

How to Write a Conclusion for Research Papers (with Examples)

The conclusion of a research paper is a crucial section that plays a significant role in the overall impact and effectiveness of your research paper. However, this is also the section that typically receives less attention compared to the introduction and the body of the paper. The conclusion serves to provide a concise summary of the key findings, their significance, their implications, and a sense of closure to the study. Discussing how can the findings be applied in real-world scenarios or inform policy, practice, or decision-making is especially valuable to practitioners and policymakers. The research paper conclusion also provides researchers with clear insights and valuable information for their own work, which they can then build on and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
The research paper conclusion should explain the significance of your findings within the broader context of your field. It restates how your results contribute to the existing body of knowledge and whether they confirm or challenge existing theories or hypotheses. Also, by identifying unanswered questions or areas requiring further investigation, your awareness of the broader research landscape can be demonstrated.
Remember to tailor the research paper conclusion to the specific needs and interests of your intended audience, which may include researchers, practitioners, policymakers, or a combination of these.
Table of Contents
What is a conclusion in a research paper, summarizing conclusion, editorial conclusion, externalizing conclusion, importance of a good research paper conclusion, how to write a conclusion for your research paper, research paper conclusion examples.
- How to write a research paper conclusion with Paperpal?
Frequently Asked Questions
A conclusion in a research paper is the final section where you summarize and wrap up your research, presenting the key findings and insights derived from your study. The research paper conclusion is not the place to introduce new information or data that was not discussed in the main body of the paper. When working on how to conclude a research paper, remember to stick to summarizing and interpreting existing content. The research paper conclusion serves the following purposes: 1
- Warn readers of the possible consequences of not attending to the problem.
- Recommend specific course(s) of action.
- Restate key ideas to drive home the ultimate point of your research paper.
- Provide a “take-home” message that you want the readers to remember about your study.

Types of conclusions for research papers
In research papers, the conclusion provides closure to the reader. The type of research paper conclusion you choose depends on the nature of your study, your goals, and your target audience. I provide you with three common types of conclusions:
A summarizing conclusion is the most common type of conclusion in research papers. It involves summarizing the main points, reiterating the research question, and restating the significance of the findings. This common type of research paper conclusion is used across different disciplines.
An editorial conclusion is less common but can be used in research papers that are focused on proposing or advocating for a particular viewpoint or policy. It involves presenting a strong editorial or opinion based on the research findings and offering recommendations or calls to action.
An externalizing conclusion is a type of conclusion that extends the research beyond the scope of the paper by suggesting potential future research directions or discussing the broader implications of the findings. This type of conclusion is often used in more theoretical or exploratory research papers.
Align your conclusion’s tone with the rest of your research paper. Start Writing with Paperpal Now!
The conclusion in a research paper serves several important purposes:
- Offers Implications and Recommendations : Your research paper conclusion is an excellent place to discuss the broader implications of your research and suggest potential areas for further study. It’s also an opportunity to offer practical recommendations based on your findings.
- Provides Closure : A good research paper conclusion provides a sense of closure to your paper. It should leave the reader with a feeling that they have reached the end of a well-structured and thought-provoking research project.
- Leaves a Lasting Impression : Writing a well-crafted research paper conclusion leaves a lasting impression on your readers. It’s your final opportunity to leave them with a new idea, a call to action, or a memorable quote.

Writing a strong conclusion for your research paper is essential to leave a lasting impression on your readers. Here’s a step-by-step process to help you create and know what to put in the conclusion of a research paper: 2
- Research Statement : Begin your research paper conclusion by restating your research statement. This reminds the reader of the main point you’ve been trying to prove throughout your paper. Keep it concise and clear.
- Key Points : Summarize the main arguments and key points you’ve made in your paper. Avoid introducing new information in the research paper conclusion. Instead, provide a concise overview of what you’ve discussed in the body of your paper.
- Address the Research Questions : If your research paper is based on specific research questions or hypotheses, briefly address whether you’ve answered them or achieved your research goals. Discuss the significance of your findings in this context.
- Significance : Highlight the importance of your research and its relevance in the broader context. Explain why your findings matter and how they contribute to the existing knowledge in your field.
- Implications : Explore the practical or theoretical implications of your research. How might your findings impact future research, policy, or real-world applications? Consider the “so what?” question.
- Future Research : Offer suggestions for future research in your area. What questions or aspects remain unanswered or warrant further investigation? This shows that your work opens the door for future exploration.
- Closing Thought : Conclude your research paper conclusion with a thought-provoking or memorable statement. This can leave a lasting impression on your readers and wrap up your paper effectively. Avoid introducing new information or arguments here.
- Proofread and Revise : Carefully proofread your conclusion for grammar, spelling, and clarity. Ensure that your ideas flow smoothly and that your conclusion is coherent and well-structured.
Write your research paper conclusion 2x faster with Paperpal. Try it now!
Remember that a well-crafted research paper conclusion is a reflection of the strength of your research and your ability to communicate its significance effectively. It should leave a lasting impression on your readers and tie together all the threads of your paper. Now you know how to start the conclusion of a research paper and what elements to include to make it impactful, let’s look at a research paper conclusion sample.
| Summarizing Conclusion | Impact of social media on adolescents’ mental health | In conclusion, our study has shown that increased usage of social media is significantly associated with higher levels of anxiety and depression among adolescents. These findings highlight the importance of understanding the complex relationship between social media and mental health to develop effective interventions and support systems for this vulnerable population. |
| Editorial Conclusion | Environmental impact of plastic waste | In light of our research findings, it is clear that we are facing a plastic pollution crisis. To mitigate this issue, we strongly recommend a comprehensive ban on single-use plastics, increased recycling initiatives, and public awareness campaigns to change consumer behavior. The responsibility falls on governments, businesses, and individuals to take immediate actions to protect our planet and future generations. |
| Externalizing Conclusion | Exploring applications of AI in healthcare | While our study has provided insights into the current applications of AI in healthcare, the field is rapidly evolving. Future research should delve deeper into the ethical, legal, and social implications of AI in healthcare, as well as the long-term outcomes of AI-driven diagnostics and treatments. Furthermore, interdisciplinary collaboration between computer scientists, medical professionals, and policymakers is essential to harness the full potential of AI while addressing its challenges. |

How to write a research paper conclusion with Paperpal?
A research paper conclusion is not just a summary of your study, but a synthesis of the key findings that ties the research together and places it in a broader context. A research paper conclusion should be concise, typically around one paragraph in length. However, some complex topics may require a longer conclusion to ensure the reader is left with a clear understanding of the study’s significance. Paperpal, an AI writing assistant trusted by over 800,000 academics globally, can help you write a well-structured conclusion for your research paper.
- Sign Up or Log In: Create a new Paperpal account or login with your details.
- Navigate to Features : Once logged in, head over to the features’ side navigation pane. Click on Templates and you’ll find a suite of generative AI features to help you write better, faster.
- Generate an outline: Under Templates, select ‘Outlines’. Choose ‘Research article’ as your document type.
- Select your section: Since you’re focusing on the conclusion, select this section when prompted.
- Choose your field of study: Identifying your field of study allows Paperpal to provide more targeted suggestions, ensuring the relevance of your conclusion to your specific area of research.
- Provide a brief description of your study: Enter details about your research topic and findings. This information helps Paperpal generate a tailored outline that aligns with your paper’s content.
- Generate the conclusion outline: After entering all necessary details, click on ‘generate’. Paperpal will then create a structured outline for your conclusion, to help you start writing and build upon the outline.
- Write your conclusion: Use the generated outline to build your conclusion. The outline serves as a guide, ensuring you cover all critical aspects of a strong conclusion, from summarizing key findings to highlighting the research’s implications.
- Refine and enhance: Paperpal’s ‘Make Academic’ feature can be particularly useful in the final stages. Select any paragraph of your conclusion and use this feature to elevate the academic tone, ensuring your writing is aligned to the academic journal standards.
By following these steps, Paperpal not only simplifies the process of writing a research paper conclusion but also ensures it is impactful, concise, and aligned with academic standards. Sign up with Paperpal today and write your research paper conclusion 2x faster .
The research paper conclusion is a crucial part of your paper as it provides the final opportunity to leave a strong impression on your readers. In the research paper conclusion, summarize the main points of your research paper by restating your research statement, highlighting the most important findings, addressing the research questions or objectives, explaining the broader context of the study, discussing the significance of your findings, providing recommendations if applicable, and emphasizing the takeaway message. The main purpose of the conclusion is to remind the reader of the main point or argument of your paper and to provide a clear and concise summary of the key findings and their implications. All these elements should feature on your list of what to put in the conclusion of a research paper to create a strong final statement for your work.
A strong conclusion is a critical component of a research paper, as it provides an opportunity to wrap up your arguments, reiterate your main points, and leave a lasting impression on your readers. Here are the key elements of a strong research paper conclusion: 1. Conciseness : A research paper conclusion should be concise and to the point. It should not introduce new information or ideas that were not discussed in the body of the paper. 2. Summarization : The research paper conclusion should be comprehensive enough to give the reader a clear understanding of the research’s main contributions. 3 . Relevance : Ensure that the information included in the research paper conclusion is directly relevant to the research paper’s main topic and objectives; avoid unnecessary details. 4 . Connection to the Introduction : A well-structured research paper conclusion often revisits the key points made in the introduction and shows how the research has addressed the initial questions or objectives. 5. Emphasis : Highlight the significance and implications of your research. Why is your study important? What are the broader implications or applications of your findings? 6 . Call to Action : Include a call to action or a recommendation for future research or action based on your findings.
The length of a research paper conclusion can vary depending on several factors, including the overall length of the paper, the complexity of the research, and the specific journal requirements. While there is no strict rule for the length of a conclusion, but it’s generally advisable to keep it relatively short. A typical research paper conclusion might be around 5-10% of the paper’s total length. For example, if your paper is 10 pages long, the conclusion might be roughly half a page to one page in length.
In general, you do not need to include citations in the research paper conclusion. Citations are typically reserved for the body of the paper to support your arguments and provide evidence for your claims. However, there may be some exceptions to this rule: 1. If you are drawing a direct quote or paraphrasing a specific source in your research paper conclusion, you should include a citation to give proper credit to the original author. 2. If your conclusion refers to or discusses specific research, data, or sources that are crucial to the overall argument, citations can be included to reinforce your conclusion’s validity.
The conclusion of a research paper serves several important purposes: 1. Summarize the Key Points 2. Reinforce the Main Argument 3. Provide Closure 4. Offer Insights or Implications 5. Engage the Reader. 6. Reflect on Limitations
Remember that the primary purpose of the research paper conclusion is to leave a lasting impression on the reader, reinforcing the key points and providing closure to your research. It’s often the last part of the paper that the reader will see, so it should be strong and well-crafted.
- Makar, G., Foltz, C., Lendner, M., & Vaccaro, A. R. (2018). How to write effective discussion and conclusion sections. Clinical spine surgery, 31(8), 345-346.
- Bunton, D. (2005). The structure of PhD conclusion chapters. Journal of English for academic purposes , 4 (3), 207-224.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- 5 Reasons for Rejection After Peer Review
- Ethical Research Practices For Research with Human Subjects
7 Ways to Improve Your Academic Writing Process
- Paraphrasing in Academic Writing: Answering Top Author Queries
Preflight For Editorial Desk: The Perfect Hybrid (AI + Human) Assistance Against Compromised Manuscripts
You may also like, how to cite in apa format (7th edition):..., how to write your research paper in apa..., how to choose a dissertation topic, how to write a phd research proposal, how to write an academic paragraph (step-by-step guide), research funding basics: what should a grant proposal..., how to write an abstract in research papers..., how to write dissertation acknowledgements, how to write the first draft of a..., mla works cited page: format, template & examples.
How to write a strong conclusion for your research paper
Last updated
17 February 2024
Reviewed by
Short on time? Get an AI generated summary of this article instead
Writing a research paper is a chance to share your knowledge and hypothesis. It's an opportunity to demonstrate your many hours of research and prove your ability to write convincingly.
Ideally, by the end of your research paper, you'll have brought your readers on a journey to reach the conclusions you've pre-determined. However, if you don't stick the landing with a good conclusion, you'll risk losing your reader’s trust.
Writing a strong conclusion for your research paper involves a few important steps, including restating the thesis and summing up everything properly.
Find out what to include and what to avoid, so you can effectively demonstrate your understanding of the topic and prove your expertise.
- Why is a good conclusion important?
A good conclusion can cement your paper in the reader’s mind. Making a strong impression in your introduction can draw your readers in, but it's the conclusion that will inspire them.
- What to include in a research paper conclusion
There are a few specifics you should include in your research paper conclusion. Offer your readers some sense of urgency or consequence by pointing out why they should care about the topic you have covered. Discuss any common problems associated with your topic and provide suggestions as to how these problems can be solved or addressed.
The conclusion should include a restatement of your initial thesis. Thesis statements are strengthened after you’ve presented supporting evidence (as you will have done in the paper), so make a point to reintroduce it at the end.
Finally, recap the main points of your research paper, highlighting the key takeaways you want readers to remember. If you've made multiple points throughout the paper, refer to the ones with the strongest supporting evidence.
- Steps for writing a research paper conclusion
Many writers find the conclusion the most challenging part of any research project . By following these three steps, you'll be prepared to write a conclusion that is effective and concise.
- Step 1: Restate the problem
Always begin by restating the research problem in the conclusion of a research paper. This serves to remind the reader of your hypothesis and refresh them on the main point of the paper.
When restating the problem, take care to avoid using exactly the same words you employed earlier in the paper.
- Step 2: Sum up the paper
After you've restated the problem, sum up the paper by revealing your overall findings. The method for this differs slightly, depending on whether you're crafting an argumentative paper or an empirical paper.
Argumentative paper: Restate your thesis and arguments
Argumentative papers involve introducing a thesis statement early on. In crafting the conclusion for an argumentative paper, always restate the thesis, outlining the way you've developed it throughout the entire paper.
It might be appropriate to mention any counterarguments in the conclusion, so you can demonstrate how your thesis is correct or how the data best supports your main points.
Empirical paper: Summarize research findings
Empirical papers break down a series of research questions. In your conclusion, discuss the findings your research revealed, including any information that surprised you.
Be clear about the conclusions you reached, and explain whether or not you expected to arrive at these particular ones.
- Step 3: Discuss the implications of your research
Argumentative papers and empirical papers also differ in this part of a research paper conclusion. Here are some tips on crafting conclusions for argumentative and empirical papers.
Argumentative paper: Powerful closing statement
In an argumentative paper, you'll have spent a great deal of time expressing the opinions you formed after doing a significant amount of research. Make a strong closing statement in your argumentative paper's conclusion to share the significance of your work.
You can outline the next steps through a bold call to action, or restate how powerful your ideas turned out to be.
Empirical paper: Directions for future research
Empirical papers are broader in scope. They usually cover a variety of aspects and can include several points of view.
To write a good conclusion for an empirical paper, suggest the type of research that could be done in the future, including methods for further investigation or outlining ways other researchers might proceed.
If you feel your research had any limitations, even if they were outside your control, you could mention these in your conclusion.
After you finish outlining your conclusion, ask someone to read it and offer feedback. In any research project you're especially close to, it can be hard to identify problem areas. Having a close friend or someone whose opinion you value read the research paper and provide honest feedback can be invaluable. Take note of any suggested edits and consider incorporating them into your paper if they make sense.
- Things to avoid in a research paper conclusion
Keep these aspects to avoid in mind as you're writing your conclusion and refer to them after you've created an outline.
Dry summary
Writing a memorable, succinct conclusion is arguably more important than a strong introduction. Take care to avoid just rephrasing your main points, and don't fall into the trap of repeating dry facts or citations.
You can provide a new perspective for your readers to think about or contextualize your research. Either way, make the conclusion vibrant and interesting, rather than a rote recitation of your research paper’s highlights.
Clichéd or generic phrasing
Your research paper conclusion should feel fresh and inspiring. Avoid generic phrases like "to sum up" or "in conclusion." These phrases tend to be overused, especially in an academic context and might turn your readers off.
The conclusion also isn't the time to introduce colloquial phrases or informal language. Retain a professional, confident tone consistent throughout your paper’s conclusion so it feels exciting and bold.
New data or evidence
While you should present strong data throughout your paper, the conclusion isn't the place to introduce new evidence. This is because readers are engaged in actively learning as they read through the body of your paper.
By the time they reach the conclusion, they will have formed an opinion one way or the other (hopefully in your favor!). Introducing new evidence in the conclusion will only serve to surprise or frustrate your reader.
Ignoring contradictory evidence
If your research reveals contradictory evidence, don't ignore it in the conclusion. This will damage your credibility as an expert and might even serve to highlight the contradictions.
Be as transparent as possible and admit to any shortcomings in your research, but don't dwell on them for too long.
Ambiguous or unclear resolutions
The point of a research paper conclusion is to provide closure and bring all your ideas together. You should wrap up any arguments you introduced in the paper and tie up any loose ends, while demonstrating why your research and data are strong.
Use direct language in your conclusion and avoid ambiguity. Even if some of the data and sources you cite are inconclusive or contradictory, note this in your conclusion to come across as confident and trustworthy.
- Examples of research paper conclusions
Your research paper should provide a compelling close to the paper as a whole, highlighting your research and hard work. While the conclusion should represent your unique style, these examples offer a starting point:
Ultimately, the data we examined all point to the same conclusion: Encouraging a good work-life balance improves employee productivity and benefits the company overall. The research suggests that when employees feel their personal lives are valued and respected by their employers, they are more likely to be productive when at work. In addition, company turnover tends to be reduced when employees have a balance between their personal and professional lives. While additional research is required to establish ways companies can support employees in creating a stronger work-life balance, it's clear the need is there.
Social media is a primary method of communication among young people. As we've seen in the data presented, most young people in high school use a variety of social media applications at least every hour, including Instagram and Facebook. While social media is an avenue for connection with peers, research increasingly suggests that social media use correlates with body image issues. Young girls with lower self-esteem tend to use social media more often than those who don't log onto social media apps every day. As new applications continue to gain popularity, and as more high school students are given smartphones, more research will be required to measure the effects of prolonged social media use.
What are the different kinds of research paper conclusions?
There are no formal types of research paper conclusions. Ultimately, the conclusion depends on the outline of your paper and the type of research you’re presenting. While some experts note that research papers can end with a new perspective or commentary, most papers should conclude with a combination of both. The most important aspect of a good research paper conclusion is that it accurately represents the body of the paper.
Can I present new arguments in my research paper conclusion?
Research paper conclusions are not the place to introduce new data or arguments. The body of your paper is where you should share research and insights, where the reader is actively absorbing the content. By the time a reader reaches the conclusion of the research paper, they should have formed their opinion. Introducing new arguments in the conclusion can take a reader by surprise, and not in a positive way. It might also serve to frustrate readers.
How long should a research paper conclusion be?
There's no set length for a research paper conclusion. However, it's a good idea not to run on too long, since conclusions are supposed to be succinct. A good rule of thumb is to keep your conclusion around 5 to 10 percent of the paper's total length. If your paper is 10 pages, try to keep your conclusion under one page.
What should I include in a research paper conclusion?
A good research paper conclusion should always include a sense of urgency, so the reader can see how and why the topic should matter to them. You can also note some recommended actions to help fix the problem and some obstacles they might encounter. A conclusion should also remind the reader of the thesis statement, along with the main points you covered in the paper. At the end of the conclusion, add a powerful closing statement that helps cement the paper in the mind of the reader.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 April 2023
Last updated: 27 February 2023
Last updated: 22 August 2024
Last updated: 5 February 2023
Last updated: 16 August 2024
Last updated: 9 March 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 4 July 2024
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper

