24/7 writing help on your phone
To install StudyMoose App tap and then “Add to Home Screen”

Motivation in the workplace
Save to my list
Remove from my list

Motivation in the workplace. (2016, Apr 22). Retrieved from https://studymoose.com/motivation-in-the-workplace-essay
"Motivation in the workplace." StudyMoose , 22 Apr 2016, https://studymoose.com/motivation-in-the-workplace-essay
StudyMoose. (2016). Motivation in the workplace . [Online]. Available at: https://studymoose.com/motivation-in-the-workplace-essay [Accessed: 9 Sep. 2024]
"Motivation in the workplace." StudyMoose, Apr 22, 2016. Accessed September 9, 2024. https://studymoose.com/motivation-in-the-workplace-essay
"Motivation in the workplace," StudyMoose , 22-Apr-2016. [Online]. Available: https://studymoose.com/motivation-in-the-workplace-essay. [Accessed: 9-Sep-2024]
StudyMoose. (2016). Motivation in the workplace . [Online]. Available at: https://studymoose.com/motivation-in-the-workplace-essay [Accessed: 9-Sep-2024]
- Modern motivation theory and Buddhist teaching for Motivation Pages: 16 (4732 words)
- Motivation & Productivity in the Workplace Pages: 6 (1719 words)
- Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivation in the Workplace Pages: 5 (1304 words)
- Equity Theory of Motivation Pages: 9 (2431 words)
- Research Proposal on Motivation Pages: 2 (545 words)
- Motivation in management Pages: 6 (1693 words)
- Impact of Motivation on employees Pages: 8 (2311 words)
- Psychology and Motivation Pages: 8 (2345 words)
- Dr Jack Perry Motivation case Pages: 6 (1728 words)
- Equity & Expectancy Theory of Motivation Pages: 6 (1549 words)

👋 Hi! I’m your smart assistant Amy!
Don’t know where to start? Type your requirements and I’ll connect you to an academic expert within 3 minutes.
The Science of Improving Motivation at Work

The topic of employee motivation can be quite daunting for managers, leaders, and human resources professionals.
Organizations that provide their members with meaningful, engaging work not only contribute to the growth of their bottom line, but also create a sense of vitality and fulfillment that echoes across their organizational cultures and their employees’ personal lives.
“An organization’s ability to learn, and translate that learning into action rapidly, is the ultimate competitive advantage.”
In the context of work, an understanding of motivation can be applied to improve employee productivity and satisfaction; help set individual and organizational goals; put stress in perspective; and structure jobs so that they offer optimal levels of challenge, control, variety, and collaboration.
This article demystifies motivation in the workplace and presents recent findings in organizational behavior that have been found to contribute positively to practices of improving motivation and work life.
Before you continue, we thought you might like to download our three Goal Achievement Exercises for free . These detailed, science-based exercises will help you or your clients create actionable goals and master techniques to create lasting behavior change.
This Article Contains:
Motivation in the workplace, motivation theories in organizational behavior, employee motivation strategies, motivation and job performance, leadership and motivation, motivation and good business, a take-home message.
Motivation in the workplace has been traditionally understood in terms of extrinsic rewards in the form of compensation, benefits, perks, awards, or career progression.
With today’s rapidly evolving knowledge economy, motivation requires more than a stick-and-carrot approach. Research shows that innovation and creativity, crucial to generating new ideas and greater productivity, are often stifled when extrinsic rewards are introduced.
Daniel Pink (2011) explains the tricky aspect of external rewards and argues that they are like drugs, where more frequent doses are needed more often. Rewards can often signal that an activity is undesirable.
Interesting and challenging activities are often rewarding in themselves. Rewards tend to focus and narrow attention and work well only if they enhance the ability to do something intrinsically valuable. Extrinsic motivation is best when used to motivate employees to perform routine and repetitive activities but can be detrimental for creative endeavors.
Anticipating rewards can also impair judgment and cause risk-seeking behavior because it activates dopamine. We don’t notice peripheral and long-term solutions when immediate rewards are offered. Studies have shown that people will often choose the low road when chasing after rewards because addictive behavior is short-term focused, and some may opt for a quick win.
Pink (2011) warns that greatness and nearsightedness are incompatible, and seven deadly flaws of rewards are soon to follow. He found that anticipating rewards often has undesirable consequences and tends to:
- Extinguish intrinsic motivation
- Decrease performance
- Encourage cheating
- Decrease creativity
- Crowd out good behavior
- Become addictive
- Foster short-term thinking
Pink (2011) suggests that we should reward only routine tasks to boost motivation and provide rationale, acknowledge that some activities are boring, and allow people to complete the task their way. When we increase variety and mastery opportunities at work, we increase motivation.
Rewards should be given only after the task is completed, preferably as a surprise, varied in frequency, and alternated between tangible rewards and praise. Providing information and meaningful, specific feedback about the effort (not the person) has also been found to be more effective than material rewards for increasing motivation (Pink, 2011).

They have shaped the landscape of our understanding of organizational behavior and our approaches to employee motivation. We discuss a few of the most frequently applied theories of motivation in organizational behavior.
Herzberg’s two-factor theory
Frederick Herzberg’s (1959) two-factor theory of motivation, also known as dual-factor theory or motivation-hygiene theory, was a result of a study that analyzed responses of 200 accountants and engineers who were asked about their positive and negative feelings about their work. Herzberg (1959) concluded that two major factors influence employee motivation and satisfaction with their jobs:
- Motivator factors, which can motivate employees to work harder and lead to on-the-job satisfaction, including experiences of greater engagement in and enjoyment of the work, feelings of recognition, and a sense of career progression
- Hygiene factors, which can potentially lead to dissatisfaction and a lack of motivation if they are absent, such as adequate compensation, effective company policies, comprehensive benefits, or good relationships with managers and coworkers
Herzberg (1959) maintained that while motivator and hygiene factors both influence motivation, they appeared to work entirely independently of each other. He found that motivator factors increased employee satisfaction and motivation, but the absence of these factors didn’t necessarily cause dissatisfaction.
Likewise, the presence of hygiene factors didn’t appear to increase satisfaction and motivation, but their absence caused an increase in dissatisfaction. It is debatable whether his theory would hold true today outside of blue-collar industries, particularly among younger generations, who may be looking for meaningful work and growth.
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
Abraham Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory proposed that employees become motivated along a continuum of needs from basic physiological needs to higher level psychological needs for growth and self-actualization . The hierarchy was originally conceptualized into five levels:
- Physiological needs that must be met for a person to survive, such as food, water, and shelter
- Safety needs that include personal and financial security, health, and wellbeing
- Belonging needs for friendships, relationships, and family
- Esteem needs that include feelings of confidence in the self and respect from others
- Self-actualization needs that define the desire to achieve everything we possibly can and realize our full potential
According to the hierarchy of needs, we must be in good health, safe, and secure with meaningful relationships and confidence before we can reach for the realization of our full potential.
For a full discussion of other theories of psychological needs and the importance of need satisfaction, see our article on How to Motivate .
Hawthorne effect
The Hawthorne effect, named after a series of social experiments on the influence of physical conditions on productivity at Western Electric’s factory in Hawthorne, Chicago, in the 1920s and 30s, was first described by Henry Landsberger in 1958 after he noticed some people tended to work harder and perform better when researchers were observing them.
Although the researchers changed many physical conditions throughout the experiments, including lighting, working hours, and breaks, increases in employee productivity were more significant in response to the attention being paid to them, rather than the physical changes themselves.
Today the Hawthorne effect is best understood as a justification for the value of providing employees with specific and meaningful feedback and recognition. It is contradicted by the existence of results-only workplace environments that allow complete autonomy and are focused on performance and deliverables rather than managing employees.
Expectancy theory
Expectancy theory proposes that we are motivated by our expectations of the outcomes as a result of our behavior and make a decision based on the likelihood of being rewarded for that behavior in a way that we perceive as valuable.
For example, an employee may be more likely to work harder if they have been promised a raise than if they only assumed they might get one.

Expectancy theory posits that three elements affect our behavioral choices:
- Expectancy is the belief that our effort will result in our desired goal and is based on our past experience and influenced by our self-confidence and anticipation of how difficult the goal is to achieve.
- Instrumentality is the belief that we will receive a reward if we meet performance expectations.
- Valence is the value we place on the reward.
Expectancy theory tells us that we are most motivated when we believe that we will receive the desired reward if we hit an achievable and valued target, and least motivated if we do not care for the reward or do not believe that our efforts will result in the reward.
Three-dimensional theory of attribution
Attribution theory explains how we attach meaning to our own and other people’s behavior and how the characteristics of these attributions can affect future motivation.
Bernard Weiner’s three-dimensional theory of attribution proposes that the nature of the specific attribution, such as bad luck or not working hard enough, is less important than the characteristics of that attribution as perceived and experienced by the individual. According to Weiner, there are three main characteristics of attributions that can influence how we behave in the future:
Stability is related to pervasiveness and permanence; an example of a stable factor is an employee believing that they failed to meet the expectation because of a lack of support or competence. An unstable factor might be not performing well due to illness or a temporary shortage of resources.
“There are no secrets to success. It is the result of preparation, hard work, and learning from failure.”
Colin Powell
According to Weiner, stable attributions for successful achievements can be informed by previous positive experiences, such as completing the project on time, and can lead to positive expectations and higher motivation for success in the future. Adverse situations, such as repeated failures to meet the deadline, can lead to stable attributions characterized by a sense of futility and lower expectations in the future.
Locus of control describes a perspective about the event as caused by either an internal or an external factor. For example, if the employee believes it was their fault the project failed, because of an innate quality such as a lack of skills or ability to meet the challenge, they may be less motivated in the future.
If they believe an external factor was to blame, such as an unrealistic deadline or shortage of staff, they may not experience such a drop in motivation.
Controllability defines how controllable or avoidable the situation was. If an employee believes they could have performed better, they may be less motivated to try again in the future than someone who believes that factors outside of their control caused the circumstances surrounding the setback.

Theory X and theory Y
Douglas McGregor proposed two theories to describe managerial views on employee motivation: theory X and theory Y. These views of employee motivation have drastically different implications for management.
He divided leaders into those who believe most employees avoid work and dislike responsibility (theory X managers) and those who say that most employees enjoy work and exert effort when they have control in the workplace (theory Y managers).
To motivate theory X employees, the company needs to push and control their staff through enforcing rules and implementing punishments.
Theory Y employees, on the other hand, are perceived as consciously choosing to be involved in their work. They are self-motivated and can exert self-management, and leaders’ responsibility is to create a supportive environment and develop opportunities for employees to take on responsibility and show creativity.
Theory X is heavily informed by what we know about intrinsic motivation and the role that the satisfaction of basic psychological needs plays in effective employee motivation.

Taking theory X and theory Y as a starting point, theory Z was developed by Dr. William Ouchi. The theory combines American and Japanese management philosophies and focuses on long-term job security, consensual decision making, slow evaluation and promotion procedures, and individual responsibility within a group context.
Its noble goals include increasing employee loyalty to the company by providing a job for life, focusing on the employee’s wellbeing, and encouraging group work and social interaction to motivate employees in the workplace.

There are several implications of these numerous theories on ways to motivate employees. They vary with whatever perspectives leadership ascribes to motivation and how that is cascaded down and incorporated into practices, policies, and culture.
The effectiveness of these approaches is further determined by whether individual preferences for motivation are considered. Nevertheless, various motivational theories can guide our focus on aspects of organizational behavior that may require intervening.
Herzberg’s two-factor theory , for example, implies that for the happiest and most productive workforce, companies need to work on improving both motivator and hygiene factors.
The theory suggests that to help motivate employees, the organization must ensure that everyone feels appreciated and supported, is given plenty of specific and meaningful feedback, and has an understanding of and confidence in how they can grow and progress professionally.
To prevent job dissatisfaction, companies must make sure to address hygiene factors by offering employees the best possible working conditions, fair pay, and supportive relationships.
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs , on the other hand, can be used to transform a business where managers struggle with the abstract concept of self-actualization and tend to focus too much on lower level needs. Chip Conley, the founder of the Joie de Vivre hotel chain and head of hospitality at Airbnb, found one way to address this dilemma by helping his employees understand the meaning of their roles during a staff retreat.
In one exercise, he asked groups of housekeepers to describe themselves and their job responsibilities by giving their group a name that reflects the nature and the purpose of what they were doing. They came up with names such as “The Serenity Sisters,” “The Clutter Busters,” and “The Peace of Mind Police.”
These designations provided a meaningful rationale and gave them a sense that they were doing more than just cleaning, instead “creating a space for a traveler who was far away from home to feel safe and protected” (Pattison, 2010). By showing them the value of their roles, Conley enabled his employees to feel respected and motivated to work harder.
The Hawthorne effect studies and Weiner’s three-dimensional theory of attribution have implications for providing and soliciting regular feedback and praise. Recognizing employees’ efforts and providing specific and constructive feedback in the areas where they can improve can help prevent them from attributing their failures to an innate lack of skills.
Praising employees for improvement or using the correct methodology, even if the ultimate results were not achieved, can encourage them to reframe setbacks as learning opportunities. This can foster an environment of psychological safety that can further contribute to the view that success is controllable by using different strategies and setting achievable goals .
Theories X, Y, and Z show that one of the most impactful ways to build a thriving organization is to craft organizational practices that build autonomy, competence, and belonging. These practices include providing decision-making discretion, sharing information broadly, minimizing incidents of incivility, and offering performance feedback.
Being told what to do is not an effective way to negotiate. Having a sense of autonomy at work fuels vitality and growth and creates environments where employees are more likely to thrive when empowered to make decisions that affect their work.
Feedback satisfies the psychological need for competence. When others value our work, we tend to appreciate it more and work harder. Particularly two-way, open, frequent, and guided feedback creates opportunities for learning.
Frequent and specific feedback helps people know where they stand in terms of their skills, competencies, and performance, and builds feelings of competence and thriving. Immediate, specific, and public praise focusing on effort and behavior and not traits is most effective. Positive feedback energizes employees to seek their full potential.
Lack of appreciation is psychologically exhausting, and studies show that recognition improves health because people experience less stress. In addition to being acknowledged by their manager, peer-to-peer recognition was shown to have a positive impact on the employee experience (Anderson, 2018). Rewarding the team around the person who did well and giving more responsibility to top performers rather than time off also had a positive impact.
Stop trying to motivate your employees – Kerry Goyette
Other approaches to motivation at work include those that focus on meaning and those that stress the importance of creating positive work environments.
Meaningful work is increasingly considered to be a cornerstone of motivation. In some cases, burnout is not caused by too much work, but by too little meaning. For many years, researchers have recognized the motivating potential of task significance and doing work that affects the wellbeing of others.
All too often, employees do work that makes a difference but never have the chance to see or to meet the people affected. Research by Adam Grant (2013) speaks to the power of long-term goals that benefit others and shows how the use of meaning to motivate those who are not likely to climb the ladder can make the job meaningful by broadening perspectives.
Creating an upbeat, positive work environment can also play an essential role in increasing employee motivation and can be accomplished through the following:
- Encouraging teamwork and sharing ideas
- Providing tools and knowledge to perform well
- Eliminating conflict as it arises
- Giving employees the freedom to work independently when appropriate
- Helping employees establish professional goals and objectives and aligning these goals with the individual’s self-esteem
- Making the cause and effect relationship clear by establishing a goal and its reward
- Offering encouragement when workers hit notable milestones
- Celebrating employee achievements and team accomplishments while avoiding comparing one worker’s achievements to those of others
- Offering the incentive of a profit-sharing program and collective goal setting and teamwork
- Soliciting employee input through regular surveys of employee satisfaction
- Providing professional enrichment through providing tuition reimbursement and encouraging employees to pursue additional education and participate in industry organizations, skills workshops, and seminars
- Motivating through curiosity and creating an environment that stimulates employee interest to learn more
- Using cooperation and competition as a form of motivation based on individual preferences
Sometimes, inexperienced leaders will assume that the same factors that motivate one employee, or the leaders themselves, will motivate others too. Some will make the mistake of introducing de-motivating factors into the workplace, such as punishment for mistakes or frequent criticism, but negative reinforcement rarely works and often backfires.

Download 3 Free Goals Exercises (PDF)
These detailed, science-based exercises will help you or your clients create actionable goals and master techniques for lasting behavior change.
Download 3 Free Goals Pack (PDF)
By filling out your name and email address below.
- Email Address *
- Your Expertise * Your expertise Therapy Coaching Education Counseling Business Healthcare Other
- Email This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
There are several positive psychology interventions that can be used in the workplace to improve important outcomes, such as reduced job stress and increased motivation, work engagement, and job performance. Numerous empirical studies have been conducted in recent years to verify the effects of these interventions.

World’s Largest Positive Psychology Resource
The Positive Psychology Toolkit© is a groundbreaking practitioner resource containing over 500 science-based exercises , activities, interventions, questionnaires, and assessments created by experts using the latest positive psychology research.
Updated monthly. 100% Science-based.
“The best positive psychology resource out there!” — Emiliya Zhivotovskaya , Flourishing Center CEO
Psychological capital interventions
Psychological capital interventions are associated with a variety of work outcomes that include improved job performance, engagement, and organizational citizenship behaviors (Avey, 2014; Luthans & Youssef-Morgan 2017). Psychological capital refers to a psychological state that is malleable and open to development and consists of four major components:
- Self-efficacy and confidence in our ability to succeed at challenging work tasks
- Optimism and positive attributions about the future of our career or company
- Hope and redirecting paths to work goals in the face of obstacles
- Resilience in the workplace and bouncing back from adverse situations (Luthans & Youssef-Morgan, 2017)
Job crafting interventions
Job crafting interventions – where employees design and have control over the characteristics of their work to create an optimal fit between work demands and their personal strengths – can lead to improved performance and greater work engagement (Bakker, Tims, & Derks, 2012; van Wingerden, Bakker, & Derks, 2016).
The concept of job crafting is rooted in the jobs demands–resources theory and suggests that employee motivation, engagement, and performance can be influenced by practices such as (Bakker et al., 2012):
- Attempts to alter social job resources, such as feedback and coaching
- Structural job resources, such as opportunities to develop at work
- Challenging job demands, such as reducing workload and creating new projects
Job crafting is a self-initiated, proactive process by which employees change elements of their jobs to optimize the fit between their job demands and personal needs, abilities, and strengths (Wrzesniewski & Dutton, 2001).

Today’s motivation research shows that participation is likely to lead to several positive behaviors as long as managers encourage greater engagement, motivation, and productivity while recognizing the importance of rest and work recovery.
One key factor for increasing work engagement is psychological safety (Kahn, 1990). Psychological safety allows an employee or team member to engage in interpersonal risk taking and refers to being able to bring our authentic self to work without fear of negative consequences to self-image, status, or career (Edmondson, 1999).
When employees perceive psychological safety, they are less likely to be distracted by negative emotions such as fear, which stems from worrying about controlling perceptions of managers and colleagues.
Dealing with fear also requires intense emotional regulation (Barsade, Brief, & Spataro, 2003), which takes away from the ability to fully immerse ourselves in our work tasks. The presence of psychological safety in the workplace decreases such distractions and allows employees to expend their energy toward being absorbed and attentive to work tasks.
Effective structural features, such as coaching leadership and context support, are some ways managers can initiate psychological safety in the workplace (Hackman, 1987). Leaders’ behavior can significantly influence how employees behave and lead to greater trust (Tyler & Lind, 1992).
Supportive, coaching-oriented, and non-defensive responses to employee concerns and questions can lead to heightened feelings of safety and ensure the presence of vital psychological capital.
Another essential factor for increasing work engagement and motivation is the balance between employees’ job demands and resources.
Job demands can stem from time pressures, physical demands, high priority, and shift work and are not necessarily detrimental. High job demands and high resources can both increase engagement, but it is important that employees perceive that they are in balance, with sufficient resources to deal with their work demands (Crawford, LePine, & Rich, 2010).
Challenging demands can be very motivating, energizing employees to achieve their goals and stimulating their personal growth. Still, they also require that employees be more attentive and absorbed and direct more energy toward their work (Bakker & Demerouti, 2014).
Unfortunately, when employees perceive that they do not have enough control to tackle these challenging demands, the same high demands will be experienced as very depleting (Karasek, 1979).
This sense of perceived control can be increased with sufficient resources like managerial and peer support and, like the effects of psychological safety, can ensure that employees are not hindered by distraction that can limit their attention, absorption, and energy.
The job demands–resources occupational stress model suggests that job demands that force employees to be attentive and absorbed can be depleting if not coupled with adequate resources, and shows how sufficient resources allow employees to sustain a positive level of engagement that does not eventually lead to discouragement or burnout (Demerouti, Bakker, Nachreiner, & Schaufeli, 2001).
And last but not least, another set of factors that are critical for increasing work engagement involves core self-evaluations and self-concept (Judge & Bono, 2001). Efficacy, self-esteem, locus of control, identity, and perceived social impact may be critical drivers of an individual’s psychological availability, as evident in the attention, absorption, and energy directed toward their work.
Self-esteem and efficacy are enhanced by increasing employees’ general confidence in their abilities, which in turn assists in making them feel secure about themselves and, therefore, more motivated and engaged in their work (Crawford et al., 2010).
Social impact, in particular, has become increasingly important in the growing tendency for employees to seek out meaningful work. One such example is the MBA Oath created by 25 graduating Harvard business students pledging to lead professional careers marked with integrity and ethics:
The MBA oath
“As a business leader, I recognize my role in society.
My purpose is to lead people and manage resources to create value that no single individual can create alone.
My decisions affect the well-being of individuals inside and outside my enterprise, today and tomorrow. Therefore, I promise that:
- I will manage my enterprise with loyalty and care, and will not advance my personal interests at the expense of my enterprise or society.
- I will understand and uphold, in letter and spirit, the laws and contracts governing my conduct and that of my enterprise.
- I will refrain from corruption, unfair competition, or business practices harmful to society.
- I will protect the human rights and dignity of all people affected by my enterprise, and I will oppose discrimination and exploitation.
- I will protect the right of future generations to advance their standard of living and enjoy a healthy planet.
- I will report the performance and risks of my enterprise accurately and honestly.
- I will invest in developing myself and others, helping the management profession continue to advance and create sustainable and inclusive prosperity.
In exercising my professional duties according to these principles, I recognize that my behavior must set an example of integrity, eliciting trust, and esteem from those I serve. I will remain accountable to my peers and to society for my actions and for upholding these standards. This oath, I make freely, and upon my honor.”
Job crafting is the process of personalizing work to better align with one’s strengths, values, and interests (Tims & Bakker, 2010).
Any job, at any level can be ‘crafted,’ and a well-crafted job offers more autonomy, deeper engagement and improved overall wellbeing.
There are three types of job crafting:
- Task crafting involves adding or removing tasks, spending more or less time on certain tasks, or redesigning tasks so that they better align with your core strengths (Berg et al., 2013).
- Relational crafting includes building, reframing, and adapting relationships to foster meaningfulness (Berg et al., 2013).
- Cognitive crafting defines how we think about our jobs, including how we perceive tasks and the meaning behind them.
If you would like to guide others through their own unique job crafting journey, our set of Job Crafting Manuals (PDF) offer a ready-made 7-session coaching trajectory.

