Want to Get your Dissertation Accepted?
Discover how we've helped doctoral students complete their dissertations and advance their academic careers!

Join 200+ Graduated Students

Get Your Dissertation Accepted On Your Next Submission
Get customized coaching for:.
- Crafting your proposal,
- Collecting and analyzing your data, or
- Preparing your defense.
Trapped in dissertation revisions?

- Code of Ethics
- Dissertation Editing
- Dissertation Coaching
- Free Consultation
How to Create a Dissertation Timeline (With Examples + Tempate)
When it’s time to start thinking about writing your dissertation, it is vital to put together a dissertation timeline. This will help you map out the months you will be spending on your dissertation, and ensure that you’re staying on track. A specific and detailed dissertation timeline will serve as an outline to guide you, step by step, through what can be a long and challenging process.
While we often refer to a dissertation in a way that makes it sound like a monolith, in reality, a dissertation consists of many moving parts. A dissertation timeline includes a series of milestones that leads up to the dissertation defense , revisions, and final submission of your dissertation. Constructing an outline of every step in the dissertation process , including rough estimates of how long each will take, will give you a realistic picture of where you are in the process at any given time.
Before embarking on your dissertation, it is a good idea to meet with your dissertation advisor and sketch out a dissertation timeline that is realistic for the size and scope of your project and includes deadlines. This will provide you with much-needed structure and a sense of what will happen next. To get an idea of what a completed dissertation looks like and the components your program requires, ask to see samples from recent graduates in your department.
These are a few frequently asked questions about crafting a dissertation timeline:
- What does a dissertation timeline look like?
- What goes in a dissertation timeline?
- How structured should a dissertation timeline be?
- What do you do with a dissertation timeline?

What Does a Dissertation Timeline Look Like?
One way to think about a dissertation timeline is as a kind of outline. While the outlining process is unique to each writer, there are commonalities shared by all of them. Likewise, when writing a dissertation timeline, you’ll want to include all of the basic elements of your dissertation as well as the amount of time you think you’ll need to execute them.
The best dissertation timeline format is the one that works for you. Though I’ve reformed somewhat over the years, for a long time I wasn’t a fan of intensely detailed outlines. Many people don’t like outlines. And that’s okay! However, writing a dissertation is not the time to be flying by the seat of your pants. To get started, a simple, linear timeline that projects the amount of time you think you’ll need to write your dissertation will suffice.
Example Dissertation Timeline
Below, you’ll find an example of a dissertation timeline, which you can view as an image in your browser or download as a spreadsheet. Feel free to use the spreadsheet as a template as you build your own dissertation timeline.
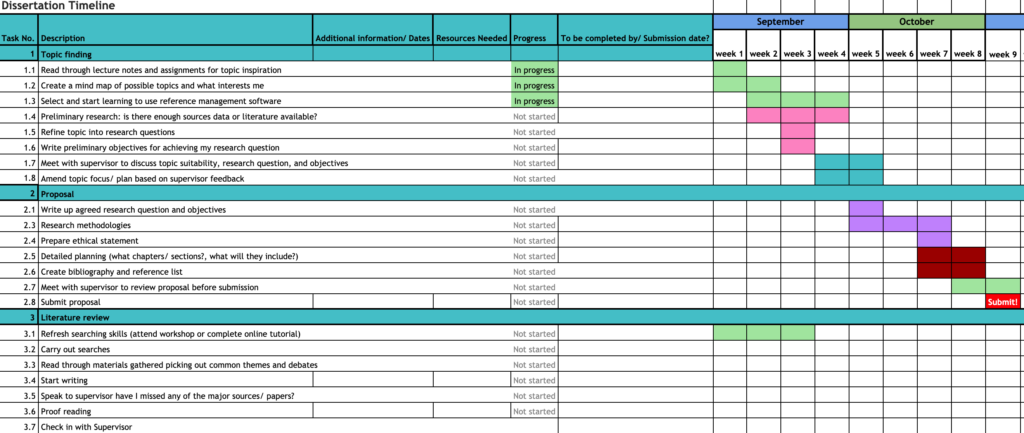
Or download the spreadsheet below:
Inclusion in a Dissertation Timeline
When constructing your dissertation timeline, include every element of the dissertation from the abstract to the conclusion. Keep in mind that you may not be writing your chapters in chronological order. For instance, after completing their first round of research and writing their research question, most graduate students will tackle their literature review next, even though it comes after the abstract and introduction in the final document.
Depending on the field being studied, most dissertations will also include sections for methodology, results, and discussion. Many programs also require a detailed conclusion that alludes to future research possibilities. Every dissertation also has an extensive list of references (pro tip: write this as you’re writing your dissertation), as well as appendices for charts, graphs, and other ephemera. And don’t forget your acknowledgments!
Dissertation Timeline Structure
The structure of your dissertation timeline will take shape once you’re engaged in the research process. While a road map may seem like an apt metaphor for a dissertation, once you get started you may notice a lot of starts and stops and circling back. After you’ve begun researching, you may realize that you need to allot more time for digging through the databases, or you may discover that you need to reformulate your research question entirely.

I’ve seen many of my own graduate students use calendars to great effect, giving themselves hard and fast deadlines to meet. Many students also build out their dissertation timelines as they progress, attaching working drafts of their abstract, introduction, and literature review to their timeline within a giant spreadsheet that links to multiple documents and sources. All of these methods are valid. Devise one that works for you.
Using a Dissertation Timeline
So once you have a thoughtful, soundly-constructed dissertation timeline, what do you do with it? First, and most importantly, try your best to adhere to it. Check in with your dissertation timeline regularly, and use it to keep yourself on track. Also, make adjustments to it as needed. If you find yourself breezing through your preliminary research but needing a bit more time for your literature review, consult your timeline and adjust accordingly.
While meeting your deadlines is important, also construct your dissertation timeline with an understanding that many graduate students face delays once they start working on their dissertation. These can include hold-ups at the department or university level in the form of late IRB approval or limited lab space or grant funding that gets cut. Anything can happen, but having a dissertation timeline will help you get back on track as soon as the storm passes.
In my own experience, I also found my dissertation timeline to be a great document to share and discuss with my dissertation chair and committee. Once I finished my comprehensive exams, I met with members of my dissertation committee and got feedback on my rough dissertation timeline to make sure my goals for submitting my dissertation and graduating were realistic. This also ensured that we were all on the same page.
When writing a dissertation, timing is everything. Creating a dissertation timeline gives you definitive time limits for research and writing, and it also influences several other major decisions that you’ll need to make. These include preparation to go on the job market, which often coincides with writing your dissertation. There is no doubt that this will be a hectic time in your graduate school career, but having a well-organized dissertation timeline is a good way to keep everything in perspective.
Related posts:

Courtney Watson, Ph.D.
Courtney Watson, Ph.D. is an Associate Professor of English at Radford University Carilion, in Roanoke, Virginia. Her areas of expertise include undergraduate and graduate curriculum development for writing courses in the health sciences and American literature with a focus on literary travel, tourism, and heritage economies. Her writing and academic scholarship has been widely published in places that include Studies in American Culture , Dialogue , and The Virginia Quarterly Review . Her research on the integration of humanities into STEM education will be published by Routledge in an upcoming collection. Dr. Watson has also been nominated by the State Council for Higher Education of Virginia’s Outstanding Faculty Rising Star Award, and she is a past winner of the National Society of Arts & Letters Regional Short Story Prize, as well as institutional awards for scholarly research and excellence in teaching. Throughout her career in higher education, Dr. Watson has served in faculty governance and administration as a frequent committee chair and program chair. As a higher education consultant, she has served as a subject matter expert, an evaluator, and a contributor to white papers exploring program development, enrollment research, and educational mergers and acquisitions.
Comments are closed.
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Create a Research Timeline for Your Thesis