- 3-minute read
- 29th August 2023
If you’re writing a research paper, the conclusion is your opportunity to summarize your findings and leave a lasting impression on your readers. In this post, we’ll take you through how to write an effective conclusion for a research paper and how you can:
· Reword your thesis statement
· Highlight the significance of your research
· Discuss limitations
· Connect to the introduction
· End with a thought-provoking statement
Rewording Your Thesis Statement
Begin your conclusion by restating your thesis statement in a way that is slightly different from the wording used in the introduction. Avoid presenting new information or evidence in your conclusion. Just summarize the main points and arguments of your essay and keep this part as concise as possible. Remember that you’ve already covered the in-depth analyses and investigations in the main body paragraphs of your essay, so it’s not necessary to restate these details in the conclusion.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Highlighting the Significance of Your Research
The conclusion is a good place to emphasize the implications of your research . Avoid ambiguous or vague language such as “I think” or “maybe,” which could weaken your position. Clearly explain why your research is significant and how it contributes to the broader field of study.
Here’s an example from a (fictional) study on the impact of social media on mental health:
Discussing Limitations
Although it’s important to emphasize the significance of your study, you can also use the conclusion to briefly address any limitations you discovered while conducting your research, such as time constraints or a shortage of resources. Doing this demonstrates a balanced and honest approach to your research.
Connecting to the Introduction
In your conclusion, you can circle back to your introduction , perhaps by referring to a quote or anecdote you discussed earlier. If you end your paper on a similar note to how you began it, you will create a sense of cohesion for the reader and remind them of the meaning and significance of your research.
Ending With a Thought-Provoking Statement
Consider ending your paper with a thought-provoking and memorable statement that relates to the impact of your research questions or hypothesis. This statement can be a call to action, a philosophical question, or a prediction for the future (positive or negative). Here’s an example that uses the same topic as above (social media and mental health):
Expert Proofreading Services
Ensure that your essay ends on a high note by having our experts proofread your research paper. Our team has experience with a wide variety of academic fields and subjects and can help make your paper stand out from the crowd – get started today and see the difference it can make in your work.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
5-minute read
Free Email Newsletter Template
Promoting a brand means sharing valuable insights to connect more deeply with your audience, and...
6-minute read
How to Write a Nonprofit Grant Proposal
If you’re seeking funding to support your charitable endeavors as a nonprofit organization, you’ll need...
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
4-minute read
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper

Table of Contents
Writing a conclusion for a research paper is a critical step that often determines the overall impact and impression the paper leaves on the reader. While some may view the conclusion as a mere formality, it is actually an opportunity to wrap up the main points, provide closure, and leave a lasting impression. In this article, we will explore the importance of a well-crafted conclusion and discuss various tips and strategies to help you write an engaging and impactful conclusion for your research paper.
Introduction
Before delving into the specifics of writing a conclusion, it is important to understand why it is such a crucial component of a research paper. The conclusion serves to summarize the main points of the paper and reemphasize their significance. A well-written conclusion can leave the reader satisfied and inspired, while a poorly executed one may undermine the credibility of the entire paper. Therefore, it is essential to give careful thought and attention to crafting an effective conclusion.
When writing a research paper, the conclusion acts as the final destination for the reader. It is the point where all the information, arguments, and evidence presented throughout the paper converge. Just as a traveler reaches the end of a journey, the reader reaches the conclusion to find closure and a sense of fulfillment. This is why the conclusion should not be taken lightly; it is a critical opportunity to leave a lasting impact on the reader.
Moreover, the conclusion is not merely a repetition of the introduction or a summary of the main points. It goes beyond that by providing a deeper understanding of the research findings and their implications. It allows the writer to reflect on the significance of their work and its potential contributions to the field. By doing so, the conclusion elevates the research paper from a mere collection of facts to a thought-provoking piece of scholarship.
In the following sections, we will explore various strategies and techniques for crafting a compelling conclusion. By understanding the importance of the conclusion and learning how to write one effectively, you will be equipped to create impactful research papers.
Structuring the Conclusion
In order to create an effective conclusion, it is important to consider its structure. A well-structured conclusion should begin by restating the thesis statement and summarizing the main points of the paper. It should then move on to provide a concise synthesis of the key findings and arguments, highlighting their implications and relevance. Finally, the conclusion should end with a thought-provoking statement that leaves the reader with a lasting impression.
Additionally, using phrases like "this research demonstrates," "the findings show," or "it is clear that" can help to highlight the significance of your research and emphasize your main conclusions.
Tips for Writing an Engaging Conclusion
Writing an engaging conclusion requires careful consideration and attention to detail. Here are some tips to help you create an impactful conclusion for your research paper:
- Revisit the Introduction: Start your conclusion by referencing your introduction. Remind the reader of the research question or problem you initially posed and show how your research has addressed it.
- Summarize Your Main Points: Provide a concise summary of the main points and arguments presented in your paper. Be sure to restate your thesis statement and highlight the key findings.
- Offer a Fresh Perspective: Use the conclusion as an opportunity to provide a fresh perspective or offer insights that go beyond the main body of the paper. This will leave the reader with something new to consider.
- Leave a Lasting Impression: End your conclusion with a thought-provoking statement or a call to action. This will leave a lasting impression on the reader and encourage further exploration of the research topic.
Addressing Counter Arguments In Conclusion
While crafting your conclusion, you can address any potential counterarguments or limitations of your research. This will demonstrate that you have considered alternative perspectives and have taken them into account in your conclusions. By acknowledging potential counterarguments, you can strengthen the credibility and validity of your research. And by openly discussing limitations, you demonstrate transparency and honesty in your research process.
Language and Tone To Be Used In Conclusion
The language and tone of your conclusion play a crucial role in shaping the overall impression of your research paper. It is important to use clear and concise language that is appropriate for the academic context. Avoid using overly informal or colloquial language that may undermine the credibility of your research. Additionally, consider the tone of your conclusion – it should be professional, confident, and persuasive, while still maintaining a respectful and objective tone.
When it comes to the language used in your conclusion, precision is key. You want to ensure that your ideas are communicated effectively and that there is no room for misinterpretation. Using clear and concise language will not only make your conclusion easier to understand but will also demonstrate your command of the subject matter.
Furthermore, it is important to strike the right balance between formality and accessibility. While academic writing typically requires a more formal tone, you should still aim to make your conclusion accessible to a wider audience. This means avoiding jargon or technical terms that may confuse readers who are not familiar with the subject matter. Instead, opt for language that is clear and straightforward, allowing anyone to grasp the main points of your research.
Another aspect to consider is the tone of your conclusion. The tone should reflect the confidence you have in your research findings and the strength of your argument. By adopting a professional and confident tone, you are more likely to convince your readers of the validity and importance of your research. However, it is crucial to strike a balance and avoid sounding arrogant or dismissive of opposing viewpoints. Maintaining a respectful and objective tone will help you engage with your audience in a more persuasive manner.
Moreover, the tone of your conclusion should align with the overall tone of your research paper. Consistency in tone throughout your paper will create a cohesive and unified piece of writing.
Common Mistakes to Avoid While Writing a Conclusion
When writing a conclusion, there are several common mistakes that researchers often make. By being aware of these pitfalls, you can avoid them and create a more effective conclusion for your research paper. Some common mistakes include:
- Repeating the Introduction: A conclusion should not simply be a reworded version of the introduction. While it is important to revisit the main points, try to present them in a fresh and broader perspective, by foregrounding the implications/impacts of your research.
- Introducing New Information: The conclusion should not introduce any new information or arguments. Instead, it should focus on summarizing and synthesizing the main points presented in the paper.
- Being Vague or General: Avoid using vague or general statements in your conclusion. Instead, be specific and provide concrete examples or evidence to support your main points.
- Ending Abruptly: A conclusion should provide a sense of closure and completeness. Avoid ending your conclusion abruptly or leaving the reader with unanswered questions.
Editing and Revising the Conclusion
Just like the rest of your research paper, the conclusion should go through a thorough editing and revising process. This will help to ensure clarity, coherence, and impact in the conclusion. As you revise your conclusion, consider the following:
- Check for Consistency: Ensure that your conclusion aligns with the main body of the paper and does not introduce any new or contradictory information.
- Eliminate Redundancy: Remove any repetitive or redundant information in your conclusion. Instead, focus on presenting the key points in a concise and engaging manner.
- Proofread for Clarity: Read your conclusion aloud or ask someone else to read it to ensure that it is clear and understandable. Check for any grammatical or spelling errors that may distract the reader.
- Seek Feedback: Consider sharing your conclusion with peers or mentors to get their feedback and insights. This can help you strengthen your conclusion and make it more impactful.
How to Write Conclusion as a Call to Action
Finally, consider using your conclusion as a call to action. Encourage the reader to take further action, such as conducting additional research or considering the implications of your findings. By providing a clear call to action, you can inspire the reader to actively engage with your research and continue the conversation on the topic.
Adapting to Different Research Paper Types
It is important to adapt your conclusion approach based on the type of research paper you are writing. Different research paper types may require different strategies and approaches to writing the conclusion. For example, a scientific research paper may focus more on summarizing the key findings and implications, while a persuasive research paper may emphasize the call to action and the potential impact of the research. Tailor your conclusion to suit the specific goals and requirements of your research paper.
Final Thoughts
A well-crafted conclusion can leave a lasting impression on the reader and enhance the impact of your research. By following the tips and strategies outlined in this article, you can create an engaging and impactful conclusion that effectively summarizes your main points, addresses potential counterarguments, and leaves the reader with a sense of closure and inspiration. Embrace the importance of the conclusion and view it as an opportunity to showcase the significance and relevance of your research.
Important Reads
How To Humanize AI Text In Scientific Articles
Elevate Your Writing Game With AI Grammar Checker Tools
A Guide to Using AI Tools to Summarize Literature Reviews
AI for Essay Writing — Exploring Top 10 Essay Writers
Role of AI in Systematic Literature Review
You might also like

This ChatGPT Alternative Will Change How You Read PDFs Forever!

Smallpdf vs SciSpace: Which ChatPDF is Right for You?

