embarrassment.
- Actual vs. others’ ought. We have an overall feeling that we are not meeting what others see as our duties and obligations, which leads to feelings of agitation including fear of potential punishment.
- Actual vs. own ought. We have an overall feeling that we are not meeting our duties and obligations, which can lead to a feeling that we have fallen short of our own moral standards.
Influences on Self-Perception
We have already learned that other people influence our self-concept and self-esteem. While interactions we have with individuals and groups are definitely important to consider, we must also note the influence that larger, more systemic forces have on our self-perception. Social and family influences, culture, and the media all play a role in shaping who we think we are and how we feel about ourselves. Although these are powerful socializing forces, there are ways to maintain some control over our self-perception.
Social and Family Influences
Various forces help socialize us into our respective social and cultural groups and play a powerful role in presenting us with options about who we can be. While we may like to think that our self-perception starts with a blank canvas, our perceptions are limited by our experiences and various social and cultural contexts.
Parents and peers shape our self-perceptions in positive and negative ways. Feedback that we get from significant others, which includes close family, can lead to positive views of self (Hargie, 2011). In the past few years, however, there has been a public discussion and debate about how much positive reinforcement people should give to others, especially children. The following questions have been raised: Do we have current and upcoming generations that have been overpraised? Is the praise given warranted? What are the positive and negative effects of praise? What is the end goal of the praise? Let’s briefly look at this discussion and its connection to self-perception.

Some experts have warned that overpraising children can lead to distorted self-concepts.
Rain0975 – participation award – CC BY-ND 2.0.
Whether praise is warranted or not is very subjective and specific to each person and context, but in general there have been questions raised about the potential negative effects of too much praise. Motivation is the underlying force that drives us to do things. Sometimes we are intrinsically motivated, meaning we want to do something for the love of doing it or the resulting internal satisfaction. Other times we are extrinsically motivated, meaning we do something to receive a reward or avoid punishment. If you put effort into completing a short documentary for a class because you love filmmaking and editing, you have been largely motivated by intrinsic forces. If you complete the documentary because you want an “A” and know that if you fail your parents will not give you money for your spring break trip, then you are motivated by extrinsic factors. Both can, of course, effectively motivate us. Praise is a form of extrinsic reward, and if there is an actual reward associated with the praise, like money or special recognition, some people speculate that intrinsic motivation will suffer. But what’s so good about intrinsic motivation? Intrinsic motivation is more substantial and long-lasting than extrinsic motivation and can lead to the development of a work ethic and sense of pride in one’s abilities. Intrinsic motivation can move people to accomplish great things over long periods of time and be happy despite the effort and sacrifices made. Extrinsic motivation dies when the reward stops. Additionally, too much praise can lead people to have a misguided sense of their abilities. College professors who are reluctant to fail students who produce failing work may be setting those students up to be shocked when their supervisor critiques their abilities or output once they get into a professional context (Hargie, 2011).
There are cultural differences in the amount of praise and positive feedback that teachers and parents give their children. For example, teachers give less positive reinforcement in Japanese and Taiwanese classrooms than do teachers in US classrooms. Chinese and Kenyan parents do not regularly praise their children because they fear it may make them too individualistic, rude, or arrogant (Wierzbicka, 2004). So the phenomenon of overpraising isn’t universal, and the debate over its potential effects is not resolved.
Research has also found that communication patterns develop between parents and children that are common to many verbally and physically abusive relationships. Such patterns have negative effects on a child’s self-efficacy and self-esteem (Morgan & Wilson, 2007). As you’ll recall from our earlier discussion, attributions are links we make to identify the cause of a behavior. In the case of aggressive or abusive parents, they are not as able to distinguish between mistakes and intentional behaviors, often seeing honest mistakes as intended and reacting negatively to the child. Such parents also communicate generally negative evaluations to their child by saying, for example, “You can’t do anything right!” or “You’re a bad girl.” When children do exhibit positive behaviors, abusive parents are more likely to use external attributions that diminish the achievement of the child by saying, for example, “You only won because the other team was off their game.” In general, abusive parents have unpredictable reactions to their children’s positive and negative behavior, which creates an uncertain and often scary climate for a child that can lead to lower self-esteem and erratic or aggressive behavior. The cycles of praise and blame are just two examples of how the family as a socializing force can influence our self-perceptions. Culture also influences how we see ourselves.
How people perceive themselves varies across cultures. For example, many cultures exhibit a phenomenon known as the self-enhancement bias , meaning that we tend to emphasize our desirable qualities relative to other people (Loughnan et al., 2011). But the degree to which people engage in self-enhancement varies. A review of many studies in this area found that people in Western countries such as the United States were significantly more likely to self-enhance than people in countries such as Japan. Many scholars explain this variation using a common measure of cultural variation that claims people in individualistic cultures are more likely to engage in competition and openly praise accomplishments than people in collectivistic cultures. The difference in self-enhancement has also been tied to economics, with scholars arguing that people in countries with greater income inequality are more likely to view themselves as superior to others or want to be perceived as superior to others (even if they don’t have economic wealth) in order to conform to the country’s values and norms. This holds true because countries with high levels of economic inequality, like the United States, typically value competition and the right to boast about winning or succeeding, while countries with more economic equality, like Japan, have a cultural norm of modesty (Loughnan, 2011).
Race also plays a role in self-perception. For example, positive self-esteem and self-efficacy tend to be higher in African American adolescent girls than Caucasian girls (Stockton et al., 2009). In fact, more recent studies have discounted much of the early research on race and self-esteem that purported that African Americans of all ages have lower self-esteem than whites. Self-perception becomes more complex when we consider biracial individuals—more specifically those born to couples comprising an African American and a white parent (Bowles, 1993). In such cases, it is challenging for biracial individuals to embrace both of their heritages, and social comparison becomes more difficult due to diverse and sometimes conflicting reference groups. Since many biracial individuals identify as and are considered African American by society, living and working within a black community can help foster more positive self-perceptions in these biracial individuals. Such a community offers a more nurturing environment and a buffer zone from racist attitudes but simultaneously distances biracial individuals from their white identity. Conversely, immersion into a predominantly white community and separation from a black community can lead biracial individuals to internalize negative views of people of color and perhaps develop a sense of inferiority. Gender intersects with culture and biracial identity to create different experiences and challenges for biracial men and women. Biracial men have more difficulty accepting their potential occupational limits, especially if they have white fathers, and biracial women have difficulty accepting their black features, such as hair and facial features. All these challenges lead to a sense of being marginalized from both ethnic groups and interfere in the development of positive self-esteem and a stable self-concept.

Biracial individuals may have challenges with self-perception as they try to integrate both racial identities into their self-concept.
Javcon117* – End of Summer Innocence – CC BY-SA 2.0.
There are some general differences in terms of gender and self-perception that relate to self-concept, self-efficacy, and envisioning ideal selves. As with any cultural differences, these are generalizations that have been supported by research, but they do not represent all individuals within a group. Regarding self-concept, men are more likely to describe themselves in terms of their group membership, and women are more likely to include references to relationships in their self-descriptions. For example, a man may note that he is a Tarheel fan, a boat enthusiast, or a member of the Rotary Club, and a woman may note that she is a mother of two or a loyal friend.
Regarding self-efficacy, men tend to have higher perceptions of self-efficacy than women (Hargie, 2011). In terms of actual and ideal selves, men and women in a variety of countries both described their ideal self as more masculine (Best & Thomas, 2004). As was noted earlier, gender differences are interesting to study but are very often exaggerated beyond the actual variations. Socialization and internalization of societal norms for gender differences accounts for much more of our perceived differences than do innate or natural differences between genders. These gender norms may be explicitly stated—for example, a mother may say to her son, “Boys don’t play with dolls”—or they may be more implicit, with girls being encouraged to pursue historically feminine professions like teaching or nursing without others actually stating the expectation.
The representations we see in the media affect our self-perception. The vast majority of media images include idealized representations of attractiveness. Despite the fact that the images of people we see in glossy magazines and on movie screens are not typically what we see when we look at the people around us in a classroom, at work, or at the grocery store, many of us continue to hold ourselves to an unrealistic standard of beauty and attractiveness. Movies, magazines, and television shows are filled with beautiful people, and less attractive actors, when they are present in the media, are typically portrayed as the butt of jokes, villains, or only as background extras (Patzer, 2008). Aside from overall attractiveness, the media also offers narrow representations of acceptable body weight.
Researchers have found that only 12 percent of prime-time characters are overweight, which is dramatically less than the national statistics for obesity among the actual US population (Patzer, 2008). Further, an analysis of how weight is discussed on prime-time sitcoms found that heavier female characters were often the targets of negative comments and jokes that audience members responded to with laughter. Conversely, positive comments about women’s bodies were related to their thinness. In short, the heavier the character, the more negative the comments, and the thinner the character, the more positive the comments. The same researchers analyzed sitcoms for content regarding male characters’ weight and found that although comments regarding their weight were made, they were fewer in number and not as negative, ultimately supporting the notion that overweight male characters are more accepted in media than overweight female characters. Much more attention has been paid in recent years to the potential negative effects of such narrow media representations. The following “Getting Critical” box explores the role of media in the construction of body image.
In terms of self-concept, media representations offer us guidance on what is acceptable or unacceptable and valued or not valued in our society. Mediated messages, in general, reinforce cultural stereotypes related to race, gender, age, sexual orientation, ability, and class. People from historically marginalized groups must look much harder than those in the dominant groups to find positive representations of their identities in media. As a critical thinker, it is important to question media messages and to examine who is included and who is excluded.
Advertising in particular encourages people to engage in social comparison, regularly communicating to us that we are inferior because we lack a certain product or that we need to change some aspect of our life to keep up with and be similar to others. For example, for many years advertising targeted to women instilled in them a fear of having a dirty house, selling them products that promised to keep their house clean, make their family happy, and impress their friends and neighbors. Now messages tell us to fear becoming old or unattractive, selling products to keep our skin tight and clear, which will in turn make us happy and popular.
“Getting Critical”
Body Image and Self-Perception
Take a look at any magazine, television show, or movie and you will most likely see very beautiful people. When you look around you in your daily life, there are likely not as many glamorous and gorgeous people. Scholars and media critics have critiqued this discrepancy for decades because it has contributed to many social issues and public health issues ranging from body dysmorphic disorder, to eating disorders, to lowered self-esteem.
Much of the media is driven by advertising, and the business of media has been to perpetuate a “culture of lack” (Dworkin & Wachs, 2009). This means that we are constantly told, via mediated images, that we lack something. In short, advertisements often tell us we don’t have enough money, enough beauty, or enough material possessions. Over the past few decades, women’s bodies in the media have gotten smaller and thinner, while men’s bodies have gotten bigger and more muscular. At the same time, the US population has become dramatically more obese. As research shows that men and women are becoming more and more dissatisfied with their bodies, which ultimately affects their self-concept and self-esteem, health and beauty product lines proliferate and cosmetic surgeries and other types of enhancements become more and more popular. From young children to older adults, people are becoming more aware of and oftentimes unhappy with their bodies, which results in a variety of self-perception problems.
- How do you think the media influences your self-perception and body image?
- Describe the typical man that is portrayed in the media. Describe the typical woman that is portrayed in the media. What impressions do these typical bodies make on others? What are the potential positive and negative effects of the way the media portrays the human body?
- Find an example of an “atypical” body represented in the media (a magazine, TV show, or movie). Is this person presented in a positive, negative, or neutral way? Why do you think this person was chosen?
Self-Presentation
How we perceive ourselves manifests in how we present ourselves to others. Self-presentation is the process of strategically concealing or revealing personal information in order to influence others’ perceptions (Human et al., 2012). We engage in this process daily and for different reasons. Although people occasionally intentionally deceive others in the process of self-presentation, in general we try to make a good impression while still remaining authentic. Since self-presentation helps meet our instrumental, relational, and identity needs, we stand to lose quite a bit if we are caught intentionally misrepresenting ourselves. In May of 2012, Yahoo!’s CEO resigned after it became known that he stated on official documents that he had two college degrees when he actually only had one. In a similar incident, a woman who had long served as the dean of admissions for the prestigious Massachusetts Institute of Technology was dismissed from her position after it was learned that she had only attended one year of college and had falsely indicated she had a bachelor’s and master’s degree (Webber & Korn, 2012). Such incidents clearly show that although people can get away with such false self-presentation for a while, the eventual consequences of being found out are dire. As communicators, we sometimes engage in more subtle forms of inauthentic self-presentation. For example, a person may state or imply that they know more about a subject or situation than they actually do in order to seem smart or “in the loop.” During a speech, a speaker works on a polished and competent delivery to distract from a lack of substantive content. These cases of strategic self-presentation may not ever be found out, but communicators should still avoid them as they do not live up to the standards of ethical communication.
Consciously and competently engaging in self-presentation can have benefits because we can provide others with a more positive and accurate picture of who we are. People who are skilled at impression management are typically more engaging and confident, which allows others to pick up on more cues from which to form impressions (Human et al., 2012). Being a skilled self-presenter draws on many of the practices used by competent communicators, including becoming a higher self-monitor. When self-presentation skills and self-monitoring skills combine, communicators can simultaneously monitor their own expressions, the reaction of others, and the situational and social context (Sosik, Avolio, & Jung, 2002). Sometimes people get help with their self-presentation. Although most people can’t afford or wouldn’t think of hiring an image consultant, some people have started generously donating their self-presentation expertise to help others. Many people who have been riding the tough job market for a year or more get discouraged and may consider giving up on their job search.