5-minute read
- 21st May 2023
Beginning a dissertation can feel both thrilling and overwhelming. One of the best things you can do to prepare for the exciting journey of doing a dissertation is to design a comprehensive timeline as your guide. Here we will take you step by step through creating your thesis timeline and provide some example templates, so you’ll be well-prepared to begin your dissertation work.
Reasons for Creating a Timeline
There are many benefits to crafting a detailed dissertation timeline. In addition to helping with time management and meeting crucial deadlines, your timeline will also help you stay motivated by reviewing the tasks you have completed as you progress. A thorough timeline will be valuable during your dissertation proposal and useful if you are applying for grants or other additional funding.
Ste0ps for Creating a Timeline for Your Thesis:
- Research and record all requirements and deadlines.
Before you write out your timeline, ensure you know all of your program’s requirements and deadlines. Academic institutions often require you to complete your dissertation within a specified timeframe.
There are likely several recommended or mandatory deadlines for approval of certain items by your adviser (and possibly the rest of your committee members). Gather all these dates beforehand so you can allot an appropriate amount of time to meet your deadlines.
It will be beneficial to meet with your adviser to understand when you are expected to complete the major phases of your dissertation work and to confirm that there aren’t any other requirements or deadlines that you may not be aware of.
- List all of your tasks and bundle them into phases.
Now that you’ve assembled your dates, working backward from your deadlines is a good rule of thumb. List all of the required tasks that must be completed to meet each milestone, from coming up with your research questions to writing each chapter of your dissertation .
Even though your list will be unique to your research project, it can help to refer to a thesis checklist . It’s also helpful to assemble tasks into different phases (e.g., dissertation proposal, research recruitment). Grouping tasks into phases gives anyone looking at your timeline a quick overview of your research plan.
- Organize your tasks into a schedule and assign task deadlines.
Now it’s time to build your timeline. There are many different free templates available online, from straightforward lists of deliverables to colorful options with room for notes and customization.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
A popular organizational approach for thesis timelines is a Gantt chart , which is a type of bar chart often used in project management in which the length of the bar corresponds to the time the task will take. The best choice for you will depend on the specifics of your research study and personal preferences. Whichever option you select, make sure you can easily edit and revise it as need be.
Sanity-Saving Tips:
● Pay attention to your work style. Some people are more productive when writing in short bursts, while others write better after taking time to get into the zone. Some people choose to start writing parts of their thesis while still conducting research, while others prefer to focus on one phase at a time. Set yourself up for success by reflecting on what type of schedule will help you create the best quality work.
● Schedule breaks. Almost everyone will work better after a well-deserved break. Make sure to schedule regular breaks into your timeline, as well as provide enough time to sleep, eat well, and do anything else you need to do to safeguard your well-being.
● Always have a plan B. Your dissertation is an extensive endeavor with many moving parts. It’s impossible to anticipate and plan for every conceivable event, but it’s helpful to expect something may occur that will cause a deviation from your original timeline. Perhaps study recruitment takes longer than you expected, or one of your committee members gets sick and you have to postpone your dissertation proposal. After you draft your timeline, check that it is not so strict that any disruption will cause a total derailment of your plan. Aim to strike a balance between goals that will inspire you to progress steadfastly and have some leeway in your timeline for the inevitable curveball that life will throw at you somewhere along the way.
Following these three steps will help you draft a timeline to steer the course of your dissertation work: research and record all requirements and deadlines; work backward from your dissertation deadline and assemble your task lists; and organize your tasks into a timeline.
Don’t forget to include ample time for editing and proofreading your dissertation . And if you are interested in any help from us, you can try a sample of our services for free . Best of luck in writing your dissertation!
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
Free email newsletter template (2024).
Promoting a brand means sharing valuable insights to connect more deeply with your audience, and...
6-minute read
How to Write a Nonprofit Grant Proposal
If you’re seeking funding to support your charitable endeavors as a nonprofit organization, you’ll need...
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
4-minute read
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
Understanding and solving intractable resource governance problems.
- Conferences and Talks
- Exploring models of electronic wastes governance in the United States and Mexico: Recycling, risk and environmental justice
- The Collaborative Resource Governance Lab (CoReGovLab)
- Water Conflicts in Mexico: A Multi-Method Approach
- Past projects
- Publications and scholarly output
- Research Interests
- Higher education and academia
- Public administration, public policy and public management research
- Research-oriented blog posts
- Stuff about research methods
- Research trajectory
- Publications
- Developing a Writing Practice
- Outlining Papers
- Publishing strategies
- Writing a book manuscript
- Writing a research paper, book chapter or dissertation/thesis chapter
- Everything Notebook
- Literature Reviews
- Note-Taking Techniques
- Organization and Time Management
- Planning Methods and Approaches
- Qualitative Methods, Qualitative Research, Qualitative Analysis
- Reading Notes of Books
- Reading Strategies
- Teaching Public Policy, Public Administration and Public Management
- My Reading Notes of Books on How to Write a Doctoral Dissertation/How to Conduct PhD Research
- Writing a Thesis (Undergraduate or Masters) or a Dissertation (PhD)
- Reading strategies for undergraduates
- Social Media in Academia
- Resources for Job Seekers in the Academic Market
- Writing Groups and Retreats
- Regional Development (Fall 2015)
- State and Local Government (Fall 2015)
- Public Policy Analysis (Fall 2016)
- Regional Development (Fall 2016)
- Public Policy Analysis (Fall 2018)
- Public Policy Analysis (Fall 2019)
- Public Policy Analysis (Spring 2016)
- POLI 351 Environmental Policy and Politics (Summer Session 2011)
- POLI 352 Comparative Politics of Public Policy (Term 2)
- POLI 375A Global Environmental Politics (Term 2)
- POLI 350A Public Policy (Term 2)
- POLI 351 Environmental Policy and Politics (Term 1)
- POLI 332 Latin American Environmental Politics (Term 2, Spring 2012)
- POLI 350A Public Policy (Term 1, Sep-Dec 2011)
- POLI 375A Global Environmental Politics (Term 1, Sep-Dec 2011)
Planning the timeline and progress of your doctoral dissertation (or Masters/undergraduate thesis)
One of my PhD students lamented this week with me that she had a lot to juggle (taking children to and from schools and to and from activities, etc.) and that she needed a strategy to make her research move forward. I had been planning to write this blog post for a while, since this is the one question I get asked the most by doctoral students (“ how do I plan my unstructured time over the summer ” being the other one).
Do you have one like this but for dissertations? From how to pick your topic to how to plan your chapters or something similar? 🙂 — Mariana Miguélez (@Scherezadda) March 27, 2018
I had to rush to get this blog post done because my student is 2 years away from the deadline her university has imposed for her thesis defence, which is why I sat down with her last night to show her how I do things. I have two other PhD students at exactly the same stage (2 years to defense) so I figured I might as well finish this blog post.
While I’ve suggested that people read one (or more) of the books that I’ve digested myself (check my Writing a Doctoral Dissertation page), one of the main things I teach my students is how to apply backcasting techniques to develop a project plan . I was trained as a project manager, and I worked in that capacity for a number of years, so I understand exactly the kind of work that needs to be done to develop good project plans.
There are a few resources for students, which I mentioned on Twitter earlier today (October 5th, 2018), many of which are listed in the thread that will appear if you click anywhere on the tweet shown below. Thanks to everyone who responded to my query, though I think many of them were professors describing their own process, which is not the same as having a doctoral dissertation (ONE GOAL) to finish in X number of years. My students are doing theirs in the 3 papers’ model, which is a bit closer to the day-to-day life of a professor, but still, the trajectory is quite different. Anyhow, here are some recommendations (click on the tweet to expand the entire thread).
Everyone: one of my PhD students today asked me how to plan her day/week/month/time table. Can you tweet me your process before I tweet/thread mine? Thanks! (I'm off to dinner because I've already written 460 words). — Dr Raul Pacheco-Vega (@raulpacheco) October 3, 2018
The core planning strategy I would thus recommend doctoral, masters and undergraduate students is to engage in a combination of Gantt Chart Design and project backcasting techniques .
The Gantt chart is a technique I learned in graduate school when I took project management courses. This is a hypothetical Gantt chart for my doctoral student, covering about 15 months.
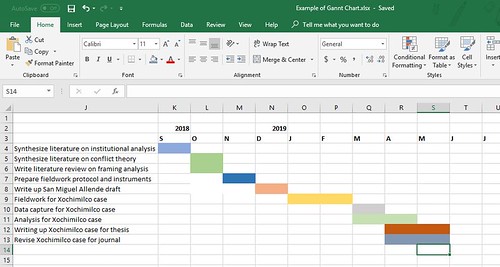
What I suggested to her was to use backcasting techniques to plan backwards from her goal (PhD thesis defense) to intermediate goals. This post explains how I backcast a project https://t.co/wAmyejeoa0 since her dissertation is a 3-papers one, I suggested she uses that model. — Dr Raul Pacheco-Vega (@raulpacheco) October 5, 2018
For Gantt Chart templates, you can see Dr. Emma Sheppard’s here.
Project planning for research students https://t.co/ku7shfB5uL excellent template by @DrESheppard which may be of interest to students from undergrad, Masters and PhD levels. pic.twitter.com/ujQVlYocH7 — Dr Raul Pacheco-Vega (@raulpacheco) September 3, 2018
Here is another resource that you can use to create Gantt Charts.
To do Gantt charts you can use Excel or Microsoft Project (which is how I learned to do them), or Visio (which has been bought by the evil company and is now Microsoft Visio). I liked this detailed approach that uses connectors between milestones and tasks https://t.co/xVjNmM1q7c — Dr Raul Pacheco-Vega (@raulpacheco) October 5, 2018
Hugh Kearns and Maria Gardiner have lots of resources on their site, and have published books on this as well.
I just realised @ithinkwell and @ithinkwellHugh have excellent FREE templates on their website https://t.co/Q859jNiM6Q for PhD students to plan their trajectories, etc. #PhDChat (thanks, Maria and Hugh!) — Dr Raul Pacheco-Vega (@raulpacheco) October 5, 2018
Dr. Patrick Dunleavy’s book “ Authoring a PhD ” is incredible and really does help students who are planning their PhD process. I recommend it to my own doctoral students.
And of course I would be remiss if I forgot to recommend Dr. Ellie Mackin Roberts (my coauthor for a forthcoming book on research planning) and her website. Ellie has A TON of downloadable printables for you to plan your own research. She is fantastic.
Both for doctoral students AND for post-PhD folks, my coauthor Dr. @EllieMackin has an entire website for research planning https://t.co/unXMqmaf2Z she offers FREE downloadable printable templates that you can use to plan your own research. — Dr Raul Pacheco-Vega (@raulpacheco) October 5, 2018
In the end, the process I recommended to my students and that I do myself is – set a target defense date and then work backwards and plan tasks, activities, and intermediate goals. For example, I have asked my students to plan submission dates for their 3 papers (to be sent to journals) and then schedule fieldwork and data analysis accordingly. This process has worked well, and I hope my description of the process will help my students and others!
In a subsequent blog post I’ll describe how to go from long-term goals (submit paper X by Y date) to daily tasks. That blog post will definitely apply to doctoral students and post-PhD folks.
If you liked this blog post, you may also be interested in my Resources for Graduate Students page, and on my reading notes of books I’ve read on how to do a doctoral degree.
You can share this blog post on the following social networks by clicking on their icon.
Posted in academia .
No comments
By Raul Pacheco-Vega – October 6, 2018
0 Responses
Stay in touch with the conversation, subscribe to the RSS feed for comments on this post .
Leave a Reply Cancel Some HTML is OK
Name (required)
Email (required, but never shared)
or, reply to this post via trackback .
About Raul Pacheco-Vega, PhD
Find me online.
My Research Output
- Google Scholar Profile
- Academia.Edu
- ResearchGate
My Social Networks
- Polycentricity Network
Recent Posts
- The value and importance of the pre-writing stage of writing
- My experience teaching residential academic writing workshops
- “State-Sponsored Activism: Bureaucrats and Social Movements in Brazil” – Jessica Rich – my reading notes
- Reading Like a Writer – Francine Prose – my reading notes
- Using the Pacheco-Vega workflows and frameworks to write and/or revise a scholarly book
Recent Comments
- Charlotte on The value and importance of the pre-writing stage of writing
- Raul Pacheco-Vega on The value and importance of the pre-writing stage of writing
- Noni on Developing a structured daily routine for writing and research
- Alan Parker on Project management for academics I: Managing a research pipeline
Follow me on Twitter:
Proudly powered by WordPress and Carrington .
Carrington Theme by Crowd Favorite