Adobe PDF Reader vs. SciSpace ChatPDF — Best Chat PDF Tools
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Paper Conclusion – Writing Guide and Examples
Research Paper Conclusion – Writing Guide and Examples
Table of Contents

Research Paper Conclusion
Definition:
A research paper conclusion is the final section of a research paper that summarizes the key findings, significance, and implications of the research. It is the writer’s opportunity to synthesize the information presented in the paper, draw conclusions, and make recommendations for future research or actions.
The conclusion should provide a clear and concise summary of the research paper, reiterating the research question or problem, the main results, and the significance of the findings. It should also discuss the limitations of the study and suggest areas for further research.
Parts of Research Paper Conclusion
The parts of a research paper conclusion typically include:
Restatement of the Thesis
The conclusion should begin by restating the thesis statement from the introduction in a different way. This helps to remind the reader of the main argument or purpose of the research.
Summary of Key Findings
The conclusion should summarize the main findings of the research, highlighting the most important results and conclusions. This section should be brief and to the point.
Implications and Significance
In this section, the researcher should explain the implications and significance of the research findings. This may include discussing the potential impact on the field or industry, highlighting new insights or knowledge gained, or pointing out areas for future research.
Limitations and Recommendations
It is important to acknowledge any limitations or weaknesses of the research and to make recommendations for how these could be addressed in future studies. This shows that the researcher is aware of the potential limitations of their work and is committed to improving the quality of research in their field.
Concluding Statement
The conclusion should end with a strong concluding statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader. This could be a call to action, a recommendation for further research, or a final thought on the topic.
How to Write Research Paper Conclusion
Here are some steps you can follow to write an effective research paper conclusion:
- Restate the research problem or question: Begin by restating the research problem or question that you aimed to answer in your research. This will remind the reader of the purpose of your study.
- Summarize the main points: Summarize the key findings and results of your research. This can be done by highlighting the most important aspects of your research and the evidence that supports them.
- Discuss the implications: Discuss the implications of your findings for the research area and any potential applications of your research. You should also mention any limitations of your research that may affect the interpretation of your findings.
- Provide a conclusion : Provide a concise conclusion that summarizes the main points of your paper and emphasizes the significance of your research. This should be a strong and clear statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader.
- Offer suggestions for future research: Lastly, offer suggestions for future research that could build on your findings and contribute to further advancements in the field.
Remember that the conclusion should be brief and to the point, while still effectively summarizing the key findings and implications of your research.
Example of Research Paper Conclusion
Here’s an example of a research paper conclusion:
Conclusion :
In conclusion, our study aimed to investigate the relationship between social media use and mental health among college students. Our findings suggest that there is a significant association between social media use and increased levels of anxiety and depression among college students. This highlights the need for increased awareness and education about the potential negative effects of social media use on mental health, particularly among college students.
Despite the limitations of our study, such as the small sample size and self-reported data, our findings have important implications for future research and practice. Future studies should aim to replicate our findings in larger, more diverse samples, and investigate the potential mechanisms underlying the association between social media use and mental health. In addition, interventions should be developed to promote healthy social media use among college students, such as mindfulness-based approaches and social media detox programs.
Overall, our study contributes to the growing body of research on the impact of social media on mental health, and highlights the importance of addressing this issue in the context of higher education. By raising awareness and promoting healthy social media use among college students, we can help to reduce the negative impact of social media on mental health and improve the well-being of young adults.
Purpose of Research Paper Conclusion
The purpose of a research paper conclusion is to provide a summary and synthesis of the key findings, significance, and implications of the research presented in the paper. The conclusion serves as the final opportunity for the writer to convey their message and leave a lasting impression on the reader.
The conclusion should restate the research problem or question, summarize the main results of the research, and explain their significance. It should also acknowledge the limitations of the study and suggest areas for future research or action.
Overall, the purpose of the conclusion is to provide a sense of closure to the research paper and to emphasize the importance of the research and its potential impact. It should leave the reader with a clear understanding of the main findings and why they matter. The conclusion serves as the writer’s opportunity to showcase their contribution to the field and to inspire further research and action.
When to Write Research Paper Conclusion
The conclusion of a research paper should be written after the body of the paper has been completed. It should not be written until the writer has thoroughly analyzed and interpreted their findings and has written a complete and cohesive discussion of the research.
Before writing the conclusion, the writer should review their research paper and consider the key points that they want to convey to the reader. They should also review the research question, hypotheses, and methodology to ensure that they have addressed all of the necessary components of the research.
Once the writer has a clear understanding of the main findings and their significance, they can begin writing the conclusion. The conclusion should be written in a clear and concise manner, and should reiterate the main points of the research while also providing insights and recommendations for future research or action.
Characteristics of Research Paper Conclusion
The characteristics of a research paper conclusion include:
- Clear and concise: The conclusion should be written in a clear and concise manner, summarizing the key findings and their significance.
- Comprehensive: The conclusion should address all of the main points of the research paper, including the research question or problem, the methodology, the main results, and their implications.
- Future-oriented : The conclusion should provide insights and recommendations for future research or action, based on the findings of the research.
- Impressive : The conclusion should leave a lasting impression on the reader, emphasizing the importance of the research and its potential impact.
- Objective : The conclusion should be based on the evidence presented in the research paper, and should avoid personal biases or opinions.
- Unique : The conclusion should be unique to the research paper and should not simply repeat information from the introduction or body of the paper.
Advantages of Research Paper Conclusion
The advantages of a research paper conclusion include:
- Summarizing the key findings : The conclusion provides a summary of the main findings of the research, making it easier for the reader to understand the key points of the study.
- Emphasizing the significance of the research: The conclusion emphasizes the importance of the research and its potential impact, making it more likely that readers will take the research seriously and consider its implications.
- Providing recommendations for future research or action : The conclusion suggests practical recommendations for future research or action, based on the findings of the study.
- Providing closure to the research paper : The conclusion provides a sense of closure to the research paper, tying together the different sections of the paper and leaving a lasting impression on the reader.
- Demonstrating the writer’s contribution to the field : The conclusion provides the writer with an opportunity to showcase their contribution to the field and to inspire further research and action.
Limitations of Research Paper Conclusion
While the conclusion of a research paper has many advantages, it also has some limitations that should be considered, including:
- I nability to address all aspects of the research: Due to the limited space available in the conclusion, it may not be possible to address all aspects of the research in detail.
- Subjectivity : While the conclusion should be objective, it may be influenced by the writer’s personal biases or opinions.
- Lack of new information: The conclusion should not introduce new information that has not been discussed in the body of the research paper.
- Lack of generalizability: The conclusions drawn from the research may not be applicable to other contexts or populations, limiting the generalizability of the study.
- Misinterpretation by the reader: The reader may misinterpret the conclusions drawn from the research, leading to a misunderstanding of the findings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Assignment – Types, Examples and Writing Guide

Research Techniques – Methods, Types and Examples

Research Questions – Types, Examples and Writing...

Implications in Research – Types, Examples and...

References in Research – Types, Examples and...

Informed Consent in Research – Types, Templates...
- How to Order
Research Paper Guide
Research Paper Conclusion
Writing a Research Paper Conclusion - Step-by-Step Guide

People also read
Research Paper Writing - A Step by Step Guide
Research Paper Examples - Free Sample Papers for Different Formats!
Guide to Creating Effective Research Paper Outline
Interesting Research Paper Topics for 2024
Research Proposal Writing - A Step-by-Step Guide
How to Start a Research Paper - 7 Easy Steps
How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper - A Step by Step Guide
Writing a Literature Review For a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
Qualitative Research - Methods, Types, and Examples
8 Types of Qualitative Research - Overview & Examples
Qualitative vs Quantitative Research - Learning the Basics
200+ Engaging Psychology Research Paper Topics for Students in 2024
Learn How to Write a Hypothesis in a Research Paper: Examples and Tips!
20+ Types of Research With Examples - A Detailed Guide
Understanding Quantitative Research - Types & Data Collection Techniques
230+ Sociology Research Topics & Ideas for Students
How to Cite a Research Paper - A Complete Guide
Excellent History Research Paper Topics- 300+ Ideas
A Guide on Writing the Method Section of a Research Paper - Examples & Tips
How To Write an Introduction Paragraph For a Research Paper: Learn with Examples
Crafting a Winning Research Paper Title: A Complete Guide
Writing a Thesis For a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
How To Write A Discussion For A Research Paper | Examples & Tips
How To Write The Results Section of A Research Paper | Steps & Examples
Writing a Problem Statement for a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
Finding Sources For a Research Paper: A Complete Guide
A Guide on How to Edit a Research Paper
200+ Ethical Research Paper Topics to Begin With (2024)
300+ Controversial Research Paper Topics & Ideas - 2024 Edition
150+ Argumentative Research Paper Topics For You - 2024
How to Write a Research Methodology for a Research Paper
Finishing a research paper feels great, but getting to the end—especially the conclusion—can be a bit tricky.
People often wonder, "How do I wrap up my findings nicely?" or "What tone should I use in the conclusion?"
If you're dealing with these questions, you're not alone! Many researchers find writing a good conclusion a bit challenging since it's a crucial part that is meant to leave a strong impression on your readers.
No need to worry!
In this guide, we'll show you how to write a conclusion that not only ties up your research paper neatly but also leaves a strong impression. We'll cover everything from summarizing effectively to creating the right feeling.
So, let’s get started.
- 1. What is a Research Paper Conclusion?
- 2. How to Write a Research Paper Conclusion: 7 Steps
- 3. Research Paper Conclusion Examples
- 4. Things to Avoid While Writing the Research Paper Conclusion
What is a Research Paper Conclusion?
A research paper conclusion is like the final chapter of your paper. It's where you bring everything together and leave a lasting impression on your readers.
In simple terms, it's the last part where you sum up what you found during your research and explain why it matters.
The conclusion isn't just a summary; it's a chance to make your research memorable and show its importance.
Types of Research Paper Conclusions
When it comes to writing the conclusion of your research paper, there isn't a one-size-fits-all approach. Different types of research papers call for different types of conclusions. Here are some common types:
- Summarizing Conclusion
This type recaps the key points and findings of your research. It's like giving your readers a quick overview of what you discovered without introducing new information. Summarizing conclusions works well for straightforward research papers.
- Reflective Conclusion
A reflective conclusion allows you to share your personal thoughts on the research process, challenges faced, and lessons learned. It adds a human touch to your paper, giving readers insight into your journey as a researcher.
- Open-ended Conclusion
Some research papers benefit from an open-ended conclusion that leaves room for further exploration. This type invites readers to think critically, ask questions, or even conduct additional research on the same topic.
How to Write a Research Paper Conclusion: 7 Steps
Writing an effective conclusion for your research paper involves more than just summarizing your findings. Follow these six essential steps to ensure your conclusion leaves a lasting impact:
Step 1: Restate the Research Problem
Start wrapping up your paper by going back to the main research question or issue you were investigating.
Remind your readers about what you were trying to find out or understand. This gives your conclusion a clear connection to the original goal of your research, helping readers see the bigger picture.
"What impact does regular exercise have on the academic performance of high school students?" Now, in the conclusion, when you restate the research problem, it might look something like this:
|
Step 2: Revisit Your Thesis Statement
Go back to the main idea or argument you had in your paper—this is called your thesis statement. Double-check that your conclusion matches and supports what you wanted to prove or talk about in the beginning.
This step is important because it keeps your conclusion connected to the main point of your research, making everything fit together nicely.
If your was: "Regular exercise positively impacts the academic performance of high school students." In the conclusion, you might like this:
|
Step 3: Summarize Key Points
Give a short and clear recap of the most important things you found in your research. Keep it simple and stick to what you've already talked about—don't bring in new details now.
The goal is to remind your readers of the important stuff you covered earlier. This helps to underline why your research is important and what you want them to take away from it.
If your key points and findings were related to the positive effects of exercise on high school student's academic performance, the summary might look like this:
|
Step 4: Discuss the Implications
Address the broader implications of your research. Explain why your findings matter and how they contribute to the existing body of knowledge in your field.
Discuss the practical applications of your research and highlight any potential areas for further exploration.
If your research was about the positive effects of exercise on high school student's academic performance, the implications might be explained like this:
|
Step 5: Connect with the Introduction
Create a seamless connection between your conclusion and the introduction. Referencing key elements from the introduction helps to create a cohesive narrative for your paper.
This connection gives your research a sense of completeness and unity.
If your introduction highlighted the general concern of declining academic performance in high school students, you could create a connection in the conclusion like this:
|
Step 6: Consider the "So What?" Factor
Ask yourself the question, "So what?" Why should readers care about your research? Clearly articulate the significance of your findings and their relevance to the broader academic or real-world context.
Demonstrating the impact of your research adds depth to your conclusion.
Let's say your research revealed a positive link between exercise and academic performance in high school students. Here's how you might address the "So what?" factor:
|
Step 7: End with a Strong Closing Statement:
Conclude your research paper with a memorable closing statement. This could be a thought-provoking reflection, a call to action, or a suggestion for future research.
A strong closing leaves a lasting impression on your readers and emphasizes the importance of your work.
For a research paper on the positive effects of exercise on high school student's academic performance, a closing statement could look like this:
|
Research Paper Conclusion Examples
When it comes to writing a conclusion for your research paper, examining examples can offer valuable insights. Let’s take a look at this comprehensive example given below:
|
Still wondering how to write the conclusion for your research paper? Check out these examples for better understanding:
Conclusion For A Research Paper APA
Conclusion For A Research Paper Example Pdf
Conclusion For A Research Paper Pdf
Conclusion For A Research Paper Middle School
Conclusion For A Scientific Paper
Conclusion For A Research Paper Sample
Things to Avoid While Writing the Research Paper Conclusion
While crafting a conclusion for your research paper, it's crucial to steer clear of common pitfalls that can diminish the impact of your final remarks.
Here are some things to avoid:
- Repetition: Avoid rehashing the exact language used in the introduction or body of your paper. A conclusion should summarize key points without duplicating content.
- Introducing New Information: Resist the temptation to introduce new ideas or data in the conclusion. This section is for summarizing existing content and reinforcing key findings.
- Overly Complex Language: Keep your conclusion clear and accessible. Avoid introducing overly complex or technical language that might confuse your readers.
- Lack of Connection to Introduction: Ensure that your conclusion ties back to the introduction. Failing to connect these sections can make your paper feel disjointed.
- Vague Statements: Steer clear of vague statements that lack substance. Clearly articulate the significance of your findings and their broader implications.
- Apologies or Excuses: Avoid including apologies or excuses for limitations in your research. While acknowledging limitations is important, the conclusion is not the place to dwell on them.
- New Arguments or Debates: The conclusion is not the space to introduce new debates or arguments. Keep the focus on summarizing your research and its implications.
- Abrupt Endings: A conclusion should not end abruptly. Instead, provide a thoughtful and well-rounded closing statement about the results of your study.
To sum it up, we've gone through important steps to make your research paper conclusion strong. We covered things like going back to your main question, talking about the most important points, and thinking about why your research matters in the real world.
Remember, a good ending is more than just a summary; it captures the heart of your research and answers the big "So what?" question.
Remember, don't say the same things too much, don't add new details at the end, and keep your language simple!
If you ever need help with your academic writing, MyPerfectWords.com is here for you. Our expert writers are committed to helping you excel in your research papers and beyond.
Take the next step towards academic success with MyPerfectWords.com, and hire our legit essay writing service today!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Dr. Barbara is a highly experienced writer and author who holds a Ph.D. degree in public health from an Ivy League school. She has worked in the medical field for many years, conducting extensive research on various health topics. Her writing has been featured in several top-tier publications.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write a Research Paper Conclusion Section
What is a conclusion in a research paper?
The conclusion in a research paper is the final paragraph or two in a research paper. In scientific papers, the conclusion usually follows the Discussion section , summarizing the importance of the findings and reminding the reader why the work presented in the paper is relevant.
However, it can be a bit confusing to distinguish the conclusion section/paragraph from a summary or a repetition of your findings, your own opinion, or the statement of the implications of your work. In fact, the conclusion should contain a bit of all of these other parts but go beyond it—but not too far beyond!
The structure and content of the conclusion section can also vary depending on whether you are writing a research manuscript or an essay. This article will explain how to write a good conclusion section, what exactly it should (and should not) contain, how it should be structured, and what you should avoid when writing it.
Table of Contents:
What does a good conclusion section do, what to include in a research paper conclusion.
- Conclusion in an Essay
- Research Paper Conclusion
- Conclusion Paragraph Outline and Example
- What Not to Do When Writing a Conclusion
The conclusion of a research paper has several key objectives. It should:
- Restate your research problem addressed in the introduction section
- Summarize your main arguments, important findings, and broader implications
- Synthesize key takeaways from your study
The specific content in the conclusion depends on whether your paper presents the results of original scientific research or constructs an argument through engagement with previously published sources.
You presented your general field of study to the reader in the introduction section, by moving from general information (the background of your work, often combined with a literature review ) to the rationale of your study and then to the specific problem or topic you addressed, formulated in the form of the statement of the problem in research or the thesis statement in an essay.
In the conclusion section, in contrast, your task is to move from your specific findings or arguments back to a more general depiction of how your research contributes to the readers’ understanding of a certain concept or helps solve a practical problem, or fills an important gap in the literature. The content of your conclusion section depends on the type of research you are doing and what type of paper you are writing. But whatever the outcome of your work is, the conclusion is where you briefly summarize it and place it within a larger context. It could be called the “take-home message” of the entire paper.
What to summarize in the conclusion
Your conclusion section needs to contain a very brief summary of your work , a very brief summary of the main findings of your work, and a mention of anything else that seems relevant when you now look at your work from a bigger perspective, even if it was not initially listed as one of your main research questions. This could be a limitation, for example, a problem with the design of your experiment that either needs to be considered when drawing any conclusions or that led you to ask a different question and therefore draw different conclusions at the end of your study (compared to when you started out).
Once you have reminded the reader of what you did and what you found, you need to go beyond that and also provide either your own opinion on why your work is relevant (and for whom, and how) or theoretical or practical implications of the study , or make a specific call for action if there is one to be made.
How to Write an Essay Conclusion
Academic essays follow quite different structures than their counterparts in STEM and the natural sciences. Humanities papers often have conclusion sections that are much longer and contain more detail than scientific papers. There are three main types of academic essay conclusions.
Summarizing conclusion
The most typical conclusion at the end of an analytical/explanatory/argumentative essay is a summarizing conclusion . This is, as the name suggests, a clear summary of the main points of your topic and thesis. Since you might have gone through a number of different arguments or subtopics in the main part of your essay, you need to remind the reader again what those were, how they fit into each other, and how they helped you develop or corroborate your hypothesis.
For an essay that analyzes how recruiters can hire the best candidates in the shortest time or on “how starving yourself will increase your lifespan, according to science”, a summary of all the points you discussed might be all you need. Note that you should not exactly repeat what you said earlier, but rather highlight the essential details and present those to your reader in a different way.
Externalizing conclusion
If you think that just reminding the reader of your main points is not enough, you can opt for an externalizing conclusion instead, that presents new points that were not presented in the paper so far. These new points can be additional facts and information or they can be ideas that are relevant to the topic and have not been mentioned before.
Such a conclusion can stimulate your readers to think about your topic or the implications of your analysis in a whole new way. For example, at the end of a historical analysis of a specific event or development, you could direct your reader’s attention to some current events that were not the topic of your essay but that provide a different context for your findings.
Editorial conclusion
In an editorial conclusion , another common type of conclusion that you will find at the end of papers and essays, you do not add new information but instead present your own experiences or opinions on the topic to round everything up. What makes this type of conclusion interesting is that you can choose to agree or disagree with the information you presented in your paper so far. For example, if you have collected and analyzed information on how a specific diet helps people lose weight, you can nevertheless have your doubts on the sustainability of that diet or its practicability in real life—if such arguments were not included in your original thesis and have therefore not been covered in the main part of your paper, the conclusion section is the place where you can get your opinion across.
How to Conclude an Empirical Research Paper
An empirical research paper is usually more concise and succinct than an essay, because, if it is written well, it focuses on one specific question, describes the method that was used to answer that one question, describes and explains the results, and guides the reader in a logical way from the introduction to the discussion without going on tangents or digging into not absolutely relevant topics.
Summarize the findings
In a scientific paper, you should include a summary of the findings. Don’t go into great detail here (you will have presented your in-depth results and discussion already), but do clearly express the answers to the research questions you investigated.
Describe your main findings, even if they weren’t necessarily the ones anticipated, and explain the conclusion they led you to. Explain these findings in as few words as possible.
Instead of beginning with “ In conclusion, in this study, we investigated the effect of stress on the brain using fMRI …”, you should try to find a way to incorporate the repetition of the essential (and only the essential) details into the summary of the key points. “ The findings of this fMRI study on the effect of stress on the brain suggest that …” or “ While it has been known for a long time that stress has an effect on the brain, the findings of this fMRI study show that, surprisingly… ” would be better ways to start a conclusion.
You should also not bring up new ideas or present new facts in the conclusion of a research paper, but stick to the background information you have presented earlier, to the findings you have already discussed, and the limitations and implications you have already described. The one thing you can add here is a practical recommendation that you haven’t clearly stated before—but even that one needs to follow logically from everything you have already discussed in the discussion section.