People who have been out of work for a while may have difficulty finding the motivation to engage in the self-presentation behaviors needed to form favorable impressions.
Steve Petrucelli – Interview Time! – CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
There are two main types of self-presentation: prosocial and self-serving (Sosik, Avolio, & Jung, 2002). Prosocial self-presentation entails behaviors that present a person as a role model and make a person more likable and attractive. For example, a supervisor may call on her employees to uphold high standards for business ethics, model that behavior in her own actions, and compliment others when they exemplify those standards. Self-serving self-presentation entails behaviors that present a person as highly skilled, willing to challenge others, and someone not to be messed with. For example, a supervisor may publicly take credit for the accomplishments of others or publicly critique an employee who failed to meet a particular standard. In summary, prosocial strategies are aimed at benefiting others, while self-serving strategies benefit the self at the expense of others.
In general, we strive to present a public image that matches up with our self-concept, but we can also use self-presentation strategies to enhance our self-concept (Hargie, 2011). When we present ourselves in order to evoke a positive evaluative response, we are engaging in self-enhancement. In the pursuit of self-enhancement, a person might try to be as appealing as possible in a particular area or with a particular person to gain feedback that will enhance one’s self-esteem. For example, a singer might train and practice for weeks before singing in front of a well-respected vocal coach but not invest as much effort in preparing to sing in front of friends. Although positive feedback from friends is beneficial, positive feedback from an experienced singer could enhance a person’s self-concept. Self-enhancement can be productive and achieved competently, or it can be used inappropriately. Using self-enhancement behaviors just to gain the approval of others or out of self-centeredness may lead people to communicate in ways that are perceived as phony or overbearing and end up making an unfavorable impression (Sosik, Avolio, & Jung, 2002).
“Getting Plugged In”
Self-Presentation Online: Social Media, Digital Trails, and Your Reputation
Although social networking has long been a way to keep in touch with friends and colleagues, the advent of social media has made the process of making connections and those all-important first impressions much more complex. Just looking at Facebook as an example, we can clearly see that the very acts of constructing a profile, posting status updates, “liking” certain things, and sharing various information via Facebook features and apps is self-presentation (Kim & Lee, 2011). People also form impressions based on the number of friends we have and the photos and posts that other people tag us in. All this information floating around can be difficult to manage. So how do we manage the impressions we make digitally given that there is a permanent record?
Research shows that people overall engage in positive and honest self-presentation on Facebook (Kim & Lee, 2011). Since people know how visible the information they post is, they may choose to only reveal things they think will form favorable impressions. But the mediated nature of Facebook also leads some people to disclose more personal information than they might otherwise in such a public or semipublic forum. These hyperpersonal disclosures run the risk of forming negative impressions based on who sees them. In general, the ease of digital communication, not just on Facebook, has presented new challenges for our self-control and information management. Sending someone a sexually provocative image used to take some effort before the age of digital cameras, but now “sexting” an explicit photo only takes a few seconds. So people who would have likely not engaged in such behavior before are more tempted to now, and it is the desire to present oneself as desirable or cool that leads people to send photos they may later regret (DiBlasio, 2012). In fact, new technology in the form of apps is trying to give people a little more control over the exchange of digital information. An iPhone app called “Snapchat” allows users to send photos that will only be visible for a few seconds. Although this isn’t a guaranteed safety net, the demand for such apps is increasing, which illustrates the point that we all now leave digital trails of information that can be useful in terms of our self-presentation but can also create new challenges in terms of managing the information floating around from which others may form impressions of us.
- What impressions do you want people to form of you based on the information they can see on your Facebook page?
- Have you ever used social media or the Internet to do “research” on a person? What things would you find favorable and unfavorable?
- Do you have any guidelines you follow regarding what information about yourself you will put online or not? If so, what are they? If not, why?
Key Takeaways
- Our self-concept is the overall idea of who we think we are. It is developed through our interactions with others and through social comparison that allows us to compare our beliefs and behaviors to others.
- Our self-esteem is based on the evaluations and judgments we make about various characteristics of our self-concept. It is developed through an assessment and evaluation of our various skills and abilities, known as self-efficacy, and through a comparison and evaluation of who we are, who we would like to be, and who we should be (self-discrepancy theory).
- Social comparison theory and self-discrepancy theory affect our self-concept and self-esteem because through comparison with others and comparison of our actual, ideal, and ought selves we make judgments about who we are and our self-worth. These judgments then affect how we communicate and behave.
- Socializing forces like family, culture, and media affect our self-perception because they give us feedback on who we are. This feedback can be evaluated positively or negatively and can lead to positive or negative patterns that influence our self-perception and then our communication.
- Self-presentation refers to the process of strategically concealing and/or revealing personal information in order to influence others’ perceptions. Prosocial self-presentation is intended to benefit others and self-serving self-presentation is intended to benefit the self at the expense of others. People also engage in self-enhancement, which is a self-presentation strategy by which people intentionally seek out positive evaluations.
- Make a list of characteristics that describe who you are (your self-concept). After looking at the list, see if you can come up with a few words that summarize the list to narrow in on the key features of your self-concept. Go back over the first list and evaluate each characteristic, for example noting whether it is something you do well/poorly, something that is good/bad, positive/negative, desirable/undesirable. Is the overall list more positive or more negative? After doing these exercises, what have you learned about your self-concept and self-esteem?
- Discuss at least one time in which you had a discrepancy or tension between two of the three selves described by self-discrepancy theory (the actual, ideal, and ought selves). What effect did this discrepancy have on your self-concept and/or self-esteem?
- Take one of the socializing forces discussed (family, culture, or media) and identify at least one positive and one negative influence that it/they have had on your self-concept and/or self-esteem.
- Getting integrated: Discuss some ways that you might strategically engage in self-presentation to influence the impressions of others in an academic, a professional, a personal, and a civic context.
Bandura, A., Self-Efficacy: The Exercise of Control (New York, NY: W. H. Freeman, 1997).
Best, D. L. and Jennifer J. Thomas, “Cultural Diversity and Cross-Cultural Perspectives,” in The Psychology of Gender, 2nd ed., eds. Alice H. Eagly, Anne E. Beall, and Robert J. Sternberg (New York, NY: Guilford Press, 2004), 296–327.
Bowles, D. D., “Biracial Identity: Children Born to African-American and White Couples,” Clinical Social Work Journal 21, no. 4 (1993): 418–22.
Brockner, J., Self-Esteem at Work (Lexington, MA: Lexington Books, 1988), 11.
Byrne, B. M., Measuring Self-Concept across the Life Span: Issues and Instrumentation (Washington, DC: American Psychological Association, 1996), 5.
Cooley, C., Human Nature and the Social Order (New York, NY: Scribner, 1902).
DiBlasio, N., “Demand for Photo-Erasing iPhone App Heats up Sexting Debate,” USA Today , May 7, 2012, accessed June 6, 2012, http://content.usatoday.com/communities/ondeadline/post/2012/05/demand-for-photo-erasing-iphone-app-heats-up-sexting-debate/1 .
Dworkin, S. L. and Faye Linda Wachs, Body Panic (New York, NY: New York University Press, 2009), 2.
Hargie, O., Skilled Interpersonal Interaction: Research, Theory, and Practice (London: Routledge, 2011), 261.
Higgins, E. T., “Self-Discrepancy: A Theory Relating Self and Affect,” Psychological Review 94, no. 3 (1987): 320–21.
Human, L. J., et al., “Your Best Self Helps Reveal Your True Self: Positive Self-Presentation Leads to More Accurate Personality Impressions,” Social Psychological and Personality Sciences 3, no. 1 (2012): 23.
Kim, J. and Jong-Eun Roselyn Lee, “The Facebook Paths to Happiness: Effects of the Number of Facebook Friends and Self-Presentation on Subjective Well-Being,” Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking 14, no. 6 (2011): 360.
Loughnan, S., et al., “Economic Inequality Is Linked to Biased Self-Perception,” Psychological Science 22, no. 10 (2011): 1254.
Morgan, W. and Steven R. Wilson, “Explaining Child Abuse as a Lack of Safe Ground,” in The Dark Side of Interpersonal Communication , eds. Brian H. Spitzberg and William R. Cupach (Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 2007), 341.
Patzer, G. L., Looks: Why They Matter More than You Ever Imagined (New York, NY: AMACOM, 2008), 147.
Sosik, J. J., Bruce J. Avolio, and Dong I. Jung, “Beneath the Mask: Examining the Relationship of Self-Presentation Attributes and Impression Management to Charismatic Leadership,” The Leadership Quarterly 13 (2002): 217.
Stockton, M. B., et al., “Self-Perception and Body Image Associations with Body Mass Index among 8–10-Year-Old African American Girls,” Journal of Pediatric Psychology 34, no. 10 (2009): 1144.
Webber, L., and Melissa Korn, “Yahoo’s CEO among Many Notable Resume Flaps,” Wall Street Journal Blogs , May 7, 2012, accessed June 9, 2012, http://blogs.wsj.com/digits/2012/05/07/yahoos-ceo-among-many-notable-resume-flaps .
Wierzbicka, A., “The English Expressions Good Boy and Good Girl and Cultural Models of Child Rearing,” Culture and Psychology 10, no. 3 (2004): 251–78.
Communication in the Real World Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Self-Presentation Theory