Time Management Resources for Graduate Students and Postdocs
Dissertation plan
Completing your dissertation can be overwhelming and stressful. It is a critical period of time to manage time effectively and execute your well-thought-out plans. In this section, we aim to provide some checkpoints or milestones that help you to complete your dissertation in a timely manner:
- Find out the requirements and deadlines set by the department and graduate school. Having the end goal in mind will help you plan your way to get there.
- Have the initial meeting with your advisor to discuss the goals of your dissertation and set up an overall timeline. For example, determine when to have the defense, when to send the dissertation to committee, when to send out the schedule poll to committee, etc.
- Create an outline of the dissertation with sections and subsections for each chapter according to the initial discussion, and map out deadlines for each section.
- Meet with your advisor to discuss and finalize the outline and roadmap, including what kind of format (by chapters or the whole dissertation) your advisor expects, and how to maintain the line of communication (face-to-face or email) and how often you should communicate, so that you can get support and feedback along the way.
- Reach out to your committee members to let them know your dissertation plan and schedule the defense date. Ask if they are willing to provide feedback on your drafts.
- Incorporate the feedback comments and edit your dissertation for submission to your committee for defense.
*You can create a timeline table to help you visualize your plan.
Execution plan:.
- On your daily schedule, block off a couple of hours when you are most effective for your dissertation writing. Having this specific time block will help you prioritize and fit other tasks around your writing. Stick to the schedule and treat it as your appointment with your advisor or doctor.
- Limit the distraction during your blocked writing time in order to fully concentrate.
- Set a daily goal. For example, writing 2 pages each day on chapter 1 or finishing the method session on chapter 2, etc.
- Find a place that you find yourself most productive and efficient, and write there.
- Monitor your progress by calendars and project management apps.
- You are not alone. Find someone who is also writing their dissertation to be your writing buddy to help encourage one another and keep each other on track.
- Work/life balance (refer to the work/life balance )
https://www.stcloudstate.edu/elhe/_files/documents/dissertation/time-management-tips.pdf
https://sph.umd.edu/sites/default/files/files/StrategiesDissertationCompletion3_8_07.pdf
| is powered by WordPress. Read the Sites@Duke Express and , or . |

A Guide to Dissertation Planning: Tips, Tools and Templates
Dissertations are a defining piece of academic research and writing for all students. To complete such a large research project while maintaining a good work-life balance, planning and organisation is essential. In this article, we’ll outline three categories for dissertation planning including project management, note-taking and information management, alongside tools and templates for planning and researching effectively.

For both undergraduates and postgraduates, a dissertation is an important piece of academic research and writing. A large research project often has many moving parts from managing information, meetings, and data to completing a lengthy write-up with drafts and edits. Although this can feel daunting, getting ahead with effective planning and organisation will make this process easier. By implementing project management techniques and tools, you can define a research and writing workflow that allows you to work systematically. This will enable you to engage in critical thinking and deep work, rather than worrying about organisation and deadlines.
To get prepared, you can do two things: First, start your preliminary readings and research to define a topic and methodology. You can do this in summer or during the first few weeks of university but the sooner, the better. This gives you time to discuss things with your supervisor, and really choose a topic of interest. Second, begin preparing the tools and techniques you’ll be using for your research and writing workflow. You can use the preliminary research phase to test these out, and see what works for you.
Below, we’ll cover three key aspects to consider when managing your dissertation, alongside some digital tools for planning, research and writing.
The 3 Categories of Dissertation Planning
Project Management and Planning
Your dissertation is a project that requires both long and short-term planning. For long-term planning, roadmaps are useful to break your work down into sections, chapters or stages. This will give you a clear outline of the steps you need to work through to complete your dissertation in a timely manner.
Most likely, your roadmap will be a mixture of the stages in your research project and the sections of your write-up. For example, stage 1 might be defined as preliminary research and proposal writing. While stage 3 might be completing your literature review, while collecting data.
This roadmap can be supplemented by a timeline of deadlines, this is when those stages or chapters need to be completed by. Your timeline will inform your short-term plans, and define the tasks that need completing on a daily, weekly or monthly basis. This approach, using a roadmap and timeline, allows you to capture all the moving parts of your dissertation, and focus on small sub-sections at a time. A clear plan can make it easy to manage setbacks, such as data collection issues, or needing more time for editing.
Note-taking
Whether you use a notebook, or digital tool, it’s ideal to have a dedicated research space for taking general notes. This might include meeting notes from supervision, important information from informational dissertation lectures, or key reminders, ideas and thoughts. It can be your go-to place for miscellaneous to-do lists, or to map out your thought processes. It’s good to have something on hand that is easy to access, and keeps your notes together in one place.
Beyond this, you’ll also need a dedicated space or system for literature and research notes. These notes are important for avoiding plagiarism, communicating your ideas, and connecting key findings together. A proper system or space can make it easier to manage this information, and find the appropriate reference material when writing. Within this system, you might also include templates or checklists, for example, a list of critical reading questions to work through when assessing a paper.
Information Management
It’s important to consider how you plan to organise your literature, important documents, and written work. Note-taking is a part of this, however, this goes a step further to carefully organise all aspects of your dissertation. For example, it’s ideal to keep track of your literature searches, the papers you’ve read, and their citations but also, your reading progress. Being able to keep track of how many passes a paper has been through, how relevant it is, or where it fits within your themes, or ideas, will provide a good foundation for writing a well-thought out dissertation.
Likewise, editing is an important part of the write-up process. You’ll have multiple drafts, revisions and feedback to consider. It’s good to have some way of keeping track of all this, to ensure all changes and edits have been completed. You might also have checklists or procedures to follow when collecting data, or working through your research. A good information management process can reduce stress, making everything easy to access and keep track of, which then allows you to focus on getting the actual work complete.
Digital Project Management and Research Tools for Dissertation Planning
Trello is a project management tool that uses boards, lists and cards to help you manage all your tasks. In a board, you can create lists, and place cards within these lists. Cards contain a range of information such as notes, checklists, and due dates. Cards and lists can be used to implement a digital kanban board system , allowing you to move cards into a ‘to-do’, ‘in progress’ or ‘complete’ list. This gives a visual representation of your progress.
This is a flexible, easy to use and versatile tool that can help with project management of your dissertation. For example, cards and lists can be used to track your literature, each card can represent a paper and lists could be 1st pass, 2nd pass, or be divided into themes. Likewise, you can use this approach to organise the various chapters or stages of your dissertation, and break down tasks in a visual way. Students have used Trello to manage academic literature reviews , daily life as an academic , and collaborate with their supervisors for feedback and revisions on their write-up.
Notion is an all-in-one note-taking and project management tool that is highly customisable. Using content blocks, pages, and databases, this tool allows you to build a workspace tailored to your needs. Databases are a key feature of Notion, this function allows you to organise and define pages using a range of properties such as tags, dates, numbers, categories and more. This database can then be displayed in a multitude of ways using different views, and filters.
For example, you can create a table with each entry being a page of meeting notes with your supervisor, you can assign a date, person, and tags to each page. You can then filter this information by date, or view it in a board format. Likewise, you can use the calendar to add deadlines, within these deadlines, you can expand the page to add information, and switch to ‘timeline’ view . This is perfect for implementing project management techniques when planning your dissertation.
Although this may sound complicated, there are many templates and resources to get you started . Notion is an ideal tool for covering all three aspects of dissertation planning from project and information management to note-taking of all kinds. Students have used Notion for literature reviews , thesis writing , long-term PhD planning , thesis management , and academic writing . The best part, these students not only share their systems, but have also created free templates to help you build your own system for research.
Asana is a project management and to-do list tool that uses boards, lists, timelines and calendars. If you’re someone who prefers using lists to organise your life and projects, Asana is ideal for you. You can use this tool to manage deadlines, reading progress, or break down your work into projects and sub-tasks. Asana can integrate with your calendar, which is perfect if you already use other calendar tools for organisation. If something like Notion is too overwhelming, using a mixture of tools with different purposes can be a more comfortable approach.
Genei is an AI-powered research tool for note-taking and literature management. Your research and reading material can be imported, and organised using projects and folders. For each file, genei produces an AI-powered summary, document outline, keyword list and overview. This tool also extracts key information such as tables, figures, and all the references mentioned. You can read through documents 70% faster but also, collect related articles by clicking on the items in the reference list. Genei can generate citations, and be used alongside other popular reference management tools, such as Zotero and Mendeley .
This tool is ideal for navigating information management and literature notes for your dissertation. You can compile notes across single documents or folders of documents using the AI-generated summaries. These notes remain linked to their original source, which removes the need for you to keep track of this information. If you find it hard to reword content, there’s also summarising and paraphrasing tools to help get you started. Genei is a great tool to use alongside project management solutions, such as Trello and Asana, and note-taking tools like Notion. You can define an efficient research and writing workflow using these range of tools, and make it easier to stay on top of your dissertation.