Discuss the implications
After summing up your key arguments or findings, conclude the paper by stating the broader implications of the research , whether in methods , approach, or findings. Express practical or theoretical takeaways from your paper. This often looks like a “call to action” or a final “sales pitch” that puts an exclamation point on your paper.
If your research topic is more theoretical in nature, your closing statement should express the significance of your argument—for example, in proposing a new understanding of a topic or laying the groundwork for future research.
Future research example
Future research into education standards should focus on establishing a more detailed picture of how novel pedagogical approaches impact young people’s ability to absorb new and difficult concepts. Moreover, observational studies are needed to gain more insight into how specific teaching models affect the retention of relationships and facts—for instance, how inquiry-based learning and its emphasis on lateral thinking can be used as a jumping-off point for more holistic classroom approaches.
Research Conclusion Example and Outline
Let’s revisit the study on the effect of stress on the brain we mentioned before and see what the common structure for a conclusion paragraph looks like, in three steps. Following these simple steps will make it easy for you to wrap everything up in one short paragraph that contains all the essential information:
One: Short summary of what you did, but integrated into the summary of your findings:
While it has been known for a long time that stress has an effect on the brain, the findings of this fMRI study in 25 university students going through mid-term exams show that, surprisingly, one’s attitude to the experienced stress significantly modulates the brain’s response to it.
Note that you don’t need to repeat any methodological or technical details here—the reader has been presented with all of these before, they have read your results section and the discussion of your results, and even (hopefully!) a discussion of the limitations and strengths of your paper. The only thing you need to remind them of here is the essential outcome of your work.
Two: Add implications, and don’t forget to specify who this might be relevant for:
Students could be considered a specific subsample of the general population, but earlier research shows that the effect that exam stress has on their physical and mental health is comparable to the effects of other types of stress on individuals of other ages and occupations. Further research into practical ways of modulating not only one’s mental stress response but potentially also one’s brain activity (e.g., via neurofeedback training) are warranted.
This is a “research implication”, and it is nicely combined with a mention of a potential limitation of the study (the student sample) that turns out not to be a limitation after all (because earlier research suggests we can generalize to other populations). If there already is a lot of research on neurofeedback for stress control, by the way, then this should have been discussed in your discussion section earlier and you wouldn’t say such studies are “warranted” here but rather specify how your findings could inspire specific future experiments or how they should be implemented in existing applications.
Three: The most important thing is that your conclusion paragraph accurately reflects the content of your paper. Compare it to your research paper title , your research paper abstract , and to your journal submission cover letter , in case you already have one—if these do not all tell the same story, then you need to go back to your paper, start again from the introduction section, and find out where you lost the logical thread. As always, consistency is key.
Problems to Avoid When Writing a Conclusion
- Do not suddenly introduce new information that has never been mentioned before (unless you are writing an essay and opting for an externalizing conclusion, see above). The conclusion section is not where you want to surprise your readers, but the take-home message of what you have already presented.
- Do not simply copy your abstract, the conclusion section of your abstract, or the first sentence of your introduction, and put it at the end of the discussion section. Even if these parts of your paper cover the same points, they should not be identical.
- Do not start the conclusion with “In conclusion”. If it has its own section heading, that is redundant, and if it is the last paragraph of the discussion section, it is inelegant and also not really necessary. The reader expects you to wrap your work up in the last paragraph, so you don’t have to announce that. Just look at the above example to see how to start a conclusion in a natural way.
- Do not forget what your research objectives were and how you initially formulated the statement of the problem in your introduction section. If your story/approach/conclusions changed because of methodological issues or information you were not aware of when you started, then make sure you go back to the beginning and adapt your entire story (not just the ending).
Consider Receiving Academic Editing Services
When you have arrived at the conclusion of your paper, you might want to head over to Wordvice AI’s AI Writing Assistant to receive a free grammar check for any academic content.
After drafting, you can also receive English editing and proofreading services , including paper editing services for your journal manuscript. If you need advice on how to write the other parts of your research paper , or on how to make a research paper outline if you are struggling with putting everything you did together, then head over to the Wordvice academic resources pages , where we have a lot more articles and videos for you.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER FEATURE
- 28 February 2018
- Correction 16 March 2018
How to write a first-class paper
- Virginia Gewin 0
Virginia Gewin is a freelance writer in Portland, Oregon.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Manuscripts may have a rigidly defined structure, but there’s still room to tell a compelling story — one that clearly communicates the science and is a pleasure to read. Scientist-authors and editors debate the importance and meaning of creativity and offer tips on how to write a top paper.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
185,98 € per year
only 3,65 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Nature 555 , 129-130 (2018)
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-018-02404-4
Interviews have been edited for clarity and length.
Updates & Corrections
Correction 16 March 2018 : This article should have made clear that Altmetric is part of Digital Science, a company owned by Holtzbrinck Publishing Group, which is also the majority shareholder in Nature’s publisher, Springer Nature. Nature Research Editing Services is also owned by Springer Nature.
Related Articles

Massive Attack’s science-led drive to lower music’s carbon footprint
Career Feature 04 SEP 24

Tales of a migratory marine biologist
Career Feature 28 AUG 24

Nail your tech-industry interviews with these six techniques
Career Column 28 AUG 24

Publishing nightmare: a researcher’s quest to keep his own work from being plagiarized
News 04 SEP 24

Intellectual property and data privacy: the hidden risks of AI
Career Guide 04 SEP 24

How can I publish open access when I can’t afford the fees?
Career Feature 02 SEP 24
NOMIS Foundation ETH Postdoctoral Fellowship
The NOMIS Foundation ETH Fellowship Programme supports postdoctoral researchers at ETH Zurich within the Centre for Origin and Prevalence of Life ...
Zurich, Canton of Zürich (CH)
Centre for Origin and Prevalence of Life at ETH Zurich
13 PhD Positions at Heidelberg University
GRK2727/1 – InCheck Innate Immune Checkpoints in Cancer and Tissue Damage
Heidelberg, Baden-Württemberg (DE) and Mannheim, Baden-Württemberg (DE)
Medical Faculties Mannheim & Heidelberg and DKFZ, Germany
Postdoctoral Associate- Environmental Epidemiology
Houston, Texas (US)
Baylor College of Medicine (BCM)
Open Faculty Positions at the State Key Laboratory of Brain Cognition & Brain-inspired Intelligence
The laboratory focuses on understanding the mechanisms of brain intelligence and developing the theory and techniques of brain-inspired intelligence.
Shanghai, China
CAS Center for Excellence in Brain Science and Intelligence Technology (CEBSIT)
Research Associate - Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP)
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper

When you're wrapping up a research paper, the conclusion is like the grand finale of a fireworks show – it's your chance to leave a lasting impression. In this article, we'll break down the steps to help you write a winning research paper conclusion that not only recaps your main points but also ties everything together. Consider it the "So what?" moment – why should people care about your research? Our professional essay writers will guide you through making your conclusion strong, clear, and something that sticks with your readers long after they've put down your paper. So, let's dive in and ensure your research ends on a high note!
What Is a Conclusion in a Research Paper
In a research paper, the conclusion serves as the final segment, where you summarize the main points and findings of your study. It's not just a repetition of what you've already said but rather a chance to tie everything together and highlight the significance of your research. As you learn how to start a research paper , a good conclusion also often discusses the implications of your findings, suggests potential areas for further research, and leaves the reader with a lasting impression of the importance and relevance of your work in the broader context of the field. Essentially, it's your last opportunity to make a strong impact and leave your readers with a clear understanding of the significance of your research. Here’s a research paper conclusion example:
In conclusion, this research paper has navigated the intricacies of sustainable urban development, shedding light on the pivotal role of community engagement and innovative planning strategies. Through applying qualitative and quantitative research methods, we've uncovered valuable insights into the challenges and opportunities inherent in fostering environmentally friendly urban spaces. The implications of these findings extend beyond the confines of this study, emphasizing the imperative for continued exploration in the realms of urban planning and environmental sustainability. By emphasizing both the practical applications and theoretical contributions, this research underscores the significance of community involvement and forward-thinking strategies in shaping the future of urban landscapes. As cities evolve, incorporating these insights into planning and development practices will create resilient and harmonious urban environments.
Conclusion Outline for Research Paper
This outline for a research paper conclusion provides a structured framework to ensure that your ending effectively summarizes the key elements of your research paper and leaves a lasting impression on your readers. Adjust the content based on the specific requirements and focus of your research.
Restate the Thesis Statement
- Briefly restate the main thesis or research question.
- Emphasize the core objective or purpose of the study.
Summarize Key Findings
- Recap the main points and key findings from each section of the paper.
- Provide a concise overview of the research journey.
Discuss Implications
- Explore the broader implications of the research findings.
- Discuss how the results contribute to the existing body of knowledge in the field.
Address Limitations
- Acknowledge any limitations or constraints encountered during the research process.
- Explain how these limitations may impact the interpretation of the findings.
Suggest Areas for Future Research
- Propose potential directions for future studies related to the topic.
- Identify gaps in the current research that warrant further exploration.
Reaffirm Significance
- Reaffirm the importance and relevance of the research in the broader context.
- Highlight the practical applications or real-world implications of the study.
Concluding Statement
- Craft a strong, memorable closing statement that leaves a lasting impression.
- Sum up the overall impact of the research and its potential contribution to the field.
Study the full guide on how to make a research paper outline here, which will also specify the conclusion writing specifics to improve your general prowess.
Tips on How to Make a Conclusion in Research
Here are key considerations regarding a conclusion for research paper to not only recap the primary ideas in your work but also delve deeper to earn a higher grade:

- Provide a concise recap of your main research outcomes.
- Remind readers of your research goals and their accomplishments.
- Stick to summarizing existing content; refrain from adding new details.
- Emphasize why your research matters and its broader implications.
- Clearly explain the practical or theoretical impact of your findings.
- Prompt readers to reflect on how your research influences their perspective.
- Briefly discuss the robustness of your research methods.
- End with a suggestion for future research or a practical application.
- Transparently address any constraints or biases in your study.
- End on a powerful note, leaving a memorable impression on your readers.
.webp)
For your inspiration, we’ve also prepared this research proposal example APA , which dwells on another important aspect of research writing.
How to Write a Research Paper Conclusion
As you finish your research paper, the conclusion takes center stage. In this section, we've got five practical tips for writing a conclusion for a research paper. We'll guide you through summarizing your key findings, revisiting your research goals, discussing the bigger picture, addressing any limitations, and ending on a powerful note. Think of it as your roadmap to creating a conclusion that not only wraps up your research but also leaves a lasting impact on your readers. Let's dive in and make sure your conclusion stands out for all the right reasons!
.webp)
Synthesize Core Discoveries. Initiate your conclusion by synthesizing the essential discoveries of your research. Offer a succinct recapitulation of the primary points and outcomes you have elucidated in your paper. This aids in reinforcing the gravity of your work and reiterates the pivotal information you have presented.
Revisit Research Objectives. Revisit the research objectives or questions you outlined at the beginning of your paper. Assess whether you have successfully addressed these objectives and if your findings align with the initial goals of your research. This reflection helps tie your conclusion back to the purpose of your study.
Discuss Implications and Contributions. Discuss the broader implications of your research and its potential contributions to the field. Consider how your findings might impact future research, applications, or understanding of the subject matter. This demonstrates the significance of your work and places it within a larger context.
Address Limitations and Future Research. Acknowledge any limitations in your study, such as constraints in data collection or potential biases. Briefly discuss how these limitations might have affected your results. Additionally, suggest areas for future research that could build upon your work, addressing any unanswered questions or unexplored aspects. This demonstrates a thoughtful approach to your research.
End with a Strong Conclusion Statement. Conclude your research paper with a strong and memorable statement that reinforces the key message you want readers to take away. This could be a call to action, a proposal for further investigation, or a reflection on the broader significance of your findings. Leave your readers with a lasting impression that emphasizes the importance of your research. Remember that you can buy a research paper anytime if you lack time or get stuck in writer’s block.
Want to Enjoy the Benefits of Academic Freedom?
With our top-notch writers and 24/7 support, you can relax and focus on what really matters
Stylistic Devices to Use in a Conclusion
Discover distinctive stylistic insights that you can apply when writing a conclusion for a research paper:
- Rhetorical Questions. When using rhetorical questions, strategically place them to engage readers' minds. For instance, you might pose a question that prompts reflection on the broader implications of your findings, leaving your audience with something to ponder.
- Powerful Language. Incorporate strong language to convey a sense of conviction and importance. Choose words that resonate with the overall tone of your research and amplify the significance of your conclusions. This adds weight to your key messages.
- Repetitions. Repetitions can be employed to reinforce essential ideas. Reiterate key phrases or concepts in a way that emphasizes their importance without sounding redundant. This technique serves to drive home your main points.
- Anecdotes. Integrating anecdotes into your conclusion can provide a human touch. Share a brief and relevant story that connects with your research, making the information more relatable and memorable for your audience.
- Vivid Imagery. Lastly, use vivid imagery to paint a picture in the minds of your readers. Appeal to their senses by describing scenarios or outcomes related to your research. This creates a more immersive and lasting impression.
If you have a larger paper to write, for example a thesis, use our custom dissertation writing can help you in no time.
How to Make a Conclusion Logically Appealing
Knowing how to write a conclusion for a research paper that is logically appealing is important for leaving a lasting impression on your readers. Here are some tips to achieve this:
Logical Sequencing
- Present your conclusion in a structured manner, following the natural flow of your paper. Readers should effortlessly follow your thought process, making your conclusion more accessible and persuasive.
Reinforce Main Arguments
- Emphasize the core arguments and findings from your research. By reinforcing key points, you solidify your stance and provide a logical culmination to your paper.
Address Counterarguments
- Acknowledge and address potential counterarguments or limitations in your research. Demonstrate intellectual honesty and strengthen your conclusion by preemptively addressing potential doubts.
Connect with Introduction
- Revisit themes or concepts introduced in your introduction to create a cohesive narrative, allowing readers to trace the logical progression of your research from start to finish.
Propose Actionable Insights
- Suggest practical applications or recommendations based on your findings. This will add a forward-looking dimension, making your conclusion more relevant and compelling.
Highlight Significance
- Clearly articulate the broader implications of your research to convey the importance of your work and its potential impact on the field, making your conclusion logically compelling.
Are you ready to produce an A-grade assignment? If not, opt for a custom research paper from our skilled writers across various disciplines.
Avoid These Things When Writing a Research Paper Conclusion
As you write your conclusion of research paper, there’s a list of things professional writers don’t recommend doing. Consider these issues carefully:

- Repetition of Exact Phrases
- Repetitively using the same phrases or sentences from the main body. Repetition can make your conclusion seem redundant and less engaging.
- Overly Lengthy Summaries
- Providing excessively detailed summaries of each section of your paper. Readers may lose interest if the conclusion becomes too long and detailed.
- Unclear Connection to the Introduction
- Failing to connect the conclusion back to the introduction. A lack of continuity may make the paper feel disjointed.
- Adding New Arguments or Ideas
- Introducing new arguments or ideas that were not addressed in the body. This can confuse the reader and disrupt the coherence of your paper.
- Overuse of Complex Jargon
- Using excessively complex or technical language without clarification. Clear communication is essential in the conclusion, ensuring broad understanding.
- Apologizing or Undermining Confidence
- Apologizing for limitations or expressing doubt about your work. Maintain a confident tone; if limitations exist, present them objectively without undermining your research.
- Sweeping Generalizations
- Making overly broad or unsupported generalizations. Such statements can weaken the credibility of your conclusion.
- Neglecting the Significance
- Failing to emphasize the broader significance of your research. Readers need to understand why your findings matter in a larger context.
- Abrupt Endings
- Concluding abruptly without a strong closing statement. A powerful ending leaves a lasting impression; avoid a sudden or weak conclusion.
Research Paper Conclusion Example
That covers the essential aspects of summarizing a research paper. The only remaining step is to review the conclusion examples for research paper provided by our team.
Like our examples? Order our research proposal writing service to write paper according to your instructions to avoid plagiarizing and to keep your academic integrity strong.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, the knowledge of how to write the conclusion of a research paper is pivotal for presenting your findings and leaving a lasting impression on your readers. By summarizing the key points, reiterating the significance of your research, and offering avenues for future exploration, you can create a conclusion that not only reinforces the value of your study but also encourages further academic discourse. Remember to balance brevity and completeness, ensuring your conclusion is concise yet comprehensive. Emphasizing the practical implications of your research and connecting it to the broader academic landscape will help solidify the impact of your work. Pay someone to write a research paper if you are having a hard time finishing your coursework on time.
Tired of Stressing Over Endless Essays and Deadlines?
Let us take the load off your shoulders! Order your custom research paper today and experience the relief of knowing that your assignment is in expert hands
How To Write A Conclusion For A Research Paper?
What should the conclusion of a research paper contain, how to start a conclusion paragraph for a research paper.

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.


- Planet Earth
- Strange News
How To Write A Conclusion For A Science Research Paper
Table of Contents:
How to write a research paper conclusion . The conclusion of a research paper is where you wrap up your ideas and leave the reader with a strong final impression. It has several key goals: Restate.
Having summed up your key arguments or findings, the conclusion ends by considering the broader implications of your research. This means expressing the key takeaways, practical or theoretical, from your paper—often in the form of a call for action or suggestions for future research.
- “In conclusion …”
- Argumentative paper: Restate your thesis and arguments
- Empirical paper: Summarize your findings
- What is your plagiarism score?
- Argumentative paper: Strong closing statement
- Empirical paper: Future research directions
Video advice: How To Write A Conclusion For A Research Paper: A Structure For A Conclusion In A PhD Journal Paper
Every research paper has a similar conclusion. Once you see the pattern in the conclusions, you will start to be able to write a better conclusion for a research paper.

Writing a Research Paper Conclusion | Step-by-Step Guide
Argumentative paper summaryThe evidence is clear: To create a truly futureproof agricultural sector, Dutch farmers must be incentivized to transition from livestock farming to sustainable vegetable farming. As well as dramatically lowering emissions, plant-based agriculture, if approached in the right way, can produce more food with less land, providing opportunities for nature regeneration areas that will themselves contribute to climate targets. Although this approach would have economic ramifications, from a long-term perspective, it would represent a significant step towards a more sustainable and resilient national economy.
How to Write a Conclusion to a Science Research Paper
Purpose – Science research papers follow a particular structure, including an introduction, review of methods, report on results and discussion of the meaning. This discussion is often considered the conclusion for the paper. This differs from other research papers, which can often include many more sections, such as a literature review or annotated bibliography. Science research papers are typically focused on a specific scientific inquiry, whereas other research papers may only be based on printed material. PurposeAll conclusions are meant to summarize the results and implications of a topic under study. This can seem like repetition most of the time, but the discussion is one of the most important parts of a science research paper because it’s where a researcher should interpret results, discuss data, raise unanswered questions, be specific and give recommendations for future studies. In short, the discussion or conclusion section provides the most in-depth analysis of the findings in the study and gives readers a sense for what they should do with the information.
Conclusion Sections in Scientific Research Reports (IMRaD)
In IMRaD* reports, conclusions often fall under the discussion section. In some disciplines and journals, however, conclusions are separated from discussions. If this is the case for the paper you are working on, you may find the following description of common conclusion moves and sample language useful.
Writing in Different Genres – This is one of the first studies to more comprehensively examine adolescents’ knowledge of and attitudes towards e-cigarette ingredients, addictive properties, safety, perceived prevalence, acceptability, and regulation*… In our study of 9th and 12th graders, participants had more favorable attitudes towards and perceived less risk from e-cigarettes than cigarettes, and they expressed less support for policies that applied to e-cigarette than cigarette regulation. Participants believed that about 30% of their closest friends used e-cigarettes, which is approximately 10% higher than the self-reported rates in the sample… As we hypothesized, adolescents who have ever used tobacco perceive greater prevalence of e-cigarette use among their parents, siblings, and peers… These findings demonstrate the importance of developing educational and health messages that correct misperceptions about use rates of e-cigarettes, since it is plausible that beliefs about how many peers use e-cigarettes can translate into increased adolescent e-cigarette use.
Video advice: How to Write Your Conclusion for a Research Paper: 4 simple steps to write your conclusion section
Learn the four components to writing a great conclusion section!

Writing a Scientific Paper
Advice about writing the results, discussion and conclusion sections of a scientific paper.
The outcomes section is simply a presentation from the data. There shouldn’t be any discussion within the results section (which goes within the discussion section). The outcomes have to be presented in enough detail for somebody unfamiliar with the scientific paper to know them. All of the results ought to be described within the text from the results section in addition to being presented either in figures or tables. Each result must only be presented once. Don’t show exactly the same data in 2 forms (data ought to be presented as whether table or perhaps a figure not both). The written text from the results section should introduce each table or figure and supply a listing of the primary points from each. The outcomes should:The simple and clearPresent summaries of huge data sets (means with standard error or deviation)Detailed data ought to be reported in tables or figures and never as lists within the textOnly provide the data that is highly relevant to the paperRefer to each table or estimate the textEach figure or table ought to be recognized by a distinctive number e.
Step 10: Research Paper Conclusion
Looking for some help on how to write a research paper conclusion? This guide explains the best methods for writing a great conclusion to your paper.
Evidence attracted from the voluminous body of sources signifies the antiwar movement increased in direct proportion towards the war’s escalating unpopularity one of the United states citizens. The highly visible and vocal antiwar movement from the period reflected this growing popular antiwar sentiment.
- Common Mistakes in a Conclusion
- Seven Common Conclusion Mistakes
- Basic Features of a Conclusion
- Restate Paper’s Principal Topic
- Restate Principal Arguments
- Summarize Counterpoints
- Future Research
- Sample Research Conclusion
- Poorly Constructed Conclusion Example
- Properly Constructed Conclusion Example
A research paper should end with a well-constructed conclusion. Many inexperienced writers underestimate the importance of having a solid conclusion to their paper. However, a paper that lacks a good conclusion will often seem incomplete to the reader and seriously detract from the quality of the paper. Learning how to end a paper with an appropriate conclusion is an essential part of becoming a quality writer. A good conclusion will greatly enhance a paper’s coherence and appeal to the reader.
How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper
For example, if you are writing a history paper, then you might discuss how the historical topic you discussed matters today. If you are writing about a foreign country, then you might use the conclusion to discuss how the information you shared may help readers understand their own country.
The final outcome of the research paper must summarize the information and reason for the paper without seeming too wooden or dry. Every fundamental conclusion must share several important elements, but there’s also several tactics you are able to alter to craft a far more effective conclusion and many you need to avoid to avoid yourself from weakening your paper’s conclusion. Here are a few writing ideas to bear in mind when designing a conclusion for your forthcoming research paper.
Academic Phrases for Writing Conclusion Section of a Research Paper
A research paper should end with a well-constructed conclusion. The conclusion is somewhat similar to the introduction. You restate your aims and objectives and summarize your main findings and evidence for the reader. You can usually do this in one paragraph with three main key points, and one strong take-home message. You should not present any new arguments in your conclusion. You can raise some open questions and set the scene for the next study. This is a good place to register your thoughts about possible future work. Try to explain to your readers what more could be done? What do you think are the next steps to take? What other questions warrant further investigation? Remember, the conclusion is the last part of the essay that your reader will see, so spend some time writing the conclusion so that you can end on a high note.
Conclusions // Purdue Writing Lab – The Purdue College Online Writing Lab serves authors from around the globe and also the Purdue College Writing Lab helps authors on Purdue’s campus.
This resource outlines the generally accepted structure for introductions, body paragraphs, and conclusions in an academic argument paper. Keep in mind that this resource contains guidelines and not strict rules about organization. Your structure needs to be flexible enough to meet the requirements of your purpose and audience.
Expert Advice on How To Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper
This post offers expert advice on how to write a conclusion for a research paper in engaging & persuasive ways that highlight the value of your research..
If you’re while preparing articles to have an academic or scientific journal, or planning one for the long run, you could be thinking about a brand new book, Help guide to Journal Publication, that is on our Advice on Publishing Research in Journals website.
Writing an academic or scientific research paper is a challenging task, so one can hardly wonder if the author breathes a sigh of relief and considers the job virtually done once the findings have been interpreted in a carefully crafted discussion. Indeed, if concluding thoughts have been offered at the end of the discussion section, the paper may be close to finished, but for most research papers, a separate conclusion is necessary, and a pause for reflecting on what has been written and accomplished is always advisable before tackling the conclusion. The tips offered here on how to write a conclusion for a research paper are designed for that thoughtful moment when making the best decisions is so vital for producing a clear, engaging and persuasive conclusion.
Related Articles:
- How To Write A Research Paper Science
- How To Write Abstract For Science Research Paper
- How To Write A Good Political Science Research Paper
- How To Write A Research Paper Biology
- How To Write A Research Paper In Biotechnology
- How To Write A Research Paper On Robotics
You may also like

Why Are Big Companies So Bad At Innovation

Which Of The Following Is True Geology

How Many Types Of Salts In Chemistry
Add comment, cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Recent discoveries

Would You Like To Travel Into Space Ielts Speaking

How Much Space Is Required For A Workstation

______ Is Regarded As The Father Of Modern Geology

Will The Innovation For Homeland Security Work
- Animals 3041
- Astronomy 8
- Biology 2281
- Chemistry 482
- Culture 1333
- Entertainment 1139
- Health 8466
- History 2152
- Human Spaceflights 1209
- Physics 913
- Planet Earth 3239
- Science 2158
- Science & Astronomy 4927
- Search For Life 599
- Skywatching 1274
- Spaceflight 4586
- Strange News 1230
- Technology 3625
- Terms and Conditions 163
Random fact

Weekend Lyrid Meteor Shower Visible From Earth, Space and … Balloon?
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Science Writing
How to Write an Effective Conclusion for a Science Lab Report
Last Updated: August 9, 2024 Fact Checked
- Discussing the Experiment
- Writing What You Learned
- Ending Your Conclusion
Finalizing Your Lab Report
This article was co-authored by Bess Ruff, MA . Bess Ruff is a Geography PhD student at Florida State University. She received her MA in Environmental Science and Management from the University of California, Santa Barbara in 2016. She has conducted survey work for marine spatial planning projects in the Caribbean and provided research support as a graduate fellow for the Sustainable Fisheries Group. There are 10 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 1,773,593 times.
A lab report describes an entire experiment from start to finish, outlining the procedures, reporting results, and analyzing data. The report is used to demonstrate what has been learned, and it will provide a way for other people to see your process for the experiment and understand how you arrived at your conclusions. The conclusion is an integral part of the report; this is the section that reiterates the experiment’s main findings and gives the reader an overview of the lab trial. Writing a solid conclusion to your lab report will demonstrate that you’ve effectively learned the objectives of your assignment.
How to Write a Lab Report Conclusion
- Restate the purpose of the experiment and your procedures.
- Describe the results or findings and if they support your hypothesis.
- Mention what you've learned from the experiment.
- Note any errors or uncertainties that could affect the results.
- Propose experiments for the future to gain more findings.
Outlining Your Conclusion

- Restate : Restate the lab experiment by describing the assignment.
- Explain : Explain the purpose of the lab experiment. What were you trying to figure out or discover? Talk briefly about the procedure you followed to complete the lab.
- Results : Explain your results. Confirm whether or not your hypothesis was supported by the results.
- Uncertainties : Account for uncertainties and errors. Explain, for example, if there were other circumstances beyond your control that might have impacted the experiment’s results.
- New : Discuss new questions or discoveries that emerged from the experiment.