Self-Presentation Theory: Understanding the Art of Impression Management
In the grand theater of life, where every social interaction is a stage and we are both the actors and the audience, self-presentation theory takes center stage. It whispers the secrets of our performances, the subtle art of crafting personas, and the intricate dance between authenticity and impression. As we pull back the curtain on this psychological narrative, we delve into the depths of human behavior, exploring how the masks we wear and the roles we play are not merely acts of deception but profound expressions of our deepest desires to connect, belong, and be understood in the ever-unfolding drama of existence.
Self-presentation theory, originating from the field of social psychology, delves into the intricate ways individuals strategically convey and portray their desired image to others. This theory explores the underlying motivations and cognitive processes governing how people present themselves in social situations, aiming to understand the dynamics of impression management.
Key Definition:
Self-presentation theory refers to the behavior and strategies individuals use to shape the perceptions that others form about them. This theory suggests that individuals strive to convey a favorable impression to others by managing their public image. It encompasses various aspects such as impression management, identity, and social interaction, and is often associated with social psychology and communication studies. According to this theory, individuals may engage in behaviors such as self-disclosure, performance, and conformity to influence how others perceive them.
Origins and Development
The concept of self-presentation theory was initially formulated by sociologist Erving Goffman, in his seminal work The Presentation of Self in Everyday Life , originally published in 1956. Goffman’s was first to create a specific theory concerning self-presentation, laying the foundation for what is now commonly referred to as impression management. His book became widely known after its publication in the United States in 1959.
Goffman’s theory draws from the imagery of theater to portray the importance of human social interaction. He proposed that in social interactions, individuals perform much like actors on a stage, managing the impressions others form of them by controlling information in various ways. This process involves a “front” where the individual presents themselves in a certain manner, and a “back” where they can step out of their role.
His work has been influential in sociology, social psychology, and anthropology, as it was the first to treat face-to-face interaction as a subject of sociological study. Goffman’s dramaturgical analysis observes a connection between the kinds of acts people put on in their daily life and theatrical performances. The theory has had a lasting impact on our understanding of social behavior and continues to be a significant reference point in studies of social interaction.
Impression Management Strategies
Much of Goffman’s early work suggests that “avoidance of shame is an important, indeed a crucial, motive in virtually all social behavior.” Goffman posits that impression management is typically a greater motivation than rational and instrumental goals. Thomas J. Scheff explains that “one tries to control the impression one makes on others, even others who are not significant to one’s life” ( Scheff, 1997. Kindle location: 4,106 ).
Self-presentation theory encompasses a spectrum of strategies employed by individuals to shape others’ perceptions of them. Impression management strategies in social interaction theory are the various techniques individuals use to influence how others perceive them. Individuals employ these strategies to present themselves in a favorable light. The motivation is to achieve specific goals or maintain certain relationships. Here are some key impression management strategies:
- Self-Promotion : Highlighting one’s own positive qualities, achievements, and skills to be seen as competent and capable.
- Ingratiation : Using flattery or praise to make oneself likable to others, often to gain their favor or approval.
- Exemplification : Demonstrating one’s own moral integrity or dedication to elicit respect and admiration from others.
- Intimidation : Projecting a sense of power or threat to influence others to comply with one’s wishes.
- Supplication : Presenting oneself as weak or needy to elicit sympathy or assistance from others.
These strategies can be assertive, involving active attempts to shape one’s image, or defensive, aimed at protecting one’s image. The choice of strategy depends on the individual’s goals, the context of the interaction, and the nature of the relationship.
The Game of Presentation
In many ways, self-presentation opposes other psychology concepts such as authenticity. We adapt to ur environments, and present ourselves accordingly. We act much different at grandma’s house than we do when out drinking with our friends. Perhaps, authenticity is context dependent. However, we can present ourselves differently in different situations without violating core self-values. The presentations may differ but the self remains unchanged.
Carl Jung mused in reflection of his childhood interactions with his friends that, “I found that they alienated me from myself. When I was with them I became different from the way I was at home.” He continues, “it seemed to me that the change in myself was due to the influence of my schoolfellows, who somehow misled me or compelled me to be different from what I thought I was” ( Jung, 2011 ).
Jonathan Haidt suggests that it is merely game. He wrote, “to win at this game you must present your best possible self to others. You must appear virtuous, whether or not you are, and you must gain the benefits of cooperation whether or not you deserve them.” He continues to warn “but everyone else is playing the same game, so you must also play defense—you must be wary of others’ self-presentations, and of their efforts to claim more for themselves than they deserve” ( Haidt, 2003. Kindle location: 1,361 ).
Healthy and Unhealthy Modes of Self-Presentation
We all self-present, creating images that fit the context. While seeking a partner, we self-present a person who is worthy of investing time in. Only in time, do some of these masks begin to fade. Impression management is essential to build new relationships, get the job, and prevent social rejection. Mahzarin R, Banaji and Anthony G. Greenwald wrote, “honesty may be an overrated virtue. If you decided to report all of your flaws to friends and to apply a similar standard of total honesty when talking to others about their shortcomings, you might soon find that you no longer have friends.” they continue, “our daily social lives demand, and generally receive, repeated lubrication with a certain amount of untruthfulness, which keeps the gears of social interaction meshing smoothly” ( Banaji & Greenwald, 2016, pp. 28-29 ).
However, this healthy practice morphs into something sinister when the presented self has nothing to do with the real self. Daniel Goleman refers to individuals that engage in unhealthy deceitful presentations as social chameleons. He wrote, “the social chameleon will seem to be whatever those he is with seem to want. The sign that someone falls into this pattern…is that they make an excellent impression, yet have few stable or satisfying intimate relationships” ( Golman, 2011. Kindle location: 2,519 ).
Goleman explains that “a more healthy pattern, of course, is to balance being true to oneself with social skills, using them with integrity.” He adds, “social chameleons, though, don’t mind in the least saying one thing and doing another, if that will win them social approval” ( Goleman, 2011. Kindle location: 2,523 ).
Situational Influences
The application of self-presentation strategies is contingent upon the social context and the specific goals an individual pursues. In professional settings, individuals may engage in self-promotion to advance their careers, while in personal relationships, they might prioritize authenticity and sincerity. The ubiquity of social media further complicates self-presentation, as individuals navigate the curation of online personas and the management of digital identities.
In the professional realm, the strategic presentation of oneself can play a crucial role in career development and success. This may involve showcasing one’s achievements, skills, and expertise to stand out in a competitive environment. However, it’s important to strike a balance between self-promotion and humility to maintain credibility and foster positive professional relationships.
On the other hand, personal relationships often thrive on genuine connections and authenticity. In these contexts, individuals may choose to present themselves in a sincere manner, emphasizing vulnerability and openness to establish meaningful connections with others. While occasional self-promotion may still occur, the emphasis is more on building trust and rapport.
Social Media and Self-Presentation
The rise of social media has introduced a new layer of complexity to self-presentation. Platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and LinkedIn offer opportunities for individuals to craft their virtual identities. This process involves selective sharing of information, curation of posts and images, and the management of online interactions. The challenge lies in maintaining a balance between projecting an aspirational image and staying true to one’s authentic self in the digital sphere.
In Goffman’s lengthy comparison between actors and audience suggests that anyone could perform, presenting a certain image. However, he points out that if the actor is a known criminal the audience would not be able to accept their performance, knowing it is a fraud. The actor may enjoy success by going on the road, performing to audiences that are not aware of the actor’s criminal past ( Goffman, 1956, p. 223 ). The internet allows the individual with a shady past to bring their show on the road to an unsuspecting audience who can buy their deceitful performance.
Navigating these diverse self-presentation strategies requires individuals to be mindful of the specific social contexts and their underlying goals. Whether it’s in the professional arena or personal relationships, the nuanced art of self-presentation continues to evolve in the digital age, shaping how individuals perceive and position themselves in the world.
Self-Presentation and Emotional Labor
The intersection of self-presentation theory with emotional labor is a topic of significant interest. Emotional labor pertains to the management of one’s emotions to meet the demands of a particular role or job. Individuals often engage in self-presentation to display appropriate emotions in various settings, leading to a convergence between impression management and emotional regulation. One of the key aspects of this intersection is the impact it has on employee well-being.
Research has shown that the need to regulate emotions in the workplace can lead to emotional exhaustion and burnout. Additionally, there are important implications for organizations, as they have a vested interest in understanding and managing the emotional labor of their employees. Effective programs may enhance employee well-being and improve the quality of service provided to customers. Moreover, the intersection of self-presentation and emotional labor can also be examined through the lens of gender and cultural differences. These examination may highlight the complexities and nuances of this phenomenon in diverse contexts. Understanding this intersection is crucial for creating supportive work environments and fostering healthy, sustainable emotional practices.
See Emotional Labor for more on this topic
Implications and Future Directions
Understanding self-presentation theory has widespread implications, spanning from interpersonal relationships to organizational dynamics. By acknowledging the nuanced strategies individuals employ to shape perceptions, psychologists and practitioners can better grasp human behavior in diverse contexts. Future research may delve into the interplay between self-presentation and cultural factors. In addition, further research may cast light on the psychological effects of sustained impression management on individuals’ well-being.
As individuals, we can understand that we, as well as others, use impression management. Before investing significant resources, we would be wise to try to unmask the presenter and make a decision based on reality rather than expertely presented deceptions.
A List of Practical Implications
Understanding the concepts related to self-presentation theory, such as impression management, self-concept, and social identity, has several practical implications in everyday life:
- Enhanced Social Interactions : By being aware of how we present ourselves, we can navigate social situations more effectively, tailoring our behavior to suit different contexts and relationships.
- Improved Professional Relationships : In the workplace, understanding self-presentation can help in managing professional personas, leading to better workplace dynamics and career advancement.
- Personal Development : Recognizing the strategies we use for impression management can lead to greater self-awareness and personal growth, as we align our external presentation with our internal values.
- Conflict Resolution : Awareness of self-presentation strategies can aid in resolving conflicts by understanding the motivations behind others’ behaviors and addressing the underlying issues.
- Mental Health : Understanding the effort involved in emotional labor and impression management can help in identifying when these efforts are leading to stress or burnout, prompting us to seek support or make changes.
- Authentic Relationships : By balancing self-presentation with authenticity, we can foster deeper and more genuine connections with others.
- Cultural Competence : Recognizing the role of social identity in self-presentation can enhance our sensitivity to cultural differences and improve cross-cultural communication.
Overall, these concepts can empower us to be more intentional in our interactions, leading to more fulfilling and effective communication in our personal and professional lives.
Associated Psychological Concepts to Self-Presentation Theory
Self-presentation theory is intricately connected to a variety of psychological concepts that help explain the behaviors and motivations behind how individuals present themselves to others. Here are some related concepts:
- Self-Concept : This refers to how people perceive themselves and their awareness of who they are. Self-presentation is often a reflection of one’s self-concept, as individuals attempt to project an image that aligns with their self-perception.
- Impression Management : This is the process by which individuals attempt to control the impressions others form of them. It involves a variety of strategies to influence others’ perceptions in a way that is favorable to the individual.
- Social Identity : The part of an individual’s self-concept derived from their membership in social groups. Self-presentation can be used to highlight certain aspects of one’s social identity.
- Cognitive Dissonance : This occurs when there is a discrepancy between one’s beliefs and behaviors. Self-presentation strategies may be employed to reduce cognitive dissonance by aligning one’s outward behavior with internal beliefs.
- Role Theory : Suggests that individuals behave in ways that align with the expectations of the social roles they occupy. Self-presentation can be seen as performing the appropriate role in a given context.
- Self-Es teem : The value one places on oneself. Self-presentation can be a means to enhance or protect one’s self-esteem by controlling how others view them.
- Self-Efficacy : One’s belief in their ability to succeed. Through self-presentation, individuals may seek to project confidence and competence to others, thereby reinforcing their own sense of self-efficacy.
These concepts are interrelated and contribute to the understanding of self-presentation theory as a whole, providing insight into the complex nature of social interactions and the motivations behind individuals’ efforts to influence how they are perceived by others.
A Few Words by Psychology Fanatic
In essence, self-presentation theory captures the multifaceted nature of human interaction, shedding light on the conscious and subconscious processes governing how individuals present themselves in the social arena. By unraveling the intricacies of impression management, researchers continue to unveil the complexities of human behavior and the underlying motivations that propel our interactions with others.
Last Update: April 29, 2024
Type your email…
References:
Goffman, Erving (1956/ 2021 ). The Presentation of Self in Everyday Life. Anchor
Goleman, Daniel ( 2005 ). Emotional Intelligence: Why It Can Matter More Than IQ. Bantam Books . Read on Kindle Books.
Haidt, Jonathan ( 2003 ). The Happiness Hypothesis: Finding Modern Truth in Ancient Wisdom. Basic Books ; 1st edition.
Jung, Carl Gustav (1961/ 2011 ). Memories, Dreams, Reflections. Vintage ; Reissue edition.
Banaji, Mahzarin R.; Greenwald, Anthony G. ( 2016 ). Blindspot: Hidden Biases of Good People. Bantam ; Reprint edition.
Scheff, Thomas J. ( 1997 ). Shame in Social Theory. Editors Lansky, M. R. and Morrison, A. P. In The Widening Scope of Shame. Routledge ; 1st edition.
Resources and Articles
Please visit Psychology Fanatic’s vast selection of articles , definitions and database of referenced books .
* Many of the quotes from books come books I have read cover to cover. I created an extensive library of notes from these books. I make reference to these books when using them to support or add to an article topic. Most of these books I read on a kindle reader. The Kindle location references seen through Psychology Fanatic is how kindle notes saves my highlights.
The peer reviewed article references mostly come from Deepdyve . This is the periodical database that I have subscribe to for nearly a decade. Over the last couple of years, I have added a DOI reference to cited articles for the reader’s convenience and reference.
Thank-you for visiting Psychology Fanatic. Psychology Fanatic represents nearly two decades of work, research, and passion.
Topic Specific Databases:
PSYCHOLOGY – EMOTIONS – RELATIONSHIPS – WELLNESS – PSYCHOLOGY TOPICS
Share this:
About the author.
T. Franklin Murphy
Related posts.

Social-Cognitive Theory
Social-Cognitive Theory, developed by Albert Bandura, emphasizes observational learning, imitation, and self-efficacy. It explores how individuals learn from others and their environment, impacting various fields…
Read More »

Affective Events Theory
Affective Events Theory (AET) explores the impact of workplace events on employee emotions, attitudes, and behaviors. It emphasizes how job conditions, interpersonal relationships, and organizational…

Emotional Sensitivity
Emotional sensitivity encompasses bodily changes, empathy, and the ability to recognize and respond to emotions. It affects individuals differently, impacting behavior, relationships, and personality types.…

Design Thinking
Design thinking combines creativity and cognition to tackle complex problems. It emphasizes empathy, collaboration, and iteration, addressing wicked problems by reframing, generating, and prototyping solutions.…

Social Comparison Theory
Social Comparison Theory, introduced by psychologist Leon Festinger, delves into individuals' self-evaluation based on comparisons with others. These evaluative processes, whether upward or downward, profoundly…

Self-Schema
This post explores the concept of self-schema, a cognitive framework that shapes our beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors about ourselves. It impacts how we perceive and…
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Discover more from psychology fanatic.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading

The Art of Self Presentation: Impression Management and Self-Identity

Table of Contents
Have you ever considered how the simple act of introducing yourself at a party, or the way you dress for a job interview, can be a strategic move? Behind these seemingly mundane actions lies a complex process we all engage in, known as self\-presentation . Self-presentation, or impression management , is not just about vanity or a superficial attempt to be liked. It’s a fundamental aspect of human interaction, deeply rooted in psychology and sociology. Let’s dive into the nuances of how we present ourselves to the world and the motives that drive us to manage impressions.
Understanding self-presentation
Self-presentation is the process by which individuals attempt to control the impressions others form of them. It’s a performance where the stage is everyday life, and the audience is the people around us. We employ a variety of verbal, nonverbal, and stylistic cues to craft an image that serves our goals. Whether it’s the confidence in our voice during a presentation, the firmness of our handshake, or the meticulous choice of attire for an event, each element is a deliberate choice in the art of self-presentation.
Verbal cues
- Language and tone: The words we choose and the tone we adopt can convey authority, warmth, intelligence, or humility.
- Storytelling: Narratives about our experiences and achievements can shape how others see us.
Non verbal cues
- Body language: Posture, gestures, and facial expressions communicate emotions and attitudes without words.
- Eye contact: Maintaining or avoiding eye contact can signal confidence, respect, or evasion.
Stylistic cues
- Dress and grooming: How we dress and groom ourselves can signal our social status, professionalism, or group affiliations.
- Accessories and props: Objects we carry or display can be symbols of our identity or status.
The motives behind self-presentation
Why do we go to such lengths to manage how others perceive us? There are two primary drivers: instrumental and expressive motives . Instrumental motives are goal-directed. We present ourselves in a certain way to achieve specific outcomes, such as gaining favor, avoiding conflict, or securing a promotion. On the other hand, expressive motives are about self-expression and identity. We manage impressions to convey who we believe we are and to maintain a consistent self-image.
Instrumental motives
- Influence: We may present ourselves as competent or likable to sway others to our point of view or to get them to do something for us.
- Obtaining rewards: A well-managed impression can lead to tangible benefits like job offers, social connections, or recognition.
Expressive motives
- Self-identity: Through self-presentation, we affirm and communicate our values, beliefs, and unique personality traits.
- Group identity: We may also use self-presentation to identify with a particular social group, aligning ourselves with its norms and values.

Maintaining consistency in self-presentation
The key to effective self-presentation is consistency. Inconsistencies between our words and actions can lead to a loss of credibility and trust. For instance, if you profess a commitment to environmental causes but are seen littering, this discrepancy can tarnish your image. Such inconsistencies can also lead to cognitive dissonance , a psychological state where we experience discomfort due to conflicting beliefs or behaviors. To resolve this discomfort, we may adjust our attitudes or behaviors to align with the image we wish to project.
Aligning actions and words
- Consistent messaging: Ensure that what you say matches what you do. This builds trust and authenticity in your image.
- Behavioral adjustments: Sometimes, to maintain consistency in our self-presentation, we may change our behavior to align with the impressions we’ve created.
Dealing with cognitive dissonance
- Awareness: Recognize when your actions do not match your expressed attitudes or the identity you’re trying to convey.
- Adjustment: Alter your behaviors or attitudes to reduce the dissonance and create a coherent self-image.
Self-presentation in the digital age
As we navigate the digital world, self-presentation has taken on new dimensions. Social media platforms have become stages where we curate images of ourselves through photos, status updates, and interactions. The line between public and private selves blurs as we manage impressions for a potentially global audience. This digital self\-presentation comes with its own challenges and opportunities for expression and influence.
Creating a digital identity
- Curated content: We carefully select which parts of our lives to share online, often emphasizing positive and flattering aspects to craft an idealized self-image.
- Feedback loops: Likes, comments, and shares provide immediate feedback, influencing future self-presentation choices.
Navigating the pitfalls
- Authenticity vs. curation: Striking a balance between presenting an ideal self and remaining authentic is a challenge in the digital world.
- Privacy concerns: Deciding how much personal information to share online is a critical aspect of digital self-presentation.
Self-presentation is a crucial part of human interaction, deeply intertwined with our social world and our sense of self. Whether we’re aware of it or not, we’re all engaged in impression management, both offline and online. By understanding the motives and methods behind self-presentation, we can navigate social situations more effectively and authentically. It’s a delicate dance of influence and expression, where the ultimate goal is to present a self that aligns with our identity and aspirations.
What do you think? How do you manage your self-presentation in different social settings? Have you ever experienced cognitive dissonance due to misalignment between your actions and the image you wanted to project?
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 5 / 5. Vote count: 1
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
Social Psychology
1 Definition, Concept and Research Methods in Social Psychology
- Definition and Concept of Social Psychology
- Research Methods in Social Psychology
- Experimental Methods
- Non-Experimental Methods
- Other Research Methods
- Research Ethics
2 Historical Perspective of Social Psychology, Social Psychology and Other Related Disciplines
- Historical Perspective
- Landmarks in the History of Social Psychology
- Social Psychology and Other Related Disciplines
- Significance of Social Psychology Today
3 Social and Person Perception – Definition, Description and Functional Factors
- Social Cognition – Description and Nature
- Social Perception – Definition
- Understanding Temporary States
- Understanding of the Most Permanent or Lasting Characteristics – Attributions
- Impression Formation
- Implicit Personality Theory
- Person Perception
- Social Categorisation
4 Cognitive Basis and Dynamics of Social Perception and Person Perception
- Cognitive and Motivational Basis of Social and Person Perception
- Bias in Attribution
- Role of Emotions and Motivation in Information Processing
- Motivated Person Perception
- Effect of Cognitive and Emotional States
5 Definition, Concept, Description, Characteristic of Attitude
- Defining Attitudes
- Attitudes, Values, and Beliefs
- Formation of Attitudes
- Functions of Attitudes
6 Components of Attitude
- ABCs of Attitudes
- Properties of Attitudes
7 Predicting Behaviour from Attitude
- Relationship between Attitude and Behaviour
- Attitudes Predict Behaviour
- Attitudes Determine Behaviour?
- Behaviour Determine Attitudes
8 Effecting Attitudinal Change and Cognitive Dissonance Theory, Compliance of Self-perception Theory, Self-affirmation
- Self Presentation
- Cognitive Dissonance
- Self Perception
- Self Affirmation
9 Introduction to Groups- Definition, Characteristics and Types of Groups
- Groups-Definition Meaning and Concepts
- Characteristics Features of Group
- Types of Group
- The Role of Groups
10 Group Process- Social Facilitation, Social Loafing, Group Interaction, Group Polarization and Group Mind
- Social Facilitation
- Social Loafing
- Group Interaction
- Group Polarization
11 Group Behaviour- Influence of Norms, Status and Roles; Introduction to Crowd Behavioural Theory, Crowd Psychology (Classical and Convergence Theories)
- Human Behaviour in Groups
- Influence of Norms Status and Roles
- Crowd Behavioural Theory
- Crowd Psychology
12 Crowd Psychology- Collective Consciousness and Collective Hysteria
- Crowd: Definition and Characteristics
- Crowd Psychology: Definition and Characteristics
- Collective Behaviour
- Collective Hysteria
13 Definition of Norms, Social Norms, Need and Characteristics Features of Norms
- Meaning of Norms
- Types of Norms
- Violation of Social Norms
- Need and Importance of Social Norms
- Characteristic Features of Social Norms
14 Norm Formation, Factors Influencing Norms, Enforcement of Norms, Norm Formation and Social Conformity
- Norm Formation
- Factors Influencing Norm Formation
- Enforcement of Norms
- Social Conformity
15 Autokinetic Experiment in Norm Formation
- Autokinetic Effect
- Sherif’s Experiment
- Salient Features of Sherif’s Autokinetic Experiments
- Critical Appraisal
- Related Latest Research on Norm Formation
16 Norms and Conformity- Asch’s Line of Length Experiments
- Solomon E. Asch – A Leading Social Psychologist
- Line and Length Experiments
- Alternatives Available with Probable Consequences
- Explanation of the Yielding Behaviour
- Variants in Asch’s Experiments
- Salient Features
- Related Research on Asch’s Findings
Share on Mastodon
Self-Presentation Theory: Self-Construction and Audience Pleasing
Cite this chapter.