Prosocial motivation is an important driver behind many individual and collective accomplishments at work.
It is a strong predictor of persistence, performance, and productivity when accompanied by intrinsic motivation. Prosocial motivation was also indicative of more affiliative citizenship behaviors when it was accompanied by motivation toward impression management motivation and was a stronger predictor of job performance when managers were perceived as trustworthy (Ciulla, 2000).
On a day-to-day basis most jobs can’t fill the tall order of making the world better, but particular incidents at work have meaning because you make a valuable contribution or you are able to genuinely help someone in need.
J. B. Ciulla
Prosocial motivation was shown to enhance the creativity of intrinsically motivated employees, the performance of employees with high core self-evaluations, and the performance evaluations of proactive employees. The psychological mechanisms that enable this are the importance placed on task significance, encouraging perspective taking, and fostering social emotions of anticipated guilt and gratitude (Ciulla, 2000).
Some argue that organizations whose products and services contribute to positive human growth are examples of what constitutes good business (Csíkszentmihályi, 2004). Businesses with a soul are those enterprises where employees experience deep engagement and develop greater complexity.
In these unique environments, employees are provided opportunities to do what they do best. In return, their organizations reap the benefits of higher productivity and lower turnover, as well as greater profit, customer satisfaction, and workplace safety. Most importantly, however, the level of engagement, involvement, or degree to which employees are positively stretched contributes to the experience of wellbeing at work (Csíkszentmihályi, 2004).

17 Tools To Increase Motivation and Goal Achievement
These 17 Motivation & Goal Achievement Exercises [PDF] contain all you need to help others set meaningful goals, increase self-drive, and experience greater accomplishment and life satisfaction.
Created by Experts. 100% Science-based.
Daniel Pink (2011) argues that when it comes to motivation, management is the problem, not the solution, as it represents antiquated notions of what motivates people. He claims that even the most sophisticated forms of empowering employees and providing flexibility are no more than civilized forms of control.
He gives an example of companies that fall under the umbrella of what is known as results-only work environments (ROWEs), which allow all their employees to work whenever and wherever they want as long their work gets done.
Valuing results rather than face time can change the cultural definition of a successful worker by challenging the notion that long hours and constant availability signal commitment (Kelly, Moen, & Tranby, 2011).
Studies show that ROWEs can increase employees’ control over their work schedule; improve work–life fit; positively affect employees’ sleep duration, energy levels, self-reported health, and exercise; and decrease tobacco and alcohol use (Moen, Kelly, & Lam, 2013; Moen, Kelly, Tranby, & Huang, 2011).
Perhaps this type of solution sounds overly ambitious, and many traditional working environments are not ready for such drastic changes. Nevertheless, it is hard to ignore the quickly amassing evidence that work environments that offer autonomy, opportunities for growth, and pursuit of meaning are good for our health, our souls, and our society.
Leave us your thoughts on this topic.
Related reading: Motivation in Education: What It Takes to Motivate Our Kids
We hope you enjoyed reading this article. Don’t forget to download our three Goal Achievement Exercises for free .
- Anderson, D. (2018, February 22). 11 Surprising statistics about employee recognition [infographic]. Best Practice in Human Resources. Retrieved from https://www.bestpracticeinhr.com/11-surprising-statistics-about-employee-recognition-infographic/
- Avey, J. B. (2014). The left side of psychological capital: New evidence on the antecedents of PsyCap. Journal of Leadership & Organizational Studies, 21( 2), 141–149.
- Bakker, A. B., & Demerouti, E. (2014). Job demands–resources theory. In P. Y. Chen & C. L. Cooper (Eds.), Wellbeing: A complete reference guide (vol. 3). John Wiley and Sons.
- Bakker, A. B., Tims, M., & Derks, D. (2012). Proactive personality and job performance: The role of job crafting and work engagement. Human Relations , 65 (10), 1359–1378
- Barsade, S. G., Brief, A. P., & Spataro, S. E. (2003). The affective revolution in organizational behavior: The emergence of a paradigm. In J. Greenberg (Ed.), Organizational behavior: The state of the science (pp. 3–52). Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
- Berg, J. M., Dutton, J. E., & Wrzesniewski, A. (2013). Job crafting and meaningful work. In B. J. Dik, Z. S. Byrne, & M. F. Steger (Eds.), Purpose and meaning in the workplace (pp. 81-104) . American Psychological Association.
- Ciulla, J. B. (2000). The working life: The promise and betrayal of modern work. Three Rivers Press.
- Crawford, E. R., LePine, J. A., & Rich, B. L. (2010). Linking job demands and resources to employee engagement and burnout: A theoretical extension and meta-analytic test. Journal of Applied Psychology , 95 (5), 834–848.
- Csíkszentmihályi, M. (2004). Good business: Leadership, flow, and the making of meaning. Penguin Books.
- Demerouti, E., Bakker, A. B., Nachreiner, F., & Schaufeli, W. B. (2001). The job demands–resources model of burnout. Journal of Applied Psychology , 863) , 499–512.
- Edmondson, A. (1999). Psychological safety and learning behavior in work teams. Administrative Science Quarterly , 44 (2), 350–383.
- Grant, A. M. (2013). Give and take: A revolutionary approach to success. Penguin.
- Hackman, J. R. (1987). The design of work teams. In J. Lorsch (Ed.), Handbook of organizational behavior (pp. 315–342). Prentice-Hall.
- Herzberg, F. (1959). The motivation to work. Wiley.
- Judge, T. A., & Bono, J. E. (2001). Relationship of core self-evaluations traits – self-esteem, generalized self-efficacy, locus of control, and emotional stability – with job satisfaction and job performance: A meta-analysis. Journal of Applied Psychology , 86 (1), 80–92.
- Kahn, W. A. (1990). Psychological conditions of personal engagement and disengagement at work. Academy of Management Journal , 33 (4), 692–724.
- Karasek, R. A., Jr. (1979). Job demands, job decision latitude, and mental strain: Implications for job redesign. Administrative Science Quarterly, 24 (2), 285–308.
- Kelly, E. L., Moen, P., & Tranby, E. (2011). Changing workplaces to reduce work-family conflict: Schedule control in a white-collar organization. American Sociological Review , 76 (2), 265–290.
- Landsberger, H. A. (1958). Hawthorne revisited: Management and the worker, its critics, and developments in human relations in industry. Cornell University.
- Luthans, F., & Youssef-Morgan, C. M. (2017). Psychological capital: An evidence-based positive approach. Annual Review of Organizational Psychology and Organizational Behavior, 4 , 339-366.
- Moen, P., Kelly, E. L., & Lam, J. (2013). Healthy work revisited: Do changes in time strain predict well-being? Journal of occupational health psychology, 18 (2), 157.
- Moen, P., Kelly, E., Tranby, E., & Huang, Q. (2011). Changing work, changing health: Can real work-time flexibility promote health behaviors and well-being? Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 52(4), 404–429.
- Pattison, K. (2010, August 26). Chip Conley took the Maslow pyramid, made it an employee pyramid and saved his company. Fast Company. Retrieved from https://www.fastcompany.com/1685009/chip-conley-took-maslow-pyramid-made-it-employee-pyramid-and-saved-his-company
- Pink, D. H. (2011). Drive: The surprising truth about what motivates us. Penguin.
- Tims, M., & Bakker, A. B. (2010). Job crafting: Towards a new model of individual job redesign. SA Journal of Industrial Psychology, 36(2) , 1-9.
- Tyler, T. R., & Lind, E. A. (1992). A relational model of authority in groups. In M. P. Zanna (Ed.), Advances in experimental social psychology (vol. 25) (pp. 115–191). Academic Press.
- von Wingerden, J., Bakker, A. B., & Derks, D. (2016). A test of a job demands–resources intervention. Journal of Managerial Psychology , 31 (3), 686–701.
- Wrzesniewski, A., & Dutton, J. E. (2001). Crafting a job: Revisioning employees as active crafters of their work. Academy of Management Review, 26 (2), 179–201.
Share this article:
Article feedback
What our readers think.
Good and helpful study thank you. It will help achieving goals for my clients. Thank you for this information
A lot of data is really given. Validation is correct. The next step is the exchange of knowledge in order to create an optimal model of motivation.
A good article, thank you for sharing. The views and work by the likes of Daniel Pink, Dan Ariely, Barry Schwartz etc have really got me questioning and reflecting on my own views on workplace motivation. There are far too many organisations and leaders who continue to rely on hedonic principles for motivation (until recently, myself included!!). An excellent book which shares these modern views is ‘Primed to Perform’ by Doshi and McGregor (2015). Based on the earlier work of Deci and Ryan’s self determination theory the book explores the principle of ‘why people work, determines how well they work’. A easy to read and enjoyable book that offers a very practical way of applying in the workplace.
Thanks for mentioning that. Sounds like a good read.
All the best, Annelé
Motivation – a piece of art every manager should obtain and remember by heart and continue to embrace.
Exceptionally good write-up on the subject applicable for personal and professional betterment. Simplified theorem appeals to think and learn at least one thing that means an inspiration to the reader. I appreciate your efforts through this contributive work.
Excelente artículo sobre motivación. Me inspira. Gracias
Very helpful for everyone studying motivation right now! It’s brilliant the way it’s witten and also brought to the reader. Thank you.
Such a brilliant piece! A super coverage of existing theories clearly written. It serves as an excellent overview (or reminder for those of us who once knew the older stuff by heart!) Thank you!
Let us know your thoughts Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related articles

How to Encourage Clients to Embrace Change
Many of us struggle with change, especially when it’s imposed upon us rather than chosen. Yet despite its inevitability, without it, there would be no [...]

Victor Vroom’s Expectancy Theory of Motivation
Motivation is vital to beginning and maintaining healthy behavior in the workplace, education, and beyond, and it drives us toward our desired outcomes (Zajda, 2023). [...]

SMART Goals, HARD Goals, PACT, or OKRs: What Works?
Goal setting is vital in business, education, and performance environments such as sports, yet it is also a key component of many coaching and counseling [...]
Read other articles by their category
- Body & Brain (52)
- Coaching & Application (39)
- Compassion (23)
- Counseling (40)
- Emotional Intelligence (21)
- Gratitude (18)
- Grief & Bereavement (18)
- Happiness & SWB (40)
- Meaning & Values (26)
- Meditation (16)
- Mindfulness (40)
- Motivation & Goals (41)
- Optimism & Mindset (29)
- Positive CBT (28)
- Positive Communication (23)
- Positive Education (37)
- Positive Emotions (32)
- Positive Leadership (16)
- Positive Parenting (14)
- Positive Psychology (21)
- Positive Workplace (35)
- Productivity (16)
- Relationships (46)
- Resilience & Coping (39)
- Self Awareness (20)
- Self Esteem (37)
- Strengths & Virtues (29)
- Stress & Burnout Prevention (33)
- Theory & Books (42)
- Therapy Exercises (37)
- Types of Therapy (54)

- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
3 Goal Achievement Exercises Pack
How it works
Transform your enterprise with the scalable mindsets, skills, & behavior change that drive performance.
Explore how BetterUp connects to your core business systems.
We pair AI with the latest in human-centered coaching to drive powerful, lasting learning and behavior change.
Build leaders that accelerate team performance and engagement.
Unlock performance potential at scale with AI-powered curated growth journeys.
Build resilience, well-being and agility to drive performance across your entire enterprise.
Transform your business, starting with your sales leaders.
Unlock business impact from the top with executive coaching.
Foster a culture of inclusion and belonging.
Accelerate the performance and potential of your agencies and employees.
See how innovative organizations use BetterUp to build a thriving workforce.
Discover how BetterUp measurably impacts key business outcomes for organizations like yours.
Daring Leadership Institute: a groundbreaking partnership that amplifies Brené Brown's empirically based, courage-building curriculum with BetterUp’s human transformation platform.

- What is coaching?
Learn how 1:1 coaching works, who its for, and if it's right for you.
Accelerate your personal and professional growth with the expert guidance of a BetterUp Coach.
Types of Coaching
Navigate career transitions, accelerate your professional growth, and achieve your career goals with expert coaching.
Enhance your communication skills for better personal and professional relationships, with tailored coaching that focuses on your needs.
Find balance, resilience, and well-being in all areas of your life with holistic coaching designed to empower you.
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.
Find your coach
-1.png)
Research, expert insights, and resources to develop courageous leaders within your organization.
Best practices, research, and tools to fuel individual and business growth.
View on-demand BetterUp events and learn about upcoming live discussions.
The latest insights and ideas for building a high-performing workplace.
- BetterUp Briefing
The online magazine that helps you understand tomorrow's workforce trends, today.
Innovative research featured in peer-reviewed journals, press, and more.
Founded in 2022 to deepen the understanding of the intersection of well-being, purpose, and performance
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.

For Business
For Individuals
Work motivation: what it is and why it is important

It is easy to believe that motivation is a feeling that shows up when we need to perform, leaving us waiting for that magical sensation to appear. When it doesn’t, we’re left to blame all of our missed deadlines or wishes for the lack of it.
So what is motivation?
What is motivation?
Motivation is the driving force that propels us toward something we need or care about. It could be as small as a dry throat motivating you to get a glass of water to calm your thirst. It could be as big as a commitment to a friend to do an Ironman together motivating you to swim in the bay before dawn every day. In this way, motivation is a force that spurs us to action and to see things through to completion.
Motivation is how we get things done when we have an objective we care about. That sounds logical and easy, except that we are also exceptionally good at losing motivation, even when we know we need something.
Types of motivation
Though there are many types of motivation , they generally fall under one of two categories: intrinsic motivation and extrinsic motivation.
Extrinsic motivation
Also known as “carrot and stick” motivation, extrinsic motivators are external . They can be rewards such as money, or avoiding negative impact such as losing your job. With extrinsic motivation, we have little to no control over the positive or negative consequences themselves. But we are motivated to manage the areas we do have control over to either gain or avoid these consequences.
Intrinsic motivation
When we are intrinsically motivated , we complete a task for the enjoyment or feeling of satisfaction we get from doing so. Unlike extrinsic motivators, this type of motivation is not rewarded by external factors. The benefits of employing intrinsic motivation in the workplace include higher levels of employee satisfaction and lower turnover rates.

Why is motivation important in the workplace?
On the surface, the impact of a well-motivated workforce is clear. Motivated employees are more productive. As we mentioned above, though, it goes further than that. Aside from the effectiveness of your teams, motivation is also shown to drive retention and improve company culture.
Let’s break down the ways a motivated workplace benefits both employees and the business.
How motivation benefits the organization
- Meet and exceed the company’s goals. Without a motivated workplace , companies could struggle to deliver on promises to customers, fail to execute daily operations, and let opportunities for the future slip away--talent will avoid demotivated workplaces.
- Higher productivity. Happy employees experience 31 percent higher productivity. Improved employee satisfaction which can lead toward a positive growth for the company.
- Championship. Motivated employees are often emotionally connected to their companies. Emotionally connected employees are 3 times more likely to become brand ambassadors.
- Delighted customers. Workers put in extra effort leading to more output and better solutions.
- Quality. Quality improves as staff take a greater pride in their work.
- Committed, experienced employees. A motivated workplace leads to higher level of staff retention and reduced turnover.
How motivation benefits the individual
- Self-efficacy and confidence in one’s ability to succeed at challenging work tasks
- Increased proactivity and creativity
- Optimism and positive attributions about the future of one’s career or company
- Hope and redirecting paths to work goals in the face of obstacles
- Resilience in the workplace and bouncing back from adverse situations
How meaning impacts motivation
Motivation is all the factors that encourage individuals to be committed to and interested in doing something over time. The feeling of intense interest and desire to act can be momentary. It lets you know you are going in the right direction, but the different aspects that drove you to feel that way are the ones that will maintain your actions.
These factors can be different from one person to another. Find them by answering these questions:
- What do I value?
- Why do I value it?
- What makes me feel vital?
- What makes me feel committed?
- What makes what I am doing purposeful?
In coaching, I have come across many people who didn’t feel motivated at work. The first symptom was a sense of loss of meaning. So when we face demotivation in the workplace, we need to start by asking what the value behind the task is.
Motivation is highly related to the meaning we assign to what we are doing. Many times that meaning is not related to the immediate results of our work or to the specific task. We assign meaning based on a larger outcome or bigger purpose we see in the work.
For example, you can feel passionate about building your own business but also dislike marketing activities. You might be highly motivated to do unpleasant marketing tasks because you know how much your business growth will depend on them. Connecting the task of promoting your business to your goal of growing it, and reminding yourself of that connection, can keep you going with better energy and attitude.
When employees don’t feel as committed or connected to part of something important , when they can’t relate to the mission of the company or simply can’t see the importance of their role at a bigger scale, they often lose motivation.

Most common causes of workplace demotivation
Some of the most common demotivators at work are fairly mundane and even trivial. They seem addressable but the degree to which they are experienced is symptomatic of a larger disconnect in purpose , meaning, and values.
- Micromanagement
- Lack of progress or growth opportunities
- Job insecurity
- No confidence in company leadership
- Poor communication
- Unpleasant coworkers
- Boredom
Although all of these factors are huge motivation killers, they are likely to affect us less when the person feels a deeper connection to what they do.
Notice also what isn’t on the list of demotivators: “difficult projects,” “ambiguity and uncertainty,” “long hours,” and “high expectations.” Although these factors can create stress for the individual, it is the type of stress that facilitates growth and learning . As long as the work or outcome is somewhat interesting or important to the individual, challenges, complexity, and stretch assignments tend to be far more motivating than easy or predefined work.
Tapping into individual motivation through curiosity, desire to make more impact, and inclination to connect with others on something larger than themselves creates a vitality that benefits both the organization and the individual.
How to increase self-motivation at work
1. renew your motivation.
Motivation needs to be refreshed , sometimes daily. When we don’t get an immediate reward, or experience pleasure by avoiding a tedious task, it is important to remind ourselves why what we are doing is relevant or contributes to something more relevant. How? Take it to the next level and always find the bigger purpose. Focus on quality
2. Be aware of the value of your work and what it reflects about you
Take pride in your craftsmanship, even when the situation prioritizes quantity--make your work the best it can be in the circumstances. Many times, we set countable goals, such as finishing 20 invoices. When we do so, we focus only on reaching the number and are less likely to pay attention to what we are doing and enjoying the process.
3. Let role models inspire you
Having someone we look up to can be a powerful way to get motivated. However, it can also be frustrating if we only focus on what they accomplished and forget the HOW. Don’t envy the person; don’t idealize. Learn more about what took them where they are and let them inspire you. Whether they are a co-worker or a famous CEO, learn their stories.
4. Organize your goals
It may seem obvious, but sometimes we forget to break down our goals into manageable actions . Smaller, frequent wins can create momentum as long as they are meaningful and clearly point toward the longer-term objective. Especially when we have too much on our plate, we tend to lose focus of what and why exactly we are doing things. To stay connected to your goal, you must have a clear vision of how every step you take is taking you closer.
5. Harness your self-compassion
Few things can diminish motivation faster than self-doubt and negative self-talk . We cannot get everything right all the time. So try to be kind to yourself when mistakes happen.

How to motivate employees
Keeping yourself motivated is its own challenge. Trying to motivate employees and teams is quite another. It takes a specific skillset and the ability to leverage a variety of leadership skills. Here are eight tips for motivating your team through both uncertain and more predictable landscapes.
1. Demonstrate interest
Ask, listen, and deliver. If you want to motivate a team member, ask them what they care about. What do they need to feel included? For your employees to feel heard, it is not enough for you to ask questions but to actually listen, provide feedback and demonstrate with actions that you take into account.
2. Coach and support
When employees don’t need to worry about controlling the perceptions of managers and colleagues, they are more likely to openly ask for feedback and provide feedback. The energy of freely working together without politics or maneuvering is incredibly rewarding and motivating. Coaching leadership and context support, promote psychological safety in the workplace. This allows you to create a trust-based relationship with your employees, thus increasing satisfaction and motivation for both sides.
3. Value individual and team contributions at a broader level
Raise awareness of the impact each team member has at a bigger level by talking about how their work influenced the management goals, for example. How is every role related to accomplishing the company’s mission? Ask them questions that generate reflection and facilitate a broader view of how their actions impact and contribute to the global operation of the company.
4. Build a positive work environment
Both motivation and demotivation can be contagious. Create a positive environment by setting an example. Say hello to everyone, ask them about their families, make jokes, bring appetizers to the meetings, and be vigilant about maintaining your own authentic enthusiasm and motivation. It is okay to dip or be discouraged occasionally, but model for your team how you continue to find your own motivation.
5. Be aware of your employees and their well-being within the company
Encourage your team members to work together and support each other. Help them see how they can benefit from learning from their colleagues and coaching each other, with healthy competition.
6. Empower your employees
Trust them and motivate them to take some initiative. Allow them to bring ideas and give them the freedom to make decisions without having to consult you, always leaving the door open for questions and coaching. Invite them to the planning and goal-setting process .
7. Address employees' quality of life
Support work-life balance by knowing your employees and letting them put their family and health as a priority. If someone asks to arrive late to attend their daughter's recital or to attend a medical appointment, say yes. Thankful employees are more likely to overachieve. On the other hand, make sure that the demands are challenging enough to avoid boredom but feasible enough to allow your employees to have a life after work.
8. Invest in career pathing
Make every step meaningful. Whether to learn or to apply for a promotion, your employee should feel that everything they are doing will translate into growth, experience, and mobility . Make sure you have talked to them about their future and to coach them into turning work into a learning process that feels meaningful.
Am I motivating my employees enough?
One of the best ways to measure the effectiveness of your motivation techniques is by frequently asking yourself some questions about your team:
- Are they taking the initiative?
- Are they united as a team?
- Do they provide feedback?
- Do they show interest and engagement during meetings?
Other, more traditional, ways to measure motivation can be informative but are often lagging measures. By the time you see them, it’s too late. However, they can still provide insight that helps you understand the full picture.
How to measure work motivation
These formal ways to understand and shape motivation include:
- Performance reviews . They will not only allow you to measure performance but to motivate them by going through the details of what is working for them and what isn’t. They are also a great opportunity to talk about the impact of their work and understand what they value and what makes them feel motivated.
- Employee motivation and engagement surveys . When anonymously answered, they tend to be a great reflection of the workplace environment. Combining a quantitative questionnaire and some open questions will allow you to pick up a good sample of what your employees' motivation and engagement stand at.
- Employee turnover and absenteeism. Are you having a high rate of employee turnover or absenteeism ? These two important metrics raise flags that reflect the motivation and satisfaction of our workforce.
Sustaining workplace motivation
Measuring your employee motivation and your own level of drive at work is the first step. Once you have a baseline, you can put some of these initiatives into practice to embrace a culture of motivation. Though workplace motivation is not a constant –– everyone has tough days –– being mindful and proactive in your approach will set you and your team up for long-term success.
Understand Yourself Better:
Big 5 Personality Test
Paulina Cal y Mayor Galindo
BetterUp Fellow Coach
How to handle a lack of motivation at work
Work the motivation: 10 ways to keep your team inspired, why the secret to great coaching lies in motivation, extrinsic motivation: what is it, and can it lead to fulfillment, goal-setting theory: why it’s important, and how to use it at work, what causes a lack of motivation plus 9 tips to get it back, how to use motivational interview questions to drive change, motivation and inspiration: examples in life and work, what moves you understanding motivation is your key to success, the ultimate guide to motivating a team — and why it matters, how building trust is the true secret to motivating sales teams, ready to be inspired here are 11 self-motivation examples, no motivation to work: 7 tips to find motivation again, what is intrinsic motivation definition and examples, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform Overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead™
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care®
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case Studies
- Why BetterUp?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Personal Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Labs
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences
What motivates us at work? More than money
Share this idea.
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pocket (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)