- Your assignment may also have specific questions that need to be answered. Make sure you answer these fully and coherently in your conclusion.
Discussing the Experiment and Hypothesis

- If you tried the experiment more than once, describe the reasons for doing so. Discuss changes that you made in your procedures.
- Brainstorm ways to explain your results in more depth. Go back through your lab notes, paying particular attention to the results you observed. [3] X Trustworthy Source University of North Carolina Writing Center UNC's on-campus and online instructional service that provides assistance to students, faculty, and others during the writing process Go to source

- Start this section with wording such as, “The results showed that…”
- You don’t need to give the raw data here. Just summarize the main points, calculate averages, or give a range of data to give an overall picture to the reader.
- Make sure to explain whether or not any statistical analyses were significant, and to what degree, such as 1%, 5%, or 10%.

- Use simple language such as, “The results supported the hypothesis,” or “The results did not support the hypothesis.”

Demonstrating What You Have Learned

- If it’s not clear in your conclusion what you learned from the lab, start off by writing, “In this lab, I learned…” This will give the reader a heads up that you will be describing exactly what you learned.
- Add details about what you learned and how you learned it. Adding dimension to your learning outcomes will convince your reader that you did, in fact, learn from the lab. Give specifics about how you learned that molecules will act in a particular environment, for example.
- Describe how what you learned in the lab could be applied to a future experiment.

- On a new line, write the question in italics. On the next line, write the answer to the question in regular text.

- If your experiment did not achieve the objectives, explain or speculate why not.
Wrapping Up Your Conclusion

- If your experiment raised questions that your collected data can’t answer, discuss this here.

- Describe what is new or innovative about your research.
- This can often set you apart from your classmates, many of whom will just write up the barest of discussion and conclusion.

Community Q&A

- Ensure the language used is straightforward with specific details. Try not to drift off topic. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0
- Once again, avoid using personal pronouns (I, myself, we, our group) in a lab report. The first-person point-of-view is often seen as subjective, whereas science is based on objectivity. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0
- If you include figures or tables in your conclusion, be sure to include a brief caption or label so that the reader knows what the figures refer to. Also, discuss the figures briefly in the text of your report. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0

- Take care with writing your lab report when working in a team setting. While the lab experiment may be a collaborative effort, your lab report is your own work. If you copy sections from someone else’s report, this will be considered plagiarism. Thanks Helpful 4 Not Helpful 0
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://phoenixcollege.libguides.com/LabReportWriting/introduction
- ↑ https://www.education.vic.gov.au/school/teachers/teachingresources/discipline/english/literacy/Pages/puttingittogether.aspx
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/brainstorming/
- ↑ https://advice.writing.utoronto.ca/types-of-writing/lab-report/
- ↑ http://www.socialresearchmethods.net/kb/hypothes.php
- ↑ https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/conclusion
- ↑ https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/introduction/researchproblem
- ↑ http://writingcenter.unc.edu/handouts/scientific-reports/
- ↑ https://phoenixcollege.libguides.com/LabReportWriting/labreportstyle
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/editing-and-proofreading/
About This Article

To write a good lab conclusion in science, start with restating the lab experiment by describing the assignment. Next, explain what you were trying to discover or figure out by doing the experiment. Then, list your results and explain how they confirmed or did not confirm your hypothesis. Additionally, include any uncertainties, such as circumstances beyond your control that may have impacted the results. Finally, discuss any new questions or discoveries that emerged from the experiment. For more advice, including how to wrap up your lab report with a final statement, keep reading. Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Maddie Briere
Oct 5, 2017
Did this article help you?
Jun 13, 2017
Saujash Barman
Sep 7, 2017
Cindy Zhang
Jan 16, 2017
Oct 29, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research paper
Writing a Research Paper Introduction | Step-by-Step Guide
Published on September 24, 2022 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on March 27, 2023.

The introduction to a research paper is where you set up your topic and approach for the reader. It has several key goals:
- Present your topic and get the reader interested
- Provide background or summarize existing research
- Position your own approach
- Detail your specific research problem and problem statement
- Give an overview of the paper’s structure
The introduction looks slightly different depending on whether your paper presents the results of original empirical research or constructs an argument by engaging with a variety of sources.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Step 1: introduce your topic, step 2: describe the background, step 3: establish your research problem, step 4: specify your objective(s), step 5: map out your paper, research paper introduction examples, frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
The first job of the introduction is to tell the reader what your topic is and why it’s interesting or important. This is generally accomplished with a strong opening hook.
The hook is a striking opening sentence that clearly conveys the relevance of your topic. Think of an interesting fact or statistic, a strong statement, a question, or a brief anecdote that will get the reader wondering about your topic.
For example, the following could be an effective hook for an argumentative paper about the environmental impact of cattle farming:
A more empirical paper investigating the relationship of Instagram use with body image issues in adolescent girls might use the following hook:
Don’t feel that your hook necessarily has to be deeply impressive or creative. Clarity and relevance are still more important than catchiness. The key thing is to guide the reader into your topic and situate your ideas.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
This part of the introduction differs depending on what approach your paper is taking.
In a more argumentative paper, you’ll explore some general background here. In a more empirical paper, this is the place to review previous research and establish how yours fits in.
Argumentative paper: Background information
After you’ve caught your reader’s attention, specify a bit more, providing context and narrowing down your topic.
Provide only the most relevant background information. The introduction isn’t the place to get too in-depth; if more background is essential to your paper, it can appear in the body .
Empirical paper: Describing previous research
For a paper describing original research, you’ll instead provide an overview of the most relevant research that has already been conducted. This is a sort of miniature literature review —a sketch of the current state of research into your topic, boiled down to a few sentences.
This should be informed by genuine engagement with the literature. Your search can be less extensive than in a full literature review, but a clear sense of the relevant research is crucial to inform your own work.
Begin by establishing the kinds of research that have been done, and end with limitations or gaps in the research that you intend to respond to.
The next step is to clarify how your own research fits in and what problem it addresses.
Argumentative paper: Emphasize importance
In an argumentative research paper, you can simply state the problem you intend to discuss, and what is original or important about your argument.
Empirical paper: Relate to the literature
In an empirical research paper, try to lead into the problem on the basis of your discussion of the literature. Think in terms of these questions:
- What research gap is your work intended to fill?
- What limitations in previous work does it address?
- What contribution to knowledge does it make?
You can make the connection between your problem and the existing research using phrases like the following.
| Although has been studied in detail, insufficient attention has been paid to . | You will address a previously overlooked aspect of your topic. |
| The implications of study deserve to be explored further. | You will build on something suggested by a previous study, exploring it in greater depth. |
| It is generally assumed that . However, this paper suggests that … | You will depart from the consensus on your topic, establishing a new position. |
Now you’ll get into the specifics of what you intend to find out or express in your research paper.
The way you frame your research objectives varies. An argumentative paper presents a thesis statement, while an empirical paper generally poses a research question (sometimes with a hypothesis as to the answer).
Argumentative paper: Thesis statement
The thesis statement expresses the position that the rest of the paper will present evidence and arguments for. It can be presented in one or two sentences, and should state your position clearly and directly, without providing specific arguments for it at this point.
Empirical paper: Research question and hypothesis
The research question is the question you want to answer in an empirical research paper.
Present your research question clearly and directly, with a minimum of discussion at this point. The rest of the paper will be taken up with discussing and investigating this question; here you just need to express it.
A research question can be framed either directly or indirectly.
- This study set out to answer the following question: What effects does daily use of Instagram have on the prevalence of body image issues among adolescent girls?
- We investigated the effects of daily Instagram use on the prevalence of body image issues among adolescent girls.
If your research involved testing hypotheses , these should be stated along with your research question. They are usually presented in the past tense, since the hypothesis will already have been tested by the time you are writing up your paper.
For example, the following hypothesis might respond to the research question above:
Scribbr Citation Checker New
The AI-powered Citation Checker helps you avoid common mistakes such as:
- Missing commas and periods
- Incorrect usage of “et al.”
- Ampersands (&) in narrative citations
- Missing reference entries

The final part of the introduction is often dedicated to a brief overview of the rest of the paper.
In a paper structured using the standard scientific “introduction, methods, results, discussion” format, this isn’t always necessary. But if your paper is structured in a less predictable way, it’s important to describe the shape of it for the reader.
If included, the overview should be concise, direct, and written in the present tense.
- This paper will first discuss several examples of survey-based research into adolescent social media use, then will go on to …
- This paper first discusses several examples of survey-based research into adolescent social media use, then goes on to …
Full examples of research paper introductions are shown in the tabs below: one for an argumentative paper, the other for an empirical paper.
- Argumentative paper
- Empirical paper
Are cows responsible for climate change? A recent study (RIVM, 2019) shows that cattle farmers account for two thirds of agricultural nitrogen emissions in the Netherlands. These emissions result from nitrogen in manure, which can degrade into ammonia and enter the atmosphere. The study’s calculations show that agriculture is the main source of nitrogen pollution, accounting for 46% of the country’s total emissions. By comparison, road traffic and households are responsible for 6.1% each, the industrial sector for 1%. While efforts are being made to mitigate these emissions, policymakers are reluctant to reckon with the scale of the problem. The approach presented here is a radical one, but commensurate with the issue. This paper argues that the Dutch government must stimulate and subsidize livestock farmers, especially cattle farmers, to transition to sustainable vegetable farming. It first establishes the inadequacy of current mitigation measures, then discusses the various advantages of the results proposed, and finally addresses potential objections to the plan on economic grounds.
The rise of social media has been accompanied by a sharp increase in the prevalence of body image issues among women and girls. This correlation has received significant academic attention: Various empirical studies have been conducted into Facebook usage among adolescent girls (Tiggermann & Slater, 2013; Meier & Gray, 2014). These studies have consistently found that the visual and interactive aspects of the platform have the greatest influence on body image issues. Despite this, highly visual social media (HVSM) such as Instagram have yet to be robustly researched. This paper sets out to address this research gap. We investigated the effects of daily Instagram use on the prevalence of body image issues among adolescent girls. It was hypothesized that daily Instagram use would be associated with an increase in body image concerns and a decrease in self-esteem ratings.
The introduction of a research paper includes several key elements:
- A hook to catch the reader’s interest
- Relevant background on the topic
- Details of your research problem
and your problem statement
- A thesis statement or research question
- Sometimes an overview of the paper
Don’t feel that you have to write the introduction first. The introduction is often one of the last parts of the research paper you’ll write, along with the conclusion.
This is because it can be easier to introduce your paper once you’ve already written the body ; you may not have the clearest idea of your arguments until you’ve written them, and things can change during the writing process .
The way you present your research problem in your introduction varies depending on the nature of your research paper . A research paper that presents a sustained argument will usually encapsulate this argument in a thesis statement .
A research paper designed to present the results of empirical research tends to present a research question that it seeks to answer. It may also include a hypothesis —a prediction that will be confirmed or disproved by your research.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, March 27). Writing a Research Paper Introduction | Step-by-Step Guide. Scribbr. Retrieved September 5, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-paper/research-paper-introduction/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, writing a research paper conclusion | step-by-step guide, research paper format | apa, mla, & chicago templates, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

Online Students
For All Online Programs
International Students
On Campus, need or have Visa
Campus Students
For All Campus Programs
What a Thesis Paper is and How to Write One

From choosing a topic and conducting research to crafting a strong argument, writing a thesis paper can be a rewarding experience.
It can also be a challenging experience. If you've never written a thesis paper before, you may not know where to start. You may not even be sure exactly what a thesis paper is. But don't worry; the right support and resources can help you navigate this writing process.
What is a Thesis Paper?

A thesis paper is a type of academic essay that you might write as a graduation requirement for certain bachelor's, master's or honors programs. Thesis papers present your own original research or analysis on a specific topic related to your field.
“In some ways, a thesis paper can look a lot like a novella,” said Shana Chartier , director of information literacy at Southern New Hampshire University (SNHU). “It’s too short to be a full-length novel, but with the standard size of 40-60 pages (for a bachelor’s) and 60-100 pages (for a master’s), it is a robust exploration of a topic, explaining one’s understanding of a topic based on personal research.”
Chartier has worked in academia for over 13 years and at SNHU for nearly eight. In her role as an instructor and director, Chartier has helped to guide students through the writing process, like editing and providing resources.
Chartier has written and published academic papers such as "Augmented Reality Gamifies the Library: A Ride Through the Technological Frontier" and "Going Beyond the One-Shot: Spiraling Information Literacy Across Four Years." Both of these academic papers required Chartier to have hands-on experience with the subject matter. Like a thesis paper, they also involved hypothesizing and doing original research to come to a conclusion.
“When writing a thesis paper, the importance of staying organized cannot be overstated,” said Chartier. “Mapping out each step of the way, making firm and soft deadlines... and having other pairs of eyes on your work to ensure academic accuracy and clean editing are crucial to writing a successful paper.”
How Do I Choose a Topic For My Thesis Paper?