- Roy F. Baumeister &
- Debra G. Hutton
Part of the book series: Springer Series in Social Psychology ((SSSOC))
2563 Accesses
59 Citations
66 Altmetric
Self-presentation is behavior that attempts to convey some information about oneself or some image of oneself to other people. It denotes a class of motivations in human behavior. These motivations are in part stable dispositions of individuals but they depend on situational factors to elicit them. Specifically, self-presentational motivations are activated by the evaluative presence of other people and by others’ (even potential) knowledge of one’s behavior.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others

Self-Determination Theory

Psychologically Flexible Self-Acceptance
Introduction to the self-determination construct.
Adler, A (1921). The neurotic constitution: Outlines of a comparative individualistic psychology and psychotherapy . New York: Moffat Yard.
Google Scholar
Aries, P. (1981). The hour of our death . New York: Knopf.
Baumeister, R. F. (1982a). A self-presentational view of social phenomena. Psychological Bulletin, 91 , 3–26.
Article Google Scholar
Baumeister, R. F. (1982b). Self-esteem, self-presentation, and future interaction: A dilemma of reputation. Journal of Personality, 50 , 29–45.
Baumeister, R. F. (1984). Choking under pressure: Self-consciousness and paradoxical effects of incentives on skillful performance. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 46 , 610–620.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Baumeister, R. F. (1985). The championship choke. Psychology Today, 19 (4:April), 48–52.
Baumeister, R. F. (1986). Identity . New York: Oxford University Press.
Baumeister, R F, Hamilton, J. C., & Tice, D. M. (1985). Public versus private expectancy of success: Confidence booster or performance pressure? Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 48 , 1447–1457.
Baumeister, R. F., & Jones, E. E. (1978). When self-presentation is constrained by the target’s prior knowledge: Consistency and compensation. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 36 , 608–618.
Baumeister, R. F., & Steinhilber, A (1984). Paradoxical effects of supportive audiences on performance under pressure: The home field disadvantage in sports championships. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 47 , 85–93.
Baumeister, R. F., & Tice, D. M. (1984). Role of self-presentation and choice in cognitive dissonance under forced compliance: Necessary or sufficient causes? Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 46 , 5–13.
Baumeister, R. F., & Tice, D. M. (1985). Self-esteem and responses to success and failure: Subsequent performance and intrinsic motivation. Journal of Personality, 53 , 450–467.
Bond, C. F. (1982). Social facilitation: A self-presentational view. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 42 , 1042–1050.
Bond, C. F., & Titus, L. J. (1983). Social facilitation: A meta-analysis of 241 studies. Psychological Bulletin, 94 , 265–292.
Braginsky, B. M., Braginsky, D. D., & Ring, K. (1969). Methods of madness: The mental hospital as a last resort . New York: Holt, Rinehart & Winston.
Castaneda, C. (1972). Journey to Ixtlan: The lessons of Don Juan . New York: Simon & Schuster.
Deaux, K, & Major, B. (1977). Sex-related patterns in the unit of perception. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 3 , 297–300.
Emmler, N. (1984). Differential involvement in delinquency: Toward an interpretation in terms of reputation management. Progress in Experimental Personality Research, 13 , 174–239.
Festinger, L., & Carlsmith, J. M. (1959). Cognitive consequences of forced compliance. Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 58 , 203–210.
Felson, R (1978). Aggression as impression management. Social Psychology Quarterly, 41 , 205–213.
Gollwitzer, P. M. (1986). Striving for specific identities: The social reality of self-symbolizing. In R. Baumeister (Ed.), Public self and private self . New York: Springer-Verlag.
Greenberg, J. (1983). Self-image versus impression management in adherence to distributive justice standards: The influence of self-awareness and self-consciousness. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 44 , 5–19.
Hinkle, L. (1957). [Untitled.] In Methods of forceful indoctrination: Observations and interviews . New York.
Hogan, R (1982). A socioanalytic theory of personality. In M. Page (Ed.), Nebraska symposium on motivation (pp. 55–89). Lincoln, NE: University of Nebraska Press.
Hogan, R, Mankin, D., Conway, J., & Fox, S. (1970). Personality correlates of undergraduate marijuana use. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 35 , 58–63.
Houghton, W. E. (1957). The Victorian frame of mind: 1830–1870 . New Haven: Yale University Press.
Jones, E. E., & Berglas, S. C. (1978). Control of attributions about the self through self-handicapping strategies: The appeal of alcohol and the role of underachievement. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 4 , 200–206.
Jones, E. E., & Pittman, T. S. (1982). Toward a general theory of strategic self-presentation. In J. Suls (Ed.), Psychological perspectives on the self (Vol. 1, pp. 231–262). Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Kassin, S. M. (1984) T. V. Cameras, public self-consciousness and mock juror performance. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 20 , 336–349.
Kett, J. F. (1977). Rites of passage: Adolescence in America 1790 to the present . New York: Basic.
Kidder, L. H., Bellettirie, G., & Cohn, E. S. (1977). Secret ambitions and public performances: The effects of anonymity on reward allocations made by men and women. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 13 , 70–80.
Kolditz, T. A, & Arkin, R. M. (1982). An impression management interpretation of the self-handicapping strategy. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 43 , 492–502.
Latané, B., Williams, K, & Harkins, S. (1979). Many hands make light the work: The causes and consequences of social loafing. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 37 , 822–832.
Lifton, R. J. (1957). [Untitled.] In Methods of forceful indoctrination: Observations and interviews . New York.
Major, B., & Adams, J. B. (1983). Role of gender, interpersonal orientation, and self-presentation in distributive-justice behavior. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 45 , 598–608.
Major, B., McFarlin, D. B., & Gagnon, D. (1984). Overworked and underpaid: On the nature of gender differences in personal entitlement. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 47 , 1399–1412.
McFarlin, D. B., Baumeister, R. F., & Blascovich, J. (1984). On knowing when to quit: Task failure, self-esteem, advice, and nonproductive persistence. Journal of Personality, 52 , 138–155.
Morris, C. (1972). The discovery of the individual: 1050–1200 . New York: Harper & Row.
Paulhus, D. (1982). Individual differences, self-presentation, and cognitive dissonance: Their concurrent operation in forced compliance. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 43 , 838–852.
Pennebaker, J. W. (1984). Confiding, ruminating, and psychosomatic disease. In J. W. Pennebaker (Chair), New paradigms in psychology . Symposium conducted at the annual convention of the American Psychological Association, Toronto, Canada, August 1984.
Pennebaker, J. W. (in press). Traumatic experience and psychosomatic disease: Exploring the roles of behavioral inhibition, obsession, and confiding. Canadian Psychology .
Sacco, W. P., & Hokanson, J. E. (1982). Depression and self-reinforcement in a public and private setting. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 42 , 377–385.
Schlenker, B. R. (1980). Impression management: The self-concept, social identity, and interpersonal relations . Monterey, CA: Brooks/Cole.
Schlenker, B. R. (1982). Translating actions into attitudes: An identity-analytic approach to the explanation of social conduct. In L. Berkowitz (Ed.), Advances in experimental social psychology (Vol. 15 pp. 194–247). New York: Academic Press.
Scott, M. B., & Lyman, S. M. (1968). Accounts. American Sociological Review, 33 , 46–62.
Silverman, I. (1964). Self-esteem and differential responsiveness to success and failure. Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 69 , 115–119.
Smith, T. W, Snyder, C. R, & Perkins, S. C. (1983). The self-serving function of hypochondriacal complaints: Physical symptoms as self-handicapping strategies. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 44 , 787–797.
Sweeney, J. (1973). An experimental investigation of the free rider problem. Social Science Research, 2 , 277–292.
Tang, T. L. P., & Baumeister, R. F. (1984). Effects of personal values, perceived surveillance, and task labels on task preference: The ideology of turning play into work. Journal of Applied Psychology, 69 , 99–105.
Tedeschi, J. T., Schlenker, B. R, & Bonoma, T. V. (1971). Cognitive dissonance: Private ratiocination or public spectacle? American Psychologist, 26 , 685–695.
Tice, D. M., & Baumeister, R F. (1985). Self-esteem, self-handicapping, and self-presentation: The benefits of not practicing. Unpublished manuscript, Case Western Reserve University.
Toch, H. (1969). Violent men . Chicago: Aldine.
Wicklund, R. A, & Gollwitzer, P. M. (1982). Symbolic self-completion . Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Zajonc, R (1965). Social facilitation. Science, 149 , 269–274.
Download references
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Department of Psychology, Syracuse University, 13210, Syracuse, New York, USA
Brian Mullen
Department of Psychology, Williams College, 01267, Williamstown, Massachusetts, USA
George R. Goethals
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 1987 Springer-Verlag New York Inc.
About this chapter
Baumeister, R.F., Hutton, D.G. (1987). Self-Presentation Theory: Self-Construction and Audience Pleasing. In: Mullen, B., Goethals, G.R. (eds) Theories of Group Behavior. Springer Series in Social Psychology. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-4634-3_4
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4612-4634-3_4
Publisher Name : Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN : 978-1-4612-9092-6
Online ISBN : 978-1-4612-4634-3
eBook Packages : Springer Book Archive
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
The Presentation of Self in Everyday Life
Theo Wargo / Getty Images
- Recommended Reading
- Key Concepts
- Major Sociologists
- News & Issues
- Research, Samples, and Statistics
- Archaeology
The Presentation of Self in Everyday Life is a book that was published in the U.S. in 1959, written by sociologist Erving Goffman . In it, Goffman uses the imagery of theater in order to portray the nuances and significance of face-to-face social interaction. Goffman puts forth a theory of social interaction that he refers to as the dramaturgical model of social life.
According to Goffman, social interaction may be likened to a theater, and people in everyday life to actors on a stage, each playing a variety of roles. The audience consists of other individuals who observe the role-playing and react to the performances. In social interaction, like in theatrical performances, there is a 'front stage' region where the actors are on stage before an audience, and their consciousness of that audience and the audience's expectations for the role they should play influence the actor's behavior. There is also a back region, or 'backstage,' where individuals can relax, be themselves, and the role or identity that they play when they are in front of others.
Central to the book and Goffman's theory is the idea that people, as they interact together in social settings, are constantly engaged in the process of "impression management," wherein each tries to present themselves and behave in a way that will prevent the embarrassment of themselves or others. This is primarily done by each person that is part of the interaction working to ensure that all parties have the same "definition of the situation," meaning that all understand what is meant to happen in that situation, what to expect from the others involved, and thus how they themselves should behave.
Though written over half a century ago, The Presentation of Self in Everday Life remains one of the most famous and widely taught sociology books, which was listed as the 10th most important sociology book of the twentieth century by the International Sociological Association in 1998.
Performance
Goffman uses the term ‘performance’ to refer to all the activity of an individual in front of a particular set of observers, or audience. Through this performance, the individual, or actor, gives meaning to themselves, to others, and to their situation. These performances deliver impressions to others, which communicates information that confirms the identity of the actor in that situation. The actor may or may not be aware of their performance or have an objective for their performance, however, the audience is constantly attributing meaning to it and to the actor.
The setting for the performance includes the scenery, props, and location in which the interaction takes place. Different settings will have different audiences and will thus require the actor to alter his performances for each setting.
Appearance functions to portray to the audience the performer’s social statuses. Appearance also tells us of the individual’s temporary social state or role, for example, whether he is engaging in work (by wearing a uniform), informal recreation, or a formal social activity. Here, dress and props serve to communicate things that have socially ascribed meaning, like gender , status, occupation, age, and personal commitments.
Manner refers to how the individual plays the role and functions to warn the audience of how the performer will act or seek to act in a role (for example, dominant, aggressive, receptive, etc.). Inconsistency and contradiction between appearance and manner may occur and will confuse and upset an audience. This can happen, for example, when one does not present himself or behave in accordance with his perceived social status or position.
The actor’s front, as labeled by Goffman, is the part of the individual’s performance which functions to define the situation for the audience. It is the image or impression he or she gives off to the audience. A social front can also be thought of like a script. Certain social scripts tend to become institutionalized in terms of the stereotyped expectations it contains. Certain situations or scenarios have social scripts that suggest how the actor should behave or interact in that situation. If the individual takes on a task or role that is new to him, he or she may find that there are already several well-established fronts among which he must choose. According to Goffman, when a task is given a new front or script, we rarely find that the script itself is completely new. Individuals commonly use pre-established scripts to follow for new situations, even if it is not completely appropriate or desired for that situation.
Front Stage, Back Stage, and Off Stage
In stage drama, as in everyday interactions, according to Goffman, there are three regions, each with different effects on an individual’s performance: front stage, backstage, and off-stage. The front stage is where the actor formally performs and adheres to conventions that have particular meaning for the audience. The actor knows he or she is being watched and acts accordingly.
When in the backstage region, the actor may behave differently than when in front of the audience on the front stage. This is where the individual truly gets to be herself and get rid of the roles that she plays when she is in front of other people.
Finally, the off-stage region is where individual actors meet the audience members independently of the team performance on the front stage. Specific performances may be given when the audience is segmented as such.
- Stigma: Notes on the Management of Spoiled Identity
- Émile Durkheim: "Suicide: A Study in Sociology"
- Overview of The History of Sexuality
- Definition of the Sociological Imagination and Overview of the Book
- An Overview of the Book Democracy in America
- Malcolm Gladwell's "The Tipping Point"
- The Main Points of "The Communist Manifesto"
- McDonaldization: Definition and Overview of the Concept
- Understanding Durkheim's Division of Labor
- Savage Inequalities: Children in America’s Schools
- A Book Overview: "The Protestant Ethic and The Spirit Of Capitalism"
- The Social Transformation of American Medicine
- The Asch Conformity Experiments
- A Biography of Erving Goffman
- Goffman's Front-Stage and Backstage Behavior
- 15 Major Sociological Studies and Publications
- Subscriber Services
- For Authors
- Publications
- Archaeology
- Art & Architecture
- Bilingual dictionaries
- Classical studies
- Encyclopedias
- English Dictionaries and Thesauri
- Language reference
- Linguistics
- Media studies
- Medicine and health
- Names studies
- Performing arts
- Science and technology
- Social sciences
- Society and culture
- Overview Pages
- Subject Reference
- English Dictionaries
- Bilingual Dictionaries
Recently viewed (0)
- Save Search
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Related Content
Related overviews.
self-monitoring
impression management
performance
Erving Goffman (1922—1982)
See all related overviews in Oxford Reference »
More Like This