“When we think about how people work, the naïve intuition we have is that people are like rats in a maze,” says behavioral economist Dan Ariely (TED Talk: What makes us feel good about our work? ) “We really have this incredibly simplistic view of why people work and what the labor market looks like.”
Instead, when you look carefully at the way people work, he says, you find out there’s a lot more at play — and at stake — than money. Ariely provides evidence that we are also driven by the meaningfulness of our work, by others’ acknowledgement — and by the amount of effort we’ve put in: the harder the task is, the prouder we are.
“When we think about labor, we usually think about motivation and payment as the same thing, but the reality is that we should probably add all kinds of things to it: meaning, creation, challenges, ownership, identity, pride, etc.,” Ariely says.
Below, take a look at some of Ariely’s other studies, as well as a few from other researchers, with interesting implications for what makes us feel good about our work.
- Seeing the fruits of our labor may make us more productive . The Study: In Man’s search for meaning: The case of Legos , Ariely asked participants to build characters from Lego’s Bionicles series. In both conditions, participants were paid decreasing amounts for each subsequent Bionicle: $3 for the first one, $2.70 for the next one, and so on. But while one group’s creations were stored under the table, to be disassembled at the end of the experiment, the other group’s Bionicles were disassembled as soon as they’d been built. “This was an endless cycle of them building and we destroying in front of their eyes,” Ariely says. . The Results: The first group made 11 Bionicles, on average, while the second group made only seven before they quit. . The Upshot: Even though there wasn’t huge meaning at stake, and even though the first group knew their work would be destroyed at the end of the experiment, seeing the results of their labor for even a short time was enough to dramatically improve performance. .
- The less appreciated we feel our work is, the more money we want to do it . The Study: Ariely gave study participants — students at MIT — a piece of paper filled with random letters, and asked them to find pairs of identical letters. Each round, they were offered less money than the previous round. People in the first group wrote their names on their sheets and handed them to the experimenter, who looked it over and said “Uh huh” before putting it in a pile. People in the second group didn’t write down their names, and the experimenter put their sheets in a pile without looking at them. People in the third group had their work shredded immediately upon completion. . The Results: People whose work was shredded needed twice as much money as those whose work was acknowledged in order to keep doing the task. People in the second group, whose work was saved but ignored, needed almost as much money as those whose work was shredded. . The Upshot: “Ignoring the performance of people is almost as bad as shredding their effort before their eyes,” Ariely says. “The good news is that adding motivation doesn’t seem to be so difficult. The bad news is that eliminating motivation seems to be incredibly easy, and if we don’t think about it carefully, we might overdo it.” .
- The harder a project is, the prouder we feel of it . The Study: In another study, Ariely gave origami novices paper and instructions to build a (pretty ugly) form. Those who did the origami project, as well as bystanders, were asked at the end how much they’d pay for the product. In a second trial, Ariely hid the instructions from some participants, resulting in a harder process — and an uglier product. . The Results: In the first experiment, the builders paid five times as much as those who just evaluated the product. In the second experiment, the lack of instructions exaggerated this difference: builders valued the ugly-but-difficult products even more highly than the easier, prettier ones, while observers valued them even less. . The Upshot: Our valuation of our own work is directly tied to the effort we’ve expended. (Plus, we erroneously think that other people will ascribe the same value to our own work as we do.) .
- Knowing that our work helps others may increase our unconscious motivation . The Study: As described in a recent New York Times Magazine profile, psychologist Adam Grant led a study at a University of Michigan fundraising call center in which students who had benefited from the center’s scholarship fundraising efforts spoke to the callers for 10 minutes. . The Results: A month later, the callers were spending 142 percent more time on the phone than before, and revenues had increased by 171 percent, according to the Times . But the callers denied the scholarship students’ visit had impacted them. . The Upshot: “It was almost as if the good feelings had bypassed the callers’ conscious cognitive processes and gone straight to a more subconscious source of motivation,” the Times reports. “They were more driven to succeed, even if they could not pinpoint the trigger for that drive.” .
- The promise of helping others makes us more likely to follow rules . The Study: Grant ran another study (also described in the Times profile) in which he put up signs at a hospital’s hand-washing stations, reading either “Hand hygiene prevents you from catching diseases” or “Hand hygiene prevents patients from catching diseases.” . The Results: Doctors and nurses used 45 percent more soap or hand sanitizer in the stations with signs that mentioned patients. . The Upshot: Helping others through what’s called “prosocial behavior” motivates us. .
- Positive reinforcement about our abilities may increase performance . The Study: Undergraduates at Harvard University gave speeches and did mock interviews with experimenters who were either nodding and smiling or shaking their heads, furrowing their eyebrows, and crossing their arms. . The Results: The participants in the first group later answered a series of numerical questions more accurately than those in the second group. . The Upshot: Stressful situations can be manageable — it all depends on how we feel. We find ourselves in a “challenge state” when we think we can handle the task (as the first group did); when we’re in a “threat state,” on the other hand, the difficulty of the task is overwhelming, and we become discouraged. We’re more motivated and perform better in a challenge state, when we have confidence in our abilities. .
- Images that trigger positive emotions may actually help us focus . The Study: Researchers at Hiroshima University had university students perform a dexterity task before and after looking at pictures of either baby or adult animals. . The Results: Performance improved in both cases, but more so (10 percent improvement!) when participants looked at cute pictures of puppies and kittens. . The Upshot: The researchers suggest that the “cuteness-triggered positive emotion” helps us narrow our focus, upping our performance on a task that requires close attention. Yes, this study may just validate your baby panda obsession.
This post was originally published on the TED Blog in April 2013.
Featured image via iStock.
About the author
Jessica Gross is a writer based in New York City. She's contributed to The New York Times Magazine, The Paris Review Daily, The Atlantic Cities, and Scientific American Mind, among other places. Jessica has a Master's degree in cultural reporting and criticism from New York University and a Bachelor's in anthropology from Princeton University.
- behavioral economics
- the way we work
TED Talk of the Day

How to make radical climate action the new normal

3 strategies for effective leadership, from a former astronaut

Feeling unseen by your boss? Here’s what you can do

Let’s stop calling them “soft skills” -- and call them “real skills” instead

There’s a know-it-all at every job — here’s how to deal

The 7 types of people you need in your life to be resilient

Perfectionism holding you back? 3 ways to shift the habit

The unseen forces that can cause your great new idea to crash and burn

Have you quietly quit? Your next step: Go to the neutral zone

6 ways to give that aren't about money
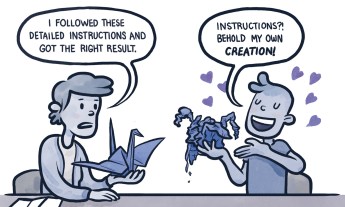
Why we’re so attached to our own creations -- even when they’re ugly
How can we improve democracy? One intriguing idea: Set up a jury system.

Dear TED: "How can I be happier at work?"

The data shows we want to end inequality. Here's how to start ...
- Undergraduate
- High School
- Architecture
- American History
- Asian History
- Antique Literature
- American Literature
- Asian Literature
- Classic English Literature
- World Literature
- Creative Writing
- Linguistics
- Criminal Justice
- Legal Issues
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Political Science
- World Affairs
- African-American Studies
- East European Studies
- Latin-American Studies
- Native-American Studies
- West European Studies
- Family and Consumer Science
- Social Issues
- Women and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Natural Sciences
- Pharmacology
- Earth science
- Agriculture
- Agricultural Studies
- Computer Science
- IT Management
- Mathematics
- Investments
- Engineering and Technology
- Engineering
- Aeronautics
- Medicine and Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Communications and Media
- Advertising
- Communication Strategies
- Public Relations
- Educational Theories
- Teacher's Career
- Chicago/Turabian
- Company Analysis
- Education Theories
- Shakespeare
- Canadian Studies
- Food Safety
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
Movie Review
- Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Marketing Plan
- Multiple Choice Quiz
- Personal Statement
- Power Point Presentation
- Power Point Presentation With Speaker Notes
- Questionnaire
- Reaction Paper
- Research Paper
- Research Proposal
- SWOT analysis
- Thesis Paper
- Online Quiz
- Literature Review
- Movie Analysis
- Statistics problem
- Math Problem
- All papers examples
- How It Works
- Money Back Policy
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- We Are Hiring
Motivation in the Modern Workplace, Essay Example
Pages: 5
Words: 1407
Hire a Writer for Custom Essay
Use 10% Off Discount: "custom10" in 1 Click 👇
You are free to use it as an inspiration or a source for your own work.
Introduction
As the concern of increasing productivity through improved employee performance has been there for ages, most companies currently pay more attention on the factors that can lead to such achievements. This translates to encouraging the employes to perform exceptionally through motivation. Motivation may be defined as the psychological method that leads to the achievement of direction, arousal, and persistence of voluntary activities that lead to accomplishment of pre-determined objectives. Examples of motivations include incentives, work place promotions, and rewards. Numerous motivational theories help businesses in encouraging workers put more efforts and hence exploit their full potential in meeting of goals and objectives. These theories suggest factors that result to job contentment. The following essay investigates factors that lead to motivation in modern work places, their impacts, and differences between motivated and unmotivated work places performances.
Motivational theories endeavor to explain what makes people behave in a particular manner in the work place. The theories also explain what makes some workers to work harder than others do or why some workers are more committed than others in their work. The study of the theories by managers enables them to understand how they can motivate employees so that they can perform at their peak levels. Application of these theories in the workplace can improve your leadership skills (Buch et al 2014, p. 20).
Setting of Clear and Reasonable Expectations
The utilization of reinforcement to motivate employees in the workplace should be a positive experience for both the worker and the manager. Failure to set clear and reasonable expectations often frustrates employees and reduces their tendency to behave in the right manner. For instance, imagine a situation where the employee was not told to do better without further details. The employee might end up guessing what the boss meant, yet he would not have adequate information to make positive changes without further additional feedback. Moreover, rewarding only the difficult or impossible tasks may result to anger or a sense of helplessness and therefore leading to worse performances than even before the reinforcement program (Hülsheger et al 2013 p. 12). Expectation of absolute perfection in tasks or consistent excellency in sales, for instance, can be considered unreasonable and may lead to increasing errors as well as declining sales as the employee gradually gives up.
Identification of Strong Motivators
Working along with employees in the identification of personalized motivators or reinforcement is more likely to motivate employees to produce the desired results. For instance, a single childless employee may not work very hard to earn a week off free babysitting, or a vegetarian may not appreciate a gift certificate to a steak house. On the contrary, the employee can work very hard past the manager’s expectation pursuing to earn a reward that he or she has chosen. However, if permitting employees to choose seems impractical to the manager, the manager can consider offering a range of rewards from which the employee can choose from in case they meet the required conditions (Hülsheger et al 2013 p. 45).
Encouraging Desirable Behaviors and habits
The desire of most managers is to encourage their employees positively. They endeavor to develop positive employee behavior such as punctuality, quality production, as well as strong teamwork. In accordance to the reinforcement theory, choosing the most appropriate positive attitudes to target at a time as well as the application of positive reinforcement techniques focusing on the elimination of negative behaviors is expected to turn undesirable negative traits into better working traits (Barrick, et al 2013 p. 34). The extinction of undesired employee traits results from the presence of positive reinforcements, which encourage the employee rather than punishment that discour5ages the employee. This means offering employees with incentives when a work or exceeds the managers expectations, positive reinforcements, as well as concentrating on the elimination of the negative traits. For instance, a manager may decide to offer a bonus for sales in excess for his or her weekly target, a long lunch break for meeting the target sales as well as a standard lunch.
Effective Use of Reinforcements
Careful Timing of reinforcements because of different strategies yields a range of results. Rewarding a positive behavior, such a good performances, every time it happens will consistently result to excellent performances. Nonetheless, rewarding the same positive occasionally also yields even better outcomes as the workers work harder in pursuit of the reward, consequently this leads to the lasting change of behavior (Barrick, et al 2013, p. 10). Irregular reinforcement also enables winning of the employees away from his or her dependence on reinforcements and hence turns the desired behavior into habit overtime. However, future reinforcement endeavors can target different behaviors with the expectation of even better results generally.
Significance of motivation to performance
In the competitive modern world of business every company wants to outdo its rivals, this is achieved through better performance than competitors. This is first attained by having the right workers in the right job. This is one factor of motivation as people to perform best in the things they love to do. For example, a social person can do better as a sales person than an unsocial person can. Motivation of workers provided by the management team enhances both quantity and quality of performance (Gillet, et al 2013, p. 21).
The connection between performance and motivation is that contented workers perform better and hence high productivity. Therefore, improved productivity is one of the significances of motivation in connection to employees’ performance. Moreover, the higher the employees are motivated, the higher the productivy in addition to quality improvement in the production process.
In addition, motivation leads to consistency, speed, and effectiveness of work processes and production. This led to high performance and production rates and, therefore increases the competitivenss of the company in comparison to others. The motivated employees work harder and smarter as they identify themselves with the organization’s goals and target (Gillet, et al 2013, p. 11).
Comparison between employees’ motivated and unmovited companies
A highly motivational company such as the Starbucks has a very high and efficient performance that can be attributed to the fact that the company is a motivator to the employees. In the company, the employees are referred to as partners. This encourages then to identify themselves with the company’s goals and hence worke towards them. Moreover, Starbucks’ “just say yes” slogan motivates workers to do their best in all areas ranging from production to customers’ satisfaction and hence high performance. Besides, through its “partner” spirit of worker, the employees are motivated to perform well as there are chances they will one day become stakeholder. Therefore, the association and motivition provided by the company to employees has improved performance, productivity, and profits. On ther hand, a company that does not motivate employess lead to low morale at the work place. Therefore, the worker do not have the desire or drive to work towards the goals of the organization. This results to company failure as the coordination of the workers is shawdy and the employees distance themselves from the company needs.
In summary, performance of businesses are positively influenced by motivation of worker. The approaches of the workforce towards the company and identifying with its goals are primarily triggered by having them motivated through various processes. The motivated employees are seen to put more efforts in production than the unmotivated ones, and hence the qwuantity and quality of products are improved. Consequently, the business is capable of meeting customers’ needs with better quality commodities than their competitors’ products. Moreover, because of increased efficiency and speed in production, the company is able to produce high quality commodities and services at lower costs than their competitors and hence improving their relative competition.
Bibliography
Gillet, N & Gagné, M & Sauvagère, S & Fouquereau, E 2013, The role of supervisor autonomy support, organizational support, and autonomous and controlled motivation in predicting employees’ satisfaction and turnover intentions, European Journal of Work and Organizational Psychology , 22 (4), 450-460.
Barrick, M & Mount, M & Li, N 2013, The theory of purposeful work behavior: The role of personality, higher-order goals, and job characteristics, Academy of Management Review , 38 (1), 132-153.
Hülsheger, U & Alberts, H & Feinholdt, A & Lang, J 2013, Benefits of mindfulness at work: The role of mindfulness in emotion regulation, emotional exhaustion, and job satisfaction, Journal of Applied Psychology , 98 (2), 310.
Buch, R & Kuvaas, B & Dysvik, A & Schyns, B 2014, If and when social and economic leader-member exchange relationships predict follower work effort: The moderating role of work motivation, Leadership & Organization Development Journal , 35 (8).
Stuck with your Essay?
Get in touch with one of our experts for instant help!
What Creates Energy in Organizations? Essay Example
Journal - Ender's Game, Movie Review Example
Time is precious
don’t waste it!
Plagiarism-free guarantee
Privacy guarantee
Secure checkout
Money back guarantee

Related Essay Samples & Examples
Voting as a civic responsibility, essay example.
Pages: 1
Words: 287
Utilitarianism and Its Applications, Essay Example
Words: 356
The Age-Related Changes of the Older Person, Essay Example
Pages: 2
Words: 448
The Problems ESOL Teachers Face, Essay Example
Pages: 8
Words: 2293
Should English Be the Primary Language? Essay Example
Pages: 4
Words: 999
The Term “Social Construction of Reality”, Essay Example
Words: 371


What keeps employees motivated
Psychologists are expanding their efforts to get research on what motivates people at work to employers at a time when the workplace is changing dramatically
Vol. 52 No. 7 Print version: page 52
- Personality
- Managing Human Capital
- Healthy Workplaces