What your thesis paper is for will determine some of the specific requirements and steps you might take, but the first step is usually the same: Choosing a topic.
“Choosing a topic can be daunting," said Rochelle Attari , a peer tutor at SNHU. "But if (you) stick with a subject (you're) interested in... choosing a topic is much more manageable.”
Similar to a thesis, Attari recently finished the capstone for her bachelor’s in psychology . Her bachelor’s concentration is in forensics, and her capstone focused on the topic of using a combined therapy model for inmates who experience substance abuse issues to reduce recidivism.
“The hardest part was deciding what I wanted to focus on,” Attari said. “But once I nailed down my topic, each milestone was more straightforward.”
In her own writing experience, Attari said brainstorming was an important step when choosing her topic. She recommends writing down different ideas on a piece of paper and doing some preliminary research on what’s already been written on your topic.
By doing this exercise, you can narrow or broaden your ideas until you’ve found a topic you’re excited about. " Brainstorming is essential when writing a paper and is not a last-minute activity,” Attari said.
How Do I Structure My Thesis Paper?
Thesis papers tend to have a standard format with common sections as the building blocks.
While the structure Attari describes below will work for many theses, it’s important to double-check with your program to see if there are any specific requirements. Writing a thesis for a Master of Fine Arts, for example, might actually look more like a fiction novel.
According to Attari, a thesis paper is often structured with the following major sections:
Introduction
- Literature review
- Methods, results
Now, let’s take a closer look at what each different section should include.
Your introduction is your opportunity to present the topic of your thesis paper. In this section, you can explain why that topic is important. The introduction is also the place to include your thesis statement, which shows your stance in the paper.
Attari said that writing an introduction can be tricky, especially when you're trying to capture your reader’s attention and state your argument.
“I have found that starting with a statement of truth about a topic that pertains to an issue I am writing about typically does the trick,” Attari said. She demonstrated this advice in an example introduction she wrote for a paper on the effects of daylight in Alaska:
In the continental United States, we can always count on the sun rising and setting around the same time each day, but in Alaska, during certain times of the year, the sun rises and does not set for weeks. Research has shown that the sun provides vitamin D and is an essential part of our health, but little is known about how daylight twenty-four hours a day affects the circadian rhythm and sleep.
In the example Attari wrote, she introduces the topic and informs the reader what the paper will cover. Somewhere in her intro, she said she would also include her thesis statement, which might be:
Twenty-four hours of daylight over an extended period does not affect sleep patterns in humans and is not the cause of daytime fatigue in northern Alaska .
Literature Review
In the literature review, you'll look at what information is already out there about your topic. “This is where scholarly articles about your topic are essential,” said Attari. “These articles will help you find the gap in research that you have identified and will also support your thesis statement."
Telling your reader what research has already been done will help them see how your research fits into the larger conversation. Most university libraries offer databases of scholarly/peer-reviewed articles that can be helpful in your search.
In the methods section of your thesis paper, you get to explain how you learned what you learned. This might include what experiment you conducted as a part of your independent research.
“For instance,” Attari said, “if you are a psychology major and have identified a gap in research on which therapies are effective for anxiety, your methods section would consist of the number of participants, the type of experiment and any other particulars you would use for that experiment.”
In this section, you'll explain the results of your study. For example, building on the psychology example Attari outlined, you might share self-reported anxiety levels for participants trying different kinds of therapies. To help you communicate your results clearly, you might include data, charts, tables or other visualizations.
The discussion section of your thesis paper is where you will analyze and interpret the results you presented in the previous section. This is where you can discuss what your findings really mean or compare them to the research you found in your literature review.
The discussion section is your chance to show why the data you collected matters and how it fits into bigger conversations in your field.
The conclusion of your thesis paper is your opportunity to sum up your argument and leave your reader thinking about why your research matters.
Attari breaks the conclusion down into simple parts. “You restate the original issue and thesis statement, explain the experiment's results and discuss possible next steps for further research,” she said.
Find Your Program
Resources to help write your thesis paper.
While your thesis paper may be based on your independent research, writing it doesn’t have to be a solitary process. Asking for help and using the resources that are available to you can make the process easier.
If you're writing a thesis paper, some resources Chartier encourages you to use are:
- Citation Handbooks: An online citation guide or handbook can help you ensure your citations are correct. APA , MLA and Chicago styles have all published their own guides.
- Citation Generators: There are many citation generator tools that help you to create citations. Some — like RefWorks — even let you directly import citations from library databases as you research.
- Your Library's Website: Many academic and public libraries allow patrons to access resources like databases or FAQs. Some FAQs at the SNHU library that might be helpful in your thesis writing process include “ How do I read a scholarly article? ” or “ What is a research question and how do I develop one? ”
It can also be helpful to check out what coaching or tutoring options are available through your school. At SNHU, for example, the Academic Support Center offers writing and grammar workshops , and students can access 24/7 tutoring and 1:1 sessions with peer tutors, like Attari.
"Students can even submit their papers and receive written feedback... like revisions and editing suggestions," she said.
If you are writing a thesis paper, there are many resources available to you. It's a long paper, but with the right mindset and support, you can successfully navigate the process.
“Pace yourself,” said Chartier. “This is a marathon, not a sprint. Setting smaller goals to get to the big finish line can make the process seem less daunting, and remember to be proud of yourself and celebrate your accomplishment once you’re done. Writing a thesis is no small task, and it’s important work for the scholarly community.”
A degree can change your life. Choose your program from 200+ SNHU degrees that can take you where you want to go.
Meg Palmer ’18 is a writer and scholar by trade who loves reading, riding her bike and singing in a barbershop quartet. She earned her bachelor’s degree in English, language and literature at Southern New Hampshire University (SNHU) and her master’s degree in writing, rhetoric and discourse at DePaul University (’20). While attending SNHU, she served as the editor-in-chief of the campus student newspaper, The Penmen Press, where she deepened her passion for writing. Meg is an adjunct professor at Johnson and Wales University, where she teaches first year writing, honors composition, and public speaking. Connect with her on LinkedIn .
Explore more content like this article

What is the Difference Between Bachelor’s and Master’s Degrees?

Academic Referencing: How to Cite a Research Paper

What is Considered Plagiarism And How to Avoid It
About southern new hampshire university.

SNHU is a nonprofit, accredited university with a mission to make high-quality education more accessible and affordable for everyone.
Founded in 1932, and online since 1995, we’ve helped countless students reach their goals with flexible, career-focused programs . Our 300-acre campus in Manchester, NH is home to over 3,000 students, and we serve over 135,000 students online. Visit our about SNHU page to learn more about our mission, accreditations, leadership team, national recognitions and awards.
A comprehensive review of energy harvesting technologies for sustainable electric vehicles
- Sustainable Technologies for Environmental Health and Safety
- Published: 06 September 2024
Cite this article

- Abhidnya Sunil Mhatre 1 &
- Prashant Shukla ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2271-818X 1
This review paper provides a comprehensive examination of energy harvesting technologies tailored for electric vehicles (EVs). Against the backdrop of the automotive industry’s rapid evolution towards electrification and sustainability, the paper explores a diverse range of techniques. The analysis encompasses the strengths, weaknesses, applicability in various scenarios, and potential implications for the future of EVs. A key finding of the review highlights regenerative braking as a pivotal and highly efficient method for energy recovery, particularly in urban settings. In addition to extending battery life, regenerative braking significantly boosts energy efficiency of EVs. The paper also delves into the challenges associated with integrated solar energy systems, emphasizing issues related to efficiency and weather dependency. Kinetic energy recovery systems (KERS) are discussed for their substantial power boost during acceleration in both motorsports and road cars. Additionally, the review explores regenerative shock absorbers, which capture energy from suspension movement, enhancing ride comfort and increasing vehicle energy economy, especially on uneven terrain. The piezoelectric system, though intriguing, is found to have low power output from mechanical vibration, prompting further exploration for integration into EVs. However, complexities and cost considerations arise in their integration with the vehicle’s suspension system.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
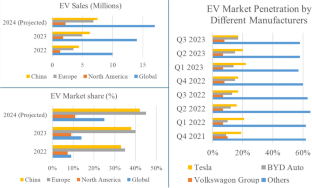
Explore related subjects
- Environmental Chemistry
Data availability
As this manuscript is a review paper, no new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Abdelrahman M, Liu G, Fan C, Zhang Z, Ali A, Li H, Azam A, Cao H, Mohamed AA (2023) Energy regenerative shock absorber based on a slotted link conversion mechanism for application in the electrical bus to power the low wattages devices. Appl Energy 347:121409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2023.121409
Article Google Scholar
Aksu U, Halicioglu R (2018) A review study on energy harvesting systems for vehicles. Tehnički Glasnik 12(4):251–259. https://doi.org/10.31803/tg-20180210153816
Ali A, Qi L, Zhang T, Li H, Azam A, Zhang Z (2021) Design of novel energy-harvesting regenerative shock absorber using barrel cam follower mechanism to power the auxiliaries of a driverless electric bus. Sustain Energy Technol Assessments 48:101565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2021.101565
Armenta-Déu C, Cortés H (2023) Analysis of kinetic energy recovery systems in electric vehicles. Vehicles 5(2):387–403. https://doi.org/10.3390/vehicles5020022
Bai S, Liu C (2021) Overview of energy harvesting and emission reduction technologies in hybrid electric vehicles. In Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews (Vol. 147). Elsevier Ltd. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2021.111188
Barton DAW, Burrow SG, Clare LR (2010) Energy harvesting from vibrations with a nonlinear oscillator. J Vib Acoust 132(2):0210091–0210097. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4000809
Bentouba S, Zioui N, Breuhaus P, Bourouis M (2023) Overview of the potential of energy harvesting sources in electric vehicles. Energies 16(13):5193. https://doi.org/10.3390/EN16135193
Bhurat S, Sharma H, Kumar A, Dixit K, Shukla P, Kunwer R (2018) Magnetization of diesel fuel for compression ignition engine to enhance efficiency and emissions. Int J Appl Eng Res 13:341–347
Google Scholar
Caban J, Vrabel J, Górnicka D, Nowak R, Jankiewicz M, Matijošius J, Palka M (2023) Overview of energy harvesting technologies used in road vehicles. Energies 16(9):3787. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16093787
Article CAS Google Scholar
Chen C, Sharafi A, Sun JQ (2020) A high density piezoelectric energy harvesting device from highway traffic – design analysis and laboratory validation. Appl Energy 269:115073. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.115073
Dahat N, Maskar P, Yadav A (2023) Design and development of regenerative shock absorber. Mater Today Proc 82:363–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2023.02.433
Day A (2014) Brake system layout design. Braking of Road Vehicles, 149–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-397314-6.00006-1
Devlet B, Ertürk M, Gürbüz EY, Keçebaş A (2023) Investigation of using modified photovoltaic solar panels for battery charge of electric L1 category vehicles. Mater Today Proc 81:10–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.11.151
Ebrahimi B, Khamesee MB, Golnaraghi MF (2008) Design and modeling of a magnetic shock absorber based on eddy current damping effect. J Sound Vib 315(4–5):875–889. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JSV.2008.02.022
Ebrahimi B, Bolandhemmat H, Khamesee MB, Golnaraghi F (2011) A hybrid electromagnetic shock absorber for active vehicle suspension systems. Veh Syst Dyn 49(1–2):311–332. https://doi.org/10.1080/00423111003602400
El-Sherif O (2011). Looking for the next gram . BMW Group. https://www.press.bmwgroup.com/global/article/detail/T0119738EN/looking-for-the-next-gram?language=en
Elliott SJ, Zilletti M (2014) Scaling of electromagnetic transducers for shunt damping and energy harvesting. J Sound Vib 333(8):2185–2195. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JSV.2013.11.036
Ershad NF, Mehrjardi R, Ehsani M (2019) Development of a kinetic energy recovery system using an active electromagnetic slip coupling. IEEE Trans Transp Electrif 5(2):456–464. https://doi.org/10.1109/TTE.2019.2891045
Fang Z, Guo X, Xu L, Zhang H (2013) An optimal algorithm for energy recovery of hydraulic electromagnetic energy-regenerative shock absorber. Appl Math Inform Sci 7(6):2207–2214. https://doi.org/10.12785/AMIS/070610
Fang Z, Guo X, Xu L, Zhang H (2013b) Experimental study of damping and energy regeneration characteristics of a hydraulic electromagnetic shock absorber. Adv Mech Eng 5:943528. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/943528
Figueiredo R, Nunes P, Brito MC (2017) The feasibility of solar parking lots for electric vehicles. Energy 140:1182–1197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2017.09.024
Galluzzi R, Circosta S, Amati N, Tonoli A (2021) Rotary regenerative shock absorbers for automotive suspensions. Mechatronics 77:102580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechatronics.2021.102580
Gong B, Guo X, Hu S, Fang Z (2016) The ride comfort and energy-regenerative characteristics analysis of hydraulic-electricity energy regenerative suspension. J Vibroeng 18(3):1765–1782. https://doi.org/10.21595/JVE.2016.16746
Guo S, Liu Y, Xu L, Guo X, Zuo L (2016) Performance evaluation and parameter sensitivity of energy-harvesting shock absorbers on different vehicles. Veh Syst Dyn 54(7):918–942. https://doi.org/10.1080/00423114.2016.1174276
Hamada AT, Orhan MF (2022) An overview of regenerative braking systems. In Journal of Energy Storage (Vol. 52). Elsevier Ltd. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.est.2022.105033
Heydari S, Fajri P, Sabzehgar R, Asrari A (2020) Optimal brake allocation in electric vehicles for maximizing energy harvesting during braking. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 35(4):1806–1814. https://doi.org/10.1109/TEC.2020.2994520
Hosseini SM, Soleymani M, Kelouwani S, Amamou AA (2023) Energy recovery and energy harvesting in electric and fuel cell vehicles, a review of recent advances. IEEE Access 11:83107–83135. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3301329
Jin Z, Li D, Hao D, Zhang Z, Guo L, Wu X, Yuan Y (2024) A portable, auxiliary photovoltaic power system for electric vehicles based on a foldable scissors mechanism. Energy Built Environ 5(1):81–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbenv.2022.08.002
Khan S, Sudhakar K, Yusof MH, Bin, Azmi WH, Ali HM (2023) Roof integrated photovoltaic for electric vehicle charging towards net zero residential buildings in Australia. Energy Sustain Dev 73:340–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esd.2023.02.005
Krishna G (2021) Understanding and identifying barriers to electric vehicle adoption through thematic analysis. Transp Res Interdiscip Perspect 10:100364. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TRIP.2021.100364
Lafarge B, Cagin S, Curea O, Perret AH (2016) From functional analysis to energy harvesting system design: application to car suspension. Int J Interact Des Manuf 10(1):37–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12008-015-0284-1
Lee H, Jang H, Park J, Jeong S, Park T, Choi S (2013) Design of a piezoelectric energy-harvesting shock absorber system for a vehicle. Integr Ferroelectr 141(1):32–44. https://doi.org/10.1080/10584587.2013.778724
Lee G, Song J, Han J, Lim Y, Park S (2023) Study on energy consumption characteristics of passenger electric vehicle according to the regenerative braking stages during real-world driving conditions. Energy 283:128745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2023.128745
Li P, Zuo L (2013) Assessment of vehicle performances with energy-harvesting shock absorbers. SAE Int J Passenger Cars Mech Syst 6(1):18–27. https://doi.org/10.4271/2013-01-0170
Li Z, Zuo L, Kuang J, Luhrs G (2013) Energy-harvesting shock absorber with a mechanical motion rectifier. Smart Mater Struct 22(2):025008. https://doi.org/10.1088/0964-1726/22/2/025008
Li H, Zheng P, Zhang T, Zou Y, Pan Y, Zhang Z, Azam A (2021) A high-efficiency energy regenerative shock absorber for powering auxiliary devices of new energy driverless buses. Appl Energy 295:117020. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APENERGY.2021.117020
Li H, Chu J, Sun S (2022) Development of a flywheel hybrid power system in vehicles without the electric drive device rated capacity limit. World Elec Veh J 13(2):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj13020027
Liang XC, Zhao JS (2015) Research on recycling vibration energy of shock absorber. Int J Veh Des 68(1–3):201–220. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJVD.2015.071079
Liebl J, Neugebauer S, Eder A, Linde M, Mazar B, Stütz W (2009) The thermoelectric generator from BMW is making use of waste heat. MTZ Worldwide 70(4):4–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03226939
Liu J, Li X, Wang Z, Zhang Y (2016) Modelling and experimental study on active energy-regenerative suspension structure with variable universe fuzzy PD control. Shock Vib 1:6170275. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/6170275
Liu Y, Chen W, Zhang Z, Hua G (2016b) Energy-regenerative shock absorber for transportation vehicles based on dual overrunning clutches: Design, modeling, and simulation. Transp Res Rec 2551:126–136. https://doi.org/10.3141/2551-15
Mathews T (2013) Flywheel Based kinetic energy recovery systems (Kers) Integrated in vehicles. Int J Eng Sci Technol 5(3):1694–1699
Mousavi GSM, Faraji F, Majazi A, Al-Haddad K (2017) A comprehensive review of flywheel energy storage system technology. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 67:477–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RSER.2016.09.060
Mishra G, Sharma SK (2017) A review of automotive thermoelectric generator. International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology. www.irjet.net
Nivas M, Naidu RKPR, Mishra DP, Salkuti SR (2022) Modeling and analysis of solar-powered electric vehicles. Int J Power Electron Drive Syst (IJPEDS) 13(1):480–487. https://doi.org/10.11591/IJPEDS.V13.I1.PP480-487
Ong HC, Mahlia TMI, Masjuki HH (2011) A review on emissions and mitigation strategies for road transport in Malaysia. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 15(8):3516–3522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2011.05.006
Özcan D, Sönmez Ü, Güvenç L (2013) Optimisation of the nonlinear suspension characteristics of a light commercial vehicle. Int J Veh Technol 1:562424. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/562424
Pan C, Chen L, Chen L, Jiang H, Li Z, Wang S (2016) Research on motor rotational speed measurement in regenerative braking system of electric vehicle. Mech Syst Signal Process 66–67:829–839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymssp.2015.06.001
Pelegov DV, Chanaron JJ (2023) Electric car market analysis using open data: sales, volatility assessment, and forecasting. Sustainability (Switzerland) 15(1):399. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15010399
Pillewar PR, Patil SN, Unde MG (2022) An implementation of solar PV array based multifunctional electrical vehicle charger. Mater Today: Proc 69:A12–A18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2023.01.003
Rahman I, Vasant PM, Singh BSM, Abdullah-Al-Wadud M, Adnan N (2016) Review of recent trends in optimization techniques for plug-in hybrid, and electric vehicle charging infrastructures. In Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews (Vol. 58, pp. 1039–1047). Elsevier Ltd. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.12.353
Rajak U, Verma TN, Allamraju KV, Kumar R, Le QH, Pugazhendhi A (2023) Effects of different biofuels and their mixtures with diesel fuel on diesel engine performance and exhausts. Sci Total Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.166501
Rao KD (2014) Modeling, simulation and control of semi active suspension system for automobiles under MATLAB Simulink using PID controller. IFAC Proceedings Volumes (IFAC-PapersOnline), 3(PART 1), 827–831. https://doi.org/10.3182/20140313-3-IN-3024.00094
Rashmi MR, Sairam KT, Suresh A (2023) Energy harvesting through piezoelectric technology. Materials Today: Proceedings. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2023.07.252
Rigogiannis N, Perpinias I, Bogatsis I, Roidos I, Vagiannis N, Zournatzis A, Kyritsis A, Papanikolaou N, Kalogirou S (2023) Energy yield estimation of on-vehicle photovoltaic systems in urban environments. Renew Energy 215:118998. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2023.118998
Sagaria S, Duarte G, Neves D, Baptista P (2022) Photovoltaic integrated electric vehicles: assessment of synergies between solar energy, vehicle types and usage patterns. J Clean Prod 348:131402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131402
Satpute NV, Satpute SN, Jugulkar LM (2016) Hybrid electromagnetic shock absorber for energy harvesting in a vehicle suspension. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part C: J Mech Eng Sci 231(8):1500–1517. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954406216663577
Satpute NV, Satpute SN, Jugulkar LM (2017) Hybrid electromagnetic shock absorber for energy harvesting in a vehicle suspension. Proc Inst Mech Eng C J Mech Eng Sci 231(8):1500–1517. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954406216663577
Shukla (2024) Fundamentals of Vehicle Integration
Shukla P, Choudhary D (2023) Experimental investigation of wear failure of sliding joint of guide pin and bracket of four wheeler disc brake assembly. Int J Veh Noise Vib 18(3/4):186–193. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJVNV.2022.128278
Shukla P, Kunwer R, Bhurat SS (2018) Design optimization of an automotive fuel tank for the minimization of evaporative losses of gasoline due to thermal conduction: experimental & analytical approach. Chem Eng Trans 71:1393–1398
Singh S, Satpute NV (2015) Design and analysis of energy-harvesting shock absorber with electromagnetic and fluid damping. J Mech Sci Technol 29(4):1591–1605. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12206-015-0331-7
Solberg G (2007) The magic of Tesla roadster regenerative braking. Tesla. https://www.tesla.com/blog/magic-tesla-roadster-regenerative-braking
Suda Y, Shiiba T (1996) A new hybrid suspension system with active control and energy regeneration. Vehicle System Dynamics 25(SUPPL):641–654. https://doi.org/10.1080/00423119608969226
Tang X, Lin T, Zuo L (2014) Design and optimization of a tubular linear electromagnetic vibration energy harvester. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron 19(2):615–622. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMECH.2013.2249666
Tang M, Cao H, Kong LJ, Azam A, Luo D, Pan Y, Zhang Z (2022) A hybrid kinetic energy harvester for applications in electric driverless buses. Int J Mech Sci 223:107317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2022.107317
Tiwari C, Dwivedi G, Verma TN (2023) Sustainability evaluation optimization and research dynamics of microalgae methyl ester in a research diesel engine. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part E: Journal of Process Mechanical Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1177/09544089231162318
Toyota Global (2023). Toyota launches all-new Prius PHEV in Japan | . Toyota. https://global.toyota/en/newsroom/toyota/38869594.html
Toyota Pressroom (2023) Unplug and Play: 2024 Toyota Prius Prime Redefines the daily drive. Toyota. https://pressroom.toyota.com/unplug-and-play-2024-toyota-prius-prime-redefines-the-daily-drive/
Tushar G et al. (2024) Consumers are driving the transition to electric cars in India. McKinsey & Company. https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/automotive-and-assembly/our-insights/consumers-are-driving-the-transition-to-electric-cars-in-india
Ukpanah I (2024) Electric vehicles: a deep dive into the statistics and trends for 2024. Greenmatch. https://www.greenmatch.co.uk/electric-vehicles
Un-Noor F, Padmanaban S, Mihet-Popa L, Mollah MN, Hossain E (2017) A comprehensive study of key electric vehicle (EV) components, technologies, challenges, impacts, and future direction of development. Energies 10(8):1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/en10081217
Vasiljević S, Aleksandrović B, Glišović J, Maslać M (2022) Regenerative braking on electric vehicles: working principles and benefits of application. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng 1271(1):012025. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899x/1271/1/012025
Wang J, Xiao F, Zhao H (2021) Thermoelectric, piezoelectric and photovoltaic harvesting technologies for pavement engineering. In Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews (Vol. 151). Elsevier Ltd. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2021.111522
Wang R, Gu F, Cattley R, Ball AD (2016a) Modelling, testing and analysis of a regenerative hydraulic shock absorber system. Energies 9(5):386. https://doi.org/10.3390/EN9050386
Wang X, Liang X, Shu G, Watkins S (2016b) Coupling analysis of linear vibration energy harvesting systems. Mech Syst Signal Process 70–71:428–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.YMSSP.2015.09.006
Wang X, Liang X, Wei H (2015) A study of electromagnetic vibration energy harvesters with different interface circuits. Mech Syst Signal Process 58:376–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.YMSSP.2014.10.004
Wang Z, Zhang T, Zhang Z, Yuan Y, Liu Y (2020) A high-efficiency regenerative shock absorber considering twin ball screws transmissions for application in range-extended electric vehicles. Energy Built Environ 1(1):36–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENBENV.2019.09.004
Wen MTX, Tien DTK (2018) Analysis of a Hybrid mechanical regenerative braking system. MATEC Web of Conf 152:1–15
Xie XD, Wang Q (2015) Energy harvesting from a vehicle suspension system. Energy 86:382–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2015.04.009
Xu Z, Shan X, Chen D, Xie T (2016) A novel tunable multi-frequency hybrid vibration energy harvester using piezoelectric and electromagnetic conversion mechanisms. Appl Sci 6(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/APP6010010
Yang W, Towfighian S (2017) A hybrid nonlinear vibration energy harvester. Mech Syst Signal Process 90:317–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.YMSSP.2016.12.032
Yang H, Wang L, Zhou B, Wei Y, Zhao Q (2018) A preliminary study on the highway piezoelectric power supply system. Int J Pavement Res Technol 11(2):168–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJPRT.2017.08.006
Yu L, Huo S, Xuan WW, Zuo L (2015) Assessment of ride comfort and braking performance using energy-harvesting shock absorber. SAE Int J Passenger Cars Mech Syst 8(2):482–491. https://doi.org/10.4271/2015-01-0649
Zamanov N (2023) Unleashing efficiency: the magic of regenerative braking in electric cars. Cyberswitching. https://cyberswitching.com/electric-cars-and-regenerative-braking-technology/
Zhang L, Cai X (2018) Control strategy of regenerative braking system in electric vehicles. Energy Procedia 152:496–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2018.09.200
Zhang Z, Zhang X, Chen W, Rasim Y, Salman W, Pan H, Yuan Y, Wang C (2016) A high-efficiency energy regenerative shock absorber using supercapacitors for renewable energy applications in range extended electric vehicle. Appl Energy 178:177–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.APENERGY.2016.06.054
Zhang Y, Guo K, Wang D, Chen C, Li X (2017) Energy conversion mechanism and regenerative potential of vehicle suspensions. Energy 119:961–970. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENERGY.2016.11.045
Zhang R, Wang X, John S (2018a) A comprehensive review of the techniques on regenerative shock absorber systems. Energies 11(5):1167. https://doi.org/10.3390/EN11051167
Zhang R, Wang X, Liu Z (2018b) A novel regenerative shock absorber with a speed doubling mechanism and its Monte Carlo simulation. J Sound Vib 417:260–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JSV.2017.12.017
Zhang R, Zhao L, Qiu X, Zhang H, Wang X (2020) A comprehensive comparison of the vehicle vibration energy harvesting abilities of the regenerative shock absorbers predicted by the quarter, half and full vehicle suspension system models. Appl Energy 272:115180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.115180
Zheng XC, Yu F, Zhang YC (2008) Novel energy-regenerative active suspension for vehicles. J Shanghai Jiaotong Univ (Science) 13(2):184–188. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12204-008-0184-7
Zhu Y, Wu H, Zhen C (2021) Regenerative braking control under sliding braking condition of electric vehicles with switched reluctance motor drive system. Energy 230:120901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.120901
Zou J, Guo X, Xu L, Tan G, Zhang C, Zhang J (2017) Design, modeling, and analysis of a novel hydraulic energy-regenerative shock absorber for vehicle suspension. Shock Vib 2017(1):3186584. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3186584
Zuo L, Zhang PS (2013) Energy harvesting, ride comfort, and road handling of regenerative vehicle suspensions. J Vib Acoust 135(1):011002. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4007562
Zuo L, Scully B, Shestani J, Zhou Y (2010) Design and characterization of an electromagnetic energy harvester for vehicle suspensions. Smart Mater Struct 19(4):045003. https://doi.org/10.1088/0964-1726/19/4/045003
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Mechanical Engineering, School of Advanced Engineering, UPES, Dehradun, 248007, India
Abhidnya Sunil Mhatre & Prashant Shukla
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
P.S.: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, writing–original draft preparation, writing–review and editing, supervision, project administration.
A.S.M.: data curation, formal analysis, writing–review and editing.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Prashant Shukla .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Mhatre, A.S., Shukla, P. A comprehensive review of energy harvesting technologies for sustainable electric vehicles. Environ Sci Pollut Res (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-34865-8
Download citation
Received : 04 December 2023
Accepted : 26 August 2024
Published : 06 September 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-34865-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Regenerative braking
- Solar energy
- Kinetic recovery system regenerative shock absorber
- Piezoelectric systems
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 1: Restate the problem. The first task of your conclusion is to remind the reader of your research problem. You will have discussed this problem in depth throughout the body, but now the point is to zoom back out from the details to the bigger picture. While you are restating a problem you've already introduced, you should avoid phrasing ...
Generate the conclusion outline: After entering all necessary details, click on 'generate'. Paperpal will then create a structured outline for your conclusion, to help you start writing and build upon the outline. Write your conclusion: Use the generated outline to build your conclusion.
Begin with a clear statement of the principal findings. This will reinforce the main take-away for the reader and set up the rest of the discussion. Explain why the outcomes of your study are important to the reader. Discuss the implications of your findings realistically based on previous literature, highlighting both the strengths and ...
Step 1: Restate the problem. Always begin by restating the research problem in the conclusion of a research paper. This serves to remind the reader of your hypothesis and refresh them on the main point of the paper. When restating the problem, take care to avoid using exactly the same words you employed earlier in the paper.
In this post, we'll take you through how to write an effective conclusion for a research paper and how you can: · Reword your thesis statement. · Highlight the significance of your research. · Discuss limitations. · Connect to the introduction. · End with a thought-provoking statement.
Offer a Fresh Perspective: Use the conclusion as an opportunity to provide a fresh perspective or offer insights that go beyond the main body of the paper. This will leave the reader with something new to consider. Leave a Lasting Impression: End your conclusion with a thought-provoking statement or a call to action.
6 Conciseness. Above all, every research paper conclusion should be written with conciseness. In general, conclusions should be short, so keep an eye on your word count as you write and aim to be as succinct as possible. You can expound on your topic in the body of your paper, but the conclusion is more for summarizing and recapping.
The conclusion is where you describe the consequences of your arguments by justifying to your readers why your arguments matter (Hamilton College, 2014). Derntl (2014) also describes conclusion as the counterpart of the introduction. Using the Hourglass Model (Swales, 1993) as a visual reference, Derntl describes conclusion as the part of the ...
Here are some steps you can follow to write an effective research paper conclusion: Restate the research problem or question: Begin by restating the research problem or question that you aimed to answer in your research. This will remind the reader of the purpose of your study. Summarize the main points: Summarize the key findings and results ...
Step 2: Summarize and reflect on your research. Step 3: Make future recommendations. Step 4: Emphasize your contributions to your field. Step 5: Wrap up your thesis or dissertation. Full conclusion example. Conclusion checklist. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about conclusion sections.
This structure is commonly adopted and accepted in the scientific fields. The research report starts with a general idea. The report then leads the reader to a discussion on a specific research area. It then ends with applicability to a bigger area. The last section, Conclusion, is the focus of this lesson.
The point of a conclusion to a research paper is to summarize your argument for the reader and, perhaps, to call the reader to action if needed. 5. Make a call to action when appropriate. If and when needed, you can state to your readers that there is a need for further research on your paper's topic.
Summarize the findings/argument. Your research paper conclusion should also revisit the evidence, findings, and limitations of your research, but as an overview, not in detail. State only the most important points, what they mean, and how they illustrate the main idea you want the reader to take away. 3. Look toward the future.
Step 7: End with a Strong Closing Statement: Conclude your research paper with a memorable closing statement. This could be a thought-provoking reflection, a call to action, or a suggestion for future research. A strong closing leaves a lasting impression on your readers and emphasizes the importance of your work.
The conclusion of a research paper has several key objectives. It should: Restate your research problem addressed in the introduction section. Summarize your main arguments, important findings, and broader implications. Synthesize key takeaways from your study. The specific content in the conclusion depends on whether your paper presents the ...
A conclusion is the final paragraph of a research paper and serves to help the reader understand why your research should matter to them. The conclusion of a conclusion should: Restate your topic and why it is important. Restate your thesis/claim. Address opposing viewpoints and explain why readers should align with your position.
In each paragraph, the first sentence defines the context, the body contains the new idea and the final sentence offers a conclusion. For the whole paper, the introduction sets the context, the ...
To write a conclusion for a research paper, begin by summarizing the main findings or results of your study. Restate your thesis statement or research question and briefly recap the key points discussed in the paper. Reflect on the significance of your findings and discuss their implications for the broader field of study or real-world ...
Empirical paper: Future research directions; Video advice: How To Write A Conclusion For A Research Paper: A Structure For A Conclusion In A PhD Journal Paper. Every research paper has a similar conclusion. Once you see the pattern in the conclusions, you will start to be able to write a better conclusion for a research paper.
Then, writing the paper and getting it ready for submission may take me 3 to 6 months. I like separating the writing into three phases. The results and the methods go first, as this is where I write what was done and how, and what the outcomes were. In a second phase, I tackle the introduction and refine the results section with input from my ...
Introduction. Your lab report introduction should set the scene for your experiment. One way to write your introduction is with a funnel (an inverted triangle) structure: Start with the broad, general research topic. Narrow your topic down your specific study focus. End with a clear research question.
1. Introduce the experiment in your conclusion. Start out the conclusion by providing a brief overview of the experiment. Describe the experiment in 1-2 sentences and discuss the objective of the experiment. Also, make sure to include your manipulated (independent), controlled and responding (dependent) variables. 2.
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
The conclusion of your thesis paper is your opportunity to sum up your argument and leave your reader thinking about why your research matters. Attari breaks the conclusion down into simple parts. "You restate the original issue and thesis statement, explain the experiment's results and discuss possible next steps for further research," she ...
This review paper provides a comprehensive examination of energy harvesting technologies tailored for electric vehicles (EVs). Against the backdrop of the automotive industry's rapid evolution towards electrification and sustainability, the paper explores a diverse range of techniques. The analysis encompasses the strengths, weaknesses, applicability in various scenarios, and potential ...