Show all results sharing these subjects:
self-presentation
Quick reference.
The conscious or unconscious control of the impression that one creates in social interactions or situations. It is one of the important forms of impression management, namely management of one's own impression on others through role playing. The phenomenon is encapsulated in Shakespeare's famous observation in As You Like It: ‘All the world's a stage, / And all the men and women merely players: / They have their exits and their entrances; / And one man in his time plays many parts’ (II.vii.139–42). It was popularized by the Canadian-born US sociologist Erving Goffman (1922–82) in his influential book The Presentation of Self in Everyday Life (1959). See also ingratiation, self-monitoring, social constructionist psychology.
From: self-presentation in A Dictionary of Psychology »
Subjects: Science and technology — Psychology
Related content in Oxford Reference
Reference entries, self-presentation n..
View all related items in Oxford Reference »
Search for: 'self-presentation' in Oxford Reference »
- Oxford University Press
PRINTED FROM OXFORD REFERENCE (www.oxfordreference.com). (c) Copyright Oxford University Press, 2023. All Rights Reserved. Under the terms of the licence agreement, an individual user may print out a PDF of a single entry from a reference work in OR for personal use (for details see Privacy Policy and Legal Notice ).
date: 31 August 2024
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
- [91.193.111.216]
- 91.193.111.216
Character limit 500 /500
12.2 Self-presentation
Learning objectives.
- Describe social roles and how they influence behavior
- Explain what social norms are and how they influence behavior
- Define script
- Describe the findings of Zimbardo’s Stanford prison experiment
As you’ve learned, social psychology is the study of how people affect one another’s thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. We have discussed situational perspectives and social psychology’s emphasis on the ways in which a person’s environment, including culture and other social influences, affect behavior. In this section, we examine situational forces that have a strong influence on human behavior including social roles, social norms, and scripts. We discuss how humans use the social environment as a source of information, or cues, on how to behave. Situational influences on our behavior have important consequences, such as whether we will help a stranger in an emergency or how we would behave in an unfamiliar environment.
Social Roles
One major social determinant of human behavior is our social roles. A social role is a pattern of behavior that is expected of a person in a given setting or group (Hare, 2003). Each one of us has several social roles. You may be, at the same time, a student, a parent, an aspiring teacher, a son or daughter, a spouse, and a lifeguard. How do these social roles influence your behavior? Social roles are defined by culturally shared knowledge. That is, nearly everyone in a given culture knows what behavior is expected of a person in a given role. For example, what is the social role for a student? If you look around a college classroom you will likely see students engaging in studious behavior, taking notes, listening to the professor, reading the textbook, and sitting quietly at their desks ( Figure 12.8 ). Of course you may see students deviating from the expected studious behavior such as texting on their phones or using Facebook on their laptops, but in all cases, the students that you observe are attending class—a part of the social role of students.
Social roles, and our related behavior, can vary across different settings. How do you behave when you are engaging in the role of son or daughter and attending a family function? Now imagine how you behave when you are engaged in the role of employee at your workplace. It is very likely that your behavior will be different. Perhaps you are more relaxed and outgoing with your family, making jokes and doing silly things. But at your workplace you might speak more professionally, and although you may be friendly, you are also serious and focused on getting the work completed. These are examples of how our social roles influence and often dictate our behavior to the extent that identity and personality can vary with context (that is, in different social groups) (Malloy, Albright, Kenny, Agatstein & Winquist, 1997).
Social Norms
As discussed previously, social roles are defined by a culture’s shared knowledge of what is expected behavior of an individual in a specific role. This shared knowledge comes from social norms. A social norm is a group’s expectation of what is appropriate and acceptable behavior for its members—how they are supposed to behave and think (Deutsch & Gerard, 1955; Berkowitz, 2004). How are we expected to act? What are we expected to talk about? What are we expected to wear? In our discussion of social roles we noted that colleges have social norms for students’ behavior in the role of student and workplaces have social norms for employees’ behaviors in the role of employee. Social norms are everywhere including in families, gangs, and on social media outlets. What are some social norms on Facebook?
Connect the Concepts
Tweens, teens, and social norms.
My 11-year-old daughter, Jessica, recently told me she needed shorts and shirts for the summer, and that she wanted me to take her to a store at the mall that is popular with preteens and teens to buy them. I have noticed that many girls have clothes from that store, so I tried teasing her. I said, “All the shirts say ‘Aero’ on the front. If you are wearing a shirt like that and you have a substitute teacher, and the other girls are all wearing that type of shirt, won’t the substitute teacher think you are all named ‘Aero’?”
My daughter replied, in typical 11-year-old fashion, “Mom, you are not funny. Can we please go shopping?”
I tried a different tactic. I asked Jessica if having clothing from that particular store will make her popular. She replied, “No, it will not make me popular. It is what the popular kids wear. It will make me feel happier.” How can a label or name brand make someone feel happier? Think back to what you’ve learned about lifespan development . What is it about pre-teens and young teens that make them want to fit in ( Figure 12.9 )? Does this change over time? Think back to your high school experience, or look around your college campus. What is the main name brand clothing you see? What messages do we get from the media about how to fit in?
Because of social roles, people tend to know what behavior is expected of them in specific, familiar settings. A script is a person’s knowledge about the sequence of events expected in a specific setting (Schank & Abelson, 1977). How do you act on the first day of school, when you walk into an elevator, or are at a restaurant? For example, at a restaurant in the United States, if we want the server’s attention, we try to make eye contact. In Brazil, you would make the sound “psst” to get the server’s attention. You can see the cultural differences in scripts. To an American, saying “psst” to a server might seem rude, yet to a Brazilian, trying to make eye contact might not seem an effective strategy. Scripts are important sources of information to guide behavior in given situations. Can you imagine being in an unfamiliar situation and not having a script for how to behave? This could be uncomfortable and confusing. How could you find out about social norms in an unfamiliar culture?
Zimbardo’s Stanford Prison Experiment
The famous Stanford prison experiment , conducted by social psychologist Philip Zimbardo and his colleagues at Stanford University, demonstrated the power of social roles, social norms, and scripts. In the summer of 1971, an advertisement was placed in a California newspaper asking for male volunteers to participate in a study about the psychological effects of prison life. More than 70 men volunteered, and these volunteers then underwent psychological testing to eliminate candidates who had underlying psychiatric issues, medical issues, or a history of crime or drug abuse. The pool of volunteers was whittled down to 24 healthy male college students. Each student was paid $15 per day and was randomly assigned to play the role of either a prisoner or a guard in the study. Based on what you have learned about research methods, why is it important that participants were randomly assigned?
A mock prison was constructed in the basement of the psychology building at Stanford. Participants assigned to play the role of prisoners were “arrested” at their homes by Palo Alto police officers, booked at a police station, and subsequently taken to the mock prison. The experiment was scheduled to run for several weeks. To the surprise of the researchers, both the “prisoners” and “guards” assumed their roles with zeal. In fact, on day 2, some of the prisoners revolted, and the guards quelled the rebellion by threatening the prisoners with night sticks. In a relatively short time, the guards came to harass the prisoners in an increasingly sadistic manner, through a complete lack of privacy, lack of basic comforts such as mattresses to sleep on, and through degrading chores and late-night counts.
The prisoners, in turn, began to show signs of severe anxiety and hopelessness—they began tolerating the guards’ abuse. Even the Stanford professor who designed the study and was the head researcher, Philip Zimbardo, found himself acting as if the prison was real and his role, as prison supervisor, was real as well. After only six days, the experiment had to be ended due to the participants’ deteriorating behavior. Zimbardo explained,
At this point it became clear that we had to end the study. We had created an overwhelmingly powerful situation—a situation in which prisoners were withdrawing and behaving in pathological ways, and in which some of the guards were behaving sadistically. Even the “good” guards felt helpless to intervene, and none of the guards quit while the study was in progress. Indeed, it should be noted that no guard ever came late for his shift, called in sick, left early, or demanded extra pay for overtime work. (Zimbardo, 2013)
The Stanford prison experiment demonstrated the power of social roles, norms, and scripts in affecting human behavior. The guards and prisoners enacted their social roles by engaging in behaviors appropriate to the roles: The guards gave orders and the prisoners followed orders. Social norms require guards to be authoritarian and prisoners to be submissive. When prisoners rebelled, they violated these social norms, which led to upheaval. The specific acts engaged by the guards and the prisoners derived from scripts. For example, guards degraded the prisoners by forcing them do push-ups and by removing all privacy. Prisoners rebelled by throwing pillows and trashing their cells. Some prisoners became so immersed in their roles that they exhibited symptoms of mental breakdown; however, according to Zimbardo, none of the participants suffered long term harm (Alexander, 2001).
The Stanford Prison Experiment has some parallels with the abuse of prisoners of war by U.S. Army troops and CIA personnel at the Abu Ghraib prison in 2003 and 2004. The offenses at Abu Ghraib were documented by photographs of the abuse, some taken by the abusers themselves ( Figure 12.10 ).
Link to Learning
Visit this website to hear an NPR interview with Philip Zimbardo where he discusses the parallels between the Stanford prison experiment and the Abu Ghraib prison in Iraq.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/psychology/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Rose M. Spielman, Kathryn Dumper, William Jenkins, Arlene Lacombe, Marilyn Lovett, Marion Perlmutter
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Psychology
- Publication date: Dec 8, 2014
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/psychology/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/psychology/pages/12-2-self-presentation
© Feb 9, 2022 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
68 Self-Presentation, Attitudes, and Persuasion
Learning outcomes.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe social roles and how they influence behavior
- Explain what social norms are and how they influence behavior
- Define script
- Describe the findings of Zimbardo’s Stanford prison experiment
- Define attitude
- Describe how people’s attitudes are internally changed through cognitive dissonance
- Explain how people’s attitudes are externally changed through persuasion
- Describe the peripheral and central routes to persuasion
Self-presentation
As you’ve learned, social psychology is the study of how people affect one another’s thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. We have discussed situational perspectives and social psychology’s emphasis on the ways in which a person’s environment, including culture and other social influences, affect behavior. In this section, we examine situational forces that have a strong influence on human behavior including social roles, social norms, and scripts. We discuss how humans use the social environment as a source of information, or cues, on how to behave. Situational influences on our behavior have important consequences, such as whether we will help a stranger in an emergency or how we would behave in an unfamiliar environment.
SOCIAL ROLES
One major social determinant of human behavior is our social roles. A social role is a pattern of behavior that is expected of a person in a given setting or group (Hare, 2003). Each one of us has several social roles. You may be, at the same time, a student, a parent, an aspiring teacher, a son or daughter, a spouse, and a lifeguard. How do these social roles influence your behavior? Social roles are defined by culturally shared knowledge. That is, nearly everyone in a given culture knows what behavior is expected of a person in a given role. For example, what is the social role for a student? If you look around a college classroom you will likely see students engaging in studious behavior, taking notes, listening to the professor, reading the textbook, and sitting quietly at their desks ( Figure ). Of course you may see students deviating from the expected studious behavior such as texting on their phones or using Facebook on their laptops, but in all cases, the students that you observe are attending class—a part of the social role of students.

Social roles, and our related behavior, can vary across different settings. How do you behave when you are engaging in the role of son or daughter and attending a family function? Now imagine how you behave when you are engaged in the role of employee at your workplace. It is very likely that your behavior will be different. Perhaps you are more relaxed and outgoing with your family, making jokes and doing silly things. But at your workplace you might speak more professionally, and although you may be friendly, you are also serious and focused on getting the work completed. These are examples of how our social roles influence and often dictate our behavior to the extent that identity and personality can vary with context (that is, in different social groups) (Malloy, Albright, Kenny, Agatstein & Winquist, 1997).
SOCIAL NORMS
As discussed previously, social roles are defined by a culture’s shared knowledge of what is expected behavior of an individual in a specific role. This shared knowledge comes from social norms. A social norm is a group’s expectation of what is appropriate and acceptable behavior for its members—how they are supposed to behave and think (Deutsch & Gerard, 1955; Berkowitz, 2004). How are we expected to act? What are we expected to talk about? What are we expected to wear? In our discussion of social roles we noted that colleges have social norms for students’ behavior in the role of student and workplaces have social norms for employees’ behaviors in the role of employee. Social norms are everywhere including in families, gangs, and on social media outlets. What are some social norms on Facebook?
My 11-year-old daughter, Jessica, recently told me she needed shorts and shirts for the summer, and that she wanted me to take her to a store at the mall that is popular with preteens and teens to buy them. I have noticed that many girls have clothes from that store, so I tried teasing her. I said, “All the shirts say ‘Aero’ on the front. If you are wearing a shirt like that and you have a substitute teacher, and the other girls are all wearing that type of shirt, won’t the substitute teacher think you are all named ‘Aero’?”
My daughter replied, in typical 11-year-old fashion, “Mom, you are not funny. Can we please go shopping?”
I tried a different tactic. I asked Jessica if having clothing from that particular store will make her popular. She replied, “No, it will not make me popular. It is what the popular kids wear. It will make me feel happier.” How can a label or name brand make someone feel happier? Think back to what you’ve learned about lifespan development . What is it about pre-teens and young teens that make them want to fit in ( Figure )? Does this change over time? Think back to your high school experience, or look around your college campus. What is the main name brand clothing you see? What messages do we get from the media about how to fit in?