The upheaval of the working world since March 2020 has no precedent in living memory. Some people went home for what they thought would be weeks, only to still be working from home more than a year and a half later. Others were left to struggle through enormous stresses in front-line occupations. It was, in short, a tough year for workplace motivation.
Yet psychological research suggests that there are ways businesses can support their employees moving forward even as the pandemic slips into a new phase of uncertainty. Much of this work comes from decades of research on the impacts of stress in the workplace and how job pressures influence motivation, said James Diefendorff, PhD, an industrial and organizational (I/O) psychologist at the University of Akron.
“Those demands consume regulatory resources, lead to faster emotional exhaustion and depletion, and require more opportunities for replenishment,” Diefendorff said. “It’s just amped up in the context of working under the various additional stressors and demands that the pandemic has introduced.”
Motivation in a pandemic
One of the key findings from I/O psychology over the past several decades is that not all workplace stresses are created equal. Some stressors are hindrances, which are things outside of an employee’s control that feel like barriers to performance: red tape, lack of resources, conflicting goals. Others are challenges, which feel like tasks that a person can overcome while growing and improving. An example of a challenge stressor might be learning a new skill to take on a new job responsibility. A meta-analysis led by Jeffery LePine, PhD, a researcher in organizational behavior at Arizona State University, found that while hindrance stressors crush motivation, challenge stressors actually boost it ( Academy of Management Journal , Vol. 48, No. 5, 2005 ). Research further suggests that people find challenge stressors motivating because they expect that if they put the work in, they can achieve an outcome they value. Hindrance stressors, on the other hand, feel insurmountable—no matter how hard you work, a satisfactory result is out of reach.
Many of the stressors introduced by COVID-19 were hindrance stressors, said Thomas Britt, PhD, an I/O psychologist at Clemson University. This was particularly true in health care, where limited personal protective equipment early in the pandemic put workers at risk. Hindrance stressors also abounded in other professions, such as in education, where teachers had to try to teach in far-from-ideal remote-learning circumstances.
The impact of the pandemic on workers is also clear through the lens of self-determination theory , a framework for understanding motivation developed by psychologists Richard Ryan, PhD, a professor at Australian Catholic University, and Edward Deci, PhD, a professor emeritus at the University of Rochester. Research into self-determination theory finds that three main psychological needs support optimal motivation: autonomy, competence, and relatedness ( Annual Reviews of Organizational Psychology and Organizational Behavior , Vol. 4, 2017 ). The pandemic has been a disaster for all three, said Susan Fowler, a San Diego–based motivation consultant who uses self-determination theory as the basis for her work. Suddenly, many workers were being told they had no choice but to stay home, Fowler said. They were being asked to do things that made them feel bumbling and helpless, such as interacting solely via Zoom. And the necessity of social distancing meant they were often isolated from their colleagues.
At the same time, working from home reduced hindrance stressors—such as commutes—for some workers. Researchers, clinicians, and coaches alike are now tapping into basic research to show people how to connect with their own motivation and goals, especially when external circumstances challenge them.
“Motivation researchers are active in workplaces, classrooms, sports . . . pretty much anywhere people would be engaged,” Ryan said. “We want to find out, what are the internal factors that facilitate that engagement?”
Building optimal motivation
Research has turned up several good answers to that question. One of the most motivating experiences employees can have is making progress on a meaningful task, said Teresa Amabile, PhD, a social and organizational psychologist at Harvard Business School. Amabile and her colleagues asked more than 200 employees at seven companies in the tech, chemical, and consumer products industries to write daily diary entries describing events at work and rate their own feelings of intrinsic motivation, extrinsic motivation, creativity, and collegiality, among other measures. They also collected periodic ratings of the workers’ creativity from colleagues ( Administrative Science Quarterly , Vol. 50, No. 3, 2005 ).
“We could look at how the events that were occurring impacted their intrinsic motivation and their creativity,” Amabile said.
When people reported more intrinsic motivation, their creativity simultaneously rose, she said. So did other desirable states such as productivity, collegiality, and commitment to work. And what spurred intrinsic motivation? Amabile and her team found that the most powerful precursor was the feeling of making progress at meaningful work.
“Here’s what’s interesting: It doesn’t have to be a huge breakthrough,” Amabile said. “It can be small, almost trivial, steps forward.”
This finding fit with previous I/O psychology research. For example, job characteristics theory, developed in 1975 by Greg Oldham, PhD, an I/O psychologist now at Tulane University, and J. Richard Hackman, PhD, a social psychologist now at Harvard University, holds that meaningfulness is one of the three factors leading to motivation, along with responsibility and knowledge of results.
Anecdotal reports during the pandemic suggest that the winnowing effect of work-from-home policies actually boosted feelings of progress for many employees, Amabile said. With time freed from long commutes, random coworker interruptions, and morning makeup and hair-care routines, workers often felt they got more meaningful work done each day.
However, there are caveats to the benefits of meaningful work, said Britt. He and his colleagues surveyed U.S. working adults in multiple industries using Amazon’s Mechanical Turk website during the pandemic and found that mental health symptoms after hindrance stressors were more severe in those who felt a “calling” to their work ( Work & Stress , Vol. 35, No. 2, 2021 ). “Encountering these demands that you can’t control and that harm your performance is going to be particularly impactful for those who feel called to do the work and feel the work is highly important,” Britt said.
Furthermore, in a study of emergency department physicians, Britt and his colleagues found that a sense of meaning in work did not buffer doctors from mental health strain early in the pandemic ( Applied Psychology , online first publication, 2020 ). That was a surprise, Britt said, but it may indicate that when hindrance stressors become too overwhelming, a sense of purpose isn’t enough to rescue one’s sense of well-being at work.
Leading to motivate
One lesson from these findings is that workplaces need to make sure their employees have the basic resources they need to perform their job duties, Britt said. In times of crisis, workers also need extra time to rest and recover from stress. Listening to employee feedback and responding to their needs can help administrators and managers reduce hindrance stressors among their workers.
There are also strategies that workers themselves can use to boost their own motivation, Diefendorff said. These range from motivation-control strategies, such as setting subgoals and rewards for meeting them, to attention-control strategies to minimize disruptions and interruptions. Emotion-regulation strategies such as minimizing anxiety and worry can also be helpful for goal-setting, he said. But workers might also need to recognize when they’re too tapped out to use these strategies effectively. “You have to have self-compassion, which basically means cutting yourself some slack as a way to give yourself the time and space you need to try to recover your depleted resources,” Diefendorff said.
In general, Amabile said, managers can help by encouraging employees to see ways in which their work is meaningful and by providing clear goals and benchmarks for progress. Step back, micromanagers: The most motivationally beneficial leadership style is one that encourages employees to manage their own workflows and solve their own problems.
This style is called leader autonomy support, and it’s characterized by a manager who encourages their employees to self-initiate tasks, to share their own perspectives, and to make their own choices, while still stepping in to support them when needed.
A meta-analysis led by Ryan found that leader autonomy support fosters employees’ sense of autonomy, competence, and relatedness within the workplace, which boosts autonomous work motivation. This self-derived motivation, in turn, is linked to feelings of well-being and engagement as well as declines in distress and improvements in positive behaviors at work ( Motivation and Emotion , Vol. 42, No. 5, 2018 ). The meta-analysis included studies from multiple countries, including Iran, the Philippines, Korea, Bulgaria, Holland, China, New Zealand, and South Africa. Ryan said that this beneficial effect of leader autonomy support seemed to hold in workplaces worldwide and that autonomy improved productivity, commitment, and satisfaction with work in both collectivist and individualistic societies.
“Regardless of culture, if you don’t have a sense of freedom and choice in your work activities, your well-being is undermined,” Ryan said.
Putting research in action
With the onset of the pandemic, motivational experts, like many other workers, moved online. Ryan and his colleagues at his consulting business, motivationWorks , found themselves coaching business leaders dealing with vastly different circumstances. Managers suddenly working with largely remote teams had to find ways to support their employees’ sense of competence to help them tackle the challenges that remote work created, Ryan said. Managers overseeing essential workers, on the other hand, faced a different set of issues.
“Especially in the health care industry, where we are doing extensive work, job stressors were manifold,” Ryan said. “Here, again, autonomy-supportive leaders were better able to hear and respond to the needs of their employees, which was crucial during this challenging period.”
Motivation research applies to a broad range of workplaces, far beyond the stereotypical white-collar office setting. Ryan and his colleagues found, for example, that autonomy, feelings of competence, and feelings of relatedness or connection within the workplace all positively influence job satisfaction and general mental health in a factory setting ( Journal of Applied Social Psychology , Vol. 23, No. 21, 1993 ). A case study led by Philip Cheng-Fei Tsai, PhD, of Wenzao Ursuline University of Languages in Taiwan, that analyzed a Taiwanese manufacturing company undergoing a downsizing found that while managers thought factory workers were most motivated by the company’s salary and benefit structure and the opportunity for education and training, the factory workers were actually most driven by relationships with their colleagues and the extent to which their jobs allowed them to cultivate their relationships with their families ( Journal of World Business , Vol. 42, No. 2, 2007 ).
“In context where people can feel a sense of autonomy, where they can feel a sense of competence, and where they can feel connected and related to the people around them, that’s where they have the highest-quality motivation,” Ryan said.
Fowler saw a particularly emotional example of this in her work with a large construction firm during the pandemic. A supervisor she was working with noticed that one of his employees was frequently late and struggling at work. The supervisor made a stab at connection and asked the employee if he was homeschooling his kids, pointing out that remote learning was a struggle in his own home. The employee broke down. His wife was an emergency room nurse, he said. They had two kids in early elementary school and no family help. He was working around the clock to try to juggle it all.
The supervisor called together his team and explained the situation. Working together, the rest of the team shuffled their own schedules to make life easier for the struggling father. The result, the supervisor told Fowler, was that the entire staff felt like they were doing something good. Given choice and autonomy, they could support the family of a health care worker and feel a sense of connectedness rather than inconvenience.
“[The supervisor] said, ‘I learned that being empathetic and just having a casual conversation with someone may be one of the greatest gifts I can give my people as a leader,’” Fowler said.
Emotional connection can be powerful. In his work with business leaders, clinical and organizational psychologist and consultant George Kohlrieser, PhD, focuses on bonding. This can be a hard sell in some business cultures—he counts among his success stories a heavy-machinery dealership in South Carolina where he helped change the culture from one of aloof detachment to one where employees felt bonded to one another. Such connections foster employees’ sense of psychological safety, or the feeling that the workplace is a safe environment to take risks and be vulnerable.
With vaccination widely available in the United States, employers are increasingly calling workers back into offices. They’ll need to feel safe there—not only from new outbreaks of COVID-19 but also from the new uncertainties introduced by a year or more of remote work. Many industries are turning to hybrid solutions for employees who can work from home and who have realized that they don’t want to go back to cubicles and commutes, Ryan said.
“People have been able to experience firsthand that they can self-regulate their work efforts and also balance work demands with the things that matter most outside of work,” Ryan said. “Their horizons have been expanded, and I think we will see increasing demands for empowering work conditions.”
The key detail to making this work, Fowler said, is ensuring that every employee gets equal consideration, even if the ultimate workplace arrangement isn’t the same across the entire company. Some jobs require face time more than others, she said, but those employees should still have their needs considered and be offered as much autonomy as possible. Certain types of job training or mentoring, for example, might need to be done in person, but employees could still get opportunities to autonomously decide when or how they fulfill these responsibilities.
“Not everyone is going to get the same deal, but everyone should have the same consideration and conversation,” Fowler said.
Life span motivation
Not all workplacerelevant research starts out in studies of employees. Carol S. Dweck, PhD, a professor of psychology at Stanford University, did much of her early research on how the types of goals people have influence their levels of motivation in school. She found that when students were motivated by the desire to learn and become better at something, they bounced back from failure much more readily than when they were motivated by external carrots and sticks, such as the desire to get outside approval or avoid negative judgment ( Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , Vol. 54, No. 1, 1988 ). Out of this research, Dweck and her colleagues coined the well-known notion of a “growth mindset,” which views intelligence as malleable and failure as an opportunity to learn.
Expanding out of the educational system, Dweck and her colleagues have discovered that their growth mindset framework applies in workplaces. For example, they’ve found that the more that employees view their company leadership as cultivating a growth mindset—rather than a fixed mindset in which ability and intelligence are immutable—the greater trust and commitment they have in their organization ( Academy of Management Annual Meeting Proceedings , 2018 ).
Researchers who study motivation in schools also provide perspective on how to teach motivation habits early, as well as how to avoid squelching kids’ intrinsic motivation before they even get their first job interview. These lessons may be particularly important as children return to the classroom after a year of disruptions and remote learning.
“There is pretty strong research that shows that the motivation in academic subjects during adolescence is an extremely strong predictor of people’s career trajectories later in life,” said Eric Anderman, PhD, a professor of educational psychology at The Ohio State University. Unfortunately, the traditional incentives of education don’t do much to kindle that motivation.
“As kids move up through the grades, the focus of school—the purpose of school—becomes more about getting grades and doing well and less about learning,” Anderman said.
Paralleling Dweck’s findings, Anderman and his colleagues have found that taking a mastery-based approach to education rather than a reward-based approach can improve motivation-related outcomes like task efficacy, knowledge, and behavioral intentions ( Journal of Educational Psychology , Vol. 112, No. 5, 2020 ). The hope is that instilling these habits early can immunize people against the motivation-killing norms they might face in the work world.
“In terms of preparing people for the real world, we do have to acknowledge that workplaces are competitive and there are going to be extrinsic outcomes,” Anderman said. “But it’s how we train people to cope with it. We don’t want to send them out of school with the message that they have to be number one at everything.”
Further reading
Mindfulness and its association with varied types of motivation: A systematic review and meta-analysis using self-determination theory Donald, J. N., et al., Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin , 2020
Toward a new curriculum of leadership competencies: Advances in motivation science call for rethinking leadership development Fowler, S., Advances in Developing Human Resources , 2018
Student motivation and associated outcomes: A meta-analysis from self-determination theory Howard, J. L., et al., Perspectives on Psychological Science , 2021
Recommended Reading
Contact apa, you may also like.
More From Forbes
Employee motivation: it really does matter.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
If you’ve ever been stuck in a job with no direction or motivation and have felt extremely discouraged, you’re not alone. Unfortunately, there are many employees who find themselves caught in the same situation. Managers and supervisors are often not taught how to motivate their employees. Regrettably, several management personnel are only advised on the performance-improvement-plan form of management. But often, the carrot produces better results than the stick.
Consider the bosses you’ve had in your career. Who were the good ones, and who were the bad ones, and — most importantly—what was the difference? After some contemplation, you’ll begin to see why the good ones were able to motivate you and make you passionate about coming into work.
Although it’s difficult in the corporate world to find employee satisfaction that is meaningful and lasting, as management, it’s your job to see to it your employees feel appreciated, which in turn will result in better teamwork, better attitudes and an eagerness to contribute.
Gregg Lederman, in his book CRAVE: You Can Enhance Employee Motivation in 10 Minutes by Friday , explains, “Strategic employee recognition is a management discipline that goes way beyond 'being the right thing to do.' Recognition should not be viewed only as a feel-good, altruistic endeavor. No, it’s a management discipline that should garner significant ROI.”
What makes Susan feel rewarded and valued won’t be the same as what motivates Kari or Chad. People are individuals, and being recognized in a way that is meaningful to them shows you care enough about them as individuals to acknowledge them as such. In my years of working with people in leadership positions, I always emphasize the importance of knowing enough about your employees to understand what they value individually as a reward. My advice is: If you don’t know, just ask. Most people are more than happy to relate what makes them feel appreciated.
If you are a supervisor or manager of a group of employees, it’s very important to understand that they aren’t robots. They require a human touch and frequent motivation. As a leader, it is your job to provide that. If you don’t, you’re going to find yourself constantly trying to fill the same positions over and over as unmotivated people get discouraged and quit.
In their book The 5 Languages of Appreciation in the Workplace: Empowering Organizations by Encouraging People , Gary Chapman and Paul White offer , “When leaders actively pursue teaching their team members how to communicate authentic appreciation in the ways desired by the recipients, the whole work culture improves. Interestingly, even managers and supervisors report they enjoy their work more! All of us thrive in an atmosphere of appreciation.”
My clients are often surprised how far a little bit of encouragement propels their employees and organization. In my experience, ignoring or discounting the importance of employee motivation often leads to disengagement.
In the HBR article "4 Reasons Good Employees Lose Their Motivation" (registration required), authors Richard E. Clark and Bror Saxberg offer this advice: “Carefully assessing the nature of the motivational failure — before taking action — is crucial. Applying the wrong strategy (say, urging an employee to work harder, when the reason is that they’re convinced they can’t do it) can actually backfire, causing motivation to falter further.”
They explain that these reasons fit into four categories: values mismatch, lack of self-efficacy, disruptive emotions and attribution errors.
Basically, the first one, values mismatch, means the employee isn’t connected with the value of the task and therefore is disinclined to perform the task. With the second “trap” (as they refer to it), the lack of self-efficacy points to the feeling that the employee is afraid they aren’t capable of performing the task, and so they are fearful of appearing incompetent.
I’ve seen that when employees are overwhelmed with negative emotions, such as frustration or anger, they feel overcome by disruptive emotions, and it interrupts their ability to be motivated enough to perform a task. When the managers I’ve worked with take the responsibility to recognize these signs and remove hindrances that are holding their employees back from their true potential, things change for the better.
It’s important to understand that the work your employees are doing needs to make a difference in some way and for you to help them see it, too. Otherwise, your employees will grow restless and feel automated. It’s up to you to inject some passion and help them to see how valuable they are to the organization. Let your employees know on a frequent basis that they are welcome any time to come to you for feedback and sincere communication, and you will reap the benefits of a motivated workforce.
- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Motivation in a Workplace Essays
Motivation and work performance, motivation and satisfaction at the workplace, popular essay topics.
- American Dream
- Artificial Intelligence
- Black Lives Matter
- Bullying Essay
- Career Goals Essay
- Causes of the Civil War
- Child Abusing
- Civil Rights Movement
- Community Service
- Cultural Identity
- Cyber Bullying
- Death Penalty
- Depression Essay
- Domestic Violence
- Freedom of Speech
- Global Warming
- Gun Control
- Human Trafficking
- I Believe Essay
- Immigration
- Importance of Education
- Israel and Palestine Conflict
- Leadership Essay
- Legalizing Marijuanas
- Mental Health
- National Honor Society
- Police Brutality
- Pollution Essay
- Racism Essay
- Romeo and Juliet
- Same Sex Marriages
- Social Media
- The Great Gatsby
- The Yellow Wallpaper
- Time Management
- To Kill a Mockingbird
- Violent Video Games
- What Makes You Unique
- Why I Want to Be a Nurse
- Send us an e-mail
Home — Essay Samples — Psychology — Personality Psychology — Motivation
Essays on Motivation
🌟 the importance of writing a motivation essay 📝.
Motivation is like that extra sprinkle of magic dust that gives us the boost we need to achieve our goals and dreams ✨✨. It's the driving force behind our actions and the fuel that keeps us going when things get tough. Writing an essay about motivation allows us to delve deeper into this fascinating topic and explore its various aspects. So, why not grab your pen (or keyboard) and let's dive into the world of motivation! 💪📚
🔍 Choosing the Perfect Motivation Essay Topic 🤔
When it comes to choosing a topic for your motivation essay, there are a few things to consider. First, think about what aspect of motivation you find most intriguing. Is it personal motivation, motivation in the workplace, or maybe the psychology behind motivation? Once you have a general idea, narrow it down further to a specific angle that interests you the most.
💡 Motivation Argumentative Essay 💪📝
An argumentative essay on motivation requires you to take a stance and provide evidence to support your viewpoint. Here are ten exciting topics to get those creative juices flowing:
- The role of intrinsic motivation in academic success
- The impact of extrinsic rewards on employee motivation
- Does social media affect motivation levels in teenagers?
- The connection between motivation and self-esteem
- How does motivation differ between genders?
- The influence of music on motivation levels
- Does money truly motivate people in the workplace?
- The effects of positive reinforcement on motivation
- The link between motivation and mental health
- How does goal-setting impact motivation?
🌪️ Motivation Cause and Effect Essay 📝
In a cause and effect essay, you explore the reasons behind certain motivations and their outcomes. Here are ten thought-provoking topics to consider:
- The causes and effects of procrastination on motivation
- How does a lack of motivation impact academic performance?
- The relationship between motivation and success in sports
- The effects of parental motivation on children's achievements
- How does motivation affect mental well-being?
- The causes and effects of burnout on motivation levels
- The impact of motivation on work-life balance
- How does motivation affect creativity and innovation?
- The causes and effects of peer pressure on motivation
- The relationship between motivation and goal attainment
💬 Motivation Opinion Essay 💭📝
In an opinion essay, you express your personal thoughts and beliefs about motivation. Here are ten intriguing topics to spark your imagination:
- Is self-motivation more effective than external motivation?
- Are rewards a necessary form of motivation?
- Should schools focus more on intrinsic motivation?
- The role of motivation in achieving work-life balance
- Is motivation a learned behavior or innate?
- The impact of motivation on personal growth and development
- Does motivation play a significant role in overcoming obstacles?
- Is fear an effective motivator?
- The role of motivation in maintaining a healthy lifestyle
- Can motivation be sustained in the long term?
📚 Motivation Informative Essay 🧠📝
An informative essay on motivation aims to educate and provide valuable insights. Here are ten fascinating topics to explore:
- The psychology behind motivation and its theories
- How to stay motivated in challenging times
- The impact of motivation on personal and professional success
- Motivation techniques for achieving fitness goals
- The role of motivation in leadership and management
- Motivation in the context of mental health and well-being
- The history of motivation research and key figures
- Motivation strategies for students and educators
- Motivation and its connection to creativity and innovation
- Motivation in different cultural and societal contexts
📜 Thesis Statement Examples 📜
Here are a few thesis statement examples to inspire your motivation essay:
- 1. "Motivation, whether intrinsic or extrinsic, plays a pivotal role in driving individuals towards achieving their goals and aspirations."
- 2. "This essay explores the multifaceted nature of motivation, examining its psychological underpinnings, societal influences, and practical applications."
- 3. "In a world filled with challenges and opportunities, understanding the mechanisms of motivation empowers individuals to overcome obstacles and reach new heights of success."
📝 Introduction Paragraph Examples 📝
Here are some introduction paragraph examples for your motivation essay:
- 1. "Motivation is the driving force behind human actions, the invisible hand that propels us toward our goals. It is the spark that ignites the fire of determination within us, pushing us to overcome obstacles and realize our dreams."
- 2. "In a world where challenges often outnumber opportunities, motivation serves as the compass guiding us through life's intricate maze. It is the unwavering belief in our abilities and the fuel that keeps our ambitions burning bright."
- 3. "Picture a world without motivation—a world where dreams remain unfulfilled, talents remain hidden, and aspirations remain dormant. Fortunately, we do not live in such a world, and this essay delves into the profound impact of motivation on human lives."
🔚 Conclusion Paragraph Examples 📝
Here are some conclusion paragraph examples for your motivation essay:
- 1. "As we conclude this journey through the realm of motivation, let us remember that it is the driving force behind our accomplishments, the cornerstone of our achievements. With unwavering motivation, we can surmount any obstacle and turn our aspirations into reality."
- 2. "In the grand tapestry of human existence, motivation weaves the threads of determination, perseverance, and success. This essay's culmination serves as a testament to the enduring power of motivation and its ability to shape our destinies."
- 3. "As we bid farewell to this exploration of motivation, let us carry forward the knowledge that motivation is not just a concept but a potent force that propels us toward greatness. With motivation as our guide, we can continue to chase our dreams and conquer new horizons."
📄 Motivation Research Paper Outline 📄
I. introduction 🌟.
- Definition of Motivation
- Importance of Studying Motivation
- Research Questions or Hypotheses
- Objectives of the Study
- Significance of the Study
- Scope and Limitations
II. Literature Review 📖
- Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
- Herzberg's Two-Factor Theory
- Self-Determination Theory
- Research on Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivation
- Studies on Workplace Motivation
- Impact of Motivation on Performance and Productivity
- Gaps in the Literature
III. Research Methodology 🔬
- Qualitative, Quantitative, or Mixed Methods
- Sampling Techniques
- Sample Size
- Surveys, Interviews, Observations, etc.
- Data Analysis Techniques
- Ethical Considerations
IV. Results and Discussion 💬
- Tables, Graphs, and Charts
- Interpretation of Data
- Comparison with Previous Studies
- Theoretical Implications
- Practical Implications
V. Conclusion 🏁
- Summary of Findings
- Conclusions Drawn from the Study
- Recommendations for Future Research
- Limitations of the Study
VI. References 📚
- Citations of all Sources Used
VII. Appendices 📑
- Additional Material (e.g., Survey Instruments, Interview Guides)
John Proctor’s Motivation in Arthur Miller’s The Crucible
Finding of what motivates you: nick vujicic, made-to-order essay as fast as you need it.
Each essay is customized to cater to your unique preferences
+ experts online
Motivation Letter (bachelor of Business Administration)
The main types of motivation, motivation and its various types, pushing beyond limits: finding motivation to succeed, let us write you an essay from scratch.
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
My Motivation to Study Medical/health Administration
Life as a student-athlete, learning styles and motivation reflection , my motivation to undergo a masters program in business, entrepreneurship, and technology, get a personalized essay in under 3 hours.
Expert-written essays crafted with your exact needs in mind
My Letter of Motivation: Electrical and Electronics Engineering
Assessment of my motivation and values, overview of the motivational theories for business, autonomy, mastery, and purpose: motivation, applying work motivation theories to business situations, drive-reduction theory and motivation, the impact of motivation and affect on judgement, my motivation to study biomedical engineering in the netherlands, research of the theories of motivation: expectancy theory and the equity theory, understanding of my personal motivation, the motivation letter for you, herzberg two-factor theory of motivation, motivation in different aspects of our lives, the importance of motivation in human resource management, my motivation to get a bachelor degree in nursing, my potential and motivation to excel in the field of medicine, my motivational letter: mechanical engineering, motivation letter for computer science scholarship, effective management and motivation of employees, your motivation to do sports.
Motivation is the drive or desire to achieve a goal or take action. Motivational states are commonly understood as forces acting within the agent that create a disposition to engage in goal-directed behavior.
Intrinsic, extrinsic, unconscious, and conscious.
Theories articulating the content of motivation: Maslow's hierarchy of needs, Herzberg's two-factor theory, Alderfer's ERG theory, Self-Determination Theory, Drive theory.
- Motivation can come from both internal (intrinsic) and external (extrinsic) sources.
- Different people are motivated by different things, such as rewards, recognition, or personal satisfaction.
- Setting specific, achievable goals can increase motivation levels.
- Motivation can fluctuate based on external factors like stress, fatigue, or distractions.
- Motivation is closely linked to productivity and success in various aspects of life.
The topic of motivation is important because it plays a crucial role in determining individual behavior, performance, and overall well-being. Understanding what motivates people can help in creating effective strategies for personal growth, goal achievement, and boosting overall satisfaction and success. It is a key aspect of psychology, education, management, and various other fields that aim to enhance human performance and well-being.
Relevant topics
- Growth Mindset
- Procrastination
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Bibliography
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
How to Overcome Burnout and Stay Motivated
- Rebecca Knight

What to do if your work is sapping too much energy.
Even if you love your job, it’s common to feel burnt out from time to time. Perhaps you just wrapped up a big project and are having trouble mustering motivation for the next one. It could be that your home life is taking up more of your energy than usual. Or maybe you’re just bored. What’s the best way to recharge? Are some forms of rejuvenation better than others? How do you know if what you’re feeling is ordinary burnout or something else, like chronic dissatisfaction?
- RK Rebecca Knight is a journalist who writes about all things related to the changing nature of careers and the workplace. Her essays and reported stories have been featured in The Boston Globe, Business Insider, The New York Times, BBC, and The Christian Science Monitor. She was shortlisted as a Reuters Institute Fellow at Oxford University in 2023. Earlier in her career, she spent a decade as an editor and reporter at the Financial Times in New York, London, and Boston.
Partner Center
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Behav Sci (Basel)