Do you want to achieve more with your time?
98% of users say genei saves them time and helps them work more productively. Why don’t you join them?
About genei
genei is an AI-powered research tool built to help make the work and research process more efficient. Our studies show genei can help improve reading speeds by up to 70%! Revolutionise your research process.
Articles you may like:

Find out how genei can benefit you
Want to Get your Dissertation Accepted?
Discover how we've helped doctoral students complete their dissertations and advance their academic careers!
Join 200+ Graduated Students

Get Your Dissertation Accepted On Your Next Submission
Get customized coaching for:.
- Crafting your proposal,
- Collecting and analyzing your data, or
- Preparing your defense.
Trapped in dissertation revisions?
Dissertation timeline, published by steve tippins on june 26, 2022 june 26, 2022.
Last Updated on: 2nd February 2024, 05:21 am
So, you’re writing a dissertation? Amazing! Congratulations! (Also, I’m sorry. And good luck.).
If you’re embarking on this difficult journey, you need to go where you’re going. Every treasure hunt begins with a good map. (This particular treasure hunt happens to be for information that fills an extremely specific gap in the scholarly literature ).
Your dissertation timeline is the map you’ll rely on as you navigate the stormy waters of your dissertation journey. It will tell you what you need to be working on at any given stage of the process, and what you should prepare for when you’re done with your current task.
Expect the Unexpected
Remember that the map is not the journey. You can plan everything out perfectly, but life happens. Life even happens to doctoral students, who have ostensibly given up having a life.
The point is, don’t beat yourself up when your experience doesn’t match up with your dissertation timeline. The timeline is there to guide you and provide useful goals, but it can be adapted along the way as things come up.

Perhaps your proposal needs five rounds of revision instead of the one or two you planned for (a common occurrence, except for those who have the foresight to hire a dissertation editor ). Maybe your committee chair decides to take an unexpected vacation. Maybe an unexpected family event happens.
All of these bumps are normal parts of the dissertation process. Don’t worry if you don’t live up to your own expectations as far as how quickly you finish. The important thing is not to go quickly, but to get to completion.
Here are the major steps you’ll need to take when writing your dissertation, from ideation to graduation.
Over 50% of doctoral candidates don’t finish their dissertations.
Step 1: Prospectus
The timeline for a dissertation begins with the generation of your idea. This usually takes the form of a prospectus . A prospectus explains, What are you planning to do? Then, you get your chair and committee to agree that it’s a reasonable topic. Most people go through more than one idea before settling on their topic, and that can take some time.
It may take you a month to come up with your idea because you’re going to be looking for a gap in the research. Once you find a gap in the research, see whether you could complete a relevant study within a reasonable time period.
A tip – most students try to tackle topics that are entirely too broad. Look at past dissertation topics in your department, and you’ll see just how specific you need to be.
Step 2: Proposal (Chapters 1 to 3)

After your prospectus, you move on to the proposal stage. At most universities, that means writing Chapters 1, 2, and 3. These three chapters are going to be about 60 to 70 pages total. You are going to have to do a lot of writing and research and get committee approval.
A timeline might say you can do your dissertation proposal in three to four months, but that is only true as long as what you’re submitting is well-written and your committee approves it. For argument’s sake, we’ll say it takes four months. The next level of your dissertation is to collect data. But before you can collect data, you have to get IRB approval.
Step 3: Institutional Review Board Approval
Approval from the Institutional Review Board, or IRB, states that what you’re going to be doing will not harm any participants in your study. IRB approval is usually relatively quick, depending on what type of research you’re doing. If you want to research small children, for example, it’s going to take longer to get approval. There must be safeguards in place to protect those children. Once you have IRB approval, you move on to collecting your data.
Step 4: Data Collection

Collecting data can be as short as a couple of hours if you are accessing data for a quantitative study from a secondary data source . In that case, you would just be getting the data you need from the database. Then, take that data, make sure it’s in the format you need, and enter it into the appropriate statistical software package. If you need help with this, check out our quantitative data analysis services.
On the other hand, if you’re doing a qualitative study and you have to track people down, it can take several months in order to just find and interview them. Then, you can process those interviews by transcribing and entering them into the appropriate statistical or software program to come up with themes.
Step 5: Analysis and Conclusion (Chapters 4 and 5)
Once you have statistical results and themes, you can write Chapter 4 and report your findings. Then, write Chapter 5 , in which you analyze your findings. Say what they mean and how it fits in the literature. Compare your findings to the literature you used to begin your study and address what future research should be done.
This phase could take anywhere from three to nine months, depending on how quickly you can collect your data. It is conceivable that you could finish your dissertation within a year or a year and a half. All of these time periods we’ve presented so far assume you’re working on your dissertation full-time. If you have a job and a family and are also working on a dissertation, it can take longer.
Step 6: Defense

Once you have finished your dissertation (Chapters 1 through 5) you have to go back to your committee, get approval, and then do your dissertation defense. This process can be as short as a month. But if your committee has problems with what you’ve done or it needs more work, it could take several months.
Variables in the Dissertation Timeline
There are a number of variables outside your control. For example, you might finish in July and then one or two of your committee members are off on research projects of their own and won’t be back until September. But in an ideal timeline, a year to a year and a half is reasonable.
While we can present ideals and hypotheticals, you do have a lot of control over the timeline. If you dedicate yourself and work ahead, you can minimize the amount of time it will take to have “Dr.” in front of your name.
Dealing With Unexpected Events

Unexpected things can come up as well. First of all, if you’re not a full-time student, life can throw many things in your way. Somebody could become sick, a pandemic could come about, or your job could increase its demands on you.
You don’t control your committee’s time, and they may have other things going on that prevent them from responding quickly. Funding interruptions can also happen. Being good at handling details is going to help you stay on track as much as possible.

That’s where a dissertation timeline comes in. Get this together from the very beginning, and you’ll be better-equipped to deal with unexpected events and finish your dissertation in as little time as possible.
Steve Tippins
Steve Tippins, PhD, has thrived in academia for over thirty years. He continues to love teaching in addition to coaching recent PhD graduates as well as students writing their dissertations. Learn more about his dissertation coaching and career coaching services. Book a Free Consultation with Steve Tippins
Related Posts

Dissertation
Dissertation memes.
Sometimes you can’t dissertate anymore and you just need to meme. Don’t worry, I’ve got you. Here are some of my favorite dissertation memes that I’ve seen lately. My Favorite Dissertation Memes For when you Read more…

Surviving Post Dissertation Stress Disorder
The process of earning a doctorate can be long and stressful – and for some people, it can even be traumatic. This may be hard for those who haven’t been through a doctoral program to Read more…