Because of social roles, people tend to know what behavior is expected of them in specific, familiar settings. A script is a person’s knowledge about the sequence of events expected in a specific setting (Schank & Abelson, 1977). How do you act on the first day of school, when you walk into an elevator, or are at a restaurant? For example, at a restaurant in the United States, if we want the server’s attention, we try to make eye contact. In Brazil, you would make the sound “psst” to get the server’s attention. You can see the cultural differences in scripts. To an American, saying “psst” to a server might seem rude, yet to a Brazilian, trying to make eye contact might not seem an effective strategy. Scripts are important sources of information to guide behavior in given situations. Can you imagine being in an unfamiliar situation and not having a script for how to behave? This could be uncomfortable and confusing. How could you find out about social norms in an unfamiliar culture?
ZIMBARDO’S STANFORD PRISON EXPERIMENT
The famous Stanford prison experiment , conducted by social psychologist Philip Zimbardo and his colleagues at Stanford University, demonstrated the power of social roles, social norms, and scripts. In the summer of 1971, an advertisement was placed in a California newspaper asking for male volunteers to participate in a study about the psychological effects of prison life. More than 70 men volunteered, and these volunteers then underwent psychological testing to eliminate candidates who had underlying psychiatric issues, medical issues, or a history of crime or drug abuse. The pool of volunteers was whittled down to 24 healthy male college students. Each student was paid $15 per day and was randomly assigned to play the role of either a prisoner or a guard in the study. Based on what you have learned about research methods, why is it important that participants were randomly assigned?
A mock prison was constructed in the basement of the psychology building at Stanford. Participants assigned to play the role of prisoners were “arrested” at their homes by Palo Alto police officers, booked at a police station, and subsequently taken to the mock prison. The experiment was scheduled to run for several weeks. To the surprise of the researchers, both the “prisoners” and “guards” assumed their roles with zeal. In fact, on day 2, some of the prisoners revolted, and the guards quelled the rebellion by threatening the prisoners with night sticks. In a relatively short time, the guards came to harass the prisoners in an increasingly sadistic manner, through a complete lack of privacy, lack of basic comforts such as mattresses to sleep on, and through degrading chores and late-night counts.
The prisoners, in turn, began to show signs of severe anxiety and hopelessness—they began tolerating the guards’ abuse. Even the Stanford professor who designed the study and was the head researcher, Philip Zimbardo, found himself acting as if the prison was real and his role, as prison supervisor, was real as well. After only six days, the experiment had to be ended due to the participants’ deteriorating behavior. Zimbardo explained,
At this point it became clear that we had to end the study. We had created an overwhelmingly powerful situation—a situation in which prisoners were withdrawing and behaving in pathological ways, and in which some of the guards were behaving sadistically. Even the “good” guards felt helpless to intervene, and none of the guards quit while the study was in progress. Indeed, it should be noted that no guard ever came late for his shift, called in sick, left early, or demanded extra pay for overtime work. (Zimbardo, 2013)
The Stanford prison experiment demonstrated the power of social roles, norms, and scripts in affecting human behavior. The guards and prisoners enacted their social roles by engaging in behaviors appropriate to the roles: The guards gave orders and the prisoners followed orders. Social norms require guards to be authoritarian and prisoners to be submissive. When prisoners rebelled, they violated these social norms, which led to upheaval. The specific acts engaged by the guards and the prisoners derived from scripts. For example, guards degraded the prisoners by forcing them do push-ups and by removing all privacy. Prisoners rebelled by throwing pillows and trashing their cells. Some prisoners became so immersed in their roles that they exhibited symptoms of mental breakdown; however, according to Zimbardo, none of the participants suffered long term harm (Alexander, 2001).
The Stanford Prison Experiment has some parallels with the abuse of prisoners of war by U.S. Army troops and CIA personnel at the Abu Ghraib prison in 2003 and 2004. The offenses at Abu Ghraib were documented by photographs of the abuse, some taken by the abusers themselves ( Figure ).

Visit this website to hear an NPR interview with Philip Zimbardo where he discusses the parallels between the Stanford prison experiment and the Abu Ghraib prison in Iraq.
Human behavior is largely influenced by our social roles, norms, and scripts. In order to know how to act in a given situation, we have shared cultural knowledge of how to behave depending on our role in society. Social norms dictate the behavior that is appropriate or inappropriate for each role. Each social role has scripts that help humans learn the sequence of appropriate behaviors in a given setting. The famous Stanford prison experiment is an example of how the power of the situation can dictate the social roles, norms, and scripts we follow in a given situation, even if this behavior is contrary to our typical behavior.
Review Questions
A(n) ________ is a set of group expectations for appropriate thoughts and behaviors of its members.
- social role
- social norm
- attribution
On his first day of soccer practice, Jose suits up in a t-shirt, shorts, and cleats and runs out to the field to join his teammates. Jose’s behavior is reflective of ________.
- social influence
- good athletic behavior
- normative behavior
When it comes to buying clothes, teenagers often follow social norms; this is likely motivated by ________.
- following parents’ rules
- saving money
- looking good
In the Stanford prison experiment, even the lead researcher succumbed to his role as a prison supervisor. This is an example of the power of ________ influencing behavior.
- social norms
- social roles
Critical Thinking Questions
Why didn’t the “good” guards in the Stanford prison experiment object to other guards’ abusive behavior? Were the student prisoners simply weak people? Why didn’t they object to being abused?
Describe how social roles, social norms, and scripts were evident in the Stanford prison experiment. How can this experiment be applied to everyday life? Are there any more recent examples where people started fulfilling a role and became abusive?
Personal Application Questions
Try attending a religious service very different from your own and see how you feel and behave without knowing the appropriate script. Or, try attending an important, personal event that you have never attended before, such as a bar mitzvah (a coming-of-age ritual in Jewish culture), a quinceañera (in some Latin American cultures a party is given to a girl who is turning 15 years old), a wedding, a funeral, or a sporting event new to you, such as horse racing or bull riding. Observe and record your feelings and behaviors in this unfamiliar setting for which you lack the appropriate script. Do you silently observe the action, or do you ask another person for help interpreting the behaviors of people at the event? Describe in what ways your behavior would change if you were to attend a similar event in the future?
Name and describe at least three social roles you have adopted for yourself. Why did you adopt these roles? What are some roles that are expected of you, but that you try to resist?
Attitudes and Persuasion
Social psychologists have documented how the power of the situation can influence our behaviors. Now we turn to how the power of the situation can influence our attitudes and beliefs. Attitude is our evaluation of a person, an idea, or an object. We have attitudes for many things ranging from products that we might pick up in the supermarket to people around the world to political policies. Typically, attitudes are favorable or unfavorable: positive or negative (Eagly & Chaiken, 1993). And, they have three components: an affective component (feelings), a behavioral component (the effect of the attitude on behavior), and a cognitive component (belief and knowledge) (Rosenberg & Hovland, 1960).
For example, you may hold a positive attitude toward recycling. This attitude should result in positive feelings toward recycling (such as “It makes me feel good to recycle” or “I enjoy knowing that I make a small difference in reducing the amount of waste that ends up in landfills”). Certainly, this attitude should be reflected in our behavior: You actually recycle as often as you can. Finally, this attitude will be reflected in favorable thoughts (for example, “Recycling is good for the environment” or “Recycling is the responsible thing to do”).
Our attitudes and beliefs are not only influenced by external forces, but also by internal influences that we control. Like our behavior, our attitudes and thoughts are not always changed by situational pressures, but they can be consciously changed by our own free will. In this section we discuss the conditions under which we would want to change our own attitudes and beliefs.
WHAT IS COGNITIVE DISSONANCE?
Social psychologists have documented that feeling good about ourselves and maintaining positive self-esteem is a powerful motivator of human behavior (Tavris & Aronson, 2008). In the United States, members of the predominant culture typically think very highly of themselves and view themselves as good people who are above average on many desirable traits (Ehrlinger, Gilovich, & Ross, 2005). Often, our behavior, attitudes, and beliefs are affected when we experience a threat to our self-esteem or positive self-image. Psychologist Leon Festinger (1957) defined cognitive dissonance as psychological discomfort arising from holding two or more inconsistent attitudes, behaviors, or cognitions (thoughts, beliefs, or opinions). Festinger’s theory of cognitive dissonance states that when we experience a conflict in our behaviors, attitudes, or beliefs that runs counter to our positive self-perceptions, we experience psychological discomfort (dissonance). For example, if you believe smoking is bad for your health but you continue to smoke, you experience conflict between your belief and behavior ( Figure ).

Later research documented that only conflicting cognitions that threaten individuals’ positive self-image cause dissonance (Greenwald & Ronis, 1978). Additional research found that dissonance is not only psychologically uncomfortable but also can cause physiological arousal (Croyle & Cooper, 1983) and activate regions of the brain important in emotions and cognitive functioning (van Veen, Krug, Schooler, & Carter, 2009). When we experience cognitive dissonance, we are motivated to decrease it because it is psychologically, physically, and mentally uncomfortable. We can reduce cognitive dissonance by bringing our cognitions, attitudes, and behaviors in line—that is, making them harmonious. This can be done in different ways, such as:
- changing our discrepant behavior (e.g., stop smoking),
- changing our cognitions through rationalization or denial (e.g., telling ourselves that health risks can be reduced by smoking filtered cigarettes),
- adding a new cognition (e.g., “Smoking suppresses my appetite so I don’t become overweight, which is good for my health.”).
A classic example of cognitive dissonance is John, a 20-year-old who enlists in the military. During boot camp he is awakened at 5:00 a.m., is chronically sleep deprived, yelled at, covered in sand flea bites, physically bruised and battered, and mentally exhausted ( Figure ). It gets worse. Recruits that make it to week 11 of boot camp have to do 54 hours of continuous training.

Not surprisingly, John is miserable. No one likes to be miserable. In this type of situation, people can change their beliefs, their attitudes, or their behaviors. The last option, a change of behaviors, is not available to John. He has signed on to the military for four years, and he cannot legally leave.
If John keeps thinking about how miserable he is, it is going to be a very long four years. He will be in a constant state of cognitive dissonance. As an alternative to this misery, John can change his beliefs or attitudes. He can tell himself, “I am becoming stronger, healthier, and sharper. I am learning discipline and how to defend myself and my country. What I am doing is really important.” If this is his belief, he will realize that he is becoming stronger through his challenges. He then will feel better and not experience cognitive dissonance, which is an uncomfortable state.
The Effect of Initiation
The military example demonstrates the observation that a difficult initiation into a group influences us to like the group more , due to the justification of effort. We do not want to have wasted time and effort to join a group that we eventually leave. A classic experiment by Aronson and Mills (1959) demonstrated this justification of effort effect. College students volunteered to join a campus group that would meet regularly to discuss the psychology of sex. Participants were randomly assigned to one of three conditions: no initiation, an easy initiation, and a difficult initiation into the group. After participating in the first discussion, which was deliberately made very boring, participants rated how much they liked the group. Participants who underwent a difficult initiation process to join the group rated the group more favorably than did participants with an easy initiation or no initiation ( Figure ).

Similar effects can be seen in a more recent study of how student effort affects course evaluations. Heckert, Latier, Ringwald-Burton, and Drazen (2006) surveyed 463 undergraduates enrolled in courses at a midwestern university about the amount of effort that their courses required of them. In addition, the students were also asked to evaluate various aspects of the course. Given what you’ve just read, it will come as no surprise that those courses that were associated with the highest level of effort were evaluated as being more valuable than those that did not. Furthermore, students indicated that they learned more in courses that required more effort, regardless of the grades that they received in those courses (Heckert et al., 2006).
Besides the classic military example and group initiation, can you think of other examples of cognitive dissonance ? Here is one: Marco and Maria live in Fairfield County, Connecticut, which is one of the wealthiest areas in the United States and has a very high cost of living. Marco telecommutes from home and Maria does not work outside of the home. They rent a very small house for more than $3000 a month. Maria shops at consignment stores for clothes and economizes where she can. They complain that they never have any money and that they cannot buy anything new. When asked why they do not move to a less expensive location, since Marco telecommutes, they respond that Fairfield County is beautiful, they love the beaches, and they feel comfortable there. How does the theory of cognitive dissonance apply to Marco and Maria’s choices?
In the previous section we discussed that the motivation to reduce cognitive dissonance leads us to change our attitudes, behaviors, and/or cognitions to make them consonant. Persuasion is the process of changing our attitude toward something based on some kind of communication. Much of the persuasion we experience comes from outside forces. How do people convince others to change their attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors ( Figure )? What communications do you receive that attempt to persuade you to change your attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors?

A subfield of social psychology studies persuasion and social influence, providing us with a plethora of information on how humans can be persuaded by others.
Yale Attitude Change Approach
The topic of persuasion has been one of the most extensively researched areas in social psychology (Fiske et al., 2010). During the Second World War, Carl Hovland extensively researched persuasion for the U.S. Army. After the war, Hovland continued his exploration of persuasion at Yale University. Out of this work came a model called the Yale attitude change approach , which describes the conditions under which people tend to change their attitudes. Hovland demonstrated that certain features of the source of a persuasive message, the content of the message, and the characteristics of the audience will influence the persuasiveness of a message (Hovland, Janis, & Kelley, 1953).
Features of the source of the persuasive message include the credibility of the speaker (Hovland & Weiss, 1951) and the physical attractiveness of the speaker (Eagly & Chaiken, 1975; Petty, Wegener, & Fabrigar, 1997). Thus, speakers who are credible, or have expertise on the topic, and who are deemed as trustworthy are more persuasive than less credible speakers. Similarly, more attractive speakers are more persuasive than less attractive speakers. The use of famous actors and athletes to advertise products on television and in print relies on this principle. The immediate and long term impact of the persuasion also depends, however, on the credibility of the messenger (Kumkale & Albarracín, 2004).
Features of the message itself that affect persuasion include subtlety (the quality of being important, but not obvious) (Petty & Cacioppo, 1986; Walster & Festinger, 1962); sidedness (that is, having more than one side) (Crowley & Hoyer, 1994; Igou & Bless, 2003; Lumsdaine & Janis, 1953); timing (Haugtvedt & Wegener, 1994; Miller & Campbell, 1959), and whether both sides are presented. Messages that are more subtle are more persuasive than direct messages. Arguments that occur first, such as in a debate, are more influential if messages are given back-to-back. However, if there is a delay after the first message, and before the audience needs to make a decision, the last message presented will tend to be more persuasive (Miller & Campbell, 1959).
Features of the audience that affect persuasion are attention (Albarracín & Wyer, 2001; Festinger & Maccoby, 1964), intelligence, self-esteem (Rhodes & Wood, 1992), and age (Krosnick & Alwin, 1989). In order to be persuaded, audience members must be paying attention. People with lower intelligence are more easily persuaded than people with higher intelligence; whereas people with moderate self-esteem are more easily persuaded than people with higher or lower self-esteem (Rhodes & Wood, 1992). Finally, younger adults aged 18–25 are more persuadable than older adults.
Elaboration Likelihood Model
An especially popular model that describes the dynamics of persuasion is the elaboration likelihood model of persuasion (Petty & Cacioppo, 1986). The elaboration likelihood model considers the variables of the attitude change approach—that is, features of the source of the persuasive message, contents of the message, and characteristics of the audience are used to determine when attitude change will occur. According to the elaboration likelihood model of persuasion, there are two main routes that play a role in delivering a persuasive message: central and peripheral ( Figure ).