Work Motivation: The Roles of Individual Needs and Social Conditions
Thuy thi diem vo.
1 Department of Business Administration, National Taiwan University of Science and Technology, No. 43, Section 4, Keelung Road, Da’an District, Taipei City 106335, Taiwan; wt.ude.tsutn.liam@31880701d (T.T.D.V.); wt.ude.tsutn.liam@nehcwc (C.-W.C.)
Kristine Velasquez Tuliao
2 Graduate Institute of Human Resource Management, National Central University, No. 300, Zhongda Road, Zhongli District, Taoyuan City 320317, Taiwan
Chung-Wen Chen
Associated data.
The data that support this study are publicly available.
Work motivation plays a vital role in the development of organizations, as it increases employee productivity and effectiveness. To expand insights into individuals’ work motivation, the authors investigated the influence of individuals’ competence, autonomy, and social relatedness on their work motivation. Additionally, the country-level moderating factors of those individual-level associations were examined. Hierarchical linear modeling (HLM) was used to analyze data from 32,614 individuals from 25 countries, obtained from the World Values Survey (WVS). Findings showed that autonomy and social relatedness positively impacted work motivation, while competence negatively influenced work motivation. Moreover, the individual-level associations were moderated by the country-level religious affiliation, political participation, humane orientation, and in-group collectivism. Contributions, practical implications, and directions for further research were then discussed.
1. Introduction
Work motivation is considered an essential catalyst for the success of organizations, as it promotes employees’ effective performance. To achieve an organization’s objectives, the employer depends on the performance of their employees [ 1 ]. However, insufficiently motivated employees perform poorly despite being skillful [ 1 , 2 ]. Employers, therefore, need their employees to work with complete motivation rather than just showing up at their workplaces [ 3 ]. Work motivation remains a vital factor in organizational psychology, as it helps explain the causes of individual conduct in organizations [ 4 ]. Consequently, studies on the factors that encourage work motivation can contribute to the theoretical underpinnings on the roots of individual and practical social conditions that optimize individuals’ performance and wellness [ 5 ].
Several decades of research have endeavored to explain the dynamics that initiate work-related behavior. The primary factor examining this aspect is motivation, as it explains why individuals do what they do [ 6 ]. The basic psychological needs have represented a vital rationalization of individual differences in work motivation. Psychological needs are considered natural psychological nutrients and humans’ inner resources. They have a close relationship with individual conduct and have a strong explicit meaning for work performance [ 7 , 8 ]. Different needs are essential drivers of individual functioning due to the satisfaction derived from dealing with them [ 9 ]. In addition to individual-level antecedents, the social context has also been regarded to have implications for work motivation. Social exchange and interaction among individuals accentuate the importance of work motivation as something to be studied with consideration of contextual factors [ 10 ].
Significant contributions have been made to the socio-psychological perspective of work motivation ( Table 1 ). However, current literature shows three deficiencies. First, over 150 papers utilize the key approaches of psychological needs to justify motivational processes in the workplace [ 11 ], which justifies the vital role of psychological needs in interpreting individual work motivation. The association between psychological needs and work motivation has often been implicitly assumed; however, the influence of psychological needs on work motivation has been inadequately tested [ 8 ]. The verification of the extent and the direction of influence will provide a better understanding of, and offer distinct implications for, the facilitation of work motivation. In examining the influence of psychological needs on work motivation, this paper mainly focuses on the intrinsic aspect of motivation. The study of Alzahrani et al. (2018) [ 12 ] argued that although intrinsic motivation is more efficient than extrinsic motivation, researchers have mostly neglected it.
Several investigated predictors of work motivation in general and intrinsic motivation in particular.
| Predictors of Work Motivation | Authors |
|---|---|
| Personal factors (age, gender, educational level, living setting, health status, and family support) | Lin, 2020 [ ] |
| Emotional intelligence | Bechter et al., 2021 [ ] |
| Interpersonal relationship quality | |
| Social exchange | Hinsz, 2008 [ ] |
| Interaction among individuals | |
| Contextual factors | |
| Cultures | Bhagat et al., 1995 [ ]; Erez, 1994/1997/2008 [ , , ] |
| Social situations | Deci & Ryan, 2012 [ ] |
| Psychological needs (but inadequacy) | Olafsen et al., 2018 [ ] |
Second, there is no study examining the country-level moderating effects of social conditions and national cultures on individual relationships between psychological needs and work motivation. Pinder (2014) [ 20 ] argued that contextual practices could influence variables at the individual level. Culture is a crucial factor influencing motivation [ 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 ]. Researchers (e.g., [ 19 ]) have further suggested that both the proximal social situations (e.g., workgroup) and the distal social situations (e.g., cultural values) in which humans operate influence their need for satisfaction and their motivation type. Intrinsic motivation interacts with prosocial motivation in judging work performance [ 21 ]. By including the social conditions in the framework, prosocial motivation is considered. Prosocial motivation refers to the desire to help and promote the welfare of others [ 22 , 23 ]. The study of Shao et al. (2019) [ 24 ] proposed that prosocial motivation promotes employee engagement in particular organizational tasks. Researchers often consider prosocial motivation as a pattern of intrinsic motivation [ 23 ]. This implies that when intrinsic motivation is investigated, prosocial motivation should be examined together to obtain a comprehensive understanding.
Third, there are few studies using a considerable number of cross-national samples to investigate factors influencing work motivation. A cross-cultural analysis makes the findings more objective by minimizing individual bias towards any particular culture. Therefore, the examination of the study is crucial to expanding insights on the influence of social situations on the individual associations between psychological needs and work motivation.
2. Literature Review and Hypothesis Development
2.1. work motivation: a conceptual background.
Work motivation is considered “a set of energetic forces that originate both within as well as beyond an individual’s being, to initiate work-related behavior, and to determine its form direction intensity and duration” [ 20 ]. Nicolescu and Verboncu (2008) [ 25 ] argued that work motivation contributes directly and indirectly to employees’ performance. Additionally, research (e.g., [ 26 ]) has postulated that work motivation could be seen as a source of positive energy that leads to employees’ self-recognition and self-fulfillment. Therefore, work motivation is an antecedent of the self-actualization of individuals and the achievement of organizations.
Literature has identified several models of work motivation. One of the primary models is Maslow’s (1954) [ 27 ] need hierarchy theory, which proposes that humans fulfill a set of needs, including physiological, safety and security, belongingness, esteem, and self-actualization. Additionally, Herzberg’s (1966) [ 28 ] motivation-hygiene theory proposed that work motivation is mainly influenced by the job’s intrinsic challenge and provision of opportunities for recognition and reinforcement. More contemporary models also emerged. For instance, the study of Nicolescu and Verboncu (2008) [ 25 ] has categorized the types of motivation into four pairs, including positive-negative, intrinsic-extrinsic, cognitive-affective, and economic-moral spiritual. Additionally, Ryan and Deci [ 29 ] focused on intrinsic motivation and extrinsic motivation.
With the existence of numerous factors that relate to work motivation, this paper mainly focuses on intrinsic motivation. Previous research found that emotional intelligence and interpersonal relationship quality predict individuals’ intrinsic motivation [ 14 ]. Additionally, the study of Lin (2020) [ 13 ] argued that personal factors, including age, gender, educational level, living setting, health status, and family support, impact people’s intrinsic motivation. To understand more about intrinsic motivation, the authors examined individuals’ psychological needs. Fulfillment of the basic needs is related to wellness and effective performance [ 7 ]. Since intrinsic motivation results in high-quality creativity, recognizing the factors influencing intrinsic motivation is important [ 5 ].
Although a significant number of important contributions have been made regarding intrinsic motivation, self-determination theory is of particular significance for this study. Self-determination theory (SDT) postulates that all humans possess a variety of basic psychological needs. One of the primary crucial needs is the need for competence [ 30 , 31 ], which makes individuals feel confident and effective in their actions. Additionally, the need for autonomy [ 32 ] is one of the important psychological needs, which makes people satisfied with optimal wellness and good performance obtained as a result of their own decisions. Moreover, SDT proposed the crucial importance of interpersonal relationships and how social forces can influence thoughts, emotions, and behaviors [ 33 ]. This means that the psychological need for social relatedness [ 34 ] also plays a significant role in human’s psychological traits. Individuals need to be cared for by others and care for others to perceive belongingness. The need for relatedness can motivate people to behave more socially [ 35 ].
Prior research (e.g., [ 36 ]) has explored self-determination theory and related theories as approaches to work motivation and organizational behavior. The study of Van den Broeck et al. (2010) [ 37 ] emphasized grasping autonomy, competence, and relatedness at workplaces. This paper contributes to the exhaustive understanding of intrinsic work motivation influenced by further examining the impact of these three factors on work motivation as well as the moderating effects of social contexts.
2.2. Main Effect
2.2.1. individuals’ competence and work motivation.
Competence is “the collective learning in the organization, especially how to coordinate diverse production skills and integrate multiple streams of technologies” [ 38 ]. The study of Hernández-March et al. (2009) [ 39 ] argued that a stronger competence was commonly found in university graduates rather than those without higher education. Competence has been considered a significant factor of work motivation that enhances productivity and profits. Harter’s (1983) [ 40 ] model of motivation proposed that competence enhances motivation because competence promotes flexibility for individuals [ 41 ]. Likewise, Patall et al. (2014) [ 42 ] indirectly argued that competence positively affects work motivation. Individuals become more engaged in activities that demonstrate their competence [ 6 ]. When people perceive that they are competent enough to attain goals, they generally feel confident and concentrate their efforts on achieving their objectives as soon as possible for their self-fulfillment.
Individuals’ competence positively relates to their work motivation.
2.2.2. Individuals’ Autonomy and Work Motivation
Autonomy is viewed as “self-determination, self-rule, liberty of rights, freedom of will and being one’s own person” [ 43 ]. Reeve (2006) [ 44 ] argued that autonomy is a primary theoretical approach in the study of human motivation and emotion. Autonomy denotes that certain conduct is performed with a sense of willingness [ 30 ]. Several researchers (e.g., [ 45 ]) investigated the positive relationship between individuals’ autonomy and work motivation. When humans are involved in actions because of their interest, they fully perform those activities volitionally [ 36 ]. Dickinson (1995) [ 46 ] also proposed that autonomous individuals are more highly motivated, and autonomy breeds more effective outcomes. Moreover, when individuals have a right to make their own decisions, they tend to be more considerate and responsible for those decisions, as they need to take accountability for their actions. Bandura (1991) [ 47 ] has argued that humans’ ability to reflect, react, and direct their actions motivates them for future purposes. Therefore, autonomy motivates individuals to work harder and overcome difficulties to achieve their objectives.
Individuals’ autonomy positively relates to their work motivation.
2.2.3. Individuals’ Social Relatedness and Work Motivation
The psychological need for social relatedness occurs when an individual has a sense of being secure, related to, or understood by others in the social environment [ 48 ]. The relatedness need is fulfilled when humans experience the feeling of close relationships with others [ 49 ]. Researchers (e.g., [ 34 ]) have postulated that the need for relatedness reflects humans’ natural tendency to feel associated with others, such as being a member of any social groups, or to love and care as well as be loved and cared for. Prior studies have shown that social relatedness strongly impacts motivation [ 50 , 51 , 52 ]. Social relatedness offers people many opportunities to communicate with others, making them more motivated at the workplace, aligning them with the group’s shared objectives. Marks (1974) [ 53 ] suggested that social relatedness encourages individuals to focus on community welfare as a reference for their behavior, resulting in enhanced work motivation. Moreover, when individuals feel that they relate to and are cared for by others, their motivation can be maximized since their relatedness need is fulfilled [ 54 ]. Therefore, establishing close relationships with others plays a vital role in promoting human motivation [ 55 ]. When people perceive that they are cared for and loved by others, they tend to create positive outcomes for common benefits to deserve the kindness received, thereby motivating them to work harder.
Individuals’ social relatedness positively relates to their work motivation.
Aside from exploring the influence of psychological needs on work motivation, this paper also considers country-level factors. Previous research (e.g., [ 56 ]) has examined the influence of social institutions and national cultures on work motivation. However, the moderating effects of country-level factors have to be investigated, given the contextual impacts on individual needs, attitudes, and behavior. Although social conditions provide the most common interpretation for nation-level variance in individual work behaviors [ 57 ], few cross-national studies examine social conditions and individual work behaviors [ 56 ]. Hence, this paper investigates the moderating effects, including religious affiliation, political participation, humane orientation, and in-group collectivism, on the psychological needs-work motivation association.
A notable theory to explain the importance of contextual factors in work motivation that is customarily linked with SDT is the concept of prosocial motivation. Prosocial motivation suggests that individuals have the desire to expend efforts in safeguarding and promoting others’ well-being [ 58 , 59 ]. It is proposed that prosocial motivation strengthens endurance, performance, and productivity, as well as generates creativity that encourages individuals to develop valuable and novel ideas [ 21 , 60 ]. Prosocial motivation is found to interact with intrinsic motivation in influencing positive work outcomes [ 21 , 61 ]. However, there are few studies examining the effects of prosocial motivation on work motivation [ 62 ].
Utilizing the concept of prosocial motivation and examining it on a country-level, this paper suggests that prosocial factors promote basic psychological needs satisfaction that reinforces motivational processes at work. Therefore, prosocial behaviors and values may enhance the positive impact of individuals’ basic psychological needs, including competence, autonomy, and social relatedness, on work motivation.
2.3. Moderating Effects
2.3.1. religious affiliation.
Religions manifest values that are usually employed as grounds to investigate what is right and wrong [ 63 ]. Religious affiliation is considered prosocial because it satisfies the need for belongingness and upholds collective well-being through gatherings to worship, seek assistance, and offer comfort within religious communities. Hence, religious affiliation promotes the satisfaction of individuals’ psychological needs, which directs motivation at work and life in general. Research (e.g., [ 64 ]) has argued that religious affiliation is an essential motivational component given its impact on psychological processes. The study of Simon and Primavera (1972) [ 65 ] investigated the relationship between religious affiliation and work motivation. To humans characterized by competence, autonomy, and social relatedness, attachment to religious principles increases their motivation to accomplish organizational goals. Religious membership will increase the influence of psychological needs on work motivation. The tendency of individuals affiliated with any religion to be demotivated is lower compared to those who are not. Individuals with religious affiliations also tend to work harder as the virtue of hard work is aligned with religious principles. Accordingly, religious affiliation may enhance the positive association between individuals’ psychological needs and work motivation.
2.3.2. Political Participation
Political participation, indicated by people’s voting habits, plays a crucial role in ensuring citizens’ well-being and security [ 66 ]. Political participation encourages shared beliefs and collective goals among individuals [ 67 ]. The communication and interaction among people help them grasp the government’s developmental strategies, motivating them to work harder. Political participation is a collective pursuit that makes societal members feel more confident, socially related, and motivated at work to achieve communal targets. Increased political participation reinforces effective public policy to enhance its members’ welfare, congruent with the perspectives of prosocial motivation. The prosocial values and behaviors derived from political participation satisfy human needs and interact positively with intrinsic motivation. Therefore, political participation may strengthen the positive influence of individuals’ competence, autonomy, and social relatedness on work motivation. Conversely, poor political participation is perceived as a separation from the society that may lead to demotivation. In a society with poor political participation, an individualistic mentality is encouraged, thereby decreasing the desire to pursue cooperative endeavors.
2.3.3. Humane Orientation
GLOBE characterizes humane orientation as “the degree to which an organization or society encourages and rewards individuals for being fair, altruistic, generous, caring, and kind to others” [ 68 ]. Research (e.g., [ 69 , 70 ]) has argued that a high humane orientation encourages members to develop a strong sense of belonging, commit to fair treatment, and manifest benevolence. The desire to help others or enhance others’ well-being indicates prosocial values and behaviors [ 71 , 72 ]. Since humane orientation is correlated with philanthropy and promotes good relations, this cultural value may enhance work motivation. Fairness, which is derived from a humane-oriented society, is one of the most vital influences on work motivation [ 1 ]. Moreover, altruism, promoted by humane-oriented societies, encourages individuals to sacrifice individual interests for shared benefits. Altruism then encourages attachment to others’ welfare and increases resources needed for prosocial behaviors such as work [ 73 , 74 ]. Members of humane-oriented countries view work in a positive light—it is an opportunity for them to perform altruistic behaviors and engage in collective actions. Therefore, people are more likely to work harder for common interests in humane-oriented societies. In such conditions, individuals with competence, autonomy, and social relatedness will be more motivated to work. By contrast, a less humane-oriented society gives prominence to material wealth and personal enjoyment [ 75 ]. Although this may be perceived as a positive influence on the association between psychological needs and work motivation, such an individualistic mindset works against the prosocial factors that further motivate individuals.
2.3.4. In-Group Collectivism
House et al. (2004) [ 68 ] defined in-group collectivism as “the degree to which individuals express pride, loyalty, and cohesiveness in their organizations or families”. Collectivistic cultures indicate the need for individuals to rely on group membership for identification [ 76 ]. High collectivism enhances equity, solidarity, loyalty, and encouragement [ 77 , 78 ]. Humans living in a collectivist culture are interdependent and recognize their responsibilities towards each other [ 79 ]. In-group collectivism transfers the concepts of social engagement, interdependence with others, and care for the group over the self (e.g., [ 79 , 80 , 81 ], thereby motivating individuals to work harder for the common interests. Oyserman et al. (2002) [ 82 ] have further argued that individualistic values encourage an independent personality, whereas collectivistic values form an interdependent one. Therefore, in-group collectivism is a prosocial value that emphasizes the importance of reciprocal relationships and encourages people to work harder to benefit the group. By contrast, low collectivism promotes individual interests and personal well-being while neglecting the value of having strong relations with others [ 70 ]. Considering that in-group collectivism promotes individuals’ prosocial behaviors of individuals, people who are competent, autonomous, and socially related to collective societies are less likely to be demotivated at the workplace. Consequently, in-group collectivism may intensify the positive influence of individuals’ competence, autonomy, and social relatedness on their work motivation.
(a–d): The positive relationship between individuals’ competence and their work motivation is enhanced as religious affiliation (a), political participation (b), humane orientation (c), and in-group collectivism (d) increase.
(a–d): The positive relationship between individuals’ autonomy and their work motivation is enhanced as religious affiliation (a), political participation (b), humane orientation (c), and in-group collectivism (d) increase.
(a–d): The positive relationship between individuals’ social relatedness and their work motivation is enhanced as religious affiliation (a), political participation (b), humane orientation (c), and in-group collectivism (d) increase.
3.1. Sample
The data came from the seventh wave (2017–2021) of the World Values Survey (WVS) [ 83 ], which examines humans’ beliefs and values. This survey is performed every five years to explore changes in people’s values and perceptions. Face-to-face interviews, or phone interviews for remote areas, were conducted by local organizations. Almost 90 percent of the world’s population is represented in the WVS. At least 1000 individuals were selected as respondents to exhibit each nation’s population. Further information regarding the WVS can be reached at the WVS website ( http://www.worldvaluessurvey.org , accessed on 14 October 2021).
The samples of this study were based on the availability of national-level data for the moderators and individual-level data for the measures of independent and dependent variables. Respondents without answers on the individual measures and corresponding country-level data were excluded from the analysis. The final data included 32,614 respondents in 25 countries aged 18 and above. The 25 countries included Argentina, Australia, Brazil, China, Colombia, Ecuador, Egypt, Germany, Greece, Guatemala, Hong Kong, Indonesia, Iran, Japan, Kazakhstan, Malaysia, Mexico, New Zealand, Philippines, Russia, South Korea, Taiwan, Thailand, Turkey, and the USA.
3.2. Dependent Variable
Consistent with previous researchers (e.g., [ 84 ]), the authors used four items to gauge individual work motivation, namely “Indicate how important work is in your life”, “People who do not work turn lazy”, “Work is a duty towards society”, and “Work should always come first, even if it means less spare”. The first item was measured on a scale from 1 to 4, in which lower scores indicate a higher level of work importance. The other three items were gauged on a scale from 1 to 5 (1 indicating strongly agree and 5 indicating strongly disagree). The scores for each item were reverse coded, and the mean scores were computed so that higher scores indicate greater work motivation.
3.3. Independent Variables
The independent variables of this study include individuals’ competence, autonomy, and social relatedness. First, people’s competence was measured by the item “What is the highest educational level that you attained” on a scale from 0 to 8, in which higher scores indicate a higher level of educational attainment. The authors used the item to gauge individual competence, as a capacity for learning is highlighted in the examination of competence [ 39 ]. Second, a scale from 1 to 10 was utilized to measure the item “How much freedom of choice and control”, which represented individual autonomy (1 indicating no choice at all and 10 indicating a great deal of choice). The authors used the item to gauge people’s autonomy as this item indicates the degree to which individual can make their own decisions. Finally, the individual’s social relatedness was gauged by twelve items, representing twelve types of organizations where individuals are active/inactive members or do not belong. The twelve items were measured on a scale from 0 to 2 (0 indicating do not belong, 1 indicating inactive member, and 2 indicating active member). The mean score of the twelve items represents the individual’s social relatedness. The membership in organizations represents social relatedness, as this indicates the reciprocal relationship between the individual and the organization through their mutual rights, responsibilities, and obligations towards each other [ 85 ].
3.4. Moderators
The four country-level moderators in this study were religious affiliation, political participation, humane orientation, and in-group collectivism. Similar to prior research (e.g., [ 86 ]), the authors used the percentage of the country’s population with religious affiliation obtained from Pew Research Center 2015 [ 87 ]. Secondly, the index of voter turnout collected from the International Institute for Democracy and Electoral Assistance [ 88 ] was utilized to gauge political participation. Voting habits are an indicator of an individual’s presence in their country’s life, and a nation with a high index of voter turnout illustrates its substantial degree of political participation [ 89 ]. Finally, two cultural values, including humane orientation and in-group collectivism, were obtained from the GLOBE study [ 68 ]. The authors used scores on cultural practices as the moderators for this study because they indicate the actual behaviors as “the way things are done in this culture” [ 68 ].
3.5. Control Variables
Several individual-level and country-level elements related to the dependent variable were considered control variables. The effects of gender, marital status, age, and income level were accounted for, as these four variables are basic personal factors that may impact individual’s motivation [ 90 ]. Gender (1 indicating male and 0 indicating female) and marital status (1 indicating married and 0 indicating other status) were dummy coded. Moreover, age was measured in years, while income level was gauged using a scale from 1 representing the lowest group to 10 representing the highest group. Along with the above individual-level controls, education and family strength were treated as country-level control variables. Education and family are primary institutions that shape individuals’ motivation [ 91 , 92 ]. Similar to prior researchers (e.g., [ 93 ]), education was computed as two-thirds of the adult literacy rate attained from the UNESCO Institute for Statistics 2020 [ 94 ] and one-third of the mean years of schooling obtained from the Human Development Report 2020 [ 95 ]. This score is commonly approved as representing access to education in a country [ 42 ]. Regarding family strength, the score was quantified by the ratio of divorces to marriages per 1000 members of the population consistent with previous researchers (e.g., [ 93 ]). The data was obtained from the United Nations Demographic Yearbook [ 96 ].
3.6. Measurement and Analysis
To perform the descriptive statistics, cross-level correlations, scale reliability, confirmatory factor analysis, convergent validity, and discriminant validity, the authors utilized SPSS software.
The framework of this study considers independent variables, dependent variables, and moderators at different levels. Thus, the authors used a hierarchical linear model (HLM) [ 97 ] to test the hypotheses. HLM was defined as a “complex form of ordinary least squares (OLS) regression that is used to analyze variance in the outcome variables when the predictor variables are at varying hierarchical levels” [ 98 ]. This technique evaluates the impacts of higher-level outcomes on lower-level ones while preserving an appropriate degree of analysis [ 99 ]. HLM has been employed in several cross-level studies (e.g., [ 100 , 101 ]).
Table 2 presents a matrix of correlations and sample statistics from the individual-level to country-level variables. Table 3 and Table 4 report convergent and discriminant validity test results, respectively. Finally, Table 5 illustrates results for hypotheses testing using HLM. Three models are presented in the table: those of individual-level main effects and control variables (Model 1), those of country-level main effects (Model 2), and country-level moderating effects (Model 3).
Descriptive statistics, cross-level correlations and scale reliability a,b,c .
| Mean | SD | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.52 | 0.66 | (0.6) | |||||||||||||
| 3.72 | 2.03 | −0.160 ** | |||||||||||||
| 7.12 | 2.20 | 0.014 ** | 0.067 ** | ||||||||||||
| 3.07 | 4.31 | 0.012 * | 0.024 ** | 0.059 ** | (0.9) | ||||||||||
| 83.55 | 18.49 | 0.186 ** | −0.165 ** | 0.043 ** | 0.076 ** | ||||||||||
| 66.01 | 18.29 | −0.077 ** | −0.076 ** | 0.081 ** | 0.064 ** | 0.215 ** | |||||||||
| 4.15 | 0.45 | 0.150 ** | −0.180 ** | −0.014 * | 0.173 ** | 0.258 ** | 0.097 ** | ||||||||
| 5.32 | 0.66 | 0.329 ** | −0.239 ** | −0.068 ** | −0.057 ** | 0.464 ** | −0.091 ** | 0.334 ** | |||||||
| 0.45 | 0.50 | 0.072 ** | 0.082 ** | −0.005 | −0.002 | −0.016 ** | −0.028 ** | −0.050 ** | −0.010 | ||||||
| 0.57 | 0.50 | 0.036 ** | −0.060 ** | −0.018 ** | 0.014 * | −0.055 ** | −0.008 | 0.092 ** | 0.021 ** | 0.020 ** | |||||
| 44.17 | 16.34 | −0.034 ** | −0.186 ** | −0.023 ** | −0.021 ** | −0.204 ** | 0.020 ** | −0.075 ** | −0.192 ** | 0.030 ** | 0.248 ** | ||||
| 4.79 | 2.07 | −0.046 ** | 0.299 ** | 0.136 ** | 0.056 ** | −0.001 | 0.029 ** | −0.034 ** | −0.102 ** | 0.036 ** | 0.043 ** | −0.109 ** | |||
| 65.40 | 7.31 | −0.035 ** | 0.005 | −0.043 ** | −0.051 ** | −0.111 ** | −0.069 ** | −0.226 ** | 0.087 ** | 0.013 * | 0.011 | 0.002 | −0.038 ** | ||
| 0.30 | 0.17 | −0.227 ** | 0.195 ** | 0.015 ** | −0.099 ** | −0.384 ** | 0.017 ** | −0.393 ** | −0.450 ** | 0.040 ** | −0.054 ** | 0.157 ** | 0.058 ** | 0.206 ** |
a n = 32,614 level 1; n = 25, level 2. b * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. c The reliability found in the parentheses is expressed as Cronbach’s alpha for scales with ≥four items.
Convergent validity.
| Composite Reliability (CR) | Average Variance Extracted (AVE) | |
|---|---|---|
| Work motivation | 0.744 | 0.431 |
| Social relatedness | 0.889 | 0.404 |
Discriminant validity—Fornell and Larcker’s criterion.
| Work Motivation | Social Relatedness | |
|---|---|---|
| Work motivation | 0.657 | |
| Social relatedness | 0.012 * | 0.636 |
* p < 0.05.
HLM results: (The DV is work motivation) a,b .
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | SE | Coefficient | SE | Coefficient | SE | ||||
| −0.063 | 0.006 | *** | −0.063 | 0.006 | *** | −0.063 | 0.006 | *** | |
| 0.036 | 0.005 | *** | 0.037 | 0.005 | *** | 0.036 | 0.005 | *** | |
| 0.042 | 0.006 | *** | 0.042 | 0.006 | *** | 0.042 | 0.006 | *** | |
| 0.010 | 0.061 | 0.007 | 0.062 | ||||||
| −0.064 | 0.054 | −0.064 | 0.055 | ||||||
| 0.019 | 0.059 | 0.033 | 0.060 | ||||||
| 0.297 | 0.066 | *** | 0.288 | 0.067 | *** | ||||
| −0.013 | 0.007 | † | |||||||
| −0.000 | 0.006 | ||||||||
| 0.032 | 0.007 | *** | |||||||
| 0.042 | 0.007 | *** | |||||||
| −0.009 | 0.007 | ||||||||
| 0.012 | 0.006 | * | |||||||
| 0.012 | 0.006 | † | |||||||
| 0.011 | 0.007 | ||||||||
| −0.006 | 0.009 | ||||||||
| −0.013 | 0.008 | ||||||||
| 0.019 | 0.007 | ** | |||||||
| −0.020 | 0.008 | * | |||||||
| 0.067 | 0.005 | *** | 0.067 | 0.005 | *** | 0.068 | 0.005 | *** | |
| 0.011 | 0.006 | * | 0.011 | 0.005 | * | 0.013 | 0.006 | * | |
| 0.025 | 0.006 | *** | 0.026 | 0.006 | *** | 0.027 | 0.006 | *** | |
| 0.002 | 0.006 | 0.002 | 0.006 | 0.003 | 0.006 | ||||
| −0.014 | 0.079 | −0.054 | 0.056 | −0.052 | 0.057 | ||||
| −0.218 | 0.080 | * | −0.067 | 0.062 | −0.077 | 0.062 | |||
a , n = 32,614 level 1; n = 25, level 2. b , †, p < 0.10, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.
For the confirmatory factor analysis, previous research (e.g., [ 102 , 103 , 104 ]) suggested that analysis of each variable requires at least three items. Factor analysis using statistical software will provide imprecise results if there are fewer than three items per variable [ 105 ]. Therefore, the authors only performed Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) for social relatedness and work motivation.
To assess the measurement, convergent and discriminant validity were tested. Composite Reliability (CR) and Average Variance Extracted (AVE) were performed to illustrate convergent validity. The study of Hair et al. (2019) [ 106 ] suggested that CR is required to be above a threshold of 0.7. On the other hand, the AVE value should be higher than a threshold of 0.5 [ 107 ]. As shown in Table 3 , CR is acceptable while AVE is slightly lower than a threshold of 0.5. Despite the limitation of AVE, the acceptable result of the discriminant validity is achieved. The discriminant validity was tested using Fornell and Larcker (1981)’s criterion [ 107 ]. This proposes that the square root of the AVE of any latent variable should be higher than its correlation with any other construct. The result of the discriminant validity test indicates that all the two latent constructs have a square root of AVE higher than its correlation with the other construct, as presented in Table 4 .
The authors argued that individuals’ competence (H1), autonomy (H2), and social relatedness (H3) positively relate to their work motivation. However, the findings only supported H2 (β2 = 0.036, p < 0.001) and H3 (β3 = 0.042, p < 0.001). In contrast, the findings presented that H1 was also significant, but in the opposite direction compared with our original prediction. The result suggests that individuals’ competence negatively relates to their work motivation.
In Hypotheses 4a–d, we proposed that higher levels of religious affiliation (4a), political participation (4b), humane orientation (4c), and in-group collectivism (4d) strengthen the relationship described in H1. However, the results only demonstrated support for the two hypotheses, H4c (γ13 = 0.032, p < 0.001) and H4d (γ14 = 0.042, p < 0.001). In contrast, the findings presented that H4a was also significant, but opposite our initial prediction. This different result proposes that a higher level of religious affiliation weakens the association between individuals’ competence and work motivation.
In Hypotheses 5a–d, the authors argued that the higher levels of religious affiliation (5a), political participation (5b), humane orientation (5c), and in-group collectivism (5d) enhance the positive relationship between individuals’ autonomy and their work motivation. However, the results only supported the two hypotheses H5b (γ22 = 0.012, p < 0.05) and H5c (γ23 = 0.012, p < 0.1), while H5a and H5d were not significant.
In Hypotheses 6a–d, the authors argued that the higher levels of religious affiliation (6a), political participation (6b), humane orientation (6c), and in-group collectivism (6d) enhance the positive relationship between individuals’ social relatedness and their work motivation. However, the results only supported H6c (γ33 = 0.019, p < 0.01). In contrast, the findings indicated that H6d was also significant, but in the opposite direction compared to our initial hypothesis. The different result suggests that higher in-group collectivism weakens the positive association between individuals’ social relatedness and work motivation. Figure 1 , Figure 2 , Figure 3 , Figure 4 and Figure 5 represent the significant moderators of the associations examined.