PhD by Publication
PhD by publication, also known as “PhD by portfolio” or “PhD by published works,” is a relatively new route to completing your dissertation requirements for your doctoral degree. In the traditional dissertation route, you have Read more…
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
How to Write a Dissertation | A Guide to Structure & Content
A dissertation or thesis is a long piece of academic writing based on original research, submitted as part of an undergraduate or postgraduate degree.
The structure of a dissertation depends on your field, but it is usually divided into at least four or five chapters (including an introduction and conclusion chapter).
The most common dissertation structure in the sciences and social sciences includes:
- An introduction to your topic
- A literature review that surveys relevant sources
- An explanation of your methodology
- An overview of the results of your research
- A discussion of the results and their implications
- A conclusion that shows what your research has contributed
Dissertations in the humanities are often structured more like a long essay , building an argument by analysing primary and secondary sources . Instead of the standard structure outlined here, you might organise your chapters around different themes or case studies.
Other important elements of the dissertation include the title page , abstract , and reference list . If in doubt about how your dissertation should be structured, always check your department’s guidelines and consult with your supervisor.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Acknowledgements, table of contents, list of figures and tables, list of abbreviations, introduction, literature review / theoretical framework, methodology, reference list.
The very first page of your document contains your dissertation’s title, your name, department, institution, degree program, and submission date. Sometimes it also includes your student number, your supervisor’s name, and the university’s logo. Many programs have strict requirements for formatting the dissertation title page .
The title page is often used as cover when printing and binding your dissertation .
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
The acknowledgements section is usually optional, and gives space for you to thank everyone who helped you in writing your dissertation. This might include your supervisors, participants in your research, and friends or family who supported you.
The abstract is a short summary of your dissertation, usually about 150-300 words long. You should write it at the very end, when you’ve completed the rest of the dissertation. In the abstract, make sure to:
- State the main topic and aims of your research
- Describe the methods you used
- Summarise the main results
- State your conclusions
Although the abstract is very short, it’s the first part (and sometimes the only part) of your dissertation that people will read, so it’s important that you get it right. If you’re struggling to write a strong abstract, read our guide on how to write an abstract .
In the table of contents, list all of your chapters and subheadings and their page numbers. The dissertation contents page gives the reader an overview of your structure and helps easily navigate the document.
All parts of your dissertation should be included in the table of contents, including the appendices. You can generate a table of contents automatically in Word.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
If you have used a lot of tables and figures in your dissertation, you should itemise them in a numbered list . You can automatically generate this list using the Insert Caption feature in Word.
If you have used a lot of abbreviations in your dissertation, you can include them in an alphabetised list of abbreviations so that the reader can easily look up their meanings.
If you have used a lot of highly specialised terms that will not be familiar to your reader, it might be a good idea to include a glossary . List the terms alphabetically and explain each term with a brief description or definition.
In the introduction, you set up your dissertation’s topic, purpose, and relevance, and tell the reader what to expect in the rest of the dissertation. The introduction should:
- Establish your research topic , giving necessary background information to contextualise your work
- Narrow down the focus and define the scope of the research
- Discuss the state of existing research on the topic, showing your work’s relevance to a broader problem or debate
- Clearly state your objectives and research questions , and indicate how you will answer them
- Give an overview of your dissertation’s structure
Everything in the introduction should be clear, engaging, and relevant to your research. By the end, the reader should understand the what , why and how of your research. Not sure how? Read our guide on how to write a dissertation introduction .
Before you start on your research, you should have conducted a literature review to gain a thorough understanding of the academic work that already exists on your topic. This means:
- Collecting sources (e.g. books and journal articles) and selecting the most relevant ones
- Critically evaluating and analysing each source
- Drawing connections between them (e.g. themes, patterns, conflicts, gaps) to make an overall point
In the dissertation literature review chapter or section, you shouldn’t just summarise existing studies, but develop a coherent structure and argument that leads to a clear basis or justification for your own research. For example, it might aim to show how your research:
- Addresses a gap in the literature
- Takes a new theoretical or methodological approach to the topic
- Proposes a solution to an unresolved problem
- Advances a theoretical debate
- Builds on and strengthens existing knowledge with new data
The literature review often becomes the basis for a theoretical framework , in which you define and analyse the key theories, concepts and models that frame your research. In this section you can answer descriptive research questions about the relationship between concepts or variables.
The methodology chapter or section describes how you conducted your research, allowing your reader to assess its validity. You should generally include:
- The overall approach and type of research (e.g. qualitative, quantitative, experimental, ethnographic)
- Your methods of collecting data (e.g. interviews, surveys, archives)
- Details of where, when, and with whom the research took place
- Your methods of analysing data (e.g. statistical analysis, discourse analysis)
- Tools and materials you used (e.g. computer programs, lab equipment)
- A discussion of any obstacles you faced in conducting the research and how you overcame them
- An evaluation or justification of your methods
Your aim in the methodology is to accurately report what you did, as well as convincing the reader that this was the best approach to answering your research questions or objectives.
Next, you report the results of your research . You can structure this section around sub-questions, hypotheses, or topics. Only report results that are relevant to your objectives and research questions. In some disciplines, the results section is strictly separated from the discussion, while in others the two are combined.
For example, for qualitative methods like in-depth interviews, the presentation of the data will often be woven together with discussion and analysis, while in quantitative and experimental research, the results should be presented separately before you discuss their meaning. If you’re unsure, consult with your supervisor and look at sample dissertations to find out the best structure for your research.
In the results section it can often be helpful to include tables, graphs and charts. Think carefully about how best to present your data, and don’t include tables or figures that just repeat what you have written – they should provide extra information or usefully visualise the results in a way that adds value to your text.
Full versions of your data (such as interview transcripts) can be included as an appendix .
The discussion is where you explore the meaning and implications of your results in relation to your research questions. Here you should interpret the results in detail, discussing whether they met your expectations and how well they fit with the framework that you built in earlier chapters. If any of the results were unexpected, offer explanations for why this might be. It’s a good idea to consider alternative interpretations of your data and discuss any limitations that might have influenced the results.
The discussion should reference other scholarly work to show how your results fit with existing knowledge. You can also make recommendations for future research or practical action.
The dissertation conclusion should concisely answer the main research question, leaving the reader with a clear understanding of your central argument. Wrap up your dissertation with a final reflection on what you did and how you did it. The conclusion often also includes recommendations for research or practice.
In this section, it’s important to show how your findings contribute to knowledge in the field and why your research matters. What have you added to what was already known?
You must include full details of all sources that you have cited in a reference list (sometimes also called a works cited list or bibliography). It’s important to follow a consistent reference style . Each style has strict and specific requirements for how to format your sources in the reference list.
The most common styles used in UK universities are Harvard referencing and Vancouver referencing . Your department will often specify which referencing style you should use – for example, psychology students tend to use APA style , humanities students often use MHRA , and law students always use OSCOLA . M ake sure to check the requirements, and ask your supervisor if you’re unsure.
To save time creating the reference list and make sure your citations are correctly and consistently formatted, you can use our free APA Citation Generator .
Your dissertation itself should contain only essential information that directly contributes to answering your research question. Documents you have used that do not fit into the main body of your dissertation (such as interview transcripts, survey questions or tables with full figures) can be added as appendices .
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- What Is a Dissertation? | 5 Essential Questions to Get Started
- What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
- How to Write a Dissertation Proposal | A Step-by-Step Guide
More interesting articles
- Checklist: Writing a dissertation
- Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates
- Dissertation binding and printing
- Dissertation Table of Contents in Word | Instructions & Examples
- Dissertation title page
- Example Theoretical Framework of a Dissertation or Thesis
- Figure & Table Lists | Word Instructions, Template & Examples
- How to Choose a Dissertation Topic | 8 Steps to Follow
- How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples
- How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples
- How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Conclusion
- How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Introduction
- How to Write an Abstract | Steps & Examples
- How to Write Recommendations in Research | Examples & Tips
- List of Abbreviations | Example, Template & Best Practices
- Operationalisation | A Guide with Examples, Pros & Cons
- Prize-Winning Thesis and Dissertation Examples
- Relevance of Your Dissertation Topic | Criteria & Tips
- Research Paper Appendix | Example & Templates
- Thesis & Dissertation Acknowledgements | Tips & Examples
- Thesis & Dissertation Database Examples
- What is a Dissertation Preface? | Definition & Examples
- What is a Glossary? | Definition, Templates, & Examples
- What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips
- What is a Theoretical Framework? | A Step-by-Step Guide
- What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
- Information for Current Students >
- Learning and Instruction Current Student Resources >
Dissertation Checklist and Timeline
Completing all of the crucial steps to the dissertation process can be complicated. Time and task management will be key to your success. Review the suggested tasks and print out this checklist to assist you in your dissertation journey.
| Student's Name: | ||
| Choose Dissertation Advisor | ||
| Choose Dissertation Committee with advisor approval on the Application to Candidacy Form | ||
Form with other students. Become familiar with the . Formatting your dissertation using these guidelines from the start will save you time. | ||
| Identify defense deadlines. Develop timelines for following steps working backwards from these deadline dates. | ||
| Dissertation Proposal Draft to Advisor | ||
| Revision 1 | ||
| Revision 2 (if needed) | ||
| Revision 3 (if needed) | ||
| Final approval from advisor | ||
| Submit human subjects form to Institutional Review Board (IRB) if needed | ||
| Search for dissertation funding, e.g., Prof. Raimondi's grant writing course | ||
| Remaining course work, e.g., independent studies for dissertation parts (if any) | ||
| Schedule Proposal Defense (check with advisor's schedule first) | ||
| Dissertation Proposal Defense (announcement) | ||
| Submit GSE Dissertation Proposal Form w/Abstract & Timeline to chair's secretary | ||
| Revise Dissertation Proposal (if needed) | ||
| Collect Data | ||
| Dissertation Chapters Drafted | ||
| Prepare and submit conference proposals (optional) | ||
| Prepare and submit manuscripts to journals (optional) | ||
| Revise Chapter XX (as needed, number of days to be determined with advisor) | ||
| Revise Chapter XX (as needed, number of days to be determined with advisor) | ||
| Revise Chapter XX (as needed, number of days to be determined with advisor) | ||
| Revise Chapter XX (as needed, number of days to be determined with advisor) | ||
| Revisions to advisor (number of days to be determined with advisor) | ||
| Prepare, practice, and give conference talks (optional) | ||
| Dissertation Approved by Advisor | ||
| Dissertation Submitted to Committee and Wait for Comments | ||
| Dissertation Chapters Revised for Committee Members | ||
| Advisor and Committee Members Agreement to Schedule Defense | ||
| Dissertation Defense Scheduled (check with advisor's and members’ schedule first) | ||
| Dissertation Defense (announcement) | ||
| Dissertation Defense | ||
| Revisions to Dissertation 1 (# of days to be determined by advisor) | ||
| Revisions to Dissertation 2 (if needed, # of days to be determined with advisor) | ||
| Revisions to Dissertation 3 (if needed, # of days to be determined with advisor) | ||
| Final Approval by Advisor and Committee Members | ||
| Final Paperwork to UB Graduate School | ||
| Send Form to Dean's Office by to March in May Graduation | ||
Check with Advisor's Availability Schedule prior to submitting drafts. Major Advisor is not available during: | ||
- Dissertation Proofreading and Editing
- Dissertation Service
- Dissertation Proposal Service
- Dissertation Chapter
- Dissertation Topic and Outline
- Statistical Analysis Services
- Model Answers and Exam Notes
- Dissertation Samples
- Essay Writing Service
- Assignment Service
- Report Service
- Coursework Service
- Literature Review Service
- Reflective Report Service
- Presentation Service
- Poster Service
- Criminal Psychology Dissertation Topics | List of Trending Ideas With Research Aims
- Cognitive Psychology Dissertation Topics | 10 Top Ideas For Research in 2024
- Social Psychology Dissertation Topics | 10 Latest Research Ideas
- Top 10 Clinical Psychology Dissertation Topics with Research Aims
- Educational Psychology Dissertation Topics | 10 Interesting Ideas For Research
- Customer Service Dissertation Topics | List of Latest Ideas For Students
- 15 Interesting Music Dissertation Topics
- Business Intelligence Dissertation Topics | List of Top Ideas With Research Aims
- Physical Education Dissertation Topics | 15 Interesting Title Examples
- 15 Top Forensic Science Dissertation Topics with Research Aims
- Islamic Finance Dissertation Topics | List of 15 Top Ideas With Research Aims
- Dissertation Examples
- Dissertation Proposal Examples
- Essay Examples
- Report Examples
- Coursework Examples
- Assignment Examples
- Literature Review Examples
- Dissertation Topic and Outline Examples
- Dissertation Chapter Examples
- Dissertation Help
- Dissertation Topics
- Academic Library
- Assignment Plagiarism Checker
- Coursework Plagiarism Checke
- Dissertation Plagiarism Checker
- Thesis Plagiarism Checker
- Report Plagiarism Checke
- Plagiarism Remover Service
- Plagiarism Checker Free Service
- Turnitin Plagiarism Checker Free Service
- Free Plagiarism Checker for Students
- Difference Between Paraphrasing & Plagiarism
- Free Similarity Checker
- How Plagiarism Checkers Work?
- How to Cite Sources to Avoid Plagiarism?
- Free Topics
- Get a Free Quote