The central route is logic driven and uses data and facts to convince people of an argument’s worthiness. For example, a car company seeking to persuade you to purchase their model will emphasize the car’s safety features and fuel economy. This is a direct route to persuasion that focuses on the quality of the information. In order for the central route of persuasion to be effective in changing attitudes, thoughts, and behaviors, the argument must be strong and, if successful, will result in lasting attitude change.
The central route to persuasion works best when the target of persuasion, or the audience, is analytical and willing to engage in processing of the information. From an advertiser’s perspective, what products would be best sold using the central route to persuasion? What audience would most likely be influenced to buy the product? One example is buying a computer. It is likely, for example, that small business owners might be especially influenced by the focus on the computer’s quality and features such as processing speed and memory capacity.
The peripheral route is an indirect route that uses peripheral cues to associate positivity with the message (Petty & Cacioppo, 1986). Instead of focusing on the facts and a product’s quality, the peripheral route relies on association with positive characteristics such as positive emotions and celebrity endorsement. For example, having a popular athlete advertise athletic shoes is a common method used to encourage young adults to purchase the shoes. This route to attitude change does not require much effort or information processing. This method of persuasion may promote positivity toward the message or product, but it typically results in less permanent attitude or behavior change. The audience does not need to be analytical or motivated to process the message. In fact, a peripheral route to persuasion may not even be noticed by the audience, for example in the strategy of product placement. Product placement refers to putting a product with a clear brand name or brand identity in a TV show or movie to promote the product (Gupta & Lord, 1998). For example, one season of the reality series American Idol prominently showed the panel of judges drinking out of cups that displayed the Coca-Cola logo. What other products would be best sold using the peripheral route to persuasion? Another example is clothing: A retailer may focus on celebrities that are wearing the same style of clothing.
Foot-in-the-door Technique
Researchers have tested many persuasion strategies that are effective in selling products and changing people’s attitude, ideas, and behaviors. One effective strategy is the foot-in-the-door technique (Cialdini, 2001; Pliner, Hart, Kohl, & Saari, 1974). Using the foot-in-the-door technique , the persuader gets a person to agree to bestow a small favor or to buy a small item, only to later request a larger favor or purchase of a bigger item. The foot-in-the-door technique was demonstrated in a study by Freedman and Fraser (1966) in which participants who agreed to post small sign in their yard or sign a petition were more likely to agree to put a large sign in their yard than people who declined the first request ( Figure ). Research on this technique also illustrates the principle of consistency (Cialdini, 2001): Our past behavior often directs our future behavior, and we have a desire to maintain consistency once we have a committed to a behavior.

A common application of foot-in-the-door is when teens ask their parents for a small permission (for example, extending curfew by a half hour) and then asking them for something larger. Having granted the smaller request increases the likelihood that parents will acquiesce with the later, larger request.
How would a store owner use the foot-in-the-door technique to sell you an expensive product? For example, say that you are buying the latest model smartphone, and the salesperson suggests you purchase the best data plan. You agree to this. The salesperson then suggests a bigger purchase—the three-year extended warranty. After agreeing to the smaller request, you are more likely to also agree to the larger request. You may have encountered this if you have bought a car. When salespeople realize that a buyer intends to purchase a certain model, they might try to get the customer to pay for many or most available options on the car.
Attitudes are our evaluations or feelings toward a person, idea, or object and typically are positive or negative. Our attitudes and beliefs are influenced not only by external forces, but also by internal influences that we control. An internal form of attitude change is cognitive dissonance or the tension we experience when our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are in conflict. In order to reduce dissonance, individuals can change their behavior, attitudes, or cognitions, or add a new cognition. External forces of persuasion include advertising; the features of advertising that influence our behaviors include the source, message, and audience. There are two primary routes to persuasion. The central route to persuasion uses facts and information to persuade potential consumers. The peripheral route uses positive association with cues such as beauty, fame, and positive emotions.
Attitudes describe our ________ of people, objects, and ideas.
- evaluations
Cognitive dissonance causes discomfort because it disrupts our sense of ________.
- unpredictability
- consistency
In order for the central route to persuasion to be effective, the audience must be ________ and ________.
- analytical; motivated
- attentive; happy
- intelligent; unemotional
- gullible; distracted
Examples of cues used in peripheral route persuasion include all of the following except
- celebrity endorsement
- positive emotions
- attractive models
- factual information
Give an example (one not used in class or your text) of cognitive dissonance and how an individual might resolve this.
Imagine that you work for an advertising agency, and you’ve been tasked with developing an advertising campaign to increase sales of Bliss Soda. How would you develop an advertisement for this product that uses a central route of persuasion? How would you develop an ad using a peripheral route of persuasion?
Cognitive dissonance often arises after making an important decision, called post-decision dissonance (or in popular terms, buyer’s remorse). Describe a recent decision you made that caused dissonance and describe how you resolved it.
Describe a time when you or someone you know used the foot-in-the-door technique to gain someone’s compliance.
[glossary-page] [glossary-term]attitude:[/glossary-term] [glossary-definition]evaluations of or feelings toward a person, idea, or object that are typically positive or negative[/glossary-definition]
[glossary-term]central route persuasion:[/glossary-term] [glossary-definition]logic-driven arguments using data and facts to convince people of an argument’s worthiness[/glossary-definition]
[glossary-term]cognitive dissonance:[/glossary-term] [glossary-definition]psychological discomfort that arises from a conflict in a person’s behaviors, attitudes, or beliefs that runs counter to one’s positive self-perception[/glossary-definition]
[glossary-term]foot-in-the-door technique:[/glossary-term] [glossary-definition]persuasion of one person by another person, encouraging a person to agree to a small favor, or to buy a small item, only to later request a larger favor or purchase of a larger item[/glossary-definition]
[glossary-term]peripheral route persuasion:[/glossary-term] [glossary-definition]one person persuades another person; an indirect route that relies on association of peripheral cues (such as positive emotions and celebrity endorsement) to associate positivity with a message[/glossary-definition]
[glossary-term]persuasion:[/glossary-term] [glossary-definition]process of changing our attitude toward something based on some form of communication[/glossary-definition]
[glossary-term]script:[/glossary-term] [glossary-definition]person’s knowledge about the sequence of events in a specific setting[/glossary-definition]
[glossary-term]social norm:[/glossary-term] [glossary-definition]group’s expectations regarding what is appropriate and acceptable for the thoughts and behavior of its members[/glossary-definition]
[glossary-term]social role:[/glossary-term] [glossary-definition]socially defined pattern of behavior that is expected of a person in a given setting or group[/glossary-definition]
[glossary-term]stanford prison experiment:[/glossary-term] [glossary-definition]Stanford University conducted an experiment in a mock prison that demonstrated the power of social roles, social norms, and scripts[/glossary-definition] [/glossary-page]
General Psychology Copyright © by Lumen Learning is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

SELF-PRESENTATION
Any behaviour that is designed to convey an image about ourselves to other people. This explains why our behaviour can change if we notice we are being watched. See impression management.

Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Latest Posts

What Happens At An ADHD Assessment

A Quick Look at the History Behind Hypnosis

A Brief History of Brainwashing: The Science of Thought Control

A Deep Dive into the Social Psychology of Leadership

Counseling Approaches to Client Care: Theories to Apply in Practice

The Future Of Education: Can You Earn A Psychology Degree Online?

Insomnia & Mental Illness: What is the Correlation?

Stop Guessing: Here Are 3 Steps to Data-Driven Psychological Decisions

Getting Help with Grief: Understanding Therapy & How It Can Help

Exploring the Psychology of Risk and Reward

Understanding ADHD in Women: Symptoms, Treatment & Support

Meeting the Milestones: A Guide to Piaget's Child Developmental Stages
Popular psychology terms, medical model, hypermnesia, affirmation, brainwashing, backup reinforcer, affiliative behavior, message-learning approach, behavioral congruence, social instinct, behavioral consistency.
Find over 25,000 psychological definitions
self-presentation
Browse dictionary by letter, psychology term of the day.
August 31st 2024
screen reader

- Personality
Self-Presentation in the Digital World
Do traditional personality theories predict digital behaviour.
Posted August 31, 2021 | Reviewed by Chloe Williams
- What Is Personality?
- Take our Agreeableness Test
- Find a therapist near me
- Personality theories can help explain real-world differences in self-presentation behaviours but they may not apply to online behaviours.
- In the real world, women have higher levels of behavioural inhibition tendencies than men and are more likely to avoid displeasing others.
- Based on this assumption, one would expect women to present themselves less on social media, but women tend to use social media more than men.
Digital technology allows people to construct and vary their self-identity more easily than they can in the real world. This novel digital- personality construction may, or may not, be helpful to that person in the long run, but it is certainly more possible than it is in the real world. Yet how this relates to "personality," as described by traditional personality theories, is not really known. Who will tend to manipulate their personality online, and would traditional personality theories predict these effects? A look at what we do know about gender differences in the real and digital worlds suggests that many aspects of digital behaviour may not conform to the expectations of personality theories developed for the real world.
Half a century ago, Goffman suggested that individuals establish social identities by employing self-presentation tactics and impression management . Self-presentational tactics are techniques for constructing or manipulating others’ impressions of the individual and ultimately help to develop that person’s identity in the eyes of the world. The ways other people react are altered by choosing how to present oneself – that is, self-presentation strategies are used for impression management . Others then uphold, shape, or alter that self-image , depending on how they react to the tactics employed. This implies that self-presentation is a form of social communication, by which people establish, maintain, and alter their social identity.
These self-presentational strategies can be " assertive " or "defensive." 1 Assertive strategies are associated with active control of the person’s self-image; and defensive strategies are associated with protecting a desired identity that is under threat. In the real world, the use of self-presentational tactics has been widely studied and has been found to relate to many behaviours and personalities 2 . Yet, despite the enormous amounts of time spent on social media , the types of self-presentational tactics employed on these platforms have not received a huge amount of study. In fact, social media appears to provide an ideal opportunity for the use of self-presentational tactics, especially assertive strategies aimed at creating an identity in the eyes of others.
Seeking to Experience Different Types of Reward
Social media allows individuals to present themselves in ways that are entirely reliant on their own behaviours – and not on factors largely beyond their ability to instantly control, such as their appearance, gender, etc. That is, the impression that the viewer of the social media post receives is dependent, almost entirely, on how or what another person posts 3,4 . Thus, the digital medium does not present the difficulties for individuals who wish to divorce the newly-presented self from the established self. New personalities or "images" may be difficult to establish in real-world interactions, as others may have known the person beforehand, and their established patterns of interaction. Alternatively, others may not let people get away with "out of character" behaviours, or they may react to their stereotype of the person in front of them, not to their actual behaviours. All of which makes real-life identity construction harder.
Engaging in such impression management may stem from motivations to experience different types of reward 5 . In terms of one personality theory, individuals displaying behavioural approach tendencies (the Behavioural Activation System; BAS) and behavioural inhibition tendencies (the Behavioural Inhibition System; BIS) will differ in terms of self-presentation behaviours. Those with strong BAS seek opportunities to receive or experience reward (approach motivation ); whereas, those with strong BIS attempt to avoid punishment (avoidance motivation). People who need to receive a lot of external praise may actively seek out social interactions and develop a lot of social goals in their lives. Those who are more concerned about not incurring other people’s displeasure may seek to defend against this possibility and tend to withdraw from people. Although this is a well-established view of personality in the real world, it has not received strong attention in terms of digital behaviours.
Real-World Personality Theories May Not Apply Online
One test bed for the application of this theory in the digital domain is predicted gender differences in social media behaviour in relation to self-presentation. Both self-presentation 1 , and BAS and BIS 6 , have been noted to show gender differences. In the real world, women have shown higher levels of BIS than men (at least, to this point in time), although levels of BAS are less clearly differentiated between genders. This view would suggest that, in order to avoid disapproval, women will present themselves less often on social media; and, where they do have a presence, adopt defensive self-presentational strategies.
The first of these hypotheses is demonstrably false – where there are any differences in usage (and there are not that many), women tend to use social media more often than men. What we don’t really know, with any certainty, is how women use social media for self-presentation, and whether this differs from men’s usage. In contrast to the BAS/BIS view of personality, developed for the real world, several studies have suggested that selfie posting can be an assertive, or even aggressive, behaviour for females – used in forming a new personality 3 . In contrast, sometimes selfie posting by males is related to less aggressive, and more defensive, aspects of personality 7 . It may be that women take the opportunity to present very different images of themselves online from their real-world personalities. All of this suggests that theories developed for personality in the real world may not apply online – certainly not in terms of putative gender-related behaviours.
We know that social media allows a new personality to be presented easily, which is not usually seen in real-world interactions, and it may be that real-world gender differences are not repeated in digital contexts. Alternatively, it may suggest that these personality theories are now simply hopelessly anachronistic – based on assumptions that no longer apply. If that were the case, it would certainly rule out any suggestion that such personalities are genetically determined – as we know that structure hasn’t changed dramatically in the last 20 years.
1. Lee, S.J., Quigley, B.M., Nesler, M.S., Corbett, A.B., & Tedeschi, J.T. (1999). Development of a self-presentation tactics scale. Personality and Individual Differences, 26(4), 701-722.
2. Laghi, F., Pallini, S., & Baiocco, R. (2015). Autopresentazione efficace, tattiche difensive e assertive e caratteristiche di personalità in Adolescenza. Rassegna di Psicologia, 32(3), 65-82.
3. Chua, T.H.H., & Chang, L. (2016). Follow me and like my beautiful selfies: Singapore teenage girls’ engagement in self-presentation and peer comparison on social media. Computers in Human Behavior, 55, 190-197.
4. Fox, J., & Rooney, M.C. (2015). The Dark Triad and trait self-objectification as predictors of men’s use and self-presentation behaviors on social networking sites. Personality and Individual Differences, 76, 161-165.
5. Hermann, A.D., Teutemacher, A.M., & Lehtman, M.J. (2015). Revisiting the unmitigated approach model of narcissism: Replication and extension. Journal of Research in Personality, 55, 41-45.
6. Carver, C.S., & White, T.L. (1994). Behavioral inhibition, behavioral activation, and affective responses to impending reward and punishment: the BIS/BAS scales. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 67(2), 319.
7. Sorokowski, P., Sorokowska, A., Frackowiak, T., Karwowski, M., Rusicka, I., & Oleszkiewicz, A. (2016). Sex differences in online selfie posting behaviors predict histrionic personality scores among men but not women. Computers in Human Behavior, 59, 368-373.