The association between competence and work motivation at different levels of humane orientation.

The association between competence and work motivation at different levels of in-group collectivism.

The association between autonomy and work motivation at different levels of political participation.

The association between autonomy and work motivation at different levels of humane orientation.

The association between social relatedness and work motivation at different levels of humane orientation.
Regarding the statistical results of the control variables, gender, marital status, and age consistently indicated significant positive relationships with work motivation across three models. On the other hand, family strength indicated a significant negative association to work motivation only in Model 1.
5. Discussion
The study’s objective was to examine the influence of individuals’ competence, autonomy, and social relatedness on their work motivation, as well as the impact of country-level moderators, including religious affiliation, political participation, humane orientation, and in-group collectivism on their relationships. Seven primary findings are crucial in this research. First, people’s autonomy and social relatedness positively relate to their work motivation. This result is in line with the findings of prior researchers (e.g., [ 45 , 52 ]), postulating that humans’ autonomy and social relatedness breeds work motivation. The study of Theurer et al. (2018) [ 108 ] argued that, among motivational elements, autonomy had been found to greatly predict positive work motivation. When people feel they have enough control over their activities, they are more confident and motivated to work. Along with autonomy, humans’ social relatedness promotes communal benefits, thereby motivating people to work harder for their organization. Second, the association between individual competence and work motivation is moderated by cultural values, including humane orientation and in-group collectivism. The findings are consistent with the viewpoints of prior researchers (e.g., [ 69 , 70 , 77 , 78 ]), namely that a society with higher levels of humane orientation and in-group collectivism strengthens altruism, solidarity, loyalty, and the encouragement of individuals, which results in work motivation. Consequently, there will be an increase in the differences in individuals’ competence and work motivation if they live in a society with greater humane orientation and in-group collectivism. Third, political participation and humane orientation moderate the relationship between individual autonomy and work motivation. These results are in line with the investigations of prior researchers (e.g., [18,45), which found that social circumstances and cultural practices promote people’s motivation. Accordingly, the differences in individuals’ autonomy based on their work motivation will be enhanced if they belong to nations with higher political participation and humane orientation. Fourth, the association between social relatedness and work motivation is moderated by humane orientation. Accordingly, in a humane-oriented society, the differences in individuals’ social relatedness based on their work motivation will be strengthened.
The remaining findings were contrary to the original propositions. Pinder (2014) [ 20 ] argued that it is possible to find that contextual practices can influence variables at the individual level in the opposite prediction in motivation research. Fifth, individuals’ competence negatively influences their work motivation. This finding proposes that more competent individuals are less motivated at work. One possible interpretation of this opposite result is that, when the majority of the organization members recognize individuals’ competence, these individuals may perceive that it is not necessary to devote most of their time and energy to work anymore. These individuals may believe that no matter how unwillingly they perform, they are still competent enough because of their prior achievements. Additionally, competent individuals recognize that they have already sacrificed their enjoyment of life for their previous successes; therefore, they tend to offset this by investing their valuable time in other aspects. This is consistent with other researchers’ investigations (e.g., [ 109 ]), which found that low-skilled individuals are more often compelled to engage in regular work activities and are more easily motivated than others. By contrast, highly competent individuals tend to be motivated by challenging tasks and improving themselves through further education. Sixth, the relationship between competence and work motivation is negatively moderated by religious affiliation. This finding suggests that religious affiliation weakens the association between individuals’ competence and work motivation. One possible explanation for this finding is that strong religious beliefs are the foundation for virtuous living [ 110 ]. Individuals with religious affiliation usually employ religious principles to guide their behavior, regardless of their competence. In other words, both competent and incompetent individuals tend to be more motivated at the workplace if they are affiliated with any religion, thereby diminishing the influence of competence in work motivation. Seventh, the relationship between social relatedness and work motivation is negatively moderated by in-group collectivism. This result proposes that a higher degree of in-group collectivism weakens the association between individuals’ social relatedness and work motivation. One possible explanation for this is that, under an in-group collective society, people put more weight on mutual relationships and encourage acts that may build up the solidarity of groups. Since in-group collectivism is viewed as a social attachment in which people emphasize the group over the self (e.g., [ 79 , 80 , 81 ]), individuals are fairly conscious of their responsibility to the group regardless of their social relatedness. Both socially related and unrelated individuals belonging to in-group collective cultures tend to work harder for common goals. Accordingly, the influence of individuals’ social relatedness on their work motivation is reduced.
6. Limitations and Future Research
Despite its significant contributions, this study has its limitations. The use of secondary data represents the fact that the data collection process was beyond the authors’ control. However, the collection of cross-national data is time-consuming and costly. The authors used the available data but strove for the efficient use of multilevel data. The secondary data also limited the measurement of individual-level factors based on the available data. Moreover, it is quite complex to gauge an individual’s work motivation appropriately, since personal work motivation may not be one-dimensional. Nevertheless, the authors made efforts to employ the measurements utilized by prior research. Moreover, it is complicated to measure social factors such as political participation. There are challenges in investigating social contexts due to the absence of direct measurements [ 111 ]. This compels the authors to identify substitute measurements for this study. Finally, this study covered 25 samples from 25 countries with different characteristics. Despite the attempt of this study to include the most relevant social conditions in the framework, the influence of other national differences and cultural sensitivities were not considered.
This paper directs further research considering that several frameworks and approaches should be employed to better examine motivation [ 112 ]. First, as some of the results were opposite to the original propositions based on the theoretical foundations employed, combining different concepts and approaches is necessary to enhance perspectives of psychological needs and social issues. For instance, the relationship between competence and work motivation can be further investigated by employing other theories to understand their association better. Similarly, the moderating effects of social contexts such as religious affiliation and in-group collectivism should be further examined to obtain a more in-depth comprehension of the roles of contextual circumstances and cultural values in individual-level relationships. Additionally, self-determination theory and the concept of prosocial motivation may be used to explore motivation towards specific behavior in organizations, such as organizational citizenship and proactive behaviors. Organizational context, such as rewards, training, and culture, can be considered as part of the framework to enhance the conception of work motivation.
7. Conclusions
This study has utilized a multilevel framework to examine the influence of psychological needs and social context on work motivation. Through this research, a deeper understanding of the roles of competence, autonomy, and social relatedness, as well as social situations and cultural values on work motivation, is achieved. The contrary findings call for integrating other concepts and approaches towards a more comprehensive knowledge of work motivation.
Along with the theoretical contribution, the study’s findings offer practical implications. The satisfaction of psychological needs promotes self-motivation, which creates positive outcomes. Hence, organizations can provide programs and activities to promote employees’ autonomy and social relatedness as this will enhance their work motivation. Employee empowerment can be advocated by encouraging them to make their own decisions at the workplace, providing constructive criticisms rather than instilling the fear of failure. Additionally, managers should encourage solidarity, support, and mutual care among employees. Putting more weight on employees’ fulfillment of needs will further increase employees’ motivation, thereby diminishing costs related to stress or turnover [ 50 ]. To establish a novel mechanism towards promoting work motivation in the entire nation, the government should pay attention to the political structure and conditions that encourage citizens’ participation. Additionally, a culture of humane orientation should be promoted in the workplace and society so that solidarity, kind assistance, and altruism among communities as well as among individuals can be strengthened. For instance, teamwork should be encouraged for employees to help each other overcome difficulties at the workplace or share responsibilities with their colleagues. This will motivate people to work harder for collective goals, contributing to the development of organizations.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.T.D.V. and K.V.T.; data collection, T.T.D.V.; methodology, T.T.D.V. and K.V.T.; formal analysis, T.T.D.V. and K.V.T.; resources, K.V.T. and C.-W.C.; writing-original draft, T.T.D.V. and K.V.T.; writing-review, editing & proofreading, T.T.D.V., K.V.T. and C.-W.C.; visualization, K.V.T.; supervision, K.V.T. and C.-W.C.; project administration, K.V.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
This paper does not receive funding from any individuals or organizations.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Data availability statement, conflicts of interest.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
511 Motivation Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
🏆 best motivation topic ideas & essay examples, 👍 good essay topics on motivation, ✅ most interesting motivation topics to write about, 💡 simple & easy motivation essay titles, 📌 writing prompts for motivation, 🔍 good research topics about motivation, ❓motivation research paper question.
- Empowerment of Students for Their Motivation So, the group of students had to come up with the ideas for the project by sharing their thoughts and encouraging one other. Hence, a teacher’s control and guidance should be clearly presented to the […]
- Social Motivation: Theory and Implications Social motivation is one of the major factors that influence the level of motivation among individuals in society. Fundamentally, positive and negative feedbacks influence the level of social motivation among individuals who aim to achieve […]
- Lack of Motivation Among Children and Its Solutions If we look at the education system, students’ interest to achieve higher education is low; in other words, students have a low motivation towards education, in the current setting.
- Apex Computers: Problems of Motivation Among Subordinates In the process of using intangible incentives, it is necessary to use, first of all, recognition of the merits of employees.
- Consumer Behaviour: Motivational Theories The purpose of this essay is to describe the motivational theories and the affect of it on the buyer or consumer.
- Motivation at Costco Company: Theory and Practices On the other hand, the company’s top executives have been instrumental in the success of Costco in that they ensure effective training and development of the employees and address any issues that might affect the […]
- Companies That Use Expectancy Theory: SAS Motivation The regard given to the employees by the managers at the SAS institute is as directed by the CEO, who feels employees are the best asset the company has. The package and the rewards that […]
- United Way Company: Alderfer’s ERG Theory of Motivation It is the responsibility of the management in any organization to keep its employees motivated in a bid to evade the unpleasant consequences that come with a demotivated staff.
- Compensation and Employee Motivation and Retention in Abu Dhabi National Oil Company Here, the paper expounds on the wide range of compensation schemes in the company and links each to the sustainability of a favorable work environment in the company and the retention of employees.
- Employee Motivation: Theories in Practice Accepting the importance of this approach, one can also admit the reconsideration of the approaches to leadership and motivation as two basic elements needed to create a positive working atmosphere and ensure that all individuals […]
- Motivation in Fashion Industry As a student set to join the industry in the future, my dream is to be the best designer and prioritize the needs of my customers.
- Employee Motivation and Reward at Google One of the factors that make most of the employees wish to work with Google Company is that the company offers an environment that promotes employee growth and development.
- Joining Street Gangs: Theoretical Motivations Both children and adults join street gangs in search for a sense of personal identity mainly due to the failure of social agents including the media, schools and churches.
- The Smart Goal-Setting Process: Motivation and Empowerment In order to achieve success in pursuing a goal, there has to be a way to measure success, which is why the second point of SMART goals theory is that the goals need to be […]
- “Extreme Measures”: Moral Value of Motivation The idea of a good will is closer to the idea of a ‘good person,’ or ‘person of good will.’ The word ‘will’ is discussions to concern by the nature of rational agency.
- The Impact of Goal Setting on Motivation and Success Correct goal setting is needed not only to determine the endpoint accurately but more importantly, it is to motivate and encourage an even faster and more efficient achievement of the goal by minimizing certainty and […]
- “Self-Motivation” by Brandon Clark Review This idea has academic backing behind it Jeske and Axtell report that appreciation of effort is one of the crucial components of fostering motivation in employees and students alike.
- Google Inc.’s Motivation, Principles and Methods This paper looks into the theories and methods used by Google to motivate its employees and the issues that the company is able to solve due to this practice.
- Motivation and Management Motivation is thus a complex problem as far as organizations are concerned due to the variation of the needs, wants as well as the desires.
- Motivation to Succeed in Life: Skills to Succeed and Achieve Aims and Goals Most of the methods usually help me to identify the strengths I have in the skills. This will help me to develop in management of my skills especially in the implementation skills.
- Motivation Theories The tool ensures a pleasurable reward for productivity and in turn creates motivation in employees to become more productive, besides when employees feel that their efforts are being rewarded they will tend to produce more […]
- Work Motivation in Starbucks Company I have performed a detailed analysis of several factors that influence the motivation of the employees of Starbucks and the relationship between these factors and the practices of the company.
- Motivation and Performance The increase in the performance and productivity of individual workers is a primary concern of the company and it is one of the ways that a business is able to counter increasing costs of running […]
- A Career in Acupuncture: Personal Motivation TCM adopts a non-invasive and holistic approach to healing, and it is this style of treatment that I have grown to prefer.
- Motivation and Leadership Theories Any organization that tend to focus on satisfying employee needs is bound to have In the case study Jonathan understands this and tries appreciating the work done by his employees.
- Employee Motivation as a Component of Performance Management Therefore, one of the areas that are given a lot of attention in strategic human resource management is the management of the expectations and demands of employees in organizations. Of critical relevance in employee motivation […]
- Leadership and Motivation: FedEx Corporation and UPS Inc. Introduction Leadership is the process of influencing people to contribute willingly to the goals and objectives of the organization. To solve this problem, the managers of FedEx used 360-degree feedback system to identify the causes […]
- IBM: Employees’ Motivation Strategy IBM is able to provide employees with resources that allow them to meet the immediate physiological and safety needs of Maslow’s hierarchy.
- Student’s Motivational Strategy: Action Research It is also important to review the context of the research, the literature related to the topic and problem, the area of focus and research questions, the intervention details, and the strategies of the data […]
- Employee Motivation at Wal-Mart in China That is, the company’s mission is to meet the expectations of its clients and not employees. In other words, if the factors that motivate employees are fully provided, they are likely to become motivated and […]
- Advantages and Disadvantages Management of Motivation Theories The other part of this advantage is that the company holds on to the excellent performers only, increasing the productivity of the company.
- Managing Employee Motivation Through System Thinking The principles of system thinking mainly caution against finding solutions in isolated parts of a system because the problem is transferred to other areas of the same system.
- The Impact of Motivation on Student’s Performance The goal of this part is to give a thorough summary of the research on student motivation and its effects on behavioral and academic development in school.
- Communication and Motivational Theory Communication is considered as an integral part of everyone’s life and individuals that are successful in both the short and the long run usually stress a lot in the communication processes.
- Motivation in Continuous Education: Back to School I decided to go back to school and change my life because I want to get a degree in human resource management, help to keep the economy growing, and to get a job working for […]
- Motivation and Human Behavior Internal motivation is the opposite, as it is not connected to the external conditions and is interlinked with the unique nature of the action and wants itself.
- Leadership: Providing Purpose, Motivation and Inspiration Purpose refers to the goals that the leader and the organization in general seek to fulfill. As such, a leader must understand and assist the subordinates to meet their personal goals.
- Siemens: Motivation Within a Creative Environment Siemens has a lot of strengths in the business environment through the motivation of its employees within a creative environment. Siemens as also managed in changing its programmes through the involvement of the employees and […]
- The Theoretical Motivations for Serial Killings In order to theorize on the motivation of serial killers, it is obligatory to define the scope of the study. Practically, the most persistent barrier to the utter understanding of the motivation of a serial […]
- Motivational Speaking: Types of Motivators A motivational speaker is a speaker who raises his/her speeches to lift up or motivate the audience. Motivation is basically to help someone to do something good i.e.to increase one’s willingness towards a right thing.
- Motivational Interviewing Owing to the evocative nature of the treatment interaction, this means that the patient is in a better position to make positive changes in his/her behavior.”Resistance” as evidenced in motivational interviewing is regarded as more […]
- Human Resource Motivation in Projects Management To fulfill the frameworks of project management, human resources are required at managerial and project members level.
- Career Development & Employee Motivation Initiatives: Chipotle Introduction Motivation and Organizational Behavior Problem Evaluation Goal of Analysis Hypothesis Recommendations and Solutions Conclusion
- Career Development and Employee Motivation Initiatives at Chipotle However, as revealed in this paper, Chipotle’s vast expansion has resulted in challenges pertaining to the sustainability of its operations and the control of the prevailing business culture. Chipotle’s culture of sustainability, reverence, and growth […]
- Improvement of Achievement Motivation for Learners The learners with the developed extrinsic motivation and external locus of control need to understand the role of the social impact in the process in order to develop their need for excellence.
- Motivation Plan: Operating Room (Surgery Department) The supervisor indicated that the department, especially the operating room, needs the personnel to integrate their competencies in handling different tasks to enhance the wellness of the patients.
- Employee Motivation and Job Satisfaction, Attitude, and Productivity Training and development of employees According to the results of the survey, a great percentage of those interviewed agreed to the fact that companies highly encourage and support education and training of workers.
- The Reason to Motivation Others in Society When they lose hope and no longer see the need to pursue the goals or task, showing them the purpose of such may offer them the necessary motivation to continue to the end; this implies […]
- Building a Better Workplace Through Motivation: Kellogg’s Case SWOT Analysis In the Kellogg’s Case, the writer discusses motivation in places of work by relating theories of motivation to Kellogg’s motivation techniques.
- Motivational Issues in the Fast Food Sector Fast food refers to a type of cuisine produced in mass and marketed by some eateries, presentation stands, and service establishments for fast and effective production and delivery.
- Motivation, Emotion, and Behavior Relationships Therefore, motivation is a result of external and internal desires that relate to the behavior of a person towards meeting a certain goal How people begin moving toward a behavior varies as emotions pull them […]
- Employee’s Lack of Motivation and Its Reasons Therefore, it is proposed to improve it through employee relations, and the first step is to demonstrate to employees that the company wants them to be motivated, which in itself shows that the company cares […]
- The Puzzle of Motivation His argument basically seeks to show that the kind of jobs done in the 21st century require a new approach to answering the question on how employees are to be maximally motivated to do these […]
- Motivation, Values, and Purpose Assignment Therefore, I am motivated to be a part of the community in the present as a student and in the future as a professional.
- Motivation Hypothesis and Theories The process motivated the interns to put in a lot of effort and reach even beyond the company’s objectives. The intern’s motivation resulted from positive attention, which made the intended conduct more likely to occur […]
- Reflection on Motivational Interviewing The other reason that makes MI particularly suitable for counselling adolescents and young adults is because it respects client’s autonomy. It just offers alternatives and allows the client to make choice.
- Motivation in Police Department This is because most of the time those in supervisory levels in the various workplaces do not know how to effectively communicate with their employees, intending to encourage them to work to reach the goals […]
- Motivation and Solution to Motivation Problem Analysis As just mentioned in the introduction, the member of staff in question has been with the company for two years yet he has not been in a position to develop a working relationship with the […]
- Human Factor and Motivation in Aviation Security For this reason, the human factor in aviation security becomes a crucial issue that should be investigated in order to improve this aspect and minimize the probability of error.
- Workplace Motivation: Advantages and Disadvantages The inclusion of new motivational practices has the potential to address the higher needs of different followers. Organizational leaders should be aware of these needs and use the most desirable techniques to motivate their workers.
- The Motivation to Take a Healthy Diet Various intrinsic and extrinsic factors influence the execution of brain in motivating a person to eat a healthy diet. The limbic structure is directly responsible for reward and motivation, a prerequisite factor for changing of […]
- Political Interests Motivations and Opinions The development of democracy influenced the evolution of this issue, making the existence of different points of view on the same issue possible.
- HSBC Bank Middle East Motivation Models and Workers Performance Moreover, the maintenance of workers’ motivation enhances the ability of employees to perform the physical and mental responsibilities to the optimal levels.
- Employee Motivation: Expectancy and Equity Theories With regard to the equity theory, it is recognizable that employees will observe the aspects of impartiality, fairness, and justice practiced by the management. Equity should be exercised within the entire organization and to all […]
- Motivational Strategies Therefore, the focus will be on the efforts of the organizations to motivate their employees and the outcomes of motivation in the organization.
- Research Methods Used in Motivation and Emotion Studies A research method is a procedure for collecting and analyzing data in a way that combines the research purpose of the study and the economy.
- Leadership and Motivation – Carlos Ghosn The purpose of this paper is to present a discussion of theories and concepts of leadership in current multinational businesses using the leadership style of Carlos Ghosn as a benchmark for effective leadership in the […]
- Motivation and Determination in the Film “The Replacements” In the finals, mistreatment of other players by the quarterback, Eddie Martell, causes the team to play poorly almost losing the game; however, help from a motivated Shaun, who returns in the second half, enables […]
- “Eat That Frog!” by Brian Tracy as a Set of Motivation Keys to Achieve Better Results The second important key to success is the ability to concentrate on the most important part of the task, to do it right, and to complete your job.
- Aristotle’s and Freud’s Motivational Theories The efficient cause is the trigger that causes a person to behave in a certain way. These biological instincts are the source of mental or psychic energy that makes human behavior and that it is […]
- Employees Motivation: “How to Kill Creativity?” Consistently with the researcher’s conclusions, it is suggested that the implementation of the abovementioned managerial and leadership practices is conducive to better creativity-related and productivity-associated outcomes and is feasible in the majority of companies.
- Motivation in the Healthcare Field Workplace In this case, the application of Maslow’s theory related to the distribution of needs is a relevant technique that allows focusing on subordinates’ priorities and their behavior in the workplace.
- Motivational Theories and Motivation at Work The first theory is the theory of scientific management developed by Fredrick Winslow Taylor, which argues that workers’ main motivation is payment.
- Lack of Motivation at Work To accomplish this, the paper will identify characteristics and the impact of lack of motivation; possible ways of curbing the problem and, finally, a review of existing literature regarding employee’s motivation.
- Motivation: What Managers Need to Know The manager must however observe that motivational factors may differ or provide different results based on the strategy used.
- Discipline and Child Abuse: Motivation and Goals The first proof of the justice and reasonableness of discipline is that it is permitted by law to be considered to be the most authoritative source to consult.
- Motivation, Behavior, and Connection Between Them Motives that influence certain actions serve as a factor that shapes habits, and the initiative that proceeds is a direct reflection of the characteristics of a person’s character.
- Students’ Motivation in Learning Mandarin Chinese It is quite remarkable that, according to the survey results, a lot of the students find the Chinese language and culture rather enticing, at the same time acknowledging that they do not like some parts […]
- Employee Motivation: Daniel Pink’s Views According to Pink, businesses and organizations should understand the different effects of intrinsic and extrinsic motivation on creativity, productivity, performance, and turnover.
- Improving Front Office Employees Motivation in a Luxury Hotel in Beijing This paper examines the methods used in the motivation of front office employees in the luxury hotels in Beijing such as the Grand Hyatt, the Marriott, and the Park Hyatt.
- Motivation and Organizational Behaviour I have learned that keeping a positive and friendly attitude is very important and leads to motivation. I speak this because that is how I feel and most of the members in my office feel.
- Motivational Theories and Organizational Performance Relations It predicts that, majority of employees will seem to be motivated if they suppose that the reward they expect to get is directly proportional to the work done, and if they value the rewards expected […]
- Intrinsic Motivation in Education The importance of the intrinsic motivation lies in the fact that it is a crucial characteristic, which allows the student to become a successful language learner.
- Motivation Importance in Our Daily Lives Psychologists’ view on origin of motivation The complexity of motivation due to unpredictability and fluctuation from one individual to another and at different times has led to various theories being postulated to explain its causes.
- Leader’s Role in Motivating Workforce This is easier said than done and if one would like to proceed in this course of action then one of the skills that has to be developed is the ability of the manager to […]
- Article’s Comparison: Genre, Target Audience, and Motivation The target audience of the selected texts is, to a certain degree, different: on the one hand, any person can be the reader of the story and article.
- Leadership Style and Employee Motivation: Burj Al Arab Hotel How effective and sustainable is the current leadership approach within the Burj Al Arab in the management of the level of employee motivation? How effective is the function of the current leadership styles in improving […]
- Korean Air Co.’s Communication and Motivation The pilot made assumptions that he would land safely in the bad weather without the advice of the controllers in the control tower.
- Employees Motivation and Organisation’s Performance The main aim of this research study is to analyze the effect of the motivation of the workforce and its impact on the growth of the business organization.
- Motivation: Content and Process Theories in Practice Regarding Anne’s situation, the case portrays the application of content theory in that as one of the first female students to be registered at Midshires University to study engineering; she had identified her needs and […]
- Motivation Theories and Principles According to experts, people get the drive to push for their goals in life whenever they have enough motivation and belief to do it. Motivation plays a crucial role in the ability of living organisms […]