- Report Generating Service
- Model Answers and Exam Notes Writing
- Reflective or Personal Report Writing
- Poster Writing
- Literature Review Writing
- Premier Sample Dissertations
- Course Work
- Cognitive Psychology Dissertation Topics
- Physical Education Dissertation Topics
- 15 Top Forensic Science Dissertation Topics
- Top 10 Clinical Psychology Dissertation Topics
- Islamic Finance Dissertation Topics
- Social Psychology Dissertation Topics
- Educational Psychology Dissertation Topics
- Business Intelligence Dissertation Topics
- Customer Service Dissertation Topics
- Criminal Psychology Dissertation Topics

- Literature Review Example
- Report Example
- Assignment Example
- Coursework Example

- Coursework Plagiarism Checker
- Turnitin Plagiarism Checker
- Paraphrasing and Plagiarism
- Best Dissertation Plagiarism Checker
- Report Plagiarism Checker
- Similarity Checker
- Plagiarism Checker Free
- FREE Topics
Get an experienced writer start working
Review our examples before placing an order, learn how to draft academic papers, dissertation gantt chart | guide & templates.

PsyD vs PhD in Clinical Psychology: Key Differences and Similarities

Crafting Effective APA Format Paragraphs: Guidelines & Examples

Planning your dissertation can feel like time has sprouted wings and taken off without you. Fear not, for the trusty companion of the dissertation, Gantt Chart is here to rescue you from the chaos of research, writing tasks, and impending deadlines.
Learn Crafting a Captivating Discussion in an Academic Report
A Complete Guide: How to Write a Research Design
In this article, we will explore the world of Gantt charts, demystify their purpose, and explore how to create a Gantt Chart. You can find here a dissertation Gantt chart guide with steps for creating the chart, a template and tips to help you create your own chart.
3-Step Dissertation Process!

Get 3+ Topics

Dissertation Proposal

Get Final Dissertation
What is dissertation gantt chart.
“A Gantt chart for dissertation is a visual representation of the tasks and milestones in completing a dissertation. It is a useful tool for planning and tracking your progress and can help you to stay on track and avoid procrastination.”
The Gantt Chart provides a dissertation timeline and guiding light amidst the foggy labyrinth of academic pursuits. It's a visual representation of the researcher or student project's timeline, providing a clear picture of the tasks that need to conquer. Remember, Rome wasn't built in a day, and neither will any dissertation be. But with a well-crafted Gantt chart, a researcher breaks down their work into manageable chunks and tackles them systematically.
Creating a Dissertation Gantt Chart: Steps to Follow
Here are the steps on how to create a dissertation Gantt chart;
- Conduct a literature review on the topic of social media and teenagers.
- Collect data on how teenagers use social media.
- Analyze the data and write a report on your findings.
- Write your dissertation.
- Estimate the time it will take to complete each task. This will help you to create a realistic timeline for your dissertation. Be sure to factor in time for unexpected delays, such as data collection taking longer than expected or having to revise your dissertation after your advisor provides feedback.
- Create a Gantt chart. There are many different software programs that you can use to create a Gantt chart, like Google Sheets, WPS sheets and more. Once you have created your chart, you can add the tasks, their estimated time frames, and any other relevant information.
- Track your progress. As you make progress on your dissertation, be sure to update your Gantt chart to reflect your progress. This will help you to stay on track and identify any areas where you might be falling behind.
- Adjust your plan as needed. Things don't always go according to plan, so it's important to be flexible and adjust your plan as needed. For example, if you find that you are spending more time on one task than you expected, you might need to adjust the time frame for other tasks.
Using a dissertation Gantt chart is a helpful way to stay on track and avoid procrastination. It also helps you to identify areas where you can improve your efficiency.
Here are a few things you don't have to worry about;
Not being afraid to change your Gantt chart as needed
Don't forget to add important comment in case of delay or over time
Neglecting unwanted commitments
How Does It Work ?

Fill the Form
Please fill the free topic form and share your requirements

Writer Starts Working
The writer starts to find a topic for you (based on your requirements)

3+ Topics Emailed!
The writer shared custom topics with you within 24 hours
Dissertation Gantt Chart Template
Here is a Gantt chart template for dissertation that help researchers and student to craft their own chart to achieve their goals.
Task | Start Date | End Date | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
Literature review | 01/01/2023 | 03/01/2023 | 3 weeks |
Data collection | 03/01/2023 | 05/01/2023 | 2 weeks |
Data analysis | 05/01/2023 | 07/01/2023 | 2 weeks |
Writing | 07/01/2023 | 09/01/2023 | 2 weeks |
Defence | 09/01/2023 | 09/01/2023 | 1 day |
This template is general that doesn’t stick to any research. Also, every dissertation or research report has its time to completion. The dissertations for graduation, master's, and PhD are often required to be completed in a different timeframe, with a different research style and methodology. Here is an example of PhD Gantt Chart ;
Task | Start Date | End Date | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
Proposal | 01/01/2023 | 03/01/2023 | 3 months |
Qualifying exams | 03/01/2023 | 05/01/2023 | 2 months |
Research | 05/01/2023 | 12/01/2024 | 8 months |
Writing | 12/01/2024 | 03/01/2025 | 3 months |
Defence | 03/01/2025 | 03/01/2025 | 1 day |
This Gantt chart provides a high-level overview of the dissertation timeline involved in a PhD program. It is important to break down your program into smaller, more manageable tasks. This will make it easier to track your progress and make adjustments to your timeline as needed.
It is also important to build in some buffer time between tasks. This will allow for unexpected delays, such as difficulty finding sources, equipment failure, or illness.
Finally, be sure to track your progress and make adjustments to your Gantt chart as needed. This will help you stay on track and avoid falling behind.
Additional Tips for Dissertation Gantt Chart
Here are some additional tips for using a dissertation Gantt chart:
- Use a software program to create your Gantt chart. There are many different software programs that you can use to create a Gantt chart. Some popular options include Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets, and Trello.
- Make your Gantt chart visual. Use colors, fonts, and symbols to make your Gantt chart easy to read and understand.
- Share your Gantt chart with others. This can help you to stay accountable and get feedback from others.
- Don't be afraid to adjust your Gantt chart as needed. Things don't always go according to plan, so it's important to be flexible and adjust your Gantt chart as needed.
Conclusion
A Gantt chart is an indispensable tool, akin to a trusty compass guiding you through uncharted waters. It helps you break down your work into manageable chunks, consider dependencies, and maintain flexibility. By embracing the power of this visual aid, you'll be able to navigate the daunting dissertation journey with confidence. So, let the Dissertation Gantt Chart be your co-pilot, ensuring that time flies not in vain but in harmony with your research and writing goals.
Get an Immediate Response
Discuss your requirements with our writers
WhatsApp Us Email Us Chat with Us
Get 3+ Free Dissertation Topics within 24 hours?
Your Number
Academic Level Select Academic Level Undergraduate Masters PhD
Area of Research
admin farhan
Related posts.