Phil Reed, Ph.D., is a professor of psychology at Swansea University.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Sticking up for yourself is no easy task. But there are concrete skills you can use to hone your assertiveness and advocate for yourself.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
- Enroll & Pay
The Seven Pillars of Self-Care
Wed, 12/01/2021.
Macy Burkett
Self-care is extremely important, especially as we enter the stressful holiday season. You can practice self-care in many ways: exercise, eat well, meditate, seek therapy, and more. Each method of self-care fits into one of the seven pillars: mental, emotional, physical, environmental, spiritual, recreational, and social. A well-balanced self-care routine involves each of these, so avoid restricting yourself to just one or two pillars. The seven pillars are broken down below with examples on how to practice each one.
Mental Self-Care involves creating a healthy mindset through mindfulness and curiosity. You can do this through journaling, meditation, thinking outside of the box, creating a brain dump list at the start of each day, and taking an intentional break from screen time (TV, internet, and phone usage).
To practice emotional self-care, you want to create healthy coping strategies for any stresses that might occur in your daily life. You can do this by watching your favorite movie, listening to music, writing positive affirmations for yourself, asking others for help when you need it, and setting boundaries to protect yourself and your heart.
Physical self-care involves taking care of your body with rest, nutrition, and movement. Some examples of physical self-care include eating meals at regular times, drinking plenty of water each day, taking a daily multivitamin, getting a good night’s sleep, and trying a new group fitness class.
- Environmental
Taking care of the places around you and the places you love, you’ll need to practice environmental self-care. To do this, rearrange your workspace with a peaceful arrangement, explore new places, declutter your living space, go for walks outdoors, and appeal to your five senses.
Activities or practice that give you a sense of meaning provide you with spiritual self-care. Some of these activities or practices could be spending time in nature, finding a community, identifying the values that are most important to you and volunteering.
- Recreational
It’s important to make time for hobbies and activities that interest you. Doing so will result in practicing recreational self-care. Some activities include taking time for hobbies, going on an adventure, taking time to relax and do nothing, playing board games or video games, and switching up your daily routine.
Building relationships and making connections with healthy boundaries is the best way to practice social self-care. Some examples of social self-care are connecting with friends, calling your relatives, writing a letter to a friend, talking to a support group, and chatting with an online community.
When you’re feeling down or stressed, listen to your body and the type of self-care it needs. Taking time for you is crucial to maintain overall health and wellness.
Source: “The 7 Pillars of Self-Care (And How To Use Them)“ by The Blissful Mind
More From Forbes
Burnout is a leading mental health issue. here’s how to keep it at bay.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
It's crucial to recognize that self-care is not a luxury or an indulgence but a necessity.
We have a tendency to power through tough times in the name of getting work done. We may experience the symptoms of physical and emotional exhaustion, but ignore the signs because we have to make a living, put food on the table, a roof over our heads, and shoes on our feet.
We also may not want to admit that we need the rest, fearing it’s a sign of a weakness. However, pushing through burnout without addressing its root causes can have serious consequences. Prolonged stress and exhaustion not only diminish our performance and enthusiasm for our work but also take a toll on our mental, emotional, and physical health.
Our brains are well-equipped to manage short-term stress due to the "fight or flight" response, which releases adrenaline and cortisol to help us react quickly to immediate threats. This acute stress response can enhance focus, energy, and performance.
Prolonged stress on the other hand overwhelms the brain's capacity to cope, leading to detrimental effects on mental and physical health. Chronic stress can cause the constant release of stress hormones, impairing memory, reducing cognitive function, and increasing anxiety and depression.
This relentless cycle can lead to chronic fatigue, anxiety, and even more severe health issues. It's crucial to recognize that self-care is not a luxury or an indulgence but a necessity. By taking the time to care for ourselves, we can break free from burnout's grip, maintain our well-being, and sustain our careers in a healthy, balanced way.
Best High-Yield Savings Accounts Of 2024
Best 5% interest savings accounts of 2024, the symptoms of burnout and mental exhaustion.
Burnout is a state of chronic stress that manifests in a variety of ways, affecting us physically, behaviorally, and emotionally. These symptoms are more than just fleeting moments of stress—they are warning signs that your mind and body are overwhelmed.
- Physical : constant fatigue yet unable to sleep; frequently sick; loss of appetite; gastrointestinal problems; more headaches and muscle pains than usual.
- Emotional : feelings of helplessness; depression; anxiety; irritability; self-doubt; reduced life satisfaction; reduced sex drive.
- Behavioral : Declining ability to concentrate and focus; impaired decision-making; social withdrawal; self-medicating with drugs or alcohol; unusual procrastination; decreased attention to physical health/wellness/hobbies.
Acknowledging when you’re feeling overwhelmed allows you to take necessary steps to protect your mental and emotional health before burnout becomes a bigger issue.
10 Tips To Combat Burnout
While these tips are designed to help combat burnout, they are not a strict checklist that you must follow to the letter. Everyone’s stress-management journey is unique, so it’s important to adopt only the strategies that resonate with you and fit comfortably into your life.
If any of these suggestions feel overwhelming or add to your stress, it’s perfectly okay to set them aside. Focus on the practices that bring you relief and align with your needs, and remember that your well-being is the priority.
- Make Self-Care Non-Negotiable. Self-care is not selfish - it's essential. Schedule time for activities that replenish you, whether it's exercising, reading, or enjoying a quiet bath. Prioritize activities that nurture both your body and mind. When you take care of yourself first, you’re better equipped to help others.
- Let Go Of The Guilt Suitcase. Guilt can be a useful emotion as it informs you that something is off, but it also expends a lot of mental energy. It keeps you self-focused rather than able to proactively deal with a situation head on. Letting go of guilt requires practice. It’s not easy. Try visualizing your guilt as a briefcase, dropping it wherever you are, and then walking on. You can throw the briefcase too if you want.
- Exorcize Emotional Vampires. Emotional vampires suck the life out of you. Try to distance yourself from those that are consistently stressed out, emotionally overloaded, and generally negative influences if they are not imperative to your work or family life. And drop the guilt suitcase when you do this!
- Routinize. A routine work uniform and a favorite morning breakfast will be one less decision you have to make, allowing the mental space for more important decisions throughout your day.
- Cultivate A Growth Mindset. Reframe challenges as opportunities. Easier said than done, but the mere practice will help propel you forward, focused, and on target. Negativity and self-doubt will tire you out and hinder your progress. Vigilantly watch your mind to see if you are shutting the door in your own face.
- Delegate Tasks And Share The Load. You don’t have to do everything on your own. At the office, consider which tasks can be shared or delegated to team members. At home, ask for help with household responsibilities or child care.
- Set Boundaries And Stick To Them. Define your work hours and stick to them. Communicate these boundaries clearly to your colleagues and supervisors. Don't be afraid to say no to extra tasks or responsibilities that will stretch you too thin.
- Take Breaks And Practice Mindfulness. Short, mindful breaks throughout the day can help you reset and recharge. Use these moments to practice deep breathing, stretch, or simply take a walk. Incorporating mindfulness into your routine helps center your thoughts, reduces anxiety, and allows you to return to your tasks with renewed focus.
- Seek Out A Support Network. Connecting with others who understand the unique challenges of balancing professional and personal life can be incredibly empowering. Build a support network of friends, colleagues, and mentors where you can share experiences, advice, and encouragement.
- Prioritize Physical Wellness. Exercise. Release those endorphins. You’ll feel better, you’ll look better, you’ll eat better, and your brain will function better. It’s hard to think of all your problems while you’re exercising. Your mind needs the time-out from problem-solving to rejuvenate. To borrow a well-known phrase: just do it.
- Seek Professional Support When Needed. If you’re feeling constantly overwhelmed or if self-care strategies aren’t alleviating your symptoms, don’t hesitate to seek professional help. Therapists and counselors can offer valuable tools and strategies tailored to your specific needs, helping you navigate through burnout more effectively. Remember, seeking help is a sign of strength, not weakness, and it's a critical step towards regaining control of your well-being.
- Practice Effective Time Management. Managing time effectively can significantly reduce stress levels. Start by organizing your tasks according to priority and break them down into smaller, manageable steps. Use planners, apps, or other tools to stay on track. By allocating your time wisely, you can ensure that you have adequate time for work, rest, and personal activities, thereby minimizing the risk of burnout.
Burnout doesn't have to define your career or your life. Prioritizing your own needs is not a sign of weakness but a fundamental aspect of maintaining a healthy, fulfilling career and personal life. Take care of yourself, lean on your support networks, and don’t hesitate to seek professional help if needed. Your well-being is worth it.
- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Self-Presentation Definition Self-presentation refers to how people attempt to present themselves to control or shape how others (called the audience) view them. It involves expressing oneself and behaving in ways that create a desired impression. Self-presentation is part of a broader set of behaviors called impression management. Impression management refers to the controlled presentation of
Ask a trusted friend or mentor to share what you can improve. Asking for feedback about specific experiences, like a recent project or presentation, will make their suggestions more relevant and easier to implement. 2. Study people who have been successful in your role. Look at how they interact with other people.
self-presentation. n. any behaviors intended to convey a particular image of, or particular information about, the self to other people. Self-presentational motives explain why an individual's behavior often changes as soon as anyone else is thought to be present or watching. Canadian-born U.S. sociologist Erving Goffman (1922-1982) likened ...
Impression Management in Sociology. Impression management, also known as self-presentation, refers to the ways that people attempt to control how they are perceived by others (Goffman, 1959). By conveying particular impressions about their abilities, attitudes, motives, status, emotional reactions, and other characteristics, people can ...
Define self-concept and discuss how we develop our self-concept. ... Self-presentation refers to the process of strategically concealing and/or revealing personal information in order to influence others' perceptions. Prosocial self-presentation is intended to benefit others and self-serving self-presentation is intended to benefit the self ...
Self-Presentation Theory: Understanding the Art of Impression Management. In the grand theater of life, where every social interaction is a stage and we are both the actors and the audience, self-presentation theory takes center stage. ... Key Definition: Self-presentation theory refers to the behavior and strategies individuals use to shape ...
People often use self-presentation as a way to build their own identity. Many people adopt values, behaviours, and beliefs for which they want others to recognize them. For example, a person might adopt a specific set of religious ideals and want to be identified as a practitioner of that religion. You may present yourself as a firm believer of ...
Self-presentation is the process of managing one's own image and impression in social situations. ScienceDirect Topics provides an overview of the theories, research, and applications of self-presentation in various domains, such as psychology, sociology, communication, and health. Learn how self-presentation influences self-esteem, identity, motivation, and interpersonal relationships.
Understanding self-presentation. Self-presentation is the process by which individuals attempt to control the impressions others form of them. It's a performance where the stage is everyday life, and the audience is the people around us. We employ a variety of verbal, nonverbal, and stylistic cues to craft an image that serves our goals.
Self-presentation is behavior that attempts to convey some information about oneself or some image of oneself to other people. It denotes a class of motivations in human behavior. These motivations are in part stable dispositions of individuals but they depend on situational factors to elicit them. Specifically, self-presentational motivations ...
The Presentation of Self in Everyday Life is a book that was published in the U.S. in 1959, written by sociologist Erving Goffman. In it, Goffman uses the imagery of theater in order to portray the nuances and significance of face-to-face social interaction. Goffman puts forth a theory of social interaction that he refers to as the ...
Search for: 'self-presentation' in Oxford Reference ». The conscious or unconscious control of the impression that one creates in social interactions or situations. It is one of the important forms of impression management, namely management of one's own impression on others through role playing. The phenomenon is encapsulated in Shakespeare's ...
As you've learned, social psychology is the study of how people affect one another's thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. We have discussed situational perspectives and social psychology's emphasis on the ways in which a person's environment, including culture and other social influences, affect behavior.
Self-presentation. As you've learned, social psychology is the study of how people affect one another's thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. We have discussed situational perspectives and social psychology's emphasis on the ways in which a person's environment, including culture and other social influences, affect behavior.
SELF-PRESENTATION. By N., Sam M.S. Any behaviour that is designed to convey an image about ourselves to other people. This explains why our behaviour can change if we notice we are being watched. See impression management. Cite this page: N., Sam M.S., "SELF-PRESENTATION," in PsychologyDictionary.org, April 13, 2013, https ...
self-presentation n. any behaviors intended to convey a particular image of, or particular information about, the self to other people. Self-presentational motives explain why an individual's behavior often changes as soon as anyone else is thought to be present or watching.
Define self-concept and discuss how we develop our self-concept. ... Self-presentation refers to the process of strategically concealing and/or revealing personal information in order to influence others' perceptions. Prosocial self-presentation is intended to benefit others and self-serving self-presentation is intended to benefit the self ...
Self-presentation is the process by which individuals represent themselves to the social world. This process occurs at both conscious and nonconscious (automatic) levels and is usually motivated by a desire to please others and/or meet the needs of the self. Self-presentation can be used as a means to manage the impressions others form of oneself.
The most basic function of self-presentation is to define the nature of a social situation (Goffman, 1959). Most social interactions are very role governed. Each person has a role to play, and the interaction proceeds smoothly when these roles are enacted effectively. For example, airline pilots are expected to be poised and dignified.
This implies that self-presentation is a form of social communication, by which people establish, maintain, and alter their social identity. These self-presentational strategies can be " assertive ...
Presentation skills are the abilities and qualities necessary for creating and delivering a compelling presentation that effectively communicates information and ideas. They encompass what you say, how you structure it, and the materials you include to support what you say, such as slides, videos, or images. You'll make presentations at various ...
4 THE PRESENTATION OF SELF ing the definition of the situation which the others come to formulate, and he can influence this definition by ex- pressing himself in such a way as to give them the kind of impression that will-lead them to act voluntarily in accord- ance with his own plan. Thus, when an individual appears
You can practice self-care in many ways: exercise, eat well, meditate, seek therapy, and more. Each method of self-care fits into one of the seven pillars: mental, emotional, physical, environmental, spiritual, recreational, and social. A well-balanced self-care routine involves each of these, so avoid restricting yourself to just one or two ...
Burnout doesn't have to define your career or your life. Prioritizing your own needs is not a sign of weakness but a fundamental aspect of maintaining a healthy, fulfilling career and personal life.