- Consumers’ Motivation and Satisfaction of 5-Star Hotel in China To analyze the motivation of consumers in 5-star hotels in China To analyze the satisfaction of consumers in 5-star hotels in China To establish the pull and push motivation aspects of consumers in 5-star hotels […]
- Tourism Motivation Categories However, the author should have captured the fact that people do not only tour places to get a break from the normal but as they do that they want to go to places they have […]
- Motivation: The Need to Achieve The need to control the events of our lives in order to feel connected to others and be competent in our skills is the primary sources of our motivation.
- Praise and Motivation of Employees Robbins is of the opinion that praise motivates the employees and can be very instrumental in employee motivation than the other incentives.
- Secretary Motivation Incentive Plans The two incentive plans that can motivate secretaries are the “individual incentive pay plans, and the Group incentive pay plan”. Therefore, an organization has to pay careful attention to the introduction of the program and […]
- Management Practices and Employee Motivational Policies Such power to create leads to employee motivation and ultimately benefits organization, assisting in the creation of more flexible work force and at the same time increases exchange of ideas and information amongst employees within […]
- Work Motivation and Reward System The primary factors in the workplace that can impact on the performance and the productivity of the employees are rewards and motivation.
- Employee Motivation and Management at the Nucor Corp. To Nucor, the top managers are required to trust the lower staff with the running of the business and delegate duties to them depending on their contribution to the businesses’ success.
- Consumer Behaviour Motivation in Sport Tourism The author is convinced that there exists no definition of sport and event consumer behavior and that sport consumer behavior represents only consumer behavior relative to the products and services offered mainly in the sport […]
- Give’Em the Pickle! Motivation in Business Thus, the video seems to suggest that lack of motivation is unhealthy for both the client and the concerned business organization.
- Mintz’s Motivation in Sweetness and Power For a long period of time, it was impossible to imagine that sugar was the main cause of people’s exploitation and slavery.
- Loyalty Motivation in “Best Places to Launch a Career” by Tanaka It is based on such factors that a company needs to take into consideration the changing face of workplace loyalty in order to make the appropriate type of hiring decisions and to understand the necessity […]
- The Puzzle of Motivation at the Workplace Dan Pink, in his speech, argues that the model of achieving positive motivation characterized by the use of incentives needs to be updated.
- Employee Motivation Methods and Their Effectiveness As a result, my staff would be more determined to achieve higher standards because they would take part in setting them in the first place.
- The Significance of Strategic Compensation for Employee Motivation and Retention In response to some of the events in the companies that changed them, motivation systems were developed as a counter to the demoralization of employees.
- Communication Failure, Lack of Motivation, and Conflicts as Common Workplace Issues Poor communication can lead to a lack of understanding and awareness, resulting in a breakdown of the relationship between employees, managers, and colleagues.
- Low Motivation and Washback Effect of Examinations In addition to the lack of parental support and inadequate resources, the pressure from examinations can negatively impact students’ motivation in English language learning.
- Personality Traits and Sources of Motivation High extrinsic and intrinsic sources of motivation and the average score in all other traits are true results but I dispute the avoiding tact outcome, with the extrinsic motivation being the main impediment to my […]
- Students’ Motivations Toward Learning In addition, the outcome of this research identified changes in behaviors and attitudes concerning students’ perceptions of learning. The article demonstrates a change in students’ perceptions of their learning effectiveness.
- Nurses’ Work Motivation and the Factors Affecting It The crucial topic of motivation is covered in the article Nurses’ Work Motivation and the Factors Affecting It: A Scoping Review.
- Motivation as a Way to Successful Learning It is likely that the motivation to learn comes from my interest in the subject or because I need that knowledge for something.
- Employee Motivation and Personal Hierarchy of Needs Esteem Needs: A decent salary, respectful attitude on the part of colleagues and management, and confidence in compliance with the position occupied. Security Needs: The availability of security measures in the personal, family, and workspace […]
- Motivational Interviewing Among Medical Workers The interviewer must use the skill of affirmation to ensure that the patient remembers the necessary information. In the case of group therapy, where patients need to be convinced of the need to quit smoking, […]
- The Issues of Student Motivation and Engagement Informing the parents of such benefits has the potential to increase their interest in motivating their children to practice and promote a home-learning environment.
- Motivational Interviewing: Helping People Change Similarly, the softening sustain talk is performed in the manner that allows the patient to reconsider the current status quo and challenge it by shifting toward a healthier diet, which leads to a rating of […]
- Student Motivation and Its Theoretical Aspects The goal of this exploration into the theoretical aspects of motivation is to analyze several theories of motivation and group these theories under the umbrella concept of the influence of sentiments.
- Motivational Strategies for Teamwork When members of a team desire to advance their skills and the team leader cannot offer the opportunities, the team members are likely to be less motivated and therefore perform poorly.
- Motivational Interviewing in a Hospital The approach can be helpful in behavioral change as it promotes offering guidance and helping people to appreciate what is in it for us.
- The Google Company’s Employee Motivation Over the years, the organization has grown to be the best in data collection and technological advantages in artificial intelligence. As a result, Google is one of the greatest businesses to use as a benchmark […]
- Professional Life: Social Interactions, Motivation, and Growth As such, the fact that other people are the source of our emotions is a piece of knowledge necessary in any professional life.
- The Role of Motivation in the Educational Process The student reviewed in the case study has a strong understanding of the sounds, a high level of interest in studying, listening to the lecturer, and is ready and willing to work in groups.
- Motivation in the Workplace: Acceptance and Recognition The verification process in the ACE-V process is vital because it negates bias and minimizes mistakes. The ACE-V method utilizes a new examiner to ensure the analysis, comparison, and evaluation steps are conducted with integrity.
- Case Study of Motivational Issues Firstly, it is the fact that the officer is close to the end of his carrier. He realizes that there is no necessity to gain a significant reputation among the management the attainments of the […]
- Generational Differences Regarding Motivation If the younger generation thinks that the older ones no longer have the motivation to work, the older generation also believes that the young have no purpose and desire to work.
- Motivational and Emotional Factors of Job Acceptance Understanding the primary factors driving Freda’s desire to agree or decline the offer is essential in ascertaining the incentives and drawbacks of each of her choices.
- Work Environment’s Impact on Motivation and Creativity The article “How your work environment influences your creativity” by Teresa Amabile explores the social and environmental influences that promote creativity and the counteractive factors.
- Individual Differences in Selection and Motivation The importance of the individual and unique distinction in employee selection, training, and motivation lies in the following aspects. In this case, it will also be possible to create a particular program of assignments and […]
- School Motivation: The Use of Extrinsic and Intrinsic Motivations I believe that it is the truth that producers are increasing the representation of minorities and people of various genders and sexualities.
- An Employee Motivation Email’s Analysis Part of the manager’s job is to keep the staff motivated; to do so, the manager can apply theoretical frameworks concerning workforce motivation, such as expectancy theory.
- Motivation in Human Organs Transplantation More than half a century has passed since the first transplantation, and throughout this period, the question of the impact of the operation on the duration and quality of life of the donor has been […]
- Motivation Strategies for Learning The first strategy is to build relations of mutual respect and understanding that will help students to socialize in possibly stressful settings. The third option is to build a system of competition among students in […]
- Motivational Team Management: The Case of Capratek In addition, the paper uses Maslow’s theory on the hierarchy of human needs and Herzberg’s Two-Factor theory to create a change management strategy that addresses the confusion in the team.
- Recruiting Team Members: Motivational Manager To attract an appropriate candidate for the position of Motivational Manager, it is essential to evaluate motivational techniques and theories that may help perceive a vacancy as desirable, develop a job posting promotional introduction on […]
- Behavioral Motivation Theory: Ethics, Law, Religion This work aims to identify the ethical and legal foundations of the behavioral motivation theory, provide examples of the manifestation of this concept from a biblical perspective, and determine how the concept relates to the […]
- The Motivation of the Video Game Player For instance, the project gave its players the dynamic and fast pace of the game, a vast and detailed map, various locations, several different weapons, and character skins, and this is not all the possibilities.
- Increasing Employee Motivation for Small Businesses Given the effects of the pandemic on business operations and human resource practices, employee safety and wellbeing has been thrust to the forefront of leadership concerns because it has become increasingly poignant for leaders to […]
- The Effect of Motivation on Cognitive Load Cognitive load is the capacity of working memory and is affected by the design of instructional material. The number of working resources affects the completion of tasks and is influenced by the design of instructional […]
- Factors for Teachers’ Motivation in Distance Learning Efficient communication with the administration of an institution is a crucial factor that affects the motivation of teachers in distance learning.
- Attention, Relevance, Confidence, Satisfaction Model of Motivation in Education To summarize, the element of familiarity can significantly increase the effectiveness of the educational process, relying only on the correct use of the student’s past experience, but it is worth considering the nuances of the […]
- Motivation of Public Sector Employees The research should consider the employees’ expectations from the working experience and the performance in the particular area of the workplace, in our case – the public sector because the expectations according to the area […]
- Managers’ Concern Over Employee Motivation Issues Thus, the responsibility of management is to monitor and direct workers in a company. Even though most people have to work for a livelihood and a job is an essential part of everyone’s lives, administrators […]
- The Puzzle of Motivation: Video Review However, it will not serve as a motivational factor because I will attract the talent by offering them more autonomy and purpose.
- The Structures, Motivations, and Qualities of Terrorist Groups This implies that the structures of terrorist groups are determined by the capacity and character of the government and society where they operate.
- Motivation Theories in the Healthcare Context The basis of such an approach is the use of some influence: monetary in the form of bonus payments, and moral in the form of praise.
- Motivation for Russian Geographic Expansion in the 18th Century Historians have argued that the motivations leading to the expansion included the need to mobilize and access new and prime lands and resources, the acquired literacy level of the Russians as compared to their conquest, […]
- Christchurch Mosque Shootings and Motivations The following paper will provide the background information on the event, review the origins of the terrorist, explore the motivations behind the shootings, and apply appropriate psychological theories to the critical analysis.
- Motivations of Lone-Wolf Terrorists The phenomenon of lone-wolf terrorism is an interesting one because it challenges one to attempt to understand the motivation of a person to commit a violent criminal act knowing of the severe consequences.
- Motivation for Juvenile Justice System The assertion of motivation among the criminal employees reflects the understanding levels of different Social factors at the workplace in the Juvenile justice system.
- Pleading Guilty: Key Motivation As a result, the defendant and their legal counsel often do not manage to properly assess the prosecutor’s claim due to the plea’s urgency and its disparity with the potential trial sentence.
- Study of the Concept of Motivation As Fowler states, a theory of goal setting, developed by Edwin Locke in 1966, assumes that a person’s behavior is determined by the goals they set for themselves and for the achievement of which they […]
- Presidential Debates: Political Interests Motivations and Opinions Unfortunately, candidates are usually motivated to gain some results and effects on the citizenry rather than think about the methods to achieve the desirable consensuses.
- Consumer’s Referent-Seeking Behaviour: The Antecedence and Motivational Factors If we are to really understand the consumer’s behaviour, the object of the behaviour needs to be identified and analyzed to establish what attribute, characteristic, or property of the object is responsible for the arousal […]
- Cases to Apply Extrinsic Motivation From the viewpoint of irrelevant motivation theory, progress in a study is conditioned by rewards promised by the university and pressure from parents and teachers.
- Marissa Ann Mayer: Leadership and Motivation Marissa Ann Mayer is the current Chief Executive Officer of Yahoo. Merissa has been ranked as one of the most powerful businesspersons in the United States.
- Analysis of Push and Pull Factors in Food Travel Motivation The implementation of the pull strategy is aimed at providing a powerful and long-term information impact through the media on the end consumer of the product.
- Impact of Motivation and Emotions on Human In their article “When we want them to fear us: The motivation to influence outgroup emotions in collective action,” Hasan-Aslih et al.introduce the concept of emotional regulation and address the influence of emotions on the […]
- Applying Motivational Interviewing Skills to Assessment His father said that he was no longer allowed to talk with his friends and took away his phone and computer and sent him to his room to study.
- Benefits of Employees Motivation Motivated employees are happy and satisfied with their job. They are always committed towards the realization of the organization goals and objectives.
- Emotional Motivation in Customer Purchase Decisions
- Motivational and Forensic Interviewing
- Hillcrest Memorial Hospital: Employee Motivation and Empowerment
- Motivational Interviewing as a Therapeutic Technique
- Motivational Interviewing in Healthcare System
- Motivational Interviewing Nurse with Patient
- Reason, Motivations, and Belief for Conducting Cyber Attack
- Management Learning: Leadership, Motivation and Job Satisfaction
- Age-Crime Relationships and Motivations
- True Altruism and Motivation to Help
- Career Motivation of Youth Professional Activity: RAKBANK
- Bilingualism and Communication: Motivation, Soft Skills and Leadership
- Role of Motivation in K-12 Students’ Practice Frequency in Music Performance
- “Employee Motivation: A Malaysian Perspective” by Ismail
- Psychological Theories and Tests of Motivation
- The Cold War and Motivations Behind It
- Effective Incentives in Motivating Workers
- Survey: Motivation at Work and Lack of It
- Teamwork Dynamics, Motivation, Conflict Resolution, and Leadership
- Motivation Theories in Fulfillment of Psychological Needs
- Motivation Improvement in Employee Relations
- Dehart-Davis’ “Gender Dimensions of Public Service Motivation”
- Causes and Motivations of Terrorism
- The Psychological Contract and Motivation
- Freud: Motivation Evaluation and Motivational Theories
- Personality and Psychology of the Motivation
- Understanding the Facets of Motivation
- Algebra I in Middle School and Its Impact on Tracking and Motivation
- Motivation, Emotion, Stress, Health and Work
- Ford Motor Company’s Motivational Profile
- Group Motivation Inventory
- Motivation and the Brain: A Psychological Attribute and Activities
- Identifying Sources of Motivation
- Employee Motivation Importance Review
- Motivation Concept: Definition, Types, Sources, Motivation and Behavior
- Motivation and Leadership Practices Around the World
- Motivation and the Brain Analysis
- Nursing Profession and Motivation
- Quality Guitars and Workforce Motivation Relations
- A Problem of Leadership Style and Employee Motivation
- Self-Regulation and Motivation in Sports
- Employee Motivation in Public Organizations
- Motivational Interviewing as a Smoking Cessation Intervention for Patients With Cancer
- Management and Motivation: Personal Development
- The Path to Success: Motivation, Business Structure
- How Instructional Practices Affect Student Motivation
- Aims and Motivations of Voyages in the Renaissance
- Employee Motivation and Individual Differences
- Quitting Smoking: Motivation and Brain
- The Administrator’s Role in Employee Motivation
- Employee Motivation: Creating a Comfortable Workplace
- Employee Motivation Program: Cost-Benefit Analysis
- Motivation Through Holistic Fitness: A Cost-Benefit Analysis
- The Role of Motivational Interviewing in SUD
- Behavior Follows Attitudes: Leadership Reflections and Work Motivation
- Employee Motivation Through Holistic Fitness
- Multiple Perspectives on Employee Motivation
- Motivation Through Holistic Fitness: A Risk Analysis
- Sources of Motivation for Pursuing a PhD
- Employee Motivation and Cross-Cultural Communication
- Cultural Dimensions Model and Employee Motivation
- Cultural Influence on Employee Motivation
- Suzie Sue Restaurant’s Workforce Motivation Strategy
- Leadership & Employee Motivation in the UK Restaurant Sector
- Introduction to Psychology: Motivation and Emotion
- Carmina Campus Company: Employee Motivation
- Motivation Approach in Dental Practice
- Motivational Theories and Common Behaviors
- Motivation and Behavior in the Workplace
- Cognition, Motivation and Success
- Learning Styles Models and Theory of Motivation
- Motivation Process in Education
- Technology Effect on Motivation in English Learners
- A Source of Motivation, and Motivational Theories
- Personal Motivational Skills Analysis and Development
- Green Hotel’s Customer Motivation and Satisfaction
- Math Curriculum and Ginsberg’s Motivational Framework
- How Motivation Influences Online Shopping
- Understanding Relationship Between Motivation and Performance
- Motivational Learning and Development in the Workplace
- Does Locus of Control and Motivation Predict Occupational Stress?
- Empowerment, Motivation and Performance
- Motivation and Conflict: Analysis and Design Methods
- Behavior and Motivation: Theory and Research
- Incentives to Increase Employees` Motivation
- Mixed Method in Motivation and Video Gaming Study
- IPhone 8 Purchase Motivation Analysis
- Employee Motivation, Termination, and Work Stress
- Motivation and Emotion Understanding
- Southwest Airlines’ Motivational Strategies
- Motivation Theories and Study of Their Effectiveness
- Workers’ Motivation Levels and Performance
- Atrium Health Company: Job Motivation and Satisfaction
- Improving Motivation at Atrium Health
- Employee Motivation for Professional Development
- Health Promotion: Motivation and Skills for Changes
- Motivation Theories and Definition
- Employee Motivation and Support Approaches
- Parenting Styles and Academic Motivation
- Motivation: Theories and Principles in Management
- Emotionally Intelligent Leadership Through Motivation and Inspiration
- Motivational Aspects of Teamwork in Schools
- Motivations to Choose Bottled Water
- Motivation Cases in a Pharmacy Department
- Nurse-Performance Evaluation Tools and Motivation
- Auckland Motel Employees’ Motivation Sources
- Self-Control Theory and Criminal Motivation
- Motivation in the Workplace: Industry Practicum
- Motivation in “Drive” by Daniel Pink
- Work Motivation and Organizational Behavior
- Memory, Thoughts, and Motivation in Learning
- Motivational Climate in Sports Training Environment
- Mobile Phone Buying Factors and Motivation
- Employee Engagement, Empowerment, and Motivation
- Chinese Luxury Hotels’ Employee Motivation
- Kaluyu Memorial Hospital’s Employee Motivation
- Salespeople’s Effective Motivational Strategies
- ABC Company’s Organizational Behaviour and Motivation
- Philosophy Teaching and Learning Motivation
- Customer Motivation in Marketing and the PRISM Model
- Team Motivation Strategies and Approaches
- Historical Insights Project for Students’ Motivation
- Students’ Motivation Strategy: Action Research
- Employee Motivation and Key Performance Indicators
- Employee Motivation: Fred Maiorino’s Case
- Head Start Program and Motivational Theory
- St. Aidan’s Hospital: Work Motivation Problem
- The Regency Grand Hotel’s Employee Motivation
- Motivational Theory in the Instructional Program
- Motivation in Adults and Young Learners
- Education, Behavior and Motivation Theories
- Autonomy Supportive Teaching and Motivational Systems Theory
- Motivation and Change in Schools
- Development, Motivation and Self-Regulation in Learning
- Expectancy Theory in Motivation Management
- Two Theories of Motivation
- Motivational Counseling and Interviewing Techniques
- Students’ Achievement Motivation: Two Scales Scoring
- Workforce Motivation: Theories and Approaches
- Emotions Function and Its Role in a Motivation
- Motivation Concept and Sources
- Work Motivation From Psychological & Coaching Perspectives
- Counselling and Helping in Motivational Interviewing
- Presidential Debates, Partisan Motivations, and Political Interest
- Four Seasons Company Motivation and Performance Management
- Motivation Importance in an Educational Environment
- Expectancy Theory in Motivation Psychology
- Employee Motivation, Conflict and Personnel Management
- Concepts and Sources of Motivation
- Mental Psychology and Motivation
- Motivation and Transfer of Learning
- WooWoo Company Management: Teamwork and Motivation
- Impact of Employee Motivation in Organizational Performance
- Facilitating Customer Support at Radisson Hotels
- Motivational Framework for Culturally Responsive Teaching Versus the Arcs Model
- Motivational Practices for Employees
- Destination Attributes and Motivations Between First-Time and Repeat Travellers in the International and Interstate Tourism: Melbourne
- Motivation in the XXI Century: New Solutions to the Old Concerns
- Relationship Between Rewards and Employee’s Motivation
- The Right Motivation and Its Effects
- Leadership Motivation: Anita Roddick, Founder of Body Shop
- Employee Motivation Theories and Benefits
- Training and Development Options for Motivation and Retention
- Management Issues: Most Relevant Motivational Theory
- Motivational Theory and Generation Y
- Motivation and Reward Systems Used in Today’s Companies
- Leadership and Motivation Ideas
- Leadership and Motivation in Global Organizations
- Employees Job Motivation
- Leadership and Motivation Theory
- Consumers’ Motivation and Satisfaction of Luxury Hotel in China
- Employee Motivation in Spanish Hotel Chains
- Does Blogging Increase the Motivation of Boys in Class
- The Impact of Employee Motivational Strategies on Organizational Performance
- The Role of Motivation in Online Collaboration From an Active Learning Perspective
- “Self-Determination Theory and the Facilitation of Intrinsic Motivation, Social Development, and Well-Being”
- Motivation Plan: Virgin Blue Company
- Teamwork and Motivation: Woowooo Inc.
- Usage of Blogging for Boys’ Motivation
- Decision Making & Motivation
- Motivation, Work Performance, Job Satisfaction
- Student Engagement and Student Motivation in a Reading Classroom for the Kindergarten Level
- Motivation Role in Organizational Management
- Motivation and Employee Involvement
- Undergraduate Students’ Views on Social Links and Their Influence on Motivation
- Motivation in Higher Education
- WeChat Users’ Motivation, Satisfaction and Loyalty
- Nurturing Motivation in Students
- Corporate Motivational Techniques at Trader Joe’s
- Adult Learning and Motivation in the Human Resources Setting
- Modern Theories of Motivation for Thailand
- Motivation Theories in Education
- Employee Motivation vs. Work and Family Issues
- Relationship Between Parental Involvement and Children’s Motivation
- Examining Reward, Motivation and Incentive Systems for the Staff Currently Employed at the Japanese Subsidiary of Sujdavdan
- Asian Efl Learners’ Perceptions of Motivational Teaching Strategies in the English Speaking Class
- Defining Motivation and Employee Satisfaction
- “Generational Buying Motivations for Fashion” by Laura Portolese Dias
- Measuring Employee Motivation
- Organizational Behavior, Motivation and Conflict Management
- Motivation in Nonprofit Organizations
- Motivation Underlying Interpersonal Attraction and Romance
- Influence of Team-Based Pay Structures on Team Members’ Performance and Motivation
- Consumers’ Buyer Behaviour and Motivations Towards Product Packaging
- Special Education: Motivation of Teachers and Performance of Students
- Organizational Development: Motivation, Communication, and Innovation
- Using a “Daily Motivational Quiz” to Increase Student Preparation, Attendance, and Participation
- HR Performance Issues and Motivation
- Motivation in Combat: The German Soldier in World War II
- McGregor’s X and Y Theories
- Motivation and Participative Decision-Making in Organizations
- Motivation and Telecommuting
- Equity Concept: Motivation and Features in Leadership
- Corporate Culture, Employee Motivation and Workforce Diversity
- Employee Selection, Retention and Motivation
- Factors Affecting Employees’ Motivation
- Cross-Cultural Management: Providing Motivation and Leadership
- Classical Theories of the Employee Motivation
- Motivation Theories in the TV Comedy Series “Sex and the Sally”
- Relationship Between Electoral Motivations and Institutional Changes
- Motivation Applicability in the Workplace
- Employee Motivation in Radisson Hotel
- Goals for Motivation Employees in HRM
- Motivational Problems in the Workplace
- Motivation in Radisson Hotel in Dubai
- Improving Employees’ Motivation
- Job Design, Work, and Motivation
- Work Motivation at the Kudler Fine Foods
- Campus Life Problem Motivation
- Canadian Flair Bartender Gavin Macmillan, His Personality and Motivation
- How Does HR Department Use Motivation to Increase Employee’s Retention Rate
- Growth and Motivation Theories: Application in Personal Behavior, Professional Goal Setting, Social Policy Formulation
- Evaluating Performance Through Motivation
- PGL Management: Motivational Strategy
- The Reasons Why Motivation Is Important
- Knowledge of Motivational Theories for Better Management
- Practicing Leadership: Motivation and Management
- Motivation as a Function of Human Resource
- Issues Affecting the Transition of First-Year Students Into University Culture About Motivation and Learning
- Concept of the Theory of Motivation by Maslow and Herzberg
- Changes in Learning and Motivation With the Advent of Online Learning
- Leadership Theories and Motivation Issues
- The Motivational Factors at the Workplace
- Motivational Program and Alcoholics Anonymous
- The Motivation Behind Employer-Offered Healthcare in the US
- Concept of Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivation Model
- Team Work and Motivation
- Leadership and Motivation Theories, Principles and Issues
- Money, Motivation and Employee Performance
- Classroom Motivation: Climate and Instructional Variables
- Workplace Motivational Plan
- Workplace Motivation Theories
- Financial Incentives in Employee Motivation
- Motivational Theories in Organization
- Individual Motivation and Performance Management
- Motivational and Cognitive Sources of Prejudice
- Motivation Theories in Business Environment
- Why Intrinsic Motivation Is Better Than Extrinsic Motivation
- Organizational Motivation and Leadership in Workplace
- Employee Motivation Factors in Banking
- Motivation and Flight Centre Staff
- Understanding the Nature of Motivation
- What a Manager Should Know About Motivation
- The Issue of Motivation in English Second Learners
- Employee Motivation: Strengths and Weaknesses
- Three Major Theories of Motivation
- Motivation, Emotion, and Learning
- Motivation: Selfish Interests
- Motivation Evaluation: Martin Luther King Jr.
- Personality and Motivation
- Self-Regulation, Depletion, and Motivation
- Motivation Concepts and Theories
- Organizational Motivation and Leadership in the Workplace
- What Was the Motivation for the Europeans to Explore?
- How Can Managers Use Their Understanding of Motivation to Improve Performance of Staff?
- Does Teacher Motivation Lead to Student Motivation?
- How Did Abraham Maslow’s Humanistic Approach to Management Influence Later Theories of Motivation?
- Are Matching Games Effective at Improving Learner Motivation in Literacy Lessons?
- How Did Keynes Conceive Entrepreneurs’ Motivation?
- Does Motivation Come From Within or Is It Stimulated by External Forces?
- How Does Motivation Affect Job Performance?
- Can External Interventions Crowd in Intrinsic Motivation?
- Describe One Process Theory of Motivation. Why Is It a Process Theory?
- How Does Work Motivation Impact Employees’ Investment at Work and Their Job Engagement?
- Does Motivation Matter When Assessing Trade Performance?
- How Motivation Theories Can Be Applied in the Workplace?
- Are Competition and Extrinsic Motivation Reliable Predictors of Academic Cheating?
- How Do Moral Judgements and Motivation Relate to Each Other?
- Does Pursuing External Incentives Compromise Public Service Motivation?
- How Can Equity Theory Explain the Motivation of Employees Working at Xandria?
- What Determines the Motivation for Further Training?
- Does Monetary Punishment Crowd Out Pro-social Motivation?
- Are Prosocially Motivated Employees More Committed to Their Organization?
- Does Motivation Affect the Outcome of a Sporting Performance?
- How Can ASDA (Farnborough) Improve Employee Motivation?
- What Motivates Cultural Tourists?
- Why Did BMW Launch the Films Campaign? What Was the Motivation?
- Learning Styles Essay Topics
- Performance Management Ideas
- Mentorship Topics
- Professionalism Research Ideas
- Team Leadership Research Ideas
- Work Environment Research Topics
- Volunteerism Paper Topics
- Work-Life Balance Essay Titles
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, March 2). 511 Motivation Essay Topic Ideas & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/motivation-essay-topics/
"511 Motivation Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." IvyPanda , 2 Mar. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/motivation-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '511 Motivation Essay Topic Ideas & Examples'. 2 March.
IvyPanda . 2024. "511 Motivation Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/motivation-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "511 Motivation Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/motivation-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "511 Motivation Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/motivation-essay-topics/.
Protect your data
This site uses cookies and related technologies for site operation, and analytics as described in our Privacy Policy . You may choose to consent to our use of these technologies, reject non-essential technologies, or further manage your preferences.
- How to Answer “What...
How to Answer “What Motivates You?” - With Examples
10 min read · Updated on August 20, 2024