Dissertation Interview Questions | Everything You Need To Know

Conducting Interviews for Your Dissertation | A Comprehensive Guide

What is Gibbs’ Reflective Cycle and How Can It Benefit You? | Applications and Example
Comments are closed.

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
How to Write a Dissertation or Thesis Proposal
Published on September 21, 2022 by Tegan George . Revised on July 18, 2023.
When starting your thesis or dissertation process, one of the first requirements is a research proposal or a prospectus. It describes what or who you want to examine, delving into why, when, where, and how you will do so, stemming from your research question and a relevant topic .
The proposal or prospectus stage is crucial for the development of your research. It helps you choose a type of research to pursue, as well as whether to pursue qualitative or quantitative methods and what your research design will look like.
You can download our templates in the format of your choice below.
Download Word template Download Google Docs template
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What should your proposal contain, dissertation question examples, what should your proposal look like, dissertation prospectus examples, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about proposals.
Prior to jumping into the research for your thesis or dissertation, you first need to develop your research proposal and have it approved by your supervisor. It should outline all of the decisions you have taken about your project, from your dissertation topic to your hypotheses and research objectives .
Depending on your department’s requirements, there may be a defense component involved, where you present your research plan in prospectus format to your committee for their approval.
Your proposal should answer the following questions:
- Why is your research necessary?
- What is already known about your topic?
- Where and when will your research be conducted?
- Who should be studied?
- How can the research best be done?
Ultimately, your proposal should persuade your supervisor or committee that your proposed project is worth pursuing.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Strong research kicks off with a solid research question , and dissertations are no exception to this.
Dissertation research questions should be:
- Focused on a single problem or issue
- Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources
- Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints
- Specific enough to answer thoroughly
- Complex enough to develop the answer over the space of a paper or thesis
- Relevant to your field of study and/or society more broadly
- What are the main factors enticing people under 30 in suburban areas to engage in the gig economy?
- Which techniques prove most effective for 1st-grade teachers at local elementary schools in engaging students with special needs?
- Which communication streams are the most effective for getting those aged 18-30 to the polls on Election Day?
An easy rule of thumb is that your proposal will usually resemble a (much) shorter version of your thesis or dissertation. While of course it won’t include the results section , discussion section , or conclusion , it serves as a “mini” version or roadmap for what you eventually seek to write.
Be sure to include:
- A succinct introduction to your topic and problem statement
- A brief literature review situating your topic within existing research
- A basic outline of the research methods you think will best answer your research question
- The perceived implications for future research
- A reference list in the citation style of your choice
The length of your proposal varies quite a bit depending on your discipline and type of work you’re conducting. While a thesis proposal is often only 3-7 pages long, a prospectus for your dissertation is usually much longer, with more detailed analysis. Dissertation proposals can be up to 25-30 pages in length.
Writing a proposal or prospectus can be a challenge, but we’ve compiled some examples for you to get your started.
- Example #1: “Geographic Representations of the Planet Mars, 1867-1907” by Maria Lane
- Example #2: “Individuals and the State in Late Bronze Age Greece: Messenian Perspectives on Mycenaean Society” by Dimitri Nakassis
- Example #3: “Manhood Up in the Air: A Study of Male Flight Attendants, Queerness, and Corporate Capitalism during the Cold War Era” by Phil Tiemeyer
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Survivorship bias
- Self-serving bias
- Availability heuristic
- Halo effect
- Hindsight bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The research methods you use depend on the type of data you need to answer your research question .
- If you want to measure something or test a hypothesis , use quantitative methods . If you want to explore ideas, thoughts and meanings, use qualitative methods .
- If you want to analyze a large amount of readily-available data, use secondary data. If you want data specific to your purposes with control over how it is generated, collect primary data.
- If you want to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables , use experimental methods. If you want to understand the characteristics of a research subject, use descriptive methods.
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical first steps in your writing process. It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding what kind of research you’d like to undertake.
Generally, an outline contains information on the different sections included in your thesis or dissertation , such as:
- Your anticipated title
- Your abstract
- Your chapters (sometimes subdivided into further topics like literature review , research methods , avenues for future research, etc.)
A well-planned research design helps ensure that your methods match your research aims, that you collect high-quality data, and that you use the right kind of analysis to answer your questions, utilizing credible sources . This allows you to draw valid , trustworthy conclusions.
The priorities of a research design can vary depending on the field, but you usually have to specify:
- Your research questions and/or hypotheses
- Your overall approach (e.g., qualitative or quantitative )
- The type of design you’re using (e.g., a survey , experiment , or case study )
- Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects
- Your data collection methods (e.g., questionnaires , observations)
- Your data collection procedures (e.g., operationalization , timing and data management)
- Your data analysis methods (e.g., statistical tests or thematic analysis )
A dissertation prospectus or proposal describes what or who you plan to research for your dissertation. It delves into why, when, where, and how you will do your research, as well as helps you choose a type of research to pursue. You should also determine whether you plan to pursue qualitative or quantitative methods and what your research design will look like.
It should outline all of the decisions you have taken about your project, from your dissertation topic to your hypotheses and research objectives , ready to be approved by your supervisor or committee.
Note that some departments require a defense component, where you present your prospectus to your committee orally.
Formulating a main research question can be a difficult task. Overall, your question should contribute to solving the problem that you have defined in your problem statement .
However, it should also fulfill criteria in three main areas:
- Researchability
- Feasibility and specificity
- Relevance and originality
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2023, July 18). How to Write a Dissertation or Thesis Proposal. Scribbr. Retrieved September 3, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/thesis-dissertation-proposal/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, a step-by-step guide to the writing process, 10 research question examples to guide your research project, dissertation & thesis outline | example & free templates, what is your plagiarism score.
/images/cornell/logo35pt_cornell_white.svg" alt="how to write a dissertation timeline"> Cornell University --> Graduate School
Thesis & dissertation.

Understanding Deadlines and Requirements
The final requirement in earning a graduate degree is the completion and defense of the master’s thesis or doctoral dissertation. Understanding the steps and associated deadlines in the thesis/dissertation submission and degree conferral process is necessary to establish a successful plan and realistic timeframe.
2024 Thesis/Dissertation Submission to the Graduate School Deadlines:
- For May 26, 2024 conferral, deadline is May 1.
- For August 31, 2024 conferral, deadline is August 1.
- December 31, 2024 conferral, deadline is December 1.
See our Planning Timeline for more detailed information.
Writing Your Thesis/Dissertation
The Graduate School offers several writing resources to help you get started, meet your goals, and complete your thesis/dissertation on time.
Before You Begin:
- Guide to Writing Your Thesis/Dissertation
- Fields Permitting the Use of Papers Option
- Required Sections, Guidelines, and Suggestions
- Formatting Requirements
- Fair Use, Copyright, Patent, and Publishing Options
Resources for Writing:
- Thesis & Dissertation Templates
- Writing from A to B
Scheduling and Taking Your Final Exam
Once you have submitted your draft thesis/dissertation to your committee you are ready to defend. This involves scheduling and taking your final exam (“B” exam), an oral exam/dissertation defense for Ph.D. candidates, or (“M” exam), an oral exam/thesis defense for Master’s candidates.
- About Exams
- Defending Your Thesis or Dissertation
- Taking Exams
Submitting Your Thesis/Dissertation
Policy requires the thesis/dissertation be submitted within 60 days of the final exam. The Graduate School uses a service called ProQuest to administer the electronic thesis/dissertation (ETD) submission and committee approval process. Once you have made any necessary revisions and the thesis/dissertation is final, you are ready to begin the approval and submission process.
Before initiating the submission process, students are required to complete an ORCID iD and complete the Survey of Earned Doctorates.
- Open Researcher and Contributor ID (ORCID iD)
- Survey of Earned Doctorates
- Thesis & Dissertation Submission Process
- Submission Fees
- Graduation Requirements
Melanie Green Editorial Services
Expert Freelance Writer with 12+ Years of Professional Experience

How to Create a Timeline for Writing Your Dissertation or Thesis

Author: Melanie Green October 19, 2016
Academic Writing , Editing Services
dissertation timeline
Writing a dissertation, thesis, or capstone project is a major undertaking for graduate students around the world. When it’s time to write about all of your research, it can be overwhelming to say the least. You should create a timeline and a plan for how you are going to tackle the work on time so you don’t compromise quality or rush through it. Use these tips to create a solid timeline to complete your project you can rely on.
Start Your Dissertation ASAP
As soon as you can, start your dissertation. If you still have to conduct an experiment, it’s okay to write the other chapters that the experiment won’t change, such as your introduction and methodology chapters. You don’t want to put off this important academic document until last minute and potentially fail graduate school. It is much better to start and finish early than to put it off.
Write These Chapters First
Most dissertations and theses have the same chapters, more or less:
- Introduction
- Literature Review
- Methodology
- Future Research/Conclusion
Fortunately, the Methodology and Literature review chapters are the easiest, so start writing them first to get them out of the way. The Methodology chapter is more or less the same across all dissertations, as you’ll need to know your research design, variables, and data sources. Do a quick search for other people’s dissertations to understand what is expected or speak with your university’s writing center.
Plan on Writing One Page an Hour
When you schedule in your calendar when you plan to write, you should plan on one page (or 250 words) taking you one hour to write. Use this as a guide to push yourself a little during writing sessions with accountability so you won’t slack off. It’s also a realistic number of words per hour that you can do. The writing of most dissertations should take somewhere between 40 and 80 hours to complete. Schedule this time after you’ve had time to gather research and conduct an experiment.
When you plan on how you’ll finish writing your dissertation, it takes away a lot of stress. Once you’ve written your dissertation, it may be time to look at professional dissertation editing services . This is especially true if you’re planning to publish it.
← Previous post
Next post →
- Campus Life
- ...a student.
- ...a veteran.
- ...an alum.
- ...a parent.
- ...faculty or staff.
- Class Schedule
- Crisis Resources
- People Finder
- Change Password
UTC RAVE Alert
Dissertation timeline, developing a realistic timeline.
Upon confirmation of a Dissertation Chair and successful completion of the Comprehensive Assessment defense, development of a realistic timeline for completing the tasks that culminate in a successful Dissertation should be established between the candidate and the faculty member Chair. Components of this process include (all steps in consultation with the Chair):
- Preparation of the Prospectus
- Prospectus defense
- Preparation of the Proposal
- Proposal defense
- IRB application
- Data collection (upon IRB approval)
- Data analysis
- Submission of the complete manuscript to the Chair
- Preparation for the Pre-Defense
- Pre-Defense
- Preparation for the final defense
- Final Defense
- Completing revisions and preparing the manuscript for formatting review
- Submission of the manuscript to the Graduate School via the university's digital repository
- Completing final formatting revisions
- Preparation for graduation
Anticipated dates will likely need to be revised along the way. The candidate must maintain a realistic schedule that allows sufficient time for each step in the process, including the project Chair’s reading of, and feedback on, drafts of the Prospectus, Proposal, and final manuscript. Sufficient time must be allotted for the committee members’ reading of those documents as well. Candidates and Chairs should recognize that each committee member may need up to 14 days to review each draft of the manuscript. During the break between semesters, committee members are responsible for syllabi preparation, course construction, and comprehensive assessment and other defenses, therefore, the customary 14-day time frame for reviewing dissertation drafts does not apply during the intersession. Committee members will return to the standard 14-day review guidelines on the first day of the semester. These factors should be considered when scheduling committee meetings and the final defense.
Minimum Degree Credit Hours
The Learning and Leadership doctoral degree requires a minimum of 66 total graduate credit hours (Ed.D.) / 75 total graduate credit hours (Ph.D.). Each candidate is required to successfully complete a minimum of 12 Dissertation credit hours (Ed.D.) / 15 Dissertation credit hours (Ph.D.) and defend the Dissertation. Candidates who do not complete the Dissertation hours within the 12 credit hour timeframe (Ed.D.) or 15 credit hour time frame (Ph.D.) must take an additional 2 Dissertation credit hours each semester through graduation. The candidate must be enrolled in a minimum of 2 Dissertation credits (LEAD 7999) during the semester in which the Final Dissertation Defense is held.
Graduation Deadlines
It is also the responsibility of the Chair and candidate to consider deadlines for particular graduation dates. University graduation deadlines are published on the Graduate School website (links: Thesis and Dissertation ). Since deadlines may change from one year to the next, candidates are advised to refer to the current deadlines when approaching the final stages of the Dissertation process. Candidates and Chairs should also consider program minimum review requirements when considering a potential graduation semester. F or doctoral candidates, the graduation application should not be completed until the Pre-Defense stage of the dissertation process is approved (link: Pre-Defense Process ).
Learning and Leadership Doctorate's Program
Lead programs.
- Hunter Hall #412
- Dept 4141
- 651 McCallie Avenue
- 423-425-5445
- [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Inclusion in a Dissertation Timeline. When constructing your dissertation timeline, include every element of the dissertation from the abstract to the conclusion. Keep in mind that you may not be writing your chapters in chronological order. For instance, after completing their first round of research and writing their research question, most ...
Create your dissertation plan - try using a timeline, calendar or mind map to highlight the key stages, specific milestones and deadlines for your dissertation. Getting Set. ... dissertation after a break. Start writing earlier rather than later - gives you more time for drafts and editing. Do not write and edit on the same day. Go back
A thorough timeline will be valuable during your dissertation proposal and useful if you are applying for grants or other additional funding. Ste0ps for Creating a Timeline for Your Thesis: Research and record all requirements and deadlines. Before you write out your timeline, ensure you know all of your program's requirements and deadlines.
Planning the timeline and progress of your doctoral dissertation (or Masters/undergraduate thesis) One of my PhD students lamented this week with me that she had a lot to juggle (taking children to and from schools and to and from activities, etc.) and that she needed a strategy to make her research move forward.
Starting the Plan. Implementing the dissertation project plan begins with organizing your tasks and setting priorities based on your outlined timeline. Start by reviewing the project plan and identifying the first set of tasks to tackle. Ensure you have all necessary resources and materials before commencing each task.
You can write your overall timeline across the top and then make individual to-do lists for each month beneath it. Start Writing Your Dissertation Before You Think You're Ready It's common for doctoral candidates to do an exhaustive amount of pre-writing work, such as background reading, a thorough literature review and methodology planning.
Dissertations typically include a literature review section or chapter. Create a list of books, articles, and other scholarly works early in the process, and continue to add to your list. Refer to the works cited to identify key literature. And take detailed notes to make the writing process easier.
Limit the distraction during your blocked writing time in order to fully concentrate. Set a daily goal. For example, writing 2 pages each day on chapter 1 or finishing the method session on chapter 2, etc. Find a place that you find yourself most productive and efficient, and write there. Monitor your progress by calendars and project ...
Final Dissertation Submission: The ultimate deadline for submitting your completed dissertation. Creating a Personal Timeline. Based on the provided timeline, create a personal schedule. Break down each stage into manageable tasks and set internal deadlines. This proactive approach will help you stay on track and avoid last-minute rushes.
Dissertations are a defining piece of academic research and writing for all students. To complete such a large research project while maintaining a good work-life balance, planning and organisation is essential. In this article, we'll outline three categories for dissertation planning including project management, note-taking and information management, alongside tools and templates for ...
A timeline might say you can do your dissertation proposal in three to four months, but that is only true as long as what you're submitting is well-written and your committee approves it. For argument's sake, we'll say it takes four months. The next level of your dissertation is to collect data. But before you can collect data, you have ...
The structure of a dissertation depends on your field, but it is usually divided into at least four or five chapters (including an introduction and conclusion chapter). The most common dissertation structure in the sciences and social sciences includes: An introduction to your topic. A literature review that surveys relevant sources.
Download Dissertation Checklist and Timeline Adobe PDF Document Download pdf. Dissertation Checklist and Timeline. Student's Name: Dissertation Process. # of Days. Due Date. Choose Dissertation Advisor. Choose Dissertation Committee with advisor approval on the Application to Candidacy Form.
Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates. Published on June 7, 2022 by Tegan George.Revised on November 21, 2023. A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical early steps in your writing process.It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding the specifics of your dissertation topic and showcasing its relevance to ...
Vertically, list the hours that you are awake during the day. Then, create a grid by drawing lines so that cells exist for each of these hours in each day. Mark when you will get your dissertation and non-dissertation tasks done. Be sure to allow time for leisure and social activities as well.
Write your dissertation. Estimate the time it will take to complete each task. This will help you to create a realistic timeline for your dissertation. Be sure to factor in time for unexpected delays, such as data collection taking longer than expected or having to revise your dissertation after your advisor provides feedback. Create a Gantt chart.
The approximate workload is 5-10 hours per week. This estimates come from an experienced formatter's educated guesses about the time it would take an average word-processing user to research and perform the above-listed tasks for a thesis or dissertation with 150 pages, 10 block quotes, 10 tables, 5 figures, 2 landscaped pages.
A dissertation is a lengthy research paper written as a requirement to earn an academic degree. Typically, students must write a dissertation toward the end of their program to both prove their knowledge and contribute new research to their field. The term dissertation is sometimes used interchangeably with thesis paper.
Prioritize your tasks. Prioritizing is key when it comes to dissertation writing! Decide what the most important tasks are and make them your top priority (look at your timeline to see which parts need to be completed first). Write a list of smaller, less time-consuming tasks, so that when you need a break from whatever you're working on, you ...
When starting your thesis or dissertation process, one of the first requirements is a research proposal or a prospectus. It describes what or who you want to examine, delving into why, when, where, and how you will do so, stemming from your research question and a relevant topic. The proposal or prospectus stage is crucial for the development ...
2024 Thesis/Dissertation Submission to the Graduate School Deadlines: For May 26, 2024 conferral, ... See our Planning Timeline for more detailed information. Writing Your Thesis/Dissertation. The Graduate School offers several writing resources to help you get started, meet your goals, and complete your thesis/dissertation on time. ...
The writing of most dissertations should take somewhere between 40 and 80 hours to complete. Schedule this time after you've had time to gather research and conduct an experiment. When you plan on how you'll finish writing your dissertation, it takes away a lot of stress. Once you've written your dissertation, it may be time to look at ...
Candidates who do not complete the Dissertation hours within the 12 credit hour timeframe (Ed.D.) or 15 credit hour time frame (Ph.D.) must take an additional 2 Dissertation credit hours each semester through graduation. The candidate must be enrolled in a minimum of 2 Dissertation credits (LEAD 7999) during the semester in which the Final ...