Do you know how to answer the “What motivates you?” interview question in a truly compelling way?
When a recruiter or hiring manager asks the common “What motivates you?” interview question, it may seem like one of those simple questions that should be easy to answer. However, if you're not prepared or have never taken the time to consider your own motivations, you may find yourself struggling to come up with a compelling response. Unfortunately, your inability to quickly respond to this simple question could leave the interviewer with doubts about your candidacy.
In this article, we'll explain why interviewers ask the “What motivates you?” interview question and provide some tips to help you prepare your response. We'll also include some great example answers that you can customize to ensure that you're always ready to respond to questions about your motivation.
Why do interviewers ask the “What motivates you?” interview question?
This question is similar to asking, “What makes you unique?” It's meant to discover whether or not you're the right fit for the job and, more importantly if you'll fit within that company's particular workplace culture and goals.
It's a useful question that can provide insight into how and why you're motivated to be a successful employee and what fulfills you in your job or career. Your answer can also provide the interviewer with additional insight into your personality and approach to work. All these things, along with your skills and experience, help the interviewer determine whether you're the best person to hire.
It is important to remember that employers who ask about what motivates you are not asking you why you've decided to pursue your career path or apply for their open position. They are simply trying to figure out what drives you to do the best job possible, achieve your mission, and contribute to your employer's success.
“What drives you?” and other ways this question is asked
Some interviewers won't ask this exact question but will instead use some variation. You need to be able to recognize it when it's asked in different ways so you can still provide the answers they're seeking. Instead of the “What motivates you?” interview question, you might hear:
What inspires you?
What drives you to meet challenges?
What excites you about your job – or about working in general?
What drives you to be successful?
What makes you want to get up every day for work?
How to prepare an answer to the “What motivates you?” interview question
As with all interview preparation, begin by researching the company in detail. The more you know about the company and the position, the easier it will be to effectively tailor your answer to match the company's needs. Try to learn about the employer's mission and values, as that can be critical for framing your answers properly.
In most cases, the hiring manager is asking this question about your work life, not your personal life. With that in mind, try to restrict your answer to professional motivations. You should also avoid any response that focuses on your desire for a great salary or benefits since employers already understand that compensation is an important factor in any employee's motivation.
Possible motivations to focus on as you develop your answer
Taking on or overcoming challenges
Developing new skills
Working with others
Working independently
Having less or more frequent direct supervision
Being part of or leading a team
Teaching or mentoring others
Creating new processes or improving existing ones
Learning new things
Being innovative or creative
Having challenging goals and deadlines
Align your answer with the position you're seeking
As we noted, it's important to know as much as possible about the employer and the job you're seeking so that you can tailor your response to align with the position. For example, if you're seeking a job dealing with data and analysis, you should try to include those concerns in your answer. You can find an example of this type of data-focused answer in our sample answer section below.
One way to ensure that your answer aligns with the position is to review the job description. Figure out which responsibilities seem to inspire you and build your answer around those duties. Remember to be honest with yourself as you do this since your response will be more believable if it truly conveys your motivations.
It's also important to not stray too far from that alignment. If the job you're seeking requires a great deal of collaboration with others, then you shouldn't respond by talking about how much you love studying spreadsheets by yourself in a corner office.
Other factors to consider as you create an answer
Consider your strengths . Typically, what motivates someone is also what they're good at, so your answer can highlight skills as well as motivation.
Reflect on the past. Think back to one of your best days at work. Why was it such a good day? What were you doing? Who were you working with?
Use actual examples. Sharing a specific example from your current job or a previous position can enable you to align your motivation with the skills that will make you successful in the job. This often makes a recruiter sit up and take notice.
Keep it short, or as short as possible . Be sure your answer isn't too long or rambling. Keep it as short as possible.
Stay positive. Don't frame your answers using negative examples about you or about others. Share the things you enjoy doing and show how they've helped you to be an excellent employee in all your jobs.
Be honest. Hopefully, you're applying for a position that you really do feel is a good fit for your skills and abilities, as well as for what drives you to be successful. Remember, though, that it's important to be honest about your motivation for a job, or it's quite possible you won't have the job for long once your employer discovers you're not a great fit.
For example, being motivated by leading a team and consistently interacting with others is not the same as being fulfilled by working mostly on your own crunching numbers or researching data. Neither is good or bad. It's just a question of which one is best for you and that specific role.
Use the STAR method . Describe your motivation examples around S ituations, T asks, A ctions, and R esults. The benefit of this method is that it can show how your motivation ultimately benefited your past company or could benefit a future one. Moreover, that process can help you tell a story rather than just reciting a quick rote answer. That approach can make you sound more interesting and make the interviewer more interested in you.
Practice. Share your answer with a family member or friend and get their feedback. Practicing will help you to answer with greater confidence.
Sample answers to “What motivates you?”
Below, we've compiled some sample responses to guide you as you develop your own answer to the “what motivates you” interview question.
Example of someone motivated by learning and skill development
“I'm driven by a desire to learn new skills. It's so satisfying to see myself improve as I gain more knowledge about a job or market sector. In my last job, I consistently signed up for training or courses that would grow my skill set, paying for some out of my own pocket. I really believe that ongoing learning makes you more innovative and valuable in the workplace.”
Related reading : What Are Skills? (With Examples and Tips on How to Improve Them)
Example for someone motivated by a desire to solve problems
“ I've been coding since middle school, when I was first exposed to it. My mom is a Software Developer and helped me whenever I needed it. Coding has been “it” for me ever since and I've become an expert in Java and C++. I think about coding from the minute I wake up until I go to sleep. Solving problems with code is what challenges me, motivates me, and drives me to be successful. ”
Example for someone who loves organizing projects and activities
“ I'm addicted to planning! Being organized at work and at home drives me to make sure I have enough time to achieve my goals and give my best in all I do. It ensures that I don't overtask myself, so I can focus on doing quality work and not get burned out by working long hours on any one project. Good time management helps me to maintain consistently excellent standards.”
Example for someone who's motivated by serving others
“ Providing outstanding customer service is what drives me. I worked as a Mobile Sales Associate for a local credit union. The days were hectic with solving customer issues and answering questions. I worked hard to understand their queries and explain the how and why of our processes and operations. It really motivated me and boosted my confidence whenever customers gave me a great review and a high rating.”
Example for a team player or leader
“I was a Team Lead in my last position, managing a team of 10. Our task was to improve outcomes, so the team had to work efficiently and deliver consistently accurate results. I made it my goal to streamline the team's processes and be more productive with less “busy work.” Working with a team to complete tasks accurately and ahead of schedule was and is what drives me every day. I want to help any company I'm with to always meet their bottom line.”
Example for someone who's driven by managing successful teams
“I've been responsible for directing software development teams and implementing repeatable processes for a variety of companies. My teams achieved 100% on-time product delivery for six straight months. The challenge of finishing the projects ahead of schedule and successfully managing teams to reach our goals is the kind of thing that's always motivated me.”
Example for a person who's driven to get results
“I'm motivated by results. I'm always excited when I have a tangible goal to meet and enough time to develop a sound strategy to accomplish it. In my current job, we have very aggressive quarterly and yearly goals. I was tasked to work with my manager and my team to create a month-by-month strategy to meet our quarter-end and year-end numbers. Accomplishing that was a great thrill and made me even more result oriented.”
Example for a person who's motivated by data
“I love numbers. Analyzing data and providing results really drives and motivates me. I love getting my hands on a spreadsheet to figure out what's driving the numbers and sharing my conclusions. In my current position, I generate our monthly sales analytics reports. Being able to provide this essential information is really motivating because the data from these reports helps the company to determine its sales goals for the upcoming months and clarifies how the organization will move forward, and I know I've made a big contribution to that.”
Proper preparation can help you approach your interview with greater confidence
Being able to effectively answer the “what motivates you” interview is critical for success in any job search. If you take the time to understand your motivations and align them with the job you're seeking, you can create compelling responses that are sure to make a positive impression on hiring managers.
Our resume experts can help you learn more about how to answer the “what motivates you” interview question. Also, be sure to get your free resume review to make sure that your resume is ready to help you land those interviews!
This article was originally written by Lisa Tynan and has been updated by Ken Chase.
Recommended reading:
How to Advance Your Career (plus 10 Insightful Tips)
Top 15 Professional Goals and How to Achieve Them
20 Key Leadership Competencies for Success (Plus Tips!)
Related Articles:
From Bland to Beautiful: How We Made This Professional's Resume Shine
How to Write a Thank-You Email After Your Second Interview
Storytelling: Your Secret Career-Making Weapon
See how your resume stacks up.
Career Advice Newsletter
Our experts gather the best career & resume tips weekly. Delivered weekly, always free.
Thanks! Career advice is on its way.
Share this article:
Let's stay in touch.
Subscribe today to get job tips and career advice that will come in handy.
Your information is secure. Please read our privacy policy for more information.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Categories: Economy Intrinsic Motivation Motivation Motivation In The Workplace. Download. Essay, Pages 5 (1137 words) Views. 8892. Motivation is the desire to do something. It plays a huge role in any workplace. You want your employees happy and wanting to come to work. People who work for the love of their job are showing intrinsic motivation.
The Science of Improving Motivation at Work
Work Motivation: What It is and Why It is Important
People in the second group, whose work was saved but ignored, needed almost as much money as those whose work was shredded. The Upshot: "Ignoring the performance of people is almost as bad as shredding their effort before their eyes," Ariely says. "The good news is that adding motivation doesn't seem to be so difficult.
Examples of motivations include incentives, work place promotions, and rewards. Numerous motivational theories help businesses in encouraging workers put more efforts and hence exploit their full potential in meeting of goals and objectives. These theories suggest factors that result to job contentment. The following essay investigates factors ...
Rousing our motivation
Understanding the Power of Intrinsic Motivation
Applying the wrong strategy (say, urging an employee to work harder, when the reason is that they're convinced they can't do it) can actually backfire, causing motivation to falter further ...
Motivational Theories and Motivation at Work Essay. According to Aamodt, motivation is "… the internal force that drives a worker to action as well as the external factors that encourage that action" (2009). Employers spend huge sums of money in employees' selection, training and placement. It is therefore very important for employees ...
Motivation and Satisfaction at the Workplace. Motivation in a workplace is what is believed to be behind the behavior and the workers. It regulates the level of performance in the workplace. Satisfaction is the pleasure or joy of making tasks and the sense of achievement in having done a given task perfectly. If the workers are motivated, their ...
A Guide to Motivating Yourself at Work
The impact of motivation on work-life balance; How does motivation affect creativity and innovation? The causes and effects of peer pressure on motivation; The relationship between motivation and goal attainment; 💬 Motivation Opinion Essay 💭📝. In an opinion essay, you express your personal thoughts and beliefs about motivation.
Communication Failure, Lack of Motivation, and Conflicts as Common Workplace Issues. Poor communication can lead to a lack of understanding and awareness, resulting in a breakdown of the relationship between employees, managers, and colleagues. The Employee Benefits Provided by the Bank of America.
Personal appreciation from the management team would be a high motivation to the employee. It would go a long way in ensuring that the employee is motivated within the firm. Public praises. It is important that when an employee performs exceptionally well, the management should praise such employees publicly.
Importance Of Motivation In The Workplace Business Essay. Motivation in the workplace is one of the most important aspects within an organization. The following study defines motivation and analyzes needs and drives which is the starting point of motivation. It also analyzes five major approaches that have led to our understanding of motivation ...
Buy Copies. Print. Even if you love your job, it's common to feel burnt out from time to time. Perhaps you just wrapped up a big project and are having trouble mustering motivation for the next ...
Work motivation: an evidence review
Work Motivation: The Roles of Individual Needs and Social ...
Motivation is to encourage people to work, individually or in groups in the ways such as to produce best results. It is the will to act and the willingness to exert high levels of effort towards organizational goals, conditioned by the efforts and ability to satisfy some individual need. The management's important task is to motivate others.
Decent Essays. 794 Words. 4 Pages. Open Document. Motivation at Work. It may seem obvious that staff should be motivated; however, from the point of human resources management this is only true if motivation leads to improvements in the work. Over the years a number of management theories have been put forward in an attempt to explain the ...
Work motivation is a crucial, yet complex resource for employees and organizations. Scholars have investigated motivation at work through many theoretical lenses that are often examined in isolation from one another. This chapter seeks to bridge these various perspectives, first by providing a review of dominant theoretical lenses and second by ...
Money as a Form of Motivation in the Work Place. This then shows that money can and is used as a motivational factor in the work place so that employees can strive to give their best and their all at the end of the day. We will write a custom essay specifically for you by our professional experts. 188 writers online.
How to Answer "What Motivates You?" - With